09.0 Genetics Vocab SIMPLE Review
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
True-breeding
Organism that produces offspring with traits identical to itself; homozygous
Allele
Different forms or "flavors" of a gene
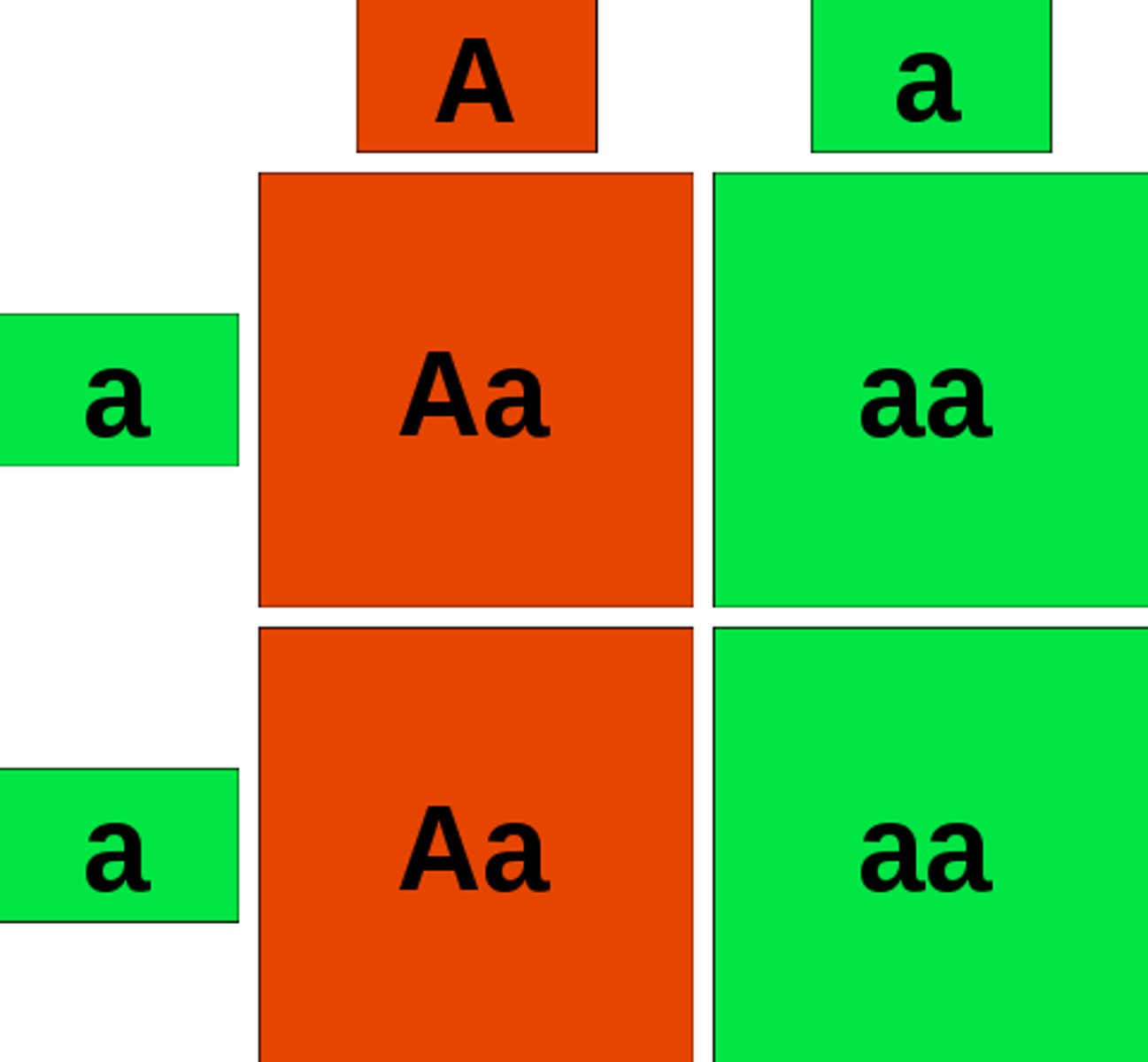
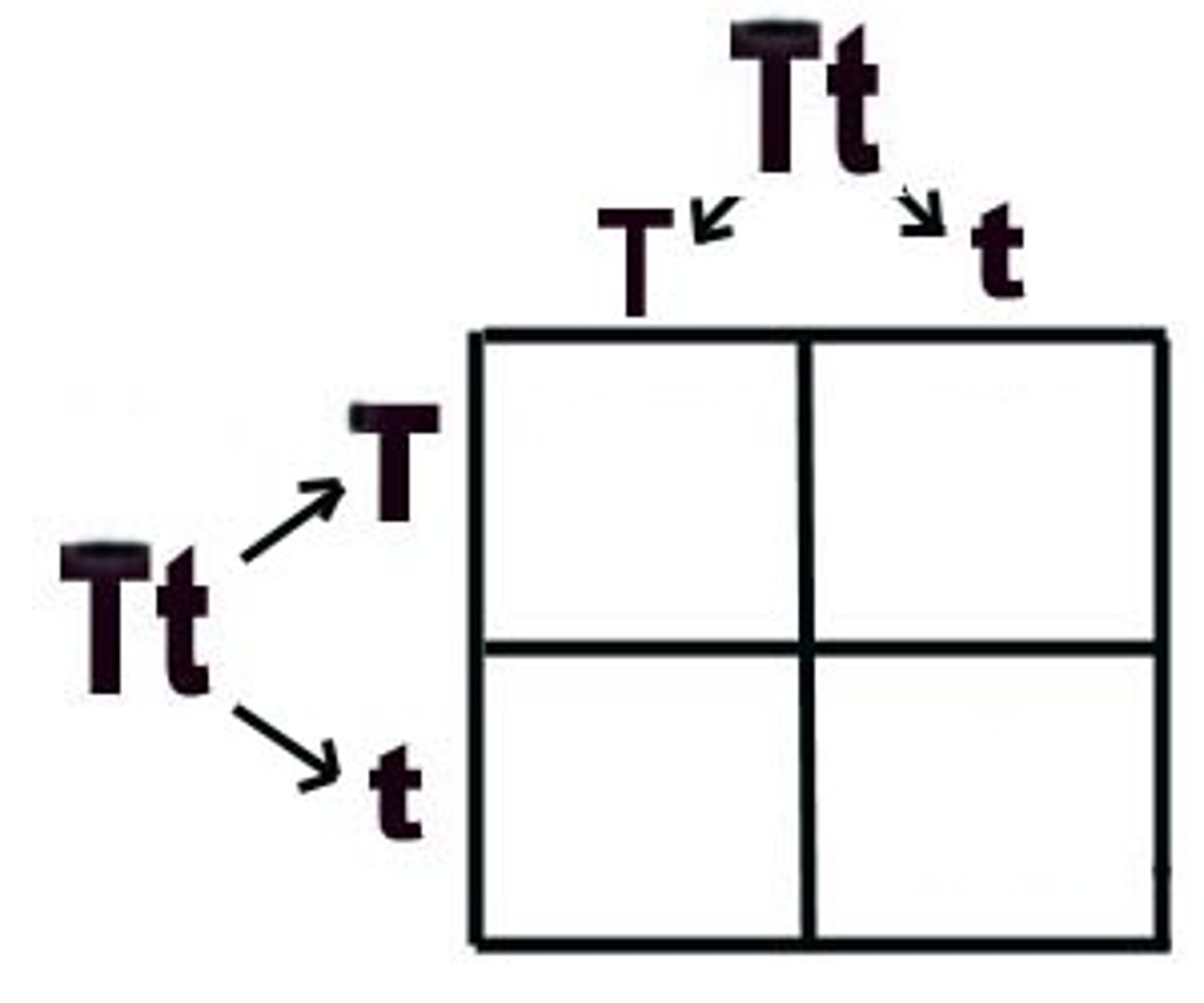
Punnett Square
A diagram used to show potential gene combinations of offspring
Genotype
Genetic make up of an organism
Phenotype
An organism's physical characteristics, or visible traits
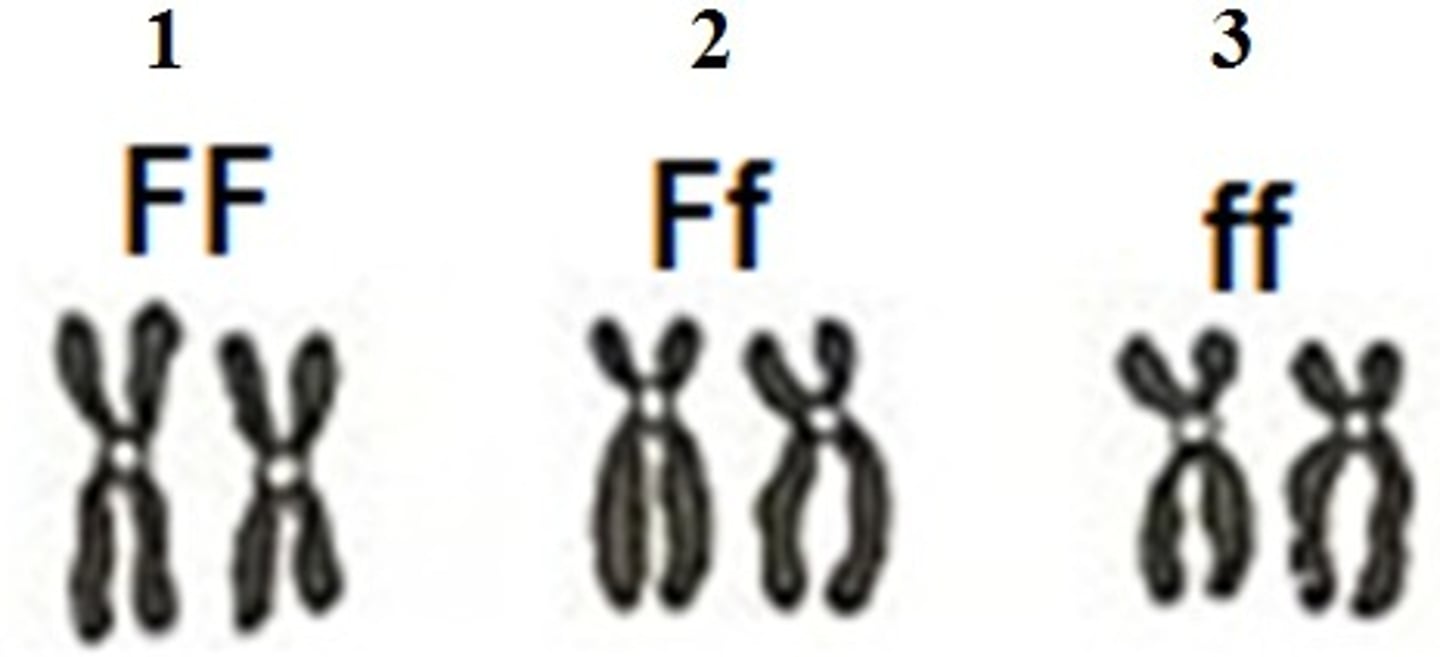
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait; TT or tt
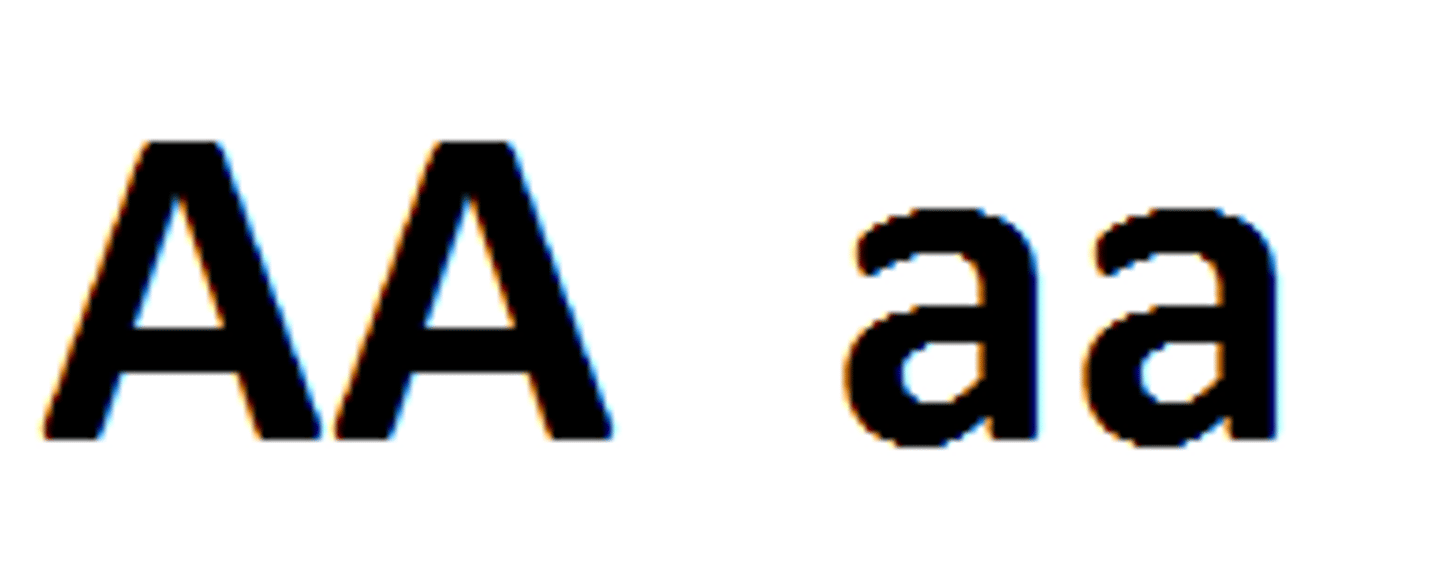
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait; Tt

Principle of Dominance
States that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
Law of Segregation
Mendelian law stating that two alleles for each trait separate during meiosis when gametes are made
Recessive
An allele that is NOT expressed when the dominant form of the trait is present; two alleles must be present to be expressed; tt

Dominant
Describes an allele that covers over, or dominates, another form of that trait

Probability
Likelihood that an event will occur
Gregor Mendel
"Father of Genetics"; studied inheritance of traits using pea plants
Independent assortment
Homologous chromosomes randomly line up double file on the equator during Metaphase I during meiosis when gametes are made
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity
Fertilization
Male and female gametes join during sexual reproduction to form a zygote
Hybrid
Another way to say "heterozygous"
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm and egg)
Trait
Specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another
F1 (first filial) generation
Offspring of the first parental cross
Gene
Sequence of nucleotides found on DNA that codes for a specific trait
P (parental) generation
Original generation in a genetic cross