6. Macromolecules
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a macromolecule?
A very large molecule
e.g. Polyethylene
Homo-polymers
The same monomer (A-A-A)
Co-polymers

Polymers with a charge
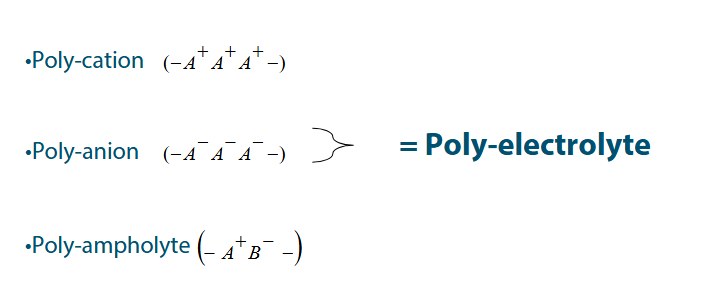
Why are polymers such excellent thickeners?
High surface area can bind more water
Occupy a large space
Entanglement
How much space is really occupied by a polymer?
Depends on the polymer
Double strand DNA is very stiff
Proteins have well-defined 3D structure, unless denatured
Many polymers are extremely flexible (= takes up less space)
Coil Diameter
Longer polymers have larger coil volume than shorter polymers
But stiffer polymers have even larger coil volume
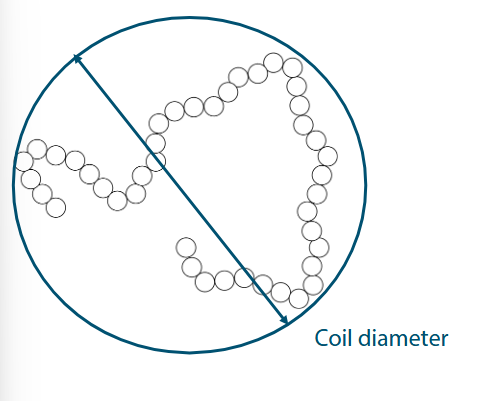
How much bigger is the stiffer polymer?
Stiffer polymers take up more space
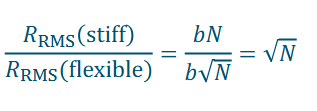
Radius of gyration
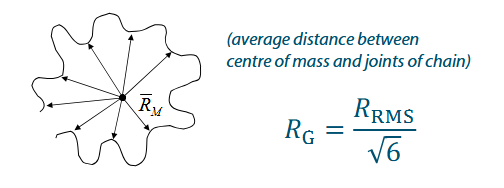
Overlap concentration (c*)
The number of segments per unit volume
((M*N)/V = N/VG)
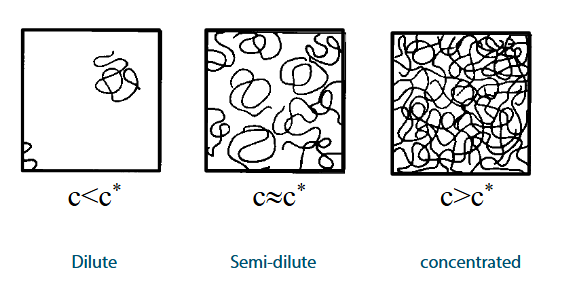
Three concentration regimes
How are real polymers different?
Interactions between segments (both inter and intra-molecular)
Limited bond flexibility
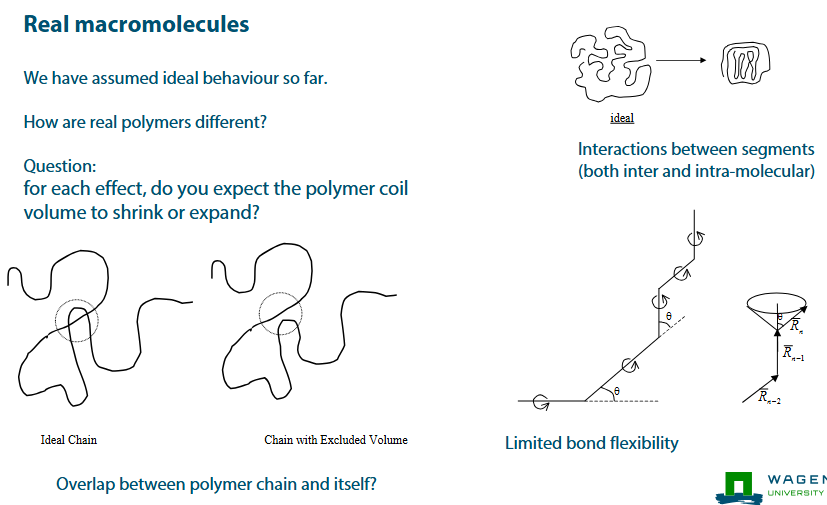
Limited bond flexibility
When bond flexibility is limited, placement of each segment is restricted
But, after a few monomers this effect is resolved
Effectively, there is a new, ‘effective’ segment size, bigger than the real segment size.
Theta solvent
Interactions between segments and solvent are very close to interactions between segments
Good solvent
Interactions between segment and solvent are more favorable than between segments
Polymer segments prefer contact with solvent. The polymer coil swells
Bad solvent
Interactions between segments and solvent are less favorable than between segments.
Polymer segments prefer contact with themselves. The polymer coil collapses.
What do different concentrations of c* mean?
Below c*: polymer coils are mostly separate
At or near c*: coils begin to merge
Above c*: the solution behaves like a concentrated polymer network
Ideal polymers
When chains have no interactions with the solvent
And no interactions with other chains
the chains do not have excluded volume (they do not feel other parts of the chain, or, in other words, there can be crossing without energy penalties)
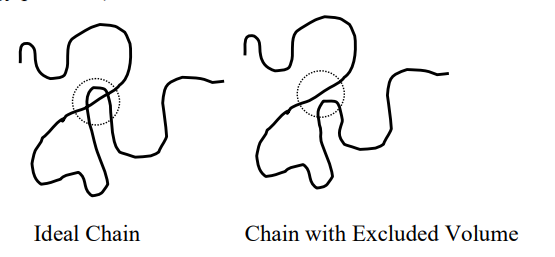
What is the reason that chain can have so many different configurations?
Thermal energy
In particular it is the (thermal) energy of the solvent molecules, due to the fat that there is an absolute temperature larger than zero.
This makes that they bounce against various parts of the chain and hence change shape
What do you call a chain in flexible polymers where two adjacent bond vectors can turn between 0 and 360 degrees.
Freely jointed chains, random coils or Gaussian chains
VG vs. Vsegment
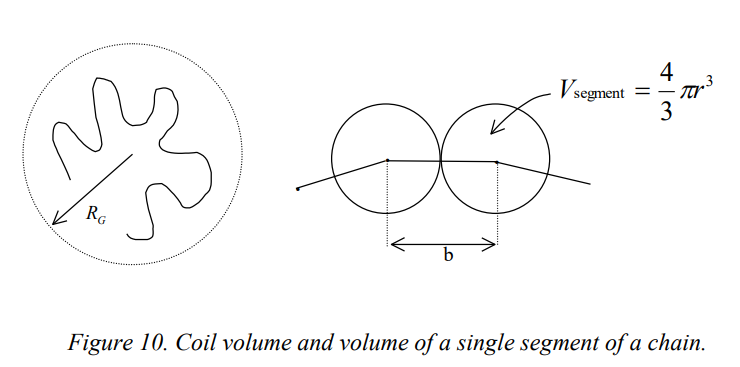
Volume fraction formula
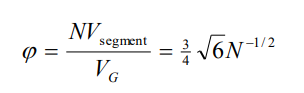
What is a dilute chain?
A “dilute chain” usually means a single polymer molecule (a chain) that is in a dilute solution regime. In this regime the coils are so far apart that they essentially do not overlap or interact with one another. Each chain behaves as if it is alone in the solvent, surrounded mostly by solvent molecules rather than other chains.
Effective segment length
Effective segment length is the distance along a molecule's backbone that behaves like a solid, unbending unit.
The shorter beff the more flexible, the longer the more rigid.
What is Neff
The number of beff segments
What is Beta
β (Beta) is defined as a multiplication factor that accounts for the limited flexibility of a real macromolecule compared to an idealized "freely jointed" chain
High beta: stiff chain, longer beff, lower Neff, takes up more space.
Low beta: when Beta = 1, the molecule behaves like an ideal “freely jointed chain” where segments can bend at any angle.
How do non-ideal linear chains behave in solution?
Interactions between chain segments (they repel each other = takes up more volume)
Intermolecular interactions between different chains (only in concentrated solution)
interactions between the chain and the solvent.
How does a good solvent affect the size of the coil?
If the affinity of the chain for the solvent is higher than the affinity for its own segments, then the size of the coil will increase
Additionally as a result the coil structure will take up solvent molecules and will swell
How does a bad solvent affect the size of the coil?
If the affinity for the solvent is less than the affinity for its own chain segments, the size of the coil will decrease.
Segments prefer to be surrounded by other segments, and not by solvent.
As a result, the oil will expel solvent from its interior and the coil will collapse
Linear expansion factor
The effect of excluded volume and chain-solvent interactions on the dimensions of the coil can be incorporated through the linear expansion factor, a
Why does a random coil macromolecule behave like a much larger particle than its actual mass suggests?
Because of its large, sparse structure, a random coil "traps" solvent molecules within its interior. When the solution flows, this trapped solvent is forced to travel with the coil, effectively increasing the particle's size and the resistance to flow.
As the number of segments (N) in a polymer chain increases, does the coil become more or less dense?
It becomes more dilute. The volume of the coil increases much faster than the number of segments, meaning the actual polymer occupies a decreasingly small fraction (often only a few percent) of the total coil volume.
How can a solution with only 1% polymer have a very high viscosity?
Because coils are so "puffy" and large, very little material is needed to fill all available space in a solution. A 1% polymer solution can result in an "effective volume fraction" of 50%, which is close to the maximum packing density for spheres