IDSC 3001-- IT Infrastructure, IT Security, Databases
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
1
New cards
Moore's Law
- computing power doubles every 18 months
- "the number of transistors on a microchip doubles every two years. The law claims that we can expect the speed and capability of our computers to increase every two years because of this, yet we will pay less for them"
- "the number of transistors on a microchip doubles every two years. The law claims that we can expect the speed and capability of our computers to increase every two years because of this, yet we will pay less for them"
2
New cards
types of computer software
1. Operating Systems
2. Application Software
3. Programming Software
2. Application Software
3. Programming Software
3
New cards
operating systems
software that controls the compute hardware and establishes standards for developing and executing applications [iOS, Windows, Linux]
4
New cards
application software
desktop applications, enterprise software, utilities, and other programs that perform specific tasks for users and organizations [Word, Chrome]
5
New cards
programming software
An Intergrated Development Environment (IDE) to write code (Java IDE)
- text editors, debugger for finding errors, complier to turn human readable codes into ones and zeros
- text editors, debugger for finding errors, complier to turn human readable codes into ones and zeros
6
New cards
desktop vs enterprise application software
- Desktop: application on personal computer, typically supporting tasks performed by a single user (games, web browsers)
- Enterprise: applications that address the needs of multiple users throughout an organization (ERP, CRM, BI)
- Enterprise: applications that address the needs of multiple users throughout an organization (ERP, CRM, BI)
7
New cards
distributed computing
a form of computing where systems in different locations communicate and collaborate to complete a task (company Intranet, webpages, email)
8
New cards
server
a program or computer that fulfills the requests of a client
9
New cards
client
a program or computer that makes requests of a server program or computer
10
New cards
service
software chucks or components constructed so that they can be easily liked with other software components
- "get credit rating"; "get customer service record"
- "get credit rating"; "get customer service record"
11
New cards
web services
small pieces of code that are accessed via the application server that permit interoperable machine-to-machine interactions over a network
- accessing a database program (results you searched for)
- making a request to a server (verify this customer's credit card number)
- accessing a database program (results you searched for)
- making a request to a server (verify this customer's credit card number)
12
New cards
Service-Oriented Architecture
a development strategy or methodology that builds all the software assets in the company using service-oriented programming methodology
- software reuse
-productivity increases
- increase agility
- software reuse
-productivity increases
- increase agility
13
New cards
Application Programming Interface (API)
programming hooks, or guidelines, published by firms that tell other programs how to get a service to perform a task such as sending or receive data
14
New cards
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
set of standards for exchanging messages containing formatted data between computer applications
15
New cards
cloud computing
- hardware and software exists "in the cloud," (somewhere on the Internet)
- you only pay for the amount of processing, storage, and telecommunications used
- you only pay for the amount of processing, storage, and telecommunications used
16
New cards
Platform as a Service
cloud providers offer services for customers to build their own applications on the provider's infrastructure
- services include hardware, operating system, tools, and hosting
- services include hardware, operating system, tools, and hosting
17
New cards
Infrastructure as a Service
cloud providers offer services that include running the remote hardware, storage, and networking. Client firms can choose the software used.
18
New cards
Software as a Service and benefits and risks
- a firm subscribes to a third-part software service delivered online
Benefits:
1. lower cost and financial risk mitigiation
2. faster deployment times and variable operating expense
3. scalable systems
4. higher quality and service levels
Risks:
1. dependence on single vendor; long-term viability of partner firms
2. users may be forced to migrate to new versions
3. reliance on network connection
4. data assets stored off-site may lead to security and legal concerns
5. limited configuration, customization and system integration options
6. user interface less sophisticated
Benefits:
1. lower cost and financial risk mitigiation
2. faster deployment times and variable operating expense
3. scalable systems
4. higher quality and service levels
Risks:
1. dependence on single vendor; long-term viability of partner firms
2. users may be forced to migrate to new versions
3. reliance on network connection
4. data assets stored off-site may lead to security and legal concerns
5. limited configuration, customization and system integration options
6. user interface less sophisticated
19
New cards
Virtualization
a type of software that allows a single computer or cluster of connected computers to function as if it were several computers
20
New cards
Internet Service Provider
organizations or firms that provide access to the internet; internet was designed to be redundant and fault-tolerant
21
New cards
Local Area Network (LAN)
a computer network covering a small physical area
22
New cards
Internet Backbone
high-speed data lines that interconnect and collectively form the core of the Internet
23
New cards
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
identifies resources on the internet along with the application protocol needed to retrieve it. ("web address")
24
New cards
Protocol
enables communications by defining the format of data and rules for exchange
25
New cards
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- works at both ends of the internet communication to ensure a perfect copy of a message is sent
- slices up the Web page into smaller chunks (packets or datagrams)
- slices up the Web page into smaller chunks (packets or datagrams)
26
New cards
Internet Protocol (IP)
routing protocol that is in charge of forwarding packets on the internet (relay work is done via routers)
27
New cards
IP address
Value used to identify a device that is connected to the Internet
28
New cards
Domain Names Systems (DNS)
Internet directory service that allows devices and services to be named and discoverable (The Internet's Phonebook)
29
New cards
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
used for email communication
30
New cards
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
used to copy files from one computer to another
31
New cards
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
allows web browsers and web servers to communicate with each other
32
New cards
Amdahl’s Law
system's speed is determined by its slowest component
33
New cards
Net Neutrality (three principles)
the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally
1. no blocking: ISP cannot bock from accessing legal internet content
2. no throttling: cannot intentionally target and slow down traffic speed of legal internet content
3. no paid prioritization: ISP cannot offer "fast lane" service to content providers who can pay more than others.
1. no blocking: ISP cannot bock from accessing legal internet content
2. no throttling: cannot intentionally target and slow down traffic speed of legal internet content
3. no paid prioritization: ISP cannot offer "fast lane" service to content providers who can pay more than others.
34
New cards

IT Infrastructure
35
New cards
Malicious software and threats
- viruses
- worms
- rootkit
- Trojan horse
- computer intrusion or hacking
- phishing
- man-in-the-middle attack
- denial-of-service attack
- botnets
- worms
- rootkit
- Trojan horse
- computer intrusion or hacking
- phishing
- man-in-the-middle attack
- denial-of-service attack
- botnets
36
New cards
viruses
Software that is capable of executing an unwanted action on the victim's computer and has a mechanism for replicating itself and infecting other files and computers
37
New cards
worms
- A more dangerous evolution of viruses, worms are self-propagating.
- Worms take advantage of security vulnerability to automatically spread, even without human actions, e.g., clicking on an infected attachment
- Worms take advantage of security vulnerability to automatically spread, even without human actions, e.g., clicking on an infected attachment
38
New cards
rootkit
- Computer software that hides the presence and activity of intruders
- Used in combination with Trojan software, hackers can change system settings and use the computer without the user or monitoring software detecting it
- Used in combination with Trojan software, hackers can change system settings and use the computer without the user or monitoring software detecting it
39
New cards
Trojan horse
- It claims to do one thing or nothing harmful but instead does damage when you run it
- Can be controlled remotely by hackers to extract passwords and other sensitive information
- Can be controlled remotely by hackers to extract passwords and other sensitive information
40
New cards
computer intrusion or hacking
Unauthorized access to a computer system, whether it be manual such as using a stolen password or automated through software to bypass network security protection via the Internet
41
New cards
phishing
Software that tricks Internet users into divulging their personal information or installing malicious software, often done using fake emails and websites that look like real and from legitimate sources
42
New cards
man-in-the-middle attack
Criminals create bogus sites that are capable of communicating directly with legitimate sites in real time.
43
New cards
denial-of-service attack
- Shutting down websites with a crushing load of seemingly legitimate requests.
- Inundating a computer, router or other networked device with more packets of data than it can process, effectively blocking any legitimate requests to access the system
- Inundating a computer, router or other networked device with more packets of data than it can process, effectively blocking any legitimate requests to access the system
44
New cards
botnets
- Hordes of surreptitiously infiltrated computers, controlled remotely.
- Networked groups of compromised or zombie computers that are controlled by hackers, usually through Trojan software to deliver spam, phishing, and DDoS attacks
45
New cards
anti-phishing tips
1. the wise always look at the URL
2. the middle part of the URL tells you the name of the site
3. when in doubt, Google it
4. Know the enemy's tricks and don't fall for them
2. the middle part of the URL tells you the name of the site
3. when in doubt, Google it
4. Know the enemy's tricks and don't fall for them
46
New cards
security actions
For users:
- Surf smart
- Stay vigilant
- Stay updated (with patches)
- Install a full suite of security software
- Secure home networks and encrypt hard drives
- Regularly update passwords
- Be disposal smart
- Regularly back up your system
- Check with your administrator
For Organizations:
- Anti-virus software
- User security training
- Software updates and patches
- Risk assessment team
- File backups and Business Continuous Plan
- Use access controls on a need-to-know basis
- Surf smart
- Stay vigilant
- Stay updated (with patches)
- Install a full suite of security software
- Secure home networks and encrypt hard drives
- Regularly update passwords
- Be disposal smart
- Regularly back up your system
- Check with your administrator
For Organizations:
- Anti-virus software
- User security training
- Software updates and patches
- Risk assessment team
- File backups and Business Continuous Plan
- Use access controls on a need-to-know basis
47
New cards
anti-virus software
- checks computer systems and drives for presence of computer viruses
- to remain effective, antivirus software must be continually updated
- to remain effective, antivirus software must be continually updated
48
New cards
intrusion detection systems
- full-time, real-time monitoring tools placed at most vulnerable points of corporate networks to detect hacking attempts and take preventive actions
- scanning software that looks for patterns such as bad passwords, removal of important files, and notifies admins
- scanning software that looks for patterns such as bad passwords, removal of important files, and notifies admins
49
New cards
security training
teaching computer users not to click on communications or software that they are not expecting to receive
50
New cards
null routing
- (black hole route) a network route or kernel routing table entry that goes nowhere. Matching packets are dropped (ignored) rather than forwarded
- mitigate distributed denial-of-service attacks
- mitigate distributed denial-of-service attacks
51
New cards
firewalls
control network traffic and block unauthorized traffic
52
New cards
network monitoring
A network monitoring system monitors and tracks network activity for issues or problems caused by malfunctioning devices or overloaded resources (servers, network connections or other devices).
https://www.mantisnet.com/blog/understanding-the-difference-between-network-monitoring-and-network-security-monitoring
https://www.mantisnet.com/blog/understanding-the-difference-between-network-monitoring-and-network-security-monitoring
53
New cards
data encryption
- Encryption: Scrambling data using a code, thereby hiding it from those who do not have the unlocking key.
- Key: Code that unlocks encryption.
- Public key encryption: Two key system used for securing electronic transmissions.
- Key: Code that unlocks encryption.
- Public key encryption: Two key system used for securing electronic transmissions.
54
New cards
multi-factor authentication
- when identity is proven by presenting more than one item for proof of credentials
- two-factor authentication (ex. DUO)
- two-factor authentication (ex. DUO)
55
New cards
password dos and don'ts
- DOS
1. Choose passwords that are tough to guess but easy for you to remember (a phrase)
2. Update your passwords regularly
3. Consider a secure password management tool such as 1Password or LastPass
- DONT
1. Do not include personal information in the passwords such as name or birthdays
2. Never save passwords in nonsecured files, emails or easily accessed locations
1. Choose passwords that are tough to guess but easy for you to remember (a phrase)
2. Update your passwords regularly
3. Consider a secure password management tool such as 1Password or LastPass
- DONT
1. Do not include personal information in the passwords such as name or birthdays
2. Never save passwords in nonsecured files, emails or easily accessed locations
56
New cards
zero-day exploits
new attacks that haven't been clearly identified and haven't been incorporate into security screening systems
57
New cards
brute-force attacks
exhausts all possible password combinations to break into an account
58
New cards
black lists
deny the entry of specific IP addresses or entities
59
New cards
whitelists
permit communication only with approved IP addresses or entities
60
New cards
cyberwarefare
Cyberwarfare is the use of cyber attacks against an enemy state, causing comparable harm to actual warfare and/or disrupting vital computer systems
Wikipedia
Wikipedia
61
New cards
types of offenders
Data harvesters: Cybercriminals who infiltrate systems and collect data for illegal resale.
Cash-out Fraudsters: Criminals that purchase assets from data harvesters to be used for illegal financial gain. They might buy goods using stolen credit cards or create false accounts.
Cash-out Fraudsters: Criminals that purchase assets from data harvesters to be used for illegal financial gain. They might buy goods using stolen credit cards or create false accounts.
62
New cards
social engineering
the art of getting people to reveal sensitive information about a system. This is usually done by impersonating someone or by convincing people to believe you have permissions to obtain such information.
63
New cards
hackers
1. Hacker: someone who breaks into a computer
- Used to refer to a particularly clever programmer.
2. White hat hackers: Uncover computer weaknesses without exploiting them.
3. Black hat hackers: Computer criminals who exploit a system’s weakness for personal gain.
4. Hacktivists: Protester seeking to make a political point by leveraging technology tools, often through system infiltration, defacement, or damage.
- Used to refer to a particularly clever programmer.
2. White hat hackers: Uncover computer weaknesses without exploiting them.
3. Black hat hackers: Computer criminals who exploit a system’s weakness for personal gain.
4. Hacktivists: Protester seeking to make a political point by leveraging technology tools, often through system infiltration, defacement, or damage.
64
New cards

IT Security
65
New cards
Relational Table
- Rows (record/ tuple) represent entities [customer]
- Columns (fields) represent attribute of entities [name, address]
- Columns (fields) represent attribute of entities [name, address]
![- Rows (record/ tuple) represent entities [customer]
- Columns (fields) represent attribute of entities [name, address]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/39366897282147cebc8684ad61277372.jpeg)
66
New cards
primary key
- A (primary) key is a column that identifies a unique row in a table Supplier_Number)
- column that identifies each record (ID)
- column that identifies each record (ID)
67
New cards
foreign key
- A foreign key is a key of a different or foreign table (e.g., Supplier_Number)
- connects parent table and host table (ID) --> an ID to an email in a separate table
- connects parent table and host table (ID) --> an ID to an email in a separate table
68
New cards
compound key
- A compound key is a group of columns that identifies a unique row in a table (e.g., city and state)
- grouping two keys (ID and name)
- grouping two keys (ID and name)
69
New cards
data redundancy
Same information being stored multiple times
- CSE, Mr.X, 53337
- CSE, Mr.X, 53337
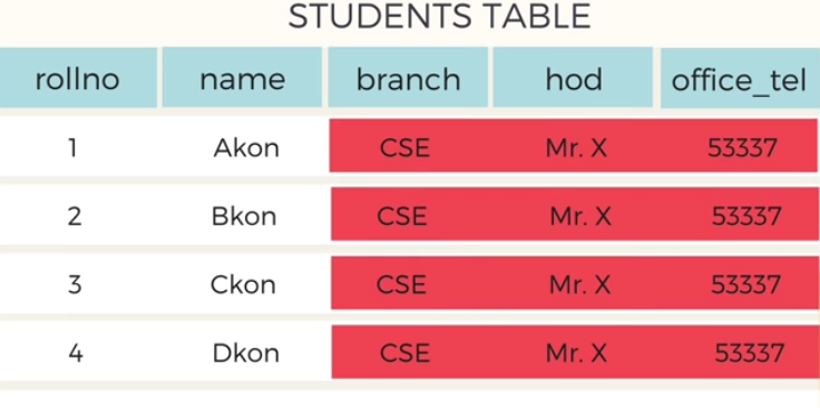
70
New cards
data integrity issues
Insertion anomaly: Need to insert redundant data (might make a mistake)
Deletion Anomaly: Loss of data in the related table (deleting info in table means won't have info anywhere else)
Update Anomaly: Need to update redundant data (might miss an update)
Deletion Anomaly: Loss of data in the related table (deleting info in table means won't have info anywhere else)
Update Anomaly: Need to update redundant data (might miss an update)
71
New cards
normalization
- Normalization is the process of converting a poorly structured table into two or more well-structured tables to eliminate data redundancy.
- The goal is to construct tables such that each table has a single relationship or theme.
- The goal is to construct tables such that each table has a single relationship or theme.
72
New cards
Structured Query Language
An international standard language for processing databases
- Read data
- Insert data
- Modify data
- Delete data
- Read data
- Insert data
- Modify data
- Delete data
73
New cards
relational operations
- Select: creates subsets of data of all records that meet stated criteria
- Project: creates subsets of columns
- Join: combines relational tables to provide users with more information that is available in individual tables
- Project: creates subsets of columns
- Join: combines relational tables to provide users with more information that is available in individual tables
74
New cards
ACID rules
- Atomicity: the money can’t be taken out of your checking account without being subsequently deposited in savings.
- Consistency: ensures that all changes to the tables follow the rules and keep the databases in a valid state.
- Isolation ensures that other banking transactions don’t affect the outcome of your transfer. Other transaction to alter your checking balance must wait until your transaction completes.
- Durability: once the transaction is saved or committed, it can’t be “lost.” That is, a power outage or system crash won’t cause any of the data to go missing.
- Consistency: ensures that all changes to the tables follow the rules and keep the databases in a valid state.
- Isolation ensures that other banking transactions don’t affect the outcome of your transfer. Other transaction to alter your checking balance must wait until your transaction completes.
- Durability: once the transaction is saved or committed, it can’t be “lost.” That is, a power outage or system crash won’t cause any of the data to go missing.
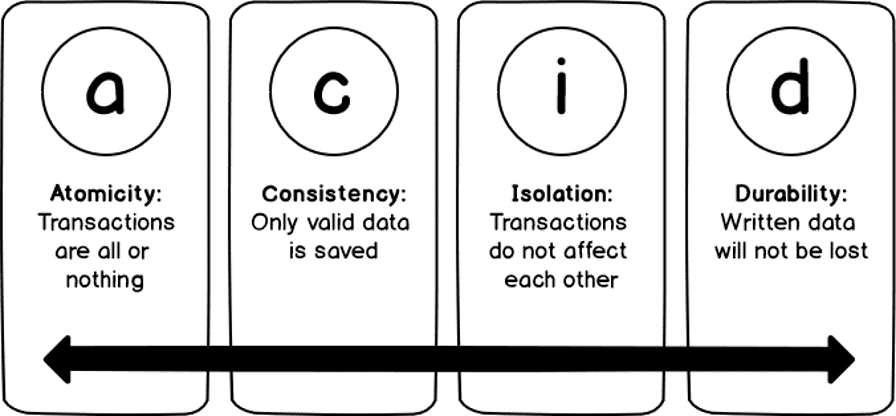
75
New cards
database management systems
- A database management system (DBMS) is a program used to create, process, and administer a database.
- A database is a structured collection of records or data that is stored in a computer system (e.g., a relational database is a collection of tables)
- A database is a structured collection of records or data that is stored in a computer system (e.g., a relational database is a collection of tables)
76
New cards

Databases