Chemistry 11: Bonding, Atomic Theory, and Periodic Trends
1/434
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
435 Terms
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond, indicating how strongly an atom can attract shared electron pairs.
How does electronegativity change across a period in the periodic table?
Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across a period due to the increasing effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which brings valence electrons closer to the nucleus.
How does electronegativity change down a group in the periodic table?
Electronegativity decreases as you move down a group because of the increase in the number of energy shells and a stronger shielding effect.
What determines the type of bond formed between two atoms?
The difference in electronegativities between two atoms determines if the bond is ionic, polar covalent, or non-polar covalent.

What does the symbol ΔEN represent?
ΔEN represents the difference in electronegativity between two atoms.
What type of bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen (C-H) and why?
C-H forms a non-polar covalent bond because the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 0.4) is small.
What type of bond is formed between carbon and oxygen (C-O) and why?
C-O forms a polar covalent bond because the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 1.0) indicates unequal sharing of electrons.
What type of bond is formed between sodium and fluorine (Na-F) and why?
Na-F forms an ionic bond due to a large difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 3.1), leading to complete transfer of electrons.

What is an ion?
An ion is an atom that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a positive or negative charge.
What is a crystal lattice?
A crystal lattice is a three-dimensional arrangement of ions held together by electrostatic forces, resulting in a stable structure.
Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity in solid state?
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state because their ions are arranged in a stable crystal lattice and cannot move freely.
What is lattice energy?
Lattice energy is the amount of energy needed to break a solid ionic compound into separate gaseous ions.
What is the lattice energy of NaCl?
The lattice energy of NaCl is 769 kJ.
What happens to sodium (Na) when it reacts with chlorine (Cl2)?
Sodium loses an electron to become a positively charged ion (cation), while chlorine gains an electron to become a negatively charged ion (anion), forming an ionic bond.

What type of bond is formed between carbon and carbon (C-C) and why?
C-C forms a non-polar covalent bond because the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 0) indicates equal sharing of electrons.
What type of bond is formed between chromium and oxygen (Cr-O) and why?
Cr-O forms an ionic bond due to a significant difference in electronegativity (ΔEN = 1.9), indicating electron transfer.
What type of bond is formed between magnesium and oxygen (Mg-O) and why?
Mg-O forms an ionic bond due to a large difference in electronegativity, leading to electron transfer.
What type of bond is formed between lithium and sulfur (Li-S) and why?
Li-S forms an ionic bond due to the significant difference in electronegativity, resulting in electron transfer.
What type of bond is formed between potassium and nitrogen (K-N) and why?
K-N forms an ionic bond due to the large difference in electronegativity, indicating electron transfer.
What is a polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared unequally between two atoms, resulting in partial charges.

What is a non-polar covalent bond?
A non-polar covalent bond is formed when electrons are shared equally between two atoms, resulting in no charge separation.
What is the significance of the bonding continuum scale?
The bonding continuum scale helps classify bonds based on the difference in electronegativity, indicating the nature of the bond from ionic to non-polar covalent.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
What is the stable balance of forces in covalent bonding?
The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons.
What are the steps for drawing Lewis dot diagrams?
1. Count all valence electrons (VE). 2. Place the least electronegative atom as the central atom (except H) and distribute other atoms around it. 3. Place 2 electrons (a single bond) between each outside atom and the central one. 4. Distribute the rest of the electrons onto the outside atoms until they have a full octet (except H). If there are not enough electrons, make double or triple bonds; if there are too many, place the remaining electrons on the central atom.
How many bonding electrons form a single bond?
1 bonding electron forms 1 single bond.
How many bonding electrons can form multiple bonds?
4 bonding electrons can form 4 single bonds, 2 double bonds, or 1 triple and 1 single bond.
What is the Lewis dot structure for water (H2O)?
H-O-H, with 2 bonding electrons between H and O.
What is the Lewis dot structure for methane (CH4)?
H-C-H with 4 bonding electrons forming 4 single bonds.
What is the valence electron (VE) count for carbon dioxide (CO2)?
VE = 4 (from C) + 2x2 (from 2 O) = 8.
What is the significance of the central atom in a Lewis structure?
The central atom is typically the least electronegative atom (except H) and is surrounded by other atoms.
What happens if there are not enough electrons to complete the octet in a Lewis structure?
Make double or triple bonds.
What is an extended octet?
An extended octet occurs when a molecule has more than 8 electrons around the central atom.
What is the bond order?
Bond order is defined as the number of bonding pairs of electrons between two atoms.
What is the Lewis structure for ammonia (NH3)?
H-N-H with a lone pair on nitrogen.
What is the Lewis structure for ethene (C2H4)?
H2C=CH2, with a double bond between the two carbon atoms.
What is the Lewis structure for sulfur dioxide (SO2)?
O=S=O, with double bonds between sulfur and each oxygen.
What is a resonance structure?
A resonance structure represents different possible configurations of electrons in a molecule that cannot be depicted by a single Lewis structure.

What is the Lewis structure for the hydroxide ion (OH-)?
H-O with a negative charge indicating an extra electron.
What does it mean if a molecule has an incomplete octet?
It means that the central atom does not have 8 electrons in its valence shell.
What is the Lewis structure for the phosphate ion (PO4^3-)?
P with 4 O atoms, typically with double bonds to some O atoms and a total of 3 extra electrons.
What is the Lewis structure for the carbonate ion (CO3^2-)?
C with 3 O atoms, one double bond and two single bonds, with a total of 2 extra electrons.
What is the Lewis structure for the nitronium ion (NO2^+)?
N with 2 O atoms, typically with a double bond to one O and a single bond to the other.
How do you determine the number of lone pairs in a Lewis structure?
Subtract the number of bonding electrons from the total valence electrons and divide by 2.
What are binary ionic compounds made of?
A positive metal ion and a negative non-metal ion.
Give an example of a binary ionic compound and its ions.
Sodium oxide (Na2O) is made from sodium ion (Na+) and oxide ion (O2-).
How do you write the formula for magnesium nitride?
Identify the ions Mg2+ and N3-, balance the charges to zero, resulting in Mg3N2.
What is the charge of the magnesium ion?
Mg2+.
What is the charge of the nitride ion?
N3-.
What is the formula for magnesium oxide?
MgO.
What is the formula for potassium sulfide?
K2S.
What is the formula for sodium hydride?
NaH.
What is the charge of a multivalent iron ion that loses 2 electrons?
Iron(II) ion (Fe2+).
What is the charge of a multivalent iron ion that loses 3 electrons?
Iron(III) ion (Fe3+).
What is the naming convention for polyatomic ions that contain oxygen?
The most common form ends with -ate.
What is the name of the polyatomic ion NO3-?
Nitrate.
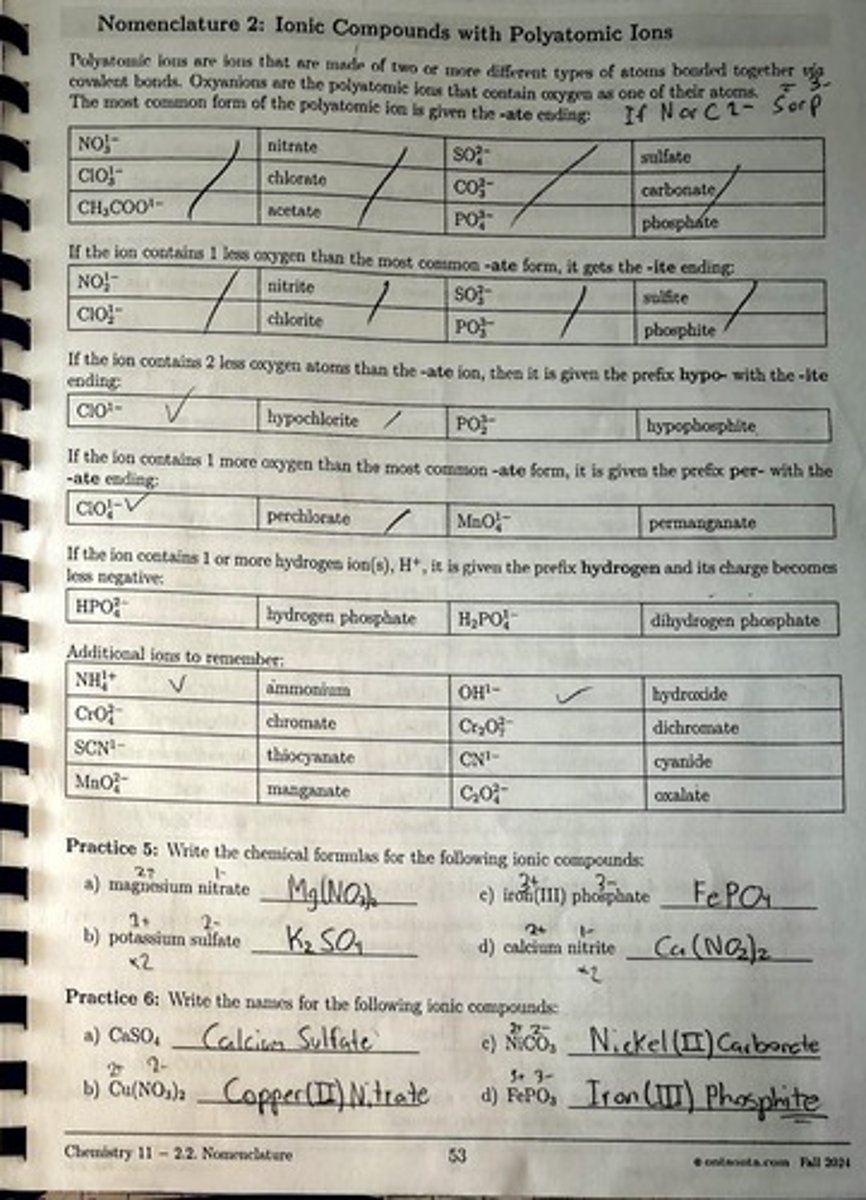
What is the name of the polyatomic ion SO4^2-?
Sulfate.
What is the name of the polyatomic ion ClO3-?
Chlorate.
What is the name of the polyatomic ion with one less oxygen than nitrate?
Nitrite (NO2-).
What prefix is used for the ion with two less oxygen atoms than the -ate form?
Hypo- (e.g., hypochlorite, ClO-).
What prefix is used for the ion with one more oxygen than the -ate form?
Per- (e.g., perchlorate, ClO4-).
What is the name of the ion HPO4^2-?
Hydrogen phosphate.
What is the formula for ammonium?
NH4+.
What is the formula for hydroxide?
OH-.
What is the formula for dichromate?
Cr2O7^2-.
What is the formula for thiocyanate?
SCN-.
What is the formula for oxalate?
C2O4^2-.
What is the formula for iron(III) phosphate?
FePO4.
What is the formula for calcium nitrite?
Ca(NO2)2.
What is the formula for calcium sulfate?
CaSO4
What is the formula for copper(II) nitrate?
Cu(NO3)2
What is the formula for nickel(II) carbonate?
NiCO3
What is the naming convention for binary acids that contain hydrogen and one other element?
They are called hydro- followed by the root of the other element and the suffix -ic acid.
What is the name of the acid with the formula HCl(aq)?
Hydrochloric acid
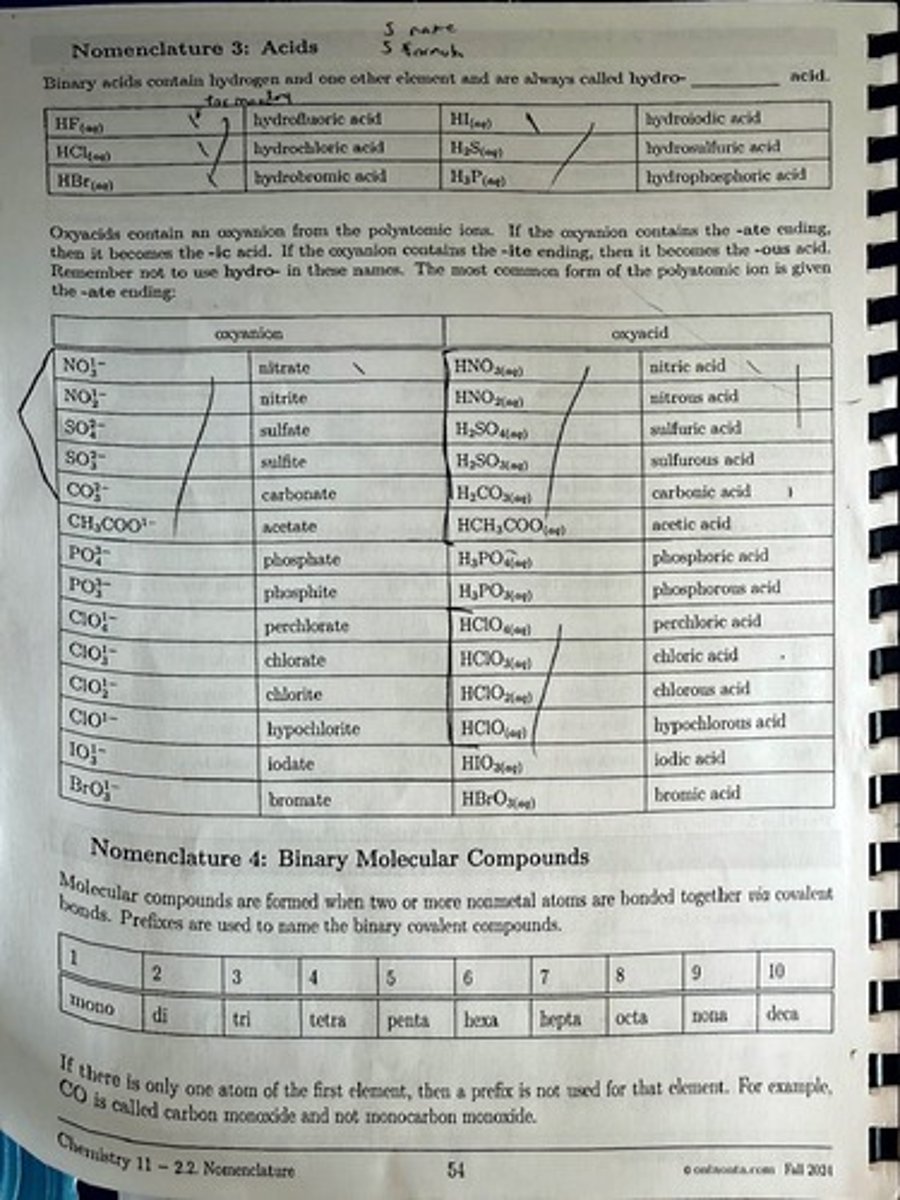
What is the name of the acid with the formula H2SO4(aq)?
Sulfuric acid
How do you name oxyacids derived from oxyanions with -ate endings?
They become -ic acids.
How do you name oxyacids derived from oxyanions with -ite endings?
They become -ous acids.
What is the name of the acid with the formula HNO3(aq)?
Nitric acid
What is the name of the acid with the formula HNO2(aq)?
Nitrous acid
What is the name of the acid with the formula H2CO3(aq)?
Carbonic acid.
What is the name of the acid with the formula H3PO4(aq)?
Phosphoric acid.
What is the name of the acid with the formula HClO3(aq)?
Chloric acid.
What is the name of the acid with the formula HClO2(aq)?
Chlorous acid.
What is the name of the acid with the formula HBrO3(aq)?
Bromic acid.
What is the prefix for two atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Di-.
What is the prefix for three atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Tri-.
What is the prefix for four atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Tetra-.
What is the prefix for five atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Penta-.
What is the prefix for six atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Hexa-.
What is the prefix for seven atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Hepta-.
What is the prefix for eight atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Octa-.
What is the prefix for nine atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Nona-.

What is the prefix for ten atoms in binary molecular compounds?
Deca-.
What are hydrates in chemistry?
Ionic compounds that contain water as part of their crystal structure.
What is the term for the ionic salt that remains after the water of hydration is removed from a hydrate?
Anhydrate.
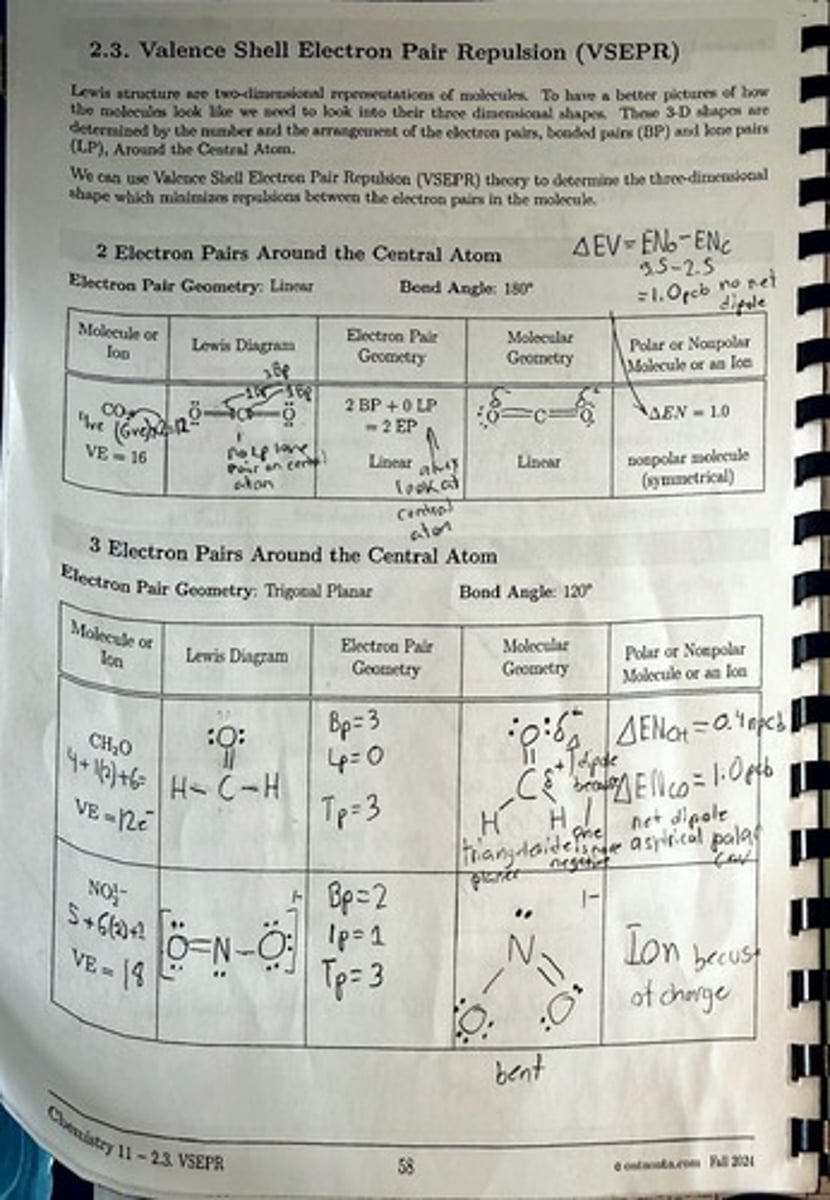
What determines the three-dimensional shapes of molecules?
The number and arrangement of electron pairs, including bonded pairs (BP) and lone pairs (LP), around the central atom.
What theory is used to determine the three-dimensional shape of molecules?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
What is the electron pair geometry for a molecule with 2 electron pairs around the central atom?
Linear.
What is the bond angle for a linear molecular geometry?
180°.
What type of molecule is formed with 2 bonded pairs and 0 lone pairs?
A nonpolar molecule with linear geometry.