Pregnancy (Cram)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
The union of sperm and egg
Fertilization
Fill in the blank: Fertilization usually occurs in the upper _____ [fraction] of the oviduct, at the _____ - _____ junction.
third, ampullary, isthmal
What process do sperm undergo before being capable of fertilizaing the egg?
Capacitation
Only one sperm should penetrate the egg, this is due to what reaction?
Zona reaction
Note: This occurs in fertilization when a sperm cell unites with the egg's plasma membrane.
Fill in the blank: During a zona reaction enzymes released by _____ granules digest receptor proteins so that they can no longer bind sperm.
cortical
Condition when multiple sperm fuse with a single egg
Polyspermy
Note: Will result in a swift abortion
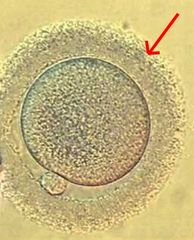
What type of cells is the red arrow pointing to?
Cumulus cells
What process is similar to a zona reaction, but it occurs in sea urchins
Vitelline block
What is a fertilized egg called UNTIL it reaches the 16 cell stage?
Zygote
True or false: Technically the life of the new individual begins at the union of the sperm and the egg. This is the moment of conception.
True. Although beliefs differ about this
The zygote receives its nutrients from its own cytoplasm, and later from “uterine milk” secreted form the uterine mucosal glands. What is the another term for this source of nutrition?
Histotrophe
Note: This contains metabolites, fat, and glycogen
Fill in the blank: As the zygote develops, a ______ must also develop to attach the zygote to the uterus.
placenta
Note: The placenta allows the zygote to derive nutrients and transfer waste products through maternal blood
What are the three distinctive phases occur in the development of the conceptus (fetus)?
- Cleavage
- Differentiation
- Growth
Put these cells in order from the earliest to most mature: Blastocyst, zygote, 8-celled stage, 6-celled stage, ootid, 2-celled stage, and morula
Ootid, zygote, 2-celled stage, 6-celled stage, 8-celled stage, morula, and blastocyst
What stage is this in the development of the fetus: The initial cell divisions (morula, blastocyst, ect.), no embryonic growth occurs?
Cleavage
Fill in the blank: The inner cell mass will eventually form the of the embryo. While the cells form the wall of the blastocyst, and will eventually form a layer of the _
The inner cell mass will eventually form the body of the embryo. While the trophoblast cells form the wall of the blastocyst, and will eventually form a layer of the placenta
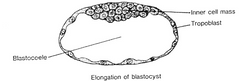
What is the maternal recognition of pregnancy in the bovine and the ovine?
Interferon τ (pronounced "tao")
Note: Bovine interferon τ and ovine interferon τ are the antiluteolyitc signal in each species respectively
What is the maternal recognition of pregnancy in the sow?
Estradiol
If a sow doesn't have four or more blastocysts, estradiol will not be produced, and she will abort without knowing she was pregnant. Why is this advantageous?
The number of piglets represents the percentage of space in the uterus. Having a small litter means means bigger piglets, increasing the chance of dystocia
What is the maternal recognition of pregnancy in the horse?
It has NOT been identifed
What is the maternal recognition of pregnancy in the dog?
Dogs do NOT have a maternal recognition of pregnancy. They always think they are pregant after estrus (ie. pseudocyesis)
What stage is this in the development of the fetus: The period when organ systems are being formed until the species can be recognized. Cells are in the process of differentiating to form specific organs in the body?
Differentiation
What are the three events that occur in differentiation?
Formation of germ layers
Formation of extra-embryonic membranes (ie. placenta)
Organ formation
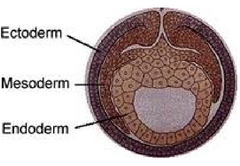
What are the three main germ layers that initially form from the inner cell mass?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
Which germ layer gives rise to the digestive system, liver, lungs, pancreas, thyroid gland, and most other glands?
Endoderm
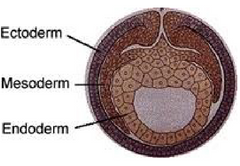
Which germ layer gives rise to the nervous system, sense organs, hair, skin, mammary glands and hooves?
Ectoderm
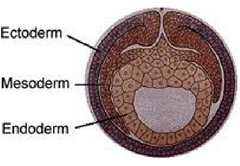
Which germ layer gives rise to the bones, muscles, circulatory system, and reproductive system and kidneys?
Mesoderm
What are the two extraembryonic membranes that form soon after the appearance of the germ layers?
Amnion
Allanto-chorion
Which extraembryonic membrane surrounds the embryo, contains fluids which suspends the embryo, protects it, and permit its free growth?
Amnion
Note: The developing embryo in the amnion is sometimes referred to as the “amniotic vesicle”
Which embryonic membrane forms the major portion of the placenta? It will surround the amnion and embryo
Allanto-chorion
What is the the amber coloured fluid that is contained within the allanto–chorion?
Fetal urine
The allanto–chorion is connected to the embryo by a series of arteries and veins. What is the structure in the fetus it connects to?
Umbilicus (ie. navel)
Which structure is a remnant of the umbilical vein?
Round/falciform ligament
Which structure is a remnant of the umbilical arteries?
Medial umbilical ligament
Which structure is a remnant of the embryonic urachus?
Median umbilical ligament
True or false: Fertilized ova float freely in the uterus for variable lengths of time.
True
Example: Humans: 6
What are the six functions of the placenta?
- Secretes progesterone (maintains the C.L.)
- Secretes various enzymes
- Exchange of nutrients and wastes
- Stores and catabolizes various compounds
- Synthesizes substances required by the fetus
- Transfers passive immunity (some species)
Which two species technically don't need colostrum because the placenta transfers passive immunity?
- Humans
- Rabbits
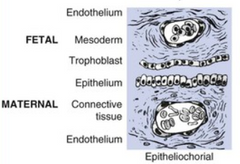
What are the two ways placentas are classified?
- Layers of tissue that intervene between maternal and fetal blood
- Area where they attach to the lining of the uterus
Which placentation type is found in ruminants, horses, whales, and lower primates?
Epitheliochorial placentation
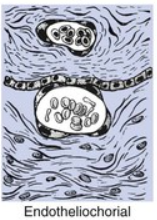
Which placentation type is found in most carnivores like cats and dogs?
Endotheliochorial placentation
Which placentation type is found in higher order primates (ie. humans), and also in guinea pigs, rabbits, mice, and rats?
Hemochorial placentation
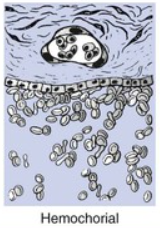
In which placentation type does the maternal blood comes in direct contact with the fetal chorion?
Hemochorial placentation ONLY
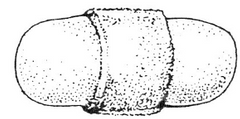
Which attachment classification of placentation is this? And which two species demonstrate it?
Zonary: Dogs, and cats
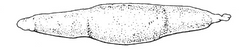
Which attachment classification of placentation is this? And which two species demonstrate it?
Diffuse: Horse, and pig
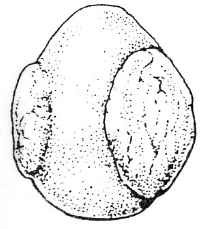
Which attachment classification of placentation is this? And which two types of animals demonstrate it?
Discoid: Humans (and monkeys), and rodents
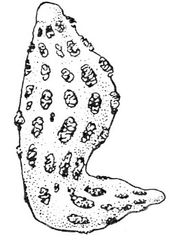
Which attachment classification of placentation is this? And which two species demonstrate it?
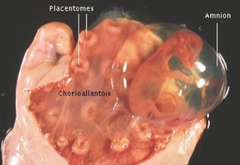
Cotyledonary: Sheep, and cows
Fill in the blank: The cotyledonary placenta has areas called _ where (uterus lining) and (allanto–chorion) are joined together
The cotyledonary placenta has areas called placentomes where caruncles (uterus lining) and cotyledons (allanto–chorion) are joined together
True or false: Species of a fetus cannot be distinguished during the phase of differentiation
True
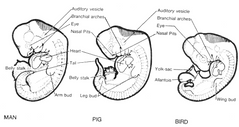
True or false: The period of differentiation is a critical period, but the developing embryo isn't as sensitive to many drugs/chemicals as fetuses in the second or third trimester.
False. The developing embryo is more sensitive to drugs/chemicals during the period of differentiation
Fun fact: Thalidomide birth defects were more likley to occur if women took the morning sickness drug in their first trimester
Fill in the blank: Once _____ formation is complete, the species can be recognized and from this point onward, it is technically referred to as a _____.
organ, fetus
People will often tell pregnant women "you're eating for two now!". But a fetus won't be absorbing many nutrients until it starts growing rapidly. Most fetal growth occurs in which trimester?
Last 1/3 of pregnany (third trimester in humans). This is when feed should be altered to account for pregnancy
Note: The term trimester doesn't always apply well to animals if their gestation doesn't split well into thirds
What is one method of measuring the growth of a fetus and may be used to gauge the approximate length of gestation?
Crown-rump length
Note: Time of spine calcification can also be used. Dogs/cat: 42 days
Period that starts at fertilization, and ends with parturition (the birth process)
Gestation
Giving birth to living offspring that develop within the mother's body
Viviparous
Which other animal (ie. not humans) has an approximately 9 month gestation and can thus be split into trimesters nicely?
Cattle
Note: 282 ± 21 days
Approximately how long is a horse gestation?
346 ± 28 days, 11 months
Approximately how long is a sheep gestation?
150 ± 18 days, 5 months
Note: You'd think alpacas and llamas would be similar to sheep, but they have a gestation of 9 months like cattle
Approximately how long is a pig gestation?
Remember: 3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days
115 ± 5 days, 4 months
Approximately how long is a dog gestation?
63 ± 3 days, 2 months
Approximately how long is a cat gestation?
60 ± 9 days, 2 months