Genetics Exam 3:Transcription (with emphasis on bacterial transcription)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Structure of RNA
RNA is made up of nucleotides, each containing:
-A phosphate group
-A ribose sugar
-A nitrogenous base (Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, or Guanine)
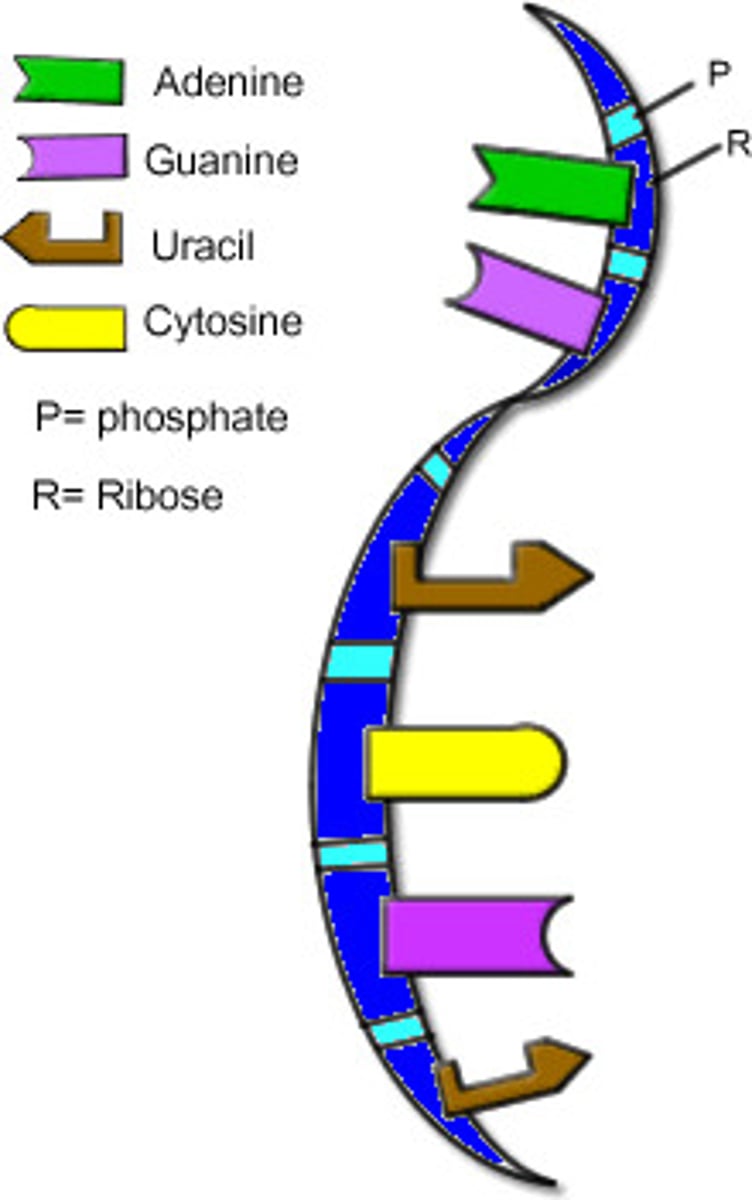
Key Difference of RNA Structure:
Uracil (U) replaces Thymine (T)
Ribose instead of deoxyribose (with one extra oxygen atom)
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology:
DNA → RNA →Protein
-Transcription: DNA is transcribed into RNA.
-Translation: RNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids (protein).
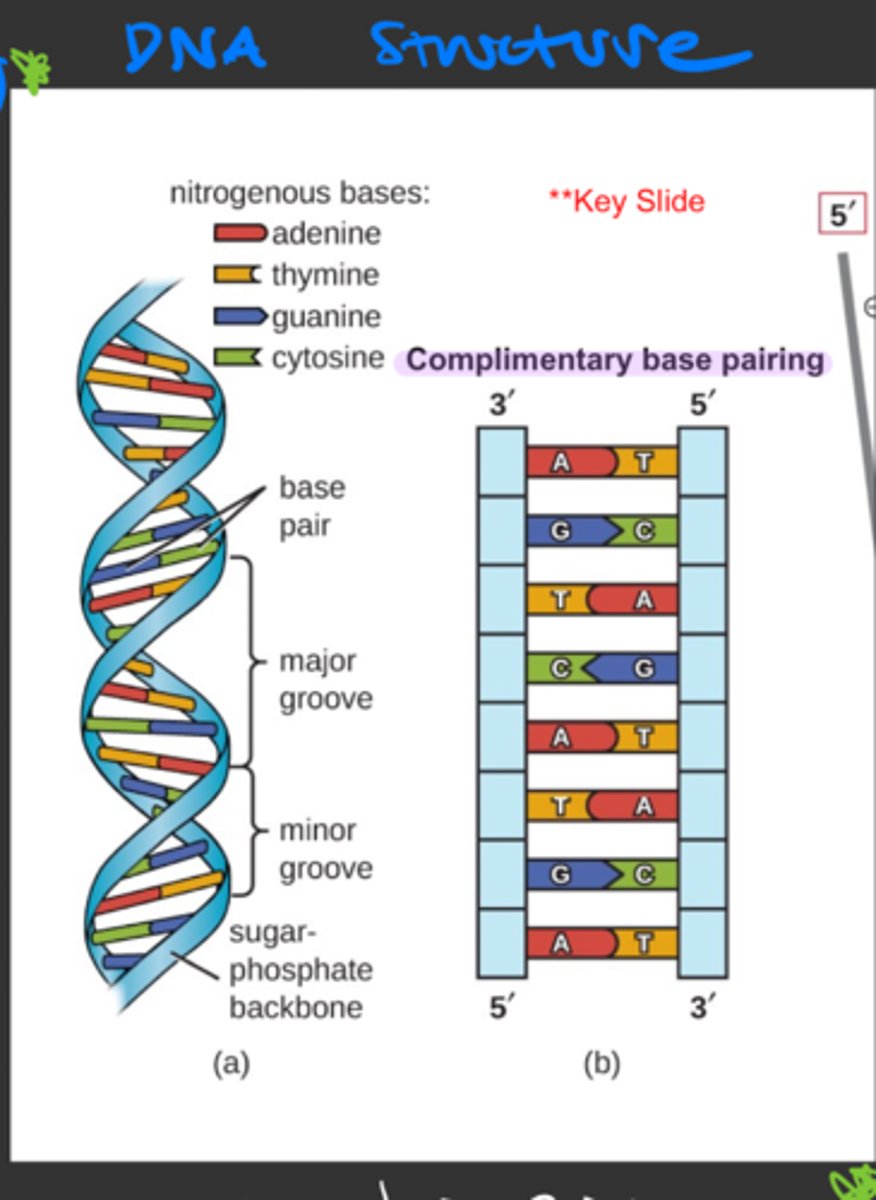
Differences between DNA and RNA:
1.DNA: Deoxyribose (missing an oxygen atom on the 2' carbon).
2.RNA: Ribose (has an oxygen atom on the 2' carbon).
3.Base: DNA: Thymine (T) RNA: Uracil (U) replaces Thymine.
Strand Structure: 4.DNA: Double-stranded.
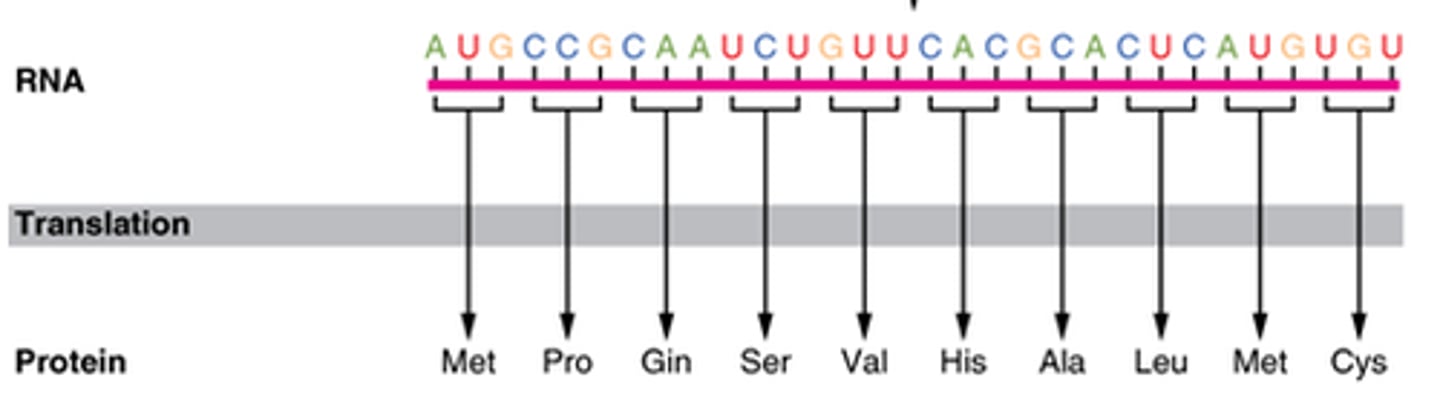
What is Transcription?
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
Goal: To produce an RNA molecule that can be used for protein synthesis or other cellular functions.
Coding Strand:
-the strand of DNA that is not used for transcription and is identical in sequence to mRNA, except it contains uracil instead of thymine
-The strand of DNA that has the same sequence as the RNA (except T → U).
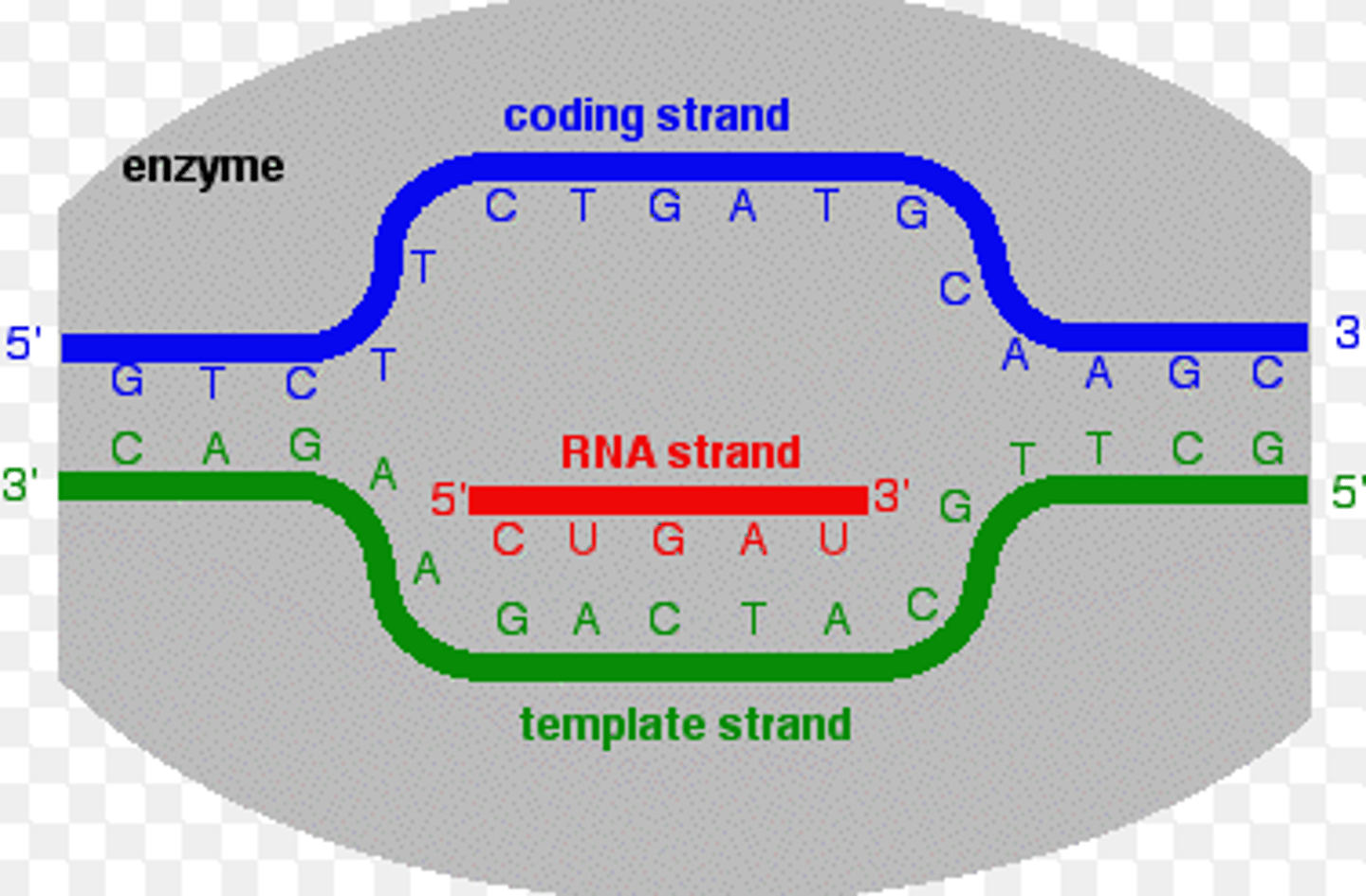
Template Strand:
The strand used by RNA polymerase to synthesize RNA (complementary to the RNA).
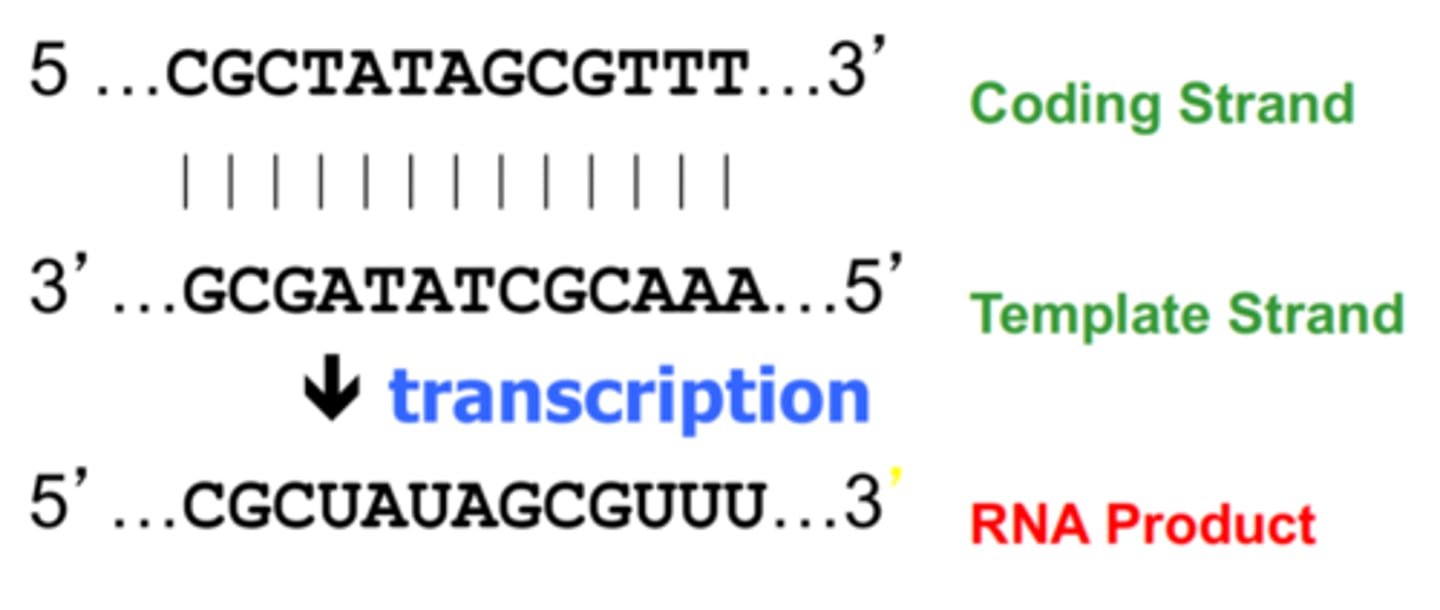
Determining RNA Sequence:
If the Coding Strand is Given: Write the RNA sequence by replacing T → U.
If the Template Strand is Given: Write the RNA sequence by pairing complementary bases (A → U, T → A, C → G, G → C).
Promoter:
-A DNA sequence that signals the beginning of transcription; it's where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription.
-Location:Upstream (before the gene)
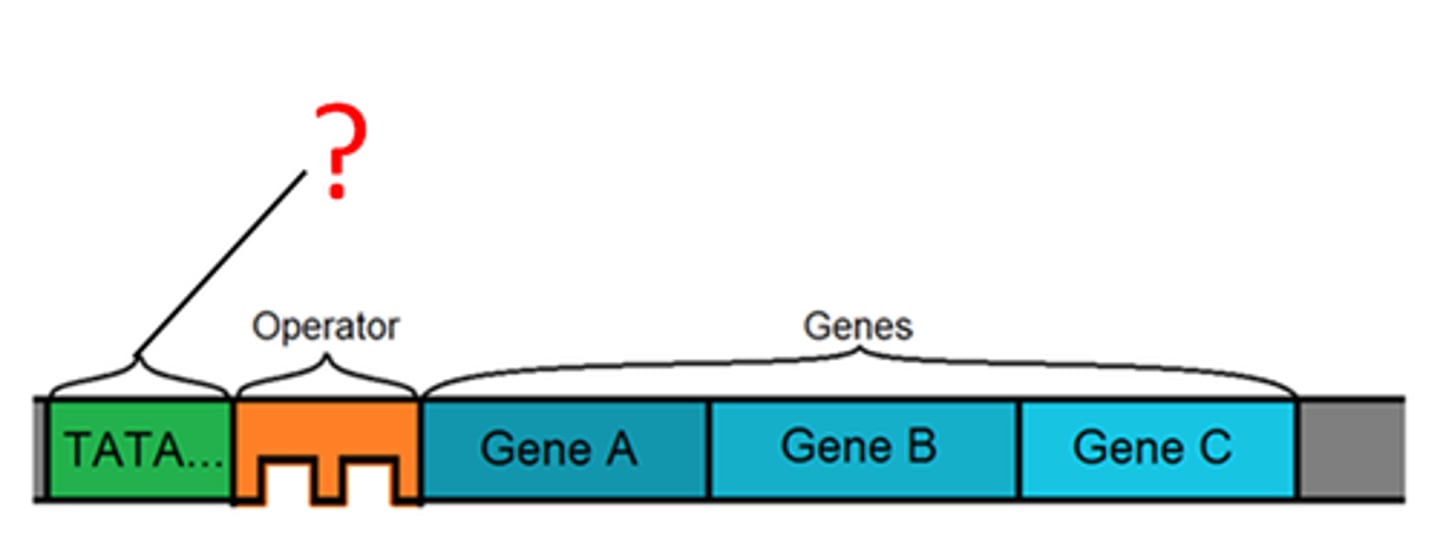
Terminator:
-A DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription.
-Location:Downstream
(after the gene)
Initiation:
-RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region.
-Sigma factor (in bacteria) helps RNA polymerase recognize the promoter.
-Transcription starts at the +1 site, just downstream of the promoter.
Elongation:
-RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides (A, U, C, G) in the 5' → 3' direction.
-It reads the template strand in the 3' → 5' direction.
-The transcription bubble forms as RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA, exposing the template strand.
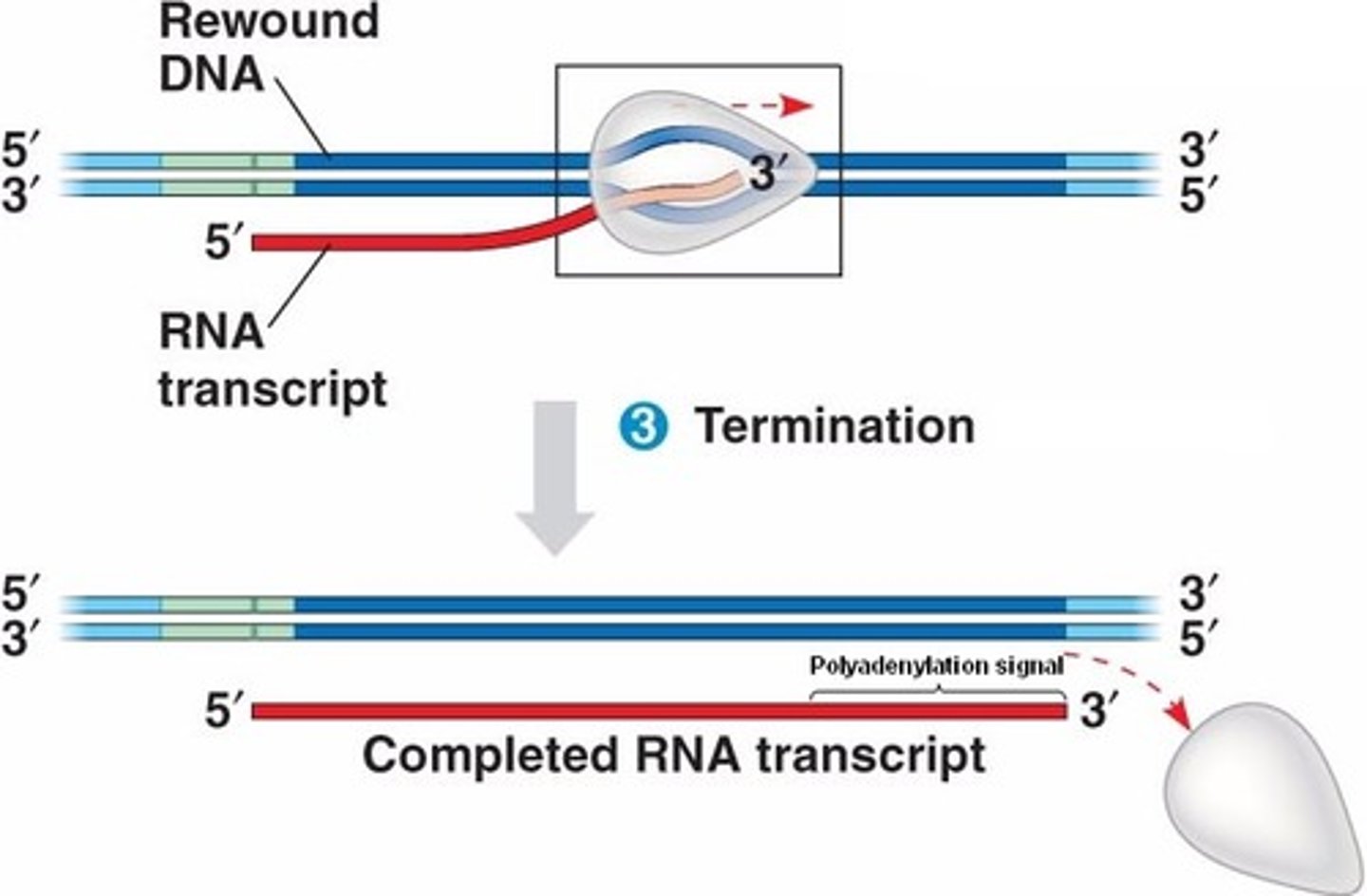
Termination:
-Rho-dependent: Rho protein helps dissociate RNA polymerase from the DNA.
-Rho-independent: A hairpin loop forms in the RNA, causing RNA polymerase to release the transcript.
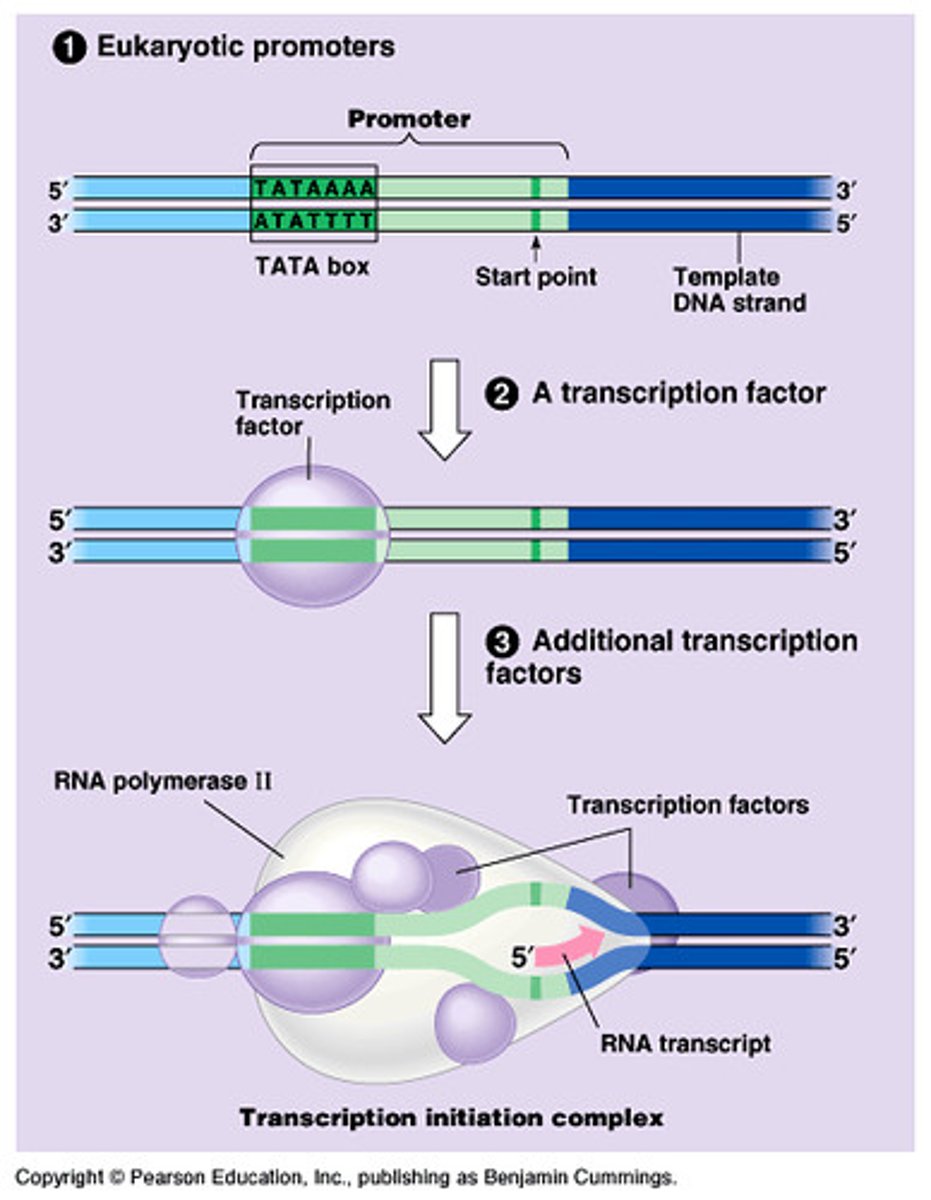
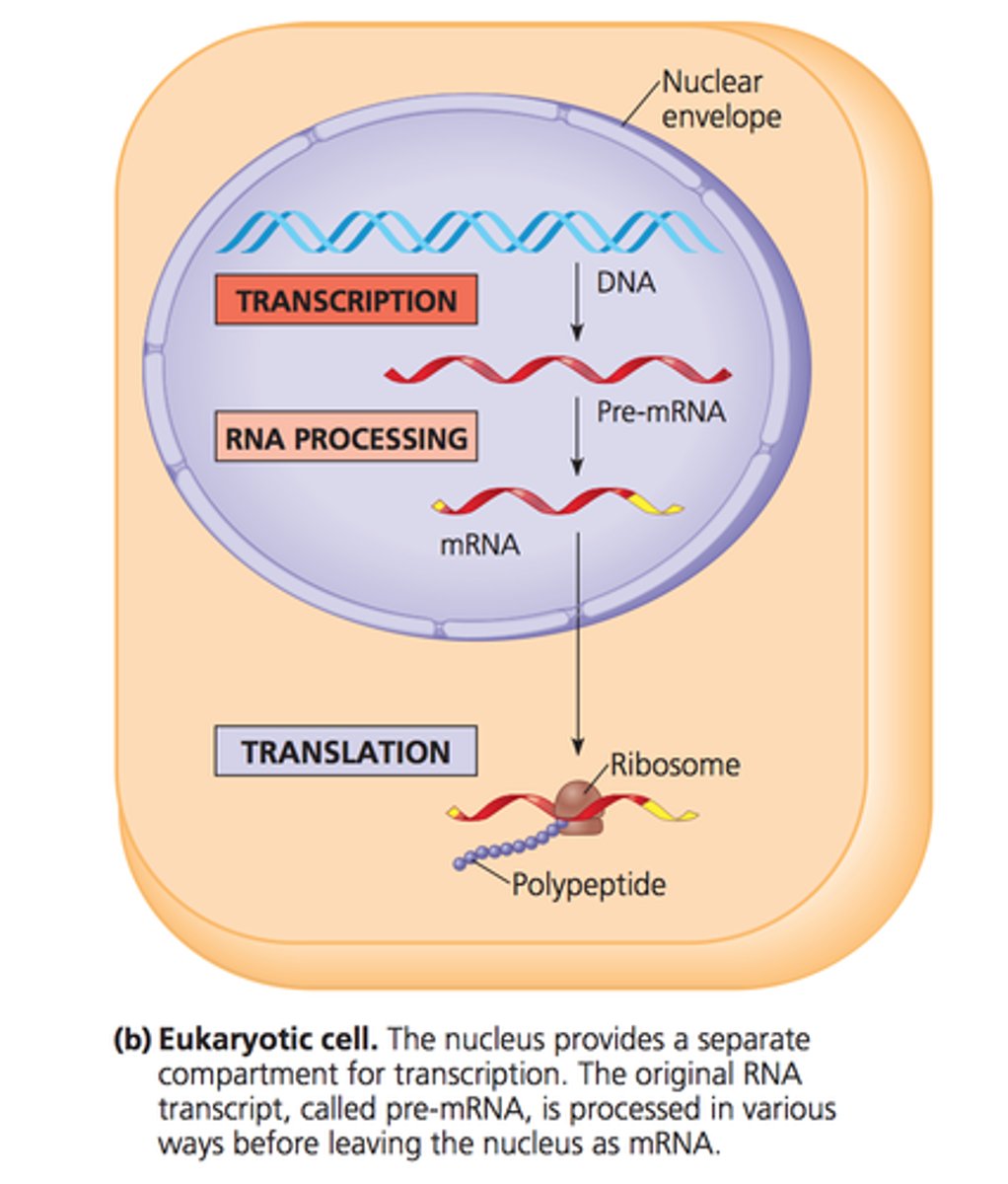
Transcription in Eukaryotes?
-DNA Accessibility: Chromatin remodeling proteins open up the DNA by relaxing histones to make the DNA accessible for transcription.
-Core Promoter: The essential DNA sequence near the start of the gene, where RNA polymerase binds.
-Regulatory Promoter: Further upstream sequences that regulate the rate of transcription.
-Basal Transcription Apparatus: A group of proteins that help initiate transcription. Includes RNA polymerase II, TATA-binding protein (TBP), and transcription factors.
Transcription in Eukaryotes Directionality:
Transcription in eukaryotes occurs 5' to 3' on the RNA strand, matching the 3' to 5' direction of the template strand.
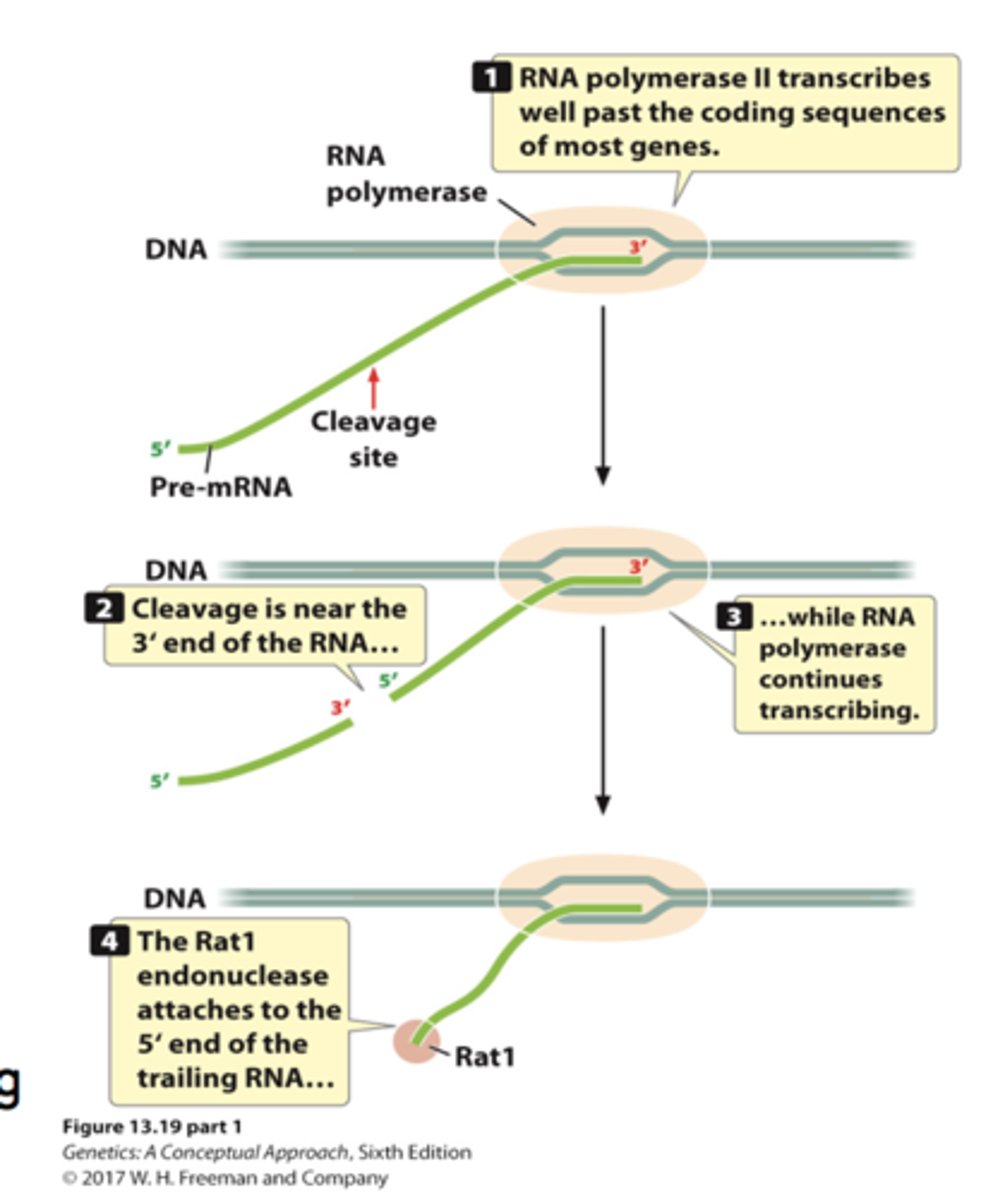
Termination in Eukaryotes:
In eukaryotes, transcription ends when RNA polymerase reaches a specific sequence or a termination signal. Often involves cleavage and polyadenylation.