APSA: Exam Two
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Pharmacists aim to help with symptom control (i.e. pain, nausea, dyspnea) in ____ (hospice/palliative) care in end of life treatment?
palliative care
Pharmacists may review drug therapy to simplify and reduce burden for the patient (i.e. switching PO medications to liquid, patches, SL forms) in ____ (hospice/palliative) care in end of life treatment.
hospice care
Palliative care can start at ___, whereas hospice care usually starts at ___.
diagnosis, 6 month prognosis
What are the five core "services" of MTM?
1. comprehensive medication review (CMR)
2. personal medication record (PMR)
3. medication action plan (MAP)
4. intervention and/or referral
5. documentation and follow up
What does MTR and CMR stand for?
MTR = medication therapy review
CMR = comprehensive medication review
*essentially the same definition!
What does PMR and PML stand for?
PMR = personal medication record
PML = personal medication list
*essentially the same definition!
What does MAP stand for?
medication action plan
in a patient's MTM, it will be notated as "My To-Do List"
In a patient's MTM, the ___ will be notated as "My To-Do List".
medication action plan (MAP)
In a patient's MTM, the ___ will be defined as 2-3 actionable goals.
medication action plan (MAP)
If a pharmacist takes action to resolve a medication-related problem, will it be documented in the medication action plan or as an intervention?
intervention
___ (MAP/intervention) = professional actions
___ (MAP/intervention) = patient's homework
intervention (a pharmacist takes action)
MAP (a patient takes action)
What are the six steps relating to the completion and follow-up of a CMR?
(1) Collect relevant information
(2) Evaluate, identify and resolve problems
(3) Collaborate with providers; plan
(4) Set the care plan in action
(5) Assess the outcomes and effectiveness
(6) Monitor the patient or transition care
For communicating with prescribers effectively, why should you send a HIPPA form in advance?
legality, decreases delay in communications
For communicating with prescribers effectively, when should you utilize the phone?
- more urgent issues
- to follow-up
*fax requests that are not urgent
What is severity level 1 of CMR intervention?
improved outcomes
What is severity level 2 of CMR intervention?
cost saving
What is severity level 3 of CMR intervention?
avoid an office visit
What is severity level 4 of CMR intervention?
avoid additional medications
What is severity level 5 of CMR intervention?
avoid an ER visit
What is severity level 6 of CMR intervention?
avoid hospitalization
What is severity level 7 of CMR intervention?
avoid a life threat
What individuals can benefit from the IPHP-Pharmacy Program?
pharmacy professionals and student pharmacists who need support for healthy recovery from substance use, mental health, or physical conditions
What's the main legal difference between self-report and reporting a colleague to the IPHP-Pharmacy Program?
if a pharmacy professional self reports, they are not at risk for losing their license but if someone else reports them, they might
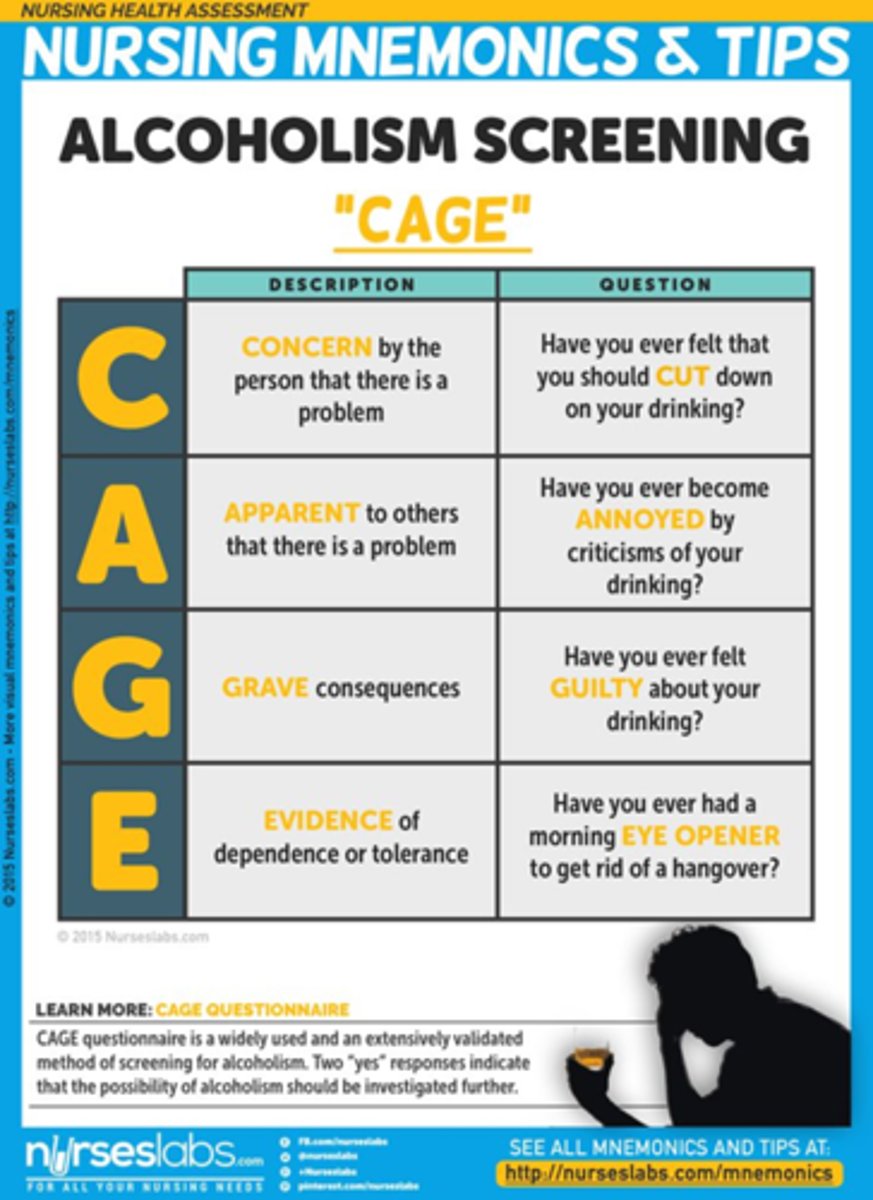
What does the CAGE questionnaire stand for?
Cutting down
Annoyance by criticism
Guilty feeling
Eye-openers
How do you administer a CAGE questionnaire?
help identify patients who need more extensive testing or treatment
What is public stigma?
society's negative attitudes towards a group of people
What is structural stigma?
system-level discrimination, such as cultural norms, institutional practices as well as health care policies that constrain resources, opportunities, and wellbeing
What is self stigma?
individuals internalize and accept negative stereotypes
What is an example of stigma against medications for opioid use disorder?
despite their proven effectiveness, FDA-approved medications are thought by many to be "trading one addition for another"
result: these medications are under prescribed, underutilized, and overly restricted
What are the brain chemistry effects of marijuana long-term?
increase glutamate to stimulate anxiety symptoms and cause other neurological effects, such as memory loss and inability to concentrate
What are the brain chemistry effects of alcohol long-term?
causes a decrease in GABA-A function by receptor down regulation (which contributes to multiple mental health disorders)
What are some physical signs for SUD?
- bloodshot eyes, pupils larger or smaller than usual
- changes in appetite or sleep
- deterioration of physical appearance
- runny nose or sniffling
- sudden change in weight
- tremors, slurred speech, impaired coordination
- unusual odors on breath, body, or clothing
What are some psychological signs for SUD?
- appearing fearful, anxious, or paranoid, with no reason
- ack of motivation; appearing tired or "spaced out"
- periods of unusual increased energy, nervousness, or instability
- sudden mood swings, increased irritability, or angry outbursts
- unexplained change in personality or attitude
What are some behavioral signs for SUD?
- difficulties in relationships
- secretive or suspicious behaviors
- frequently getting into legal trouble
- neglecting responsibilities
- sudden change in friends, favorite hangouts, and hobbies
- unexplained need for money or financial problems
What is the appropriate "people-first language" when talking about SUD?
people with substance use disorder
(T or F) Harm reduction focuses on eliminating risky behavior altogether instead of reducing the risk.
false! (the opposite)
What is the appropriate order for making a TPN?
1. base solution (amino acid, dextrose, sterile water)
2. phosphates
3. other electrolytes
4. calcium gluconate
5. multivitamins
6. lipids
Usually for TPNs, the standard error accepted is +/- ___%.
5
When making a TPN, you should observe the compatibility between ___ and ___ and avoid adding them in succession.
phosphate, calcium
What is the appropriate beyond-use-date (BUD) for TPNs?
24 hours
In a "2-in-1" nutritional product, a __ micron filter is appropriate, whereas in a "3-in-1" product, a __ micron filter is required.
0.22, 1.2 (larger filter required to allow lipid particles to pass through!)
note: filter should be placed closest to the patient as possible to ensure safety
Can TPN lipid creaming or cracking be fixed and used?
lipid creaming
Upper limit for peripheral administration is ___ mOsm/L.
900
What is always added last when making a TPN? Why?
lipids (low pH of dextrose can destabilize lipid emulsion)
There are limits to peripheral administration of TPNs, specifically for ___ (must be 10% or less) and ___ (must be 2.5-4%).
dextrose, amino acids
Do NOT use calcium ___ in TPN! Instead, use calcium ___.
chloride; gluconate
When compounding TPNs, do not block first air which is ___ (horizontal/vertical) air flow!
horizontal
In a horizontal flow hood, all work should be performed at least ___ inches from the front edge of the work surface.
6
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "wrong drug"?
recommend to discontinue the drug and re-evaluate condition wd
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "dose too high"?
recommend specific drug/dose/SIG
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "dose too low"?
recommend specific drug/dose (higher) /SIG
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "adverse drug reaction"?
recommend to discontinue the drug and re-evaluate condition
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "inappropriate adherence"?
recommend specific adherence tip
What is the recommendation if the drug therapy problem is "need additional drug therapy"?
recommend specific, new drug/dose/SIG
What memory assessment involves a four item delayed free recall and cued recall?
memory impairment screen
process:
1. give 4 listed items
2. ask to read the item when given category cue
3. distract for 2-3 minutes
4. ask to recall
What memory assessment involves two components: 1. 3-item recall test and 2. clock drawing test?
mini-cog

What memory assessment observes 5 areas of cognitive functioning: orientation, registration, recall, language, and attention/calculation?
mini-mental state examination
note: does NOT test mood or thought process
Although the mini-mental state examination assesses orientation, registration, recall, language, and attention/calculation, it does NOT test for ___ or ___.
mood; thought process
Who benefit most from medication reconciliation?
pts more likely to have readmission to hospital
pts with 3+ chronic conditions, 8+ medications
How does medication reconciliation improve patient safety?
ensures adherence
finds drug errors
find ADRs and can move to eliminate them
Within ___ hours of admission and within ___ day(s) of discharge should med reconciliation occur.
24 (hours)
14 (days)
When should a medication reconciliation occur at?
A. admission to a hospital from the ER
B. prior to a planned surgery and expected admission
C. discharge to nursing facility
D. unit transfer from inpatient to ICU
E. all of the above
all of the above
"a med rec should happen at every transition"
What are some common drug therapy problems found during medication reconciliation?
Medications with no indication (ineffective drug)
Therapeutic duplications
Omission (medication not included in the list)
Dosing errors
Non-adherence
Change in frequency
What are the 3 different types of discrepancies associated with medication reconciliation?
1. intentional
2. undocumented intentional
3. unintentional (omission, comission)
What are two type of "unintentional" discrepancies?
1. omission: a pre-admission medication wasn't ordered without clinical reason
2. comission: a medication was ordered that is NOT part of the patient's home medication list
Which of the following is NOT an available source to complete a medication reconciliation?
A. patient intake interview
B. community pharmacy
C. pharmacist-patient interview
D. EHR
none of the above (all are appropriate sources)
What is the "8P Screening Tool"?
eight factors that place patients at higher risk of readmission
What are the 8 factors that place patients at higher risk of readmission?
1. medication problems (i.e. 10+ meds, high risk meds)
2. psychological problems (i.e. positive depression questionnaire or prior history)
3. principal diagnosis (i.e. cancer, stroke, DM, COPD, HF)
4. physical limitations (i.e. frailty)
5. poor health literacy (i.e. inability to do teach back)
6. patient support (i.e. lack of system)
7. prior hospitalization (i.e. non-elective within past 6 mo)
8. palliative care (i.e. "Would you be surprised if this patient died in the next year?")
Medicare and Medicaid will pay community pharmacists for med recs, if they
meet the following: ___ chronic disease states and ___ medications.
3+
8+
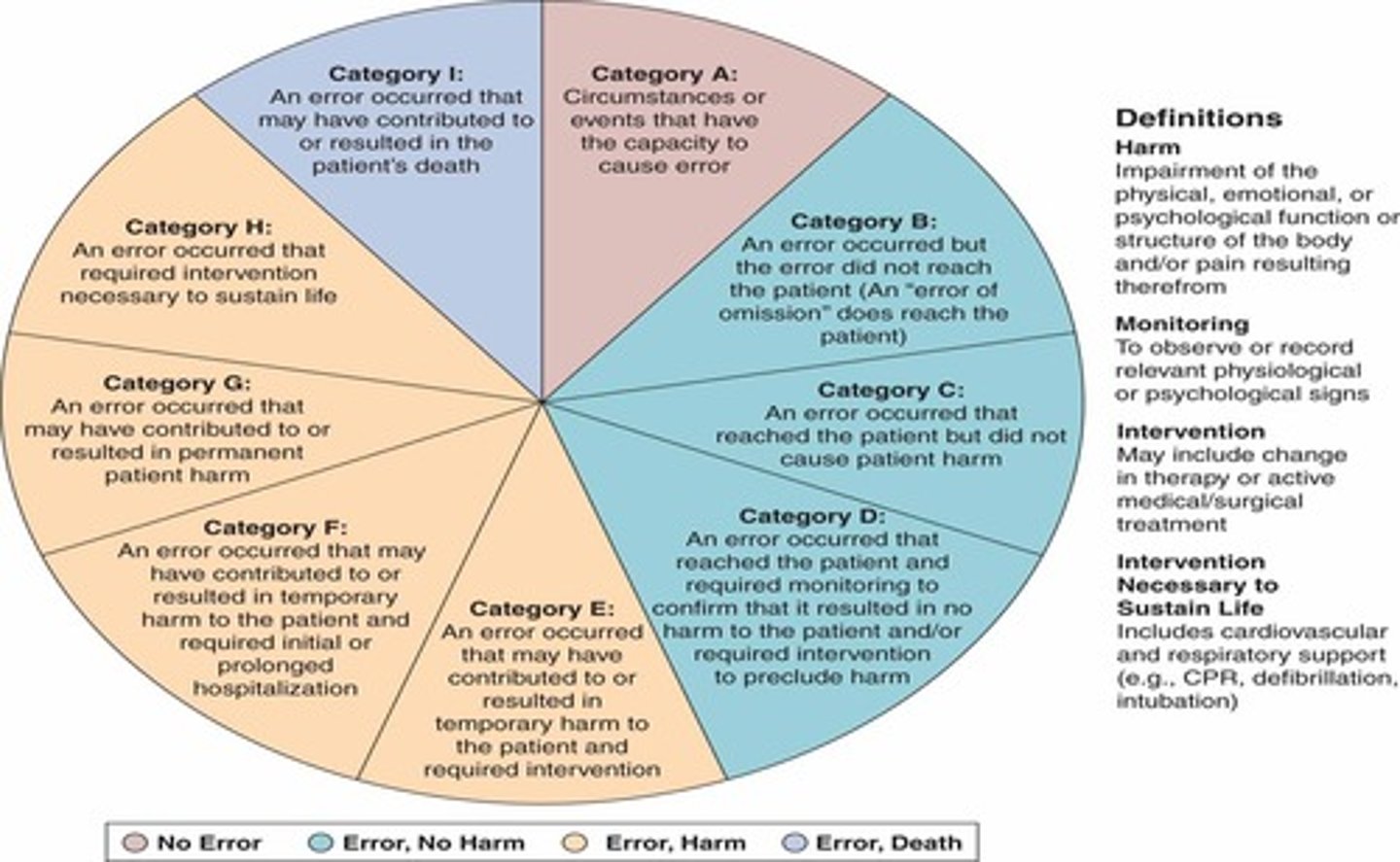
What category of the NCC-MERP index results in death?
category I = error resulted in patient death
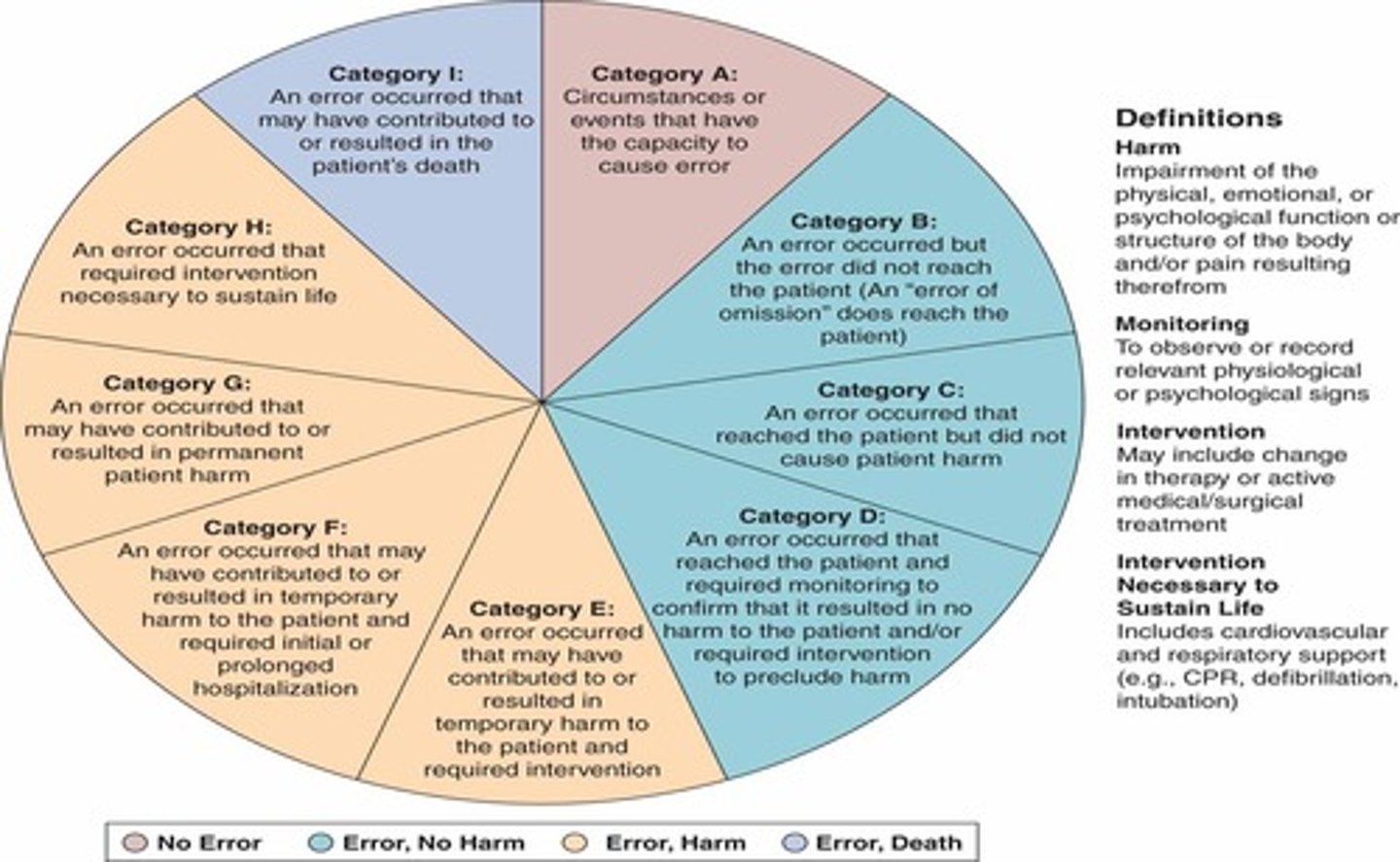
What categories of the NCC-MERP index result in error AND harm to the patient?
category E = in need for intervention (temporary harm)
category F = initial or prolonged hospitalization (temporary harm)
category G = permanent harm
category H = near-death event (i.e. anaphylaxis)
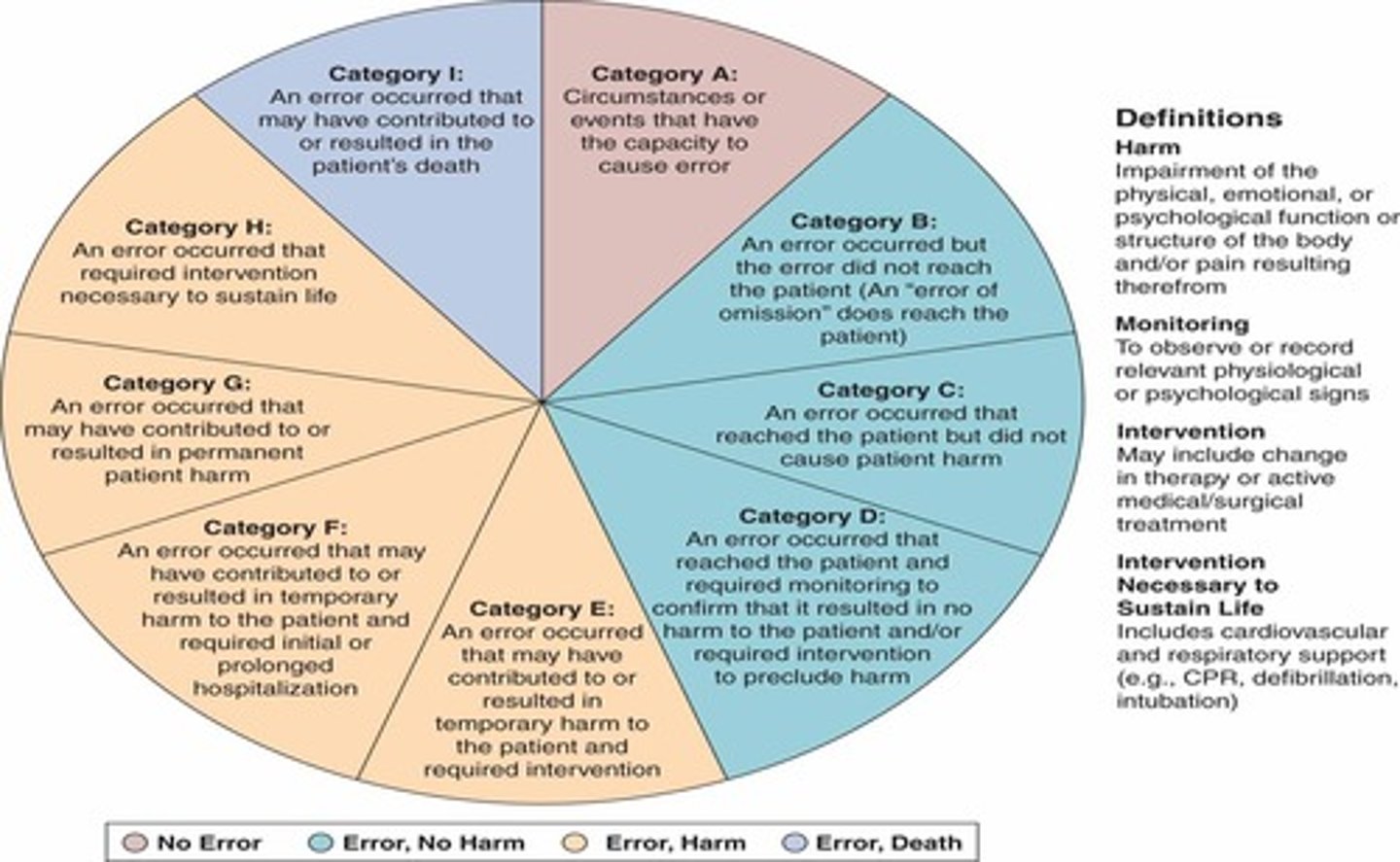
What categories of the NCC-MERP index result in error BUT no harm to the patient?
category B = did not reach patient
category C = did reach patient, but did not cause harm
category D = resulted in the need for increased monitoring but no harm