CHEM 3300 / Topic 1a: Point Groups
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are the three principles of molecular point symmetry?
All symmetry elements intercept in one point.
Molecules are treated as the only molecule present, i.e. the rest of the universe is non-existent.
Point groups are derived from rotation and reflection operations.
Let’s define terms.
What’s a point group?
What’s a symmetry element?
What’s a symmetry operation?
Point group: A group defined by its symmetry operations or a classification to a molecule based on symmetry.
Symmetry element: Point, line, or plane with respect to which the symmetry operation is performed.
Symmetry operation: Actions leaving molecule appearing unchanged or actions to check if there is any symmetry,
Why do we care about symmetry and point groups?
Description of molecular shapes and properties.
Description of molecular orbitals.
Assists in spectroscopy.
What are the four primary symmetry operations and their symmetry elements used in chemistry?
Rotation (Cn) about the proper rotation axis/axes.
Reflection perpendicular to the mirror plane (σ).
Reflection through an inversion centre (i).
Rotation and reflection perpendicular to a proper rotation axis (Sn) with its improper rotation axis/axes.
How do you perform the identity (E) operation?
Leave the molecule as is.
How do you perform rotation (Cn)?
In whatever axis I choose, how many times can I rotate the molecule without changing its appearance in space?
What is the n in Cn?
The number of steps I can take while still looking the same.
How do you perform inversion (i)?
If I displace all atoms to the other side of its axis, will it look the same?
How do you perform reflection (σ)?
If I put a mirror on my molecule, with the plane of the mirror either being vertical or horizontal with respect to my principal rotation axis, will it look the same?
Where are the symmetry elements of the following?
σv
σh
σd
σv : parallel to Cn
σh : perpendicular to Cn
σd : between two 2-fold axes that are perpendicular to the principal Cn
How do you perform improper rotation (Sn)? What is n in Sn?
If I rotate my molecule by its 360º/n and reflect via a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis, will I get get the same molecule each time I rotate and reflect and all the way back to the starting position?
n in Sn is how many times I can rotate and reflect while leaving the molecule unchanged.
What can other symmetry operations can S2 and S1 equal to?
S2 and S1 can equal to i and σ, respectively.
How do you draw the Lewis structure of a molecule?
Write the correct skeletal structure of the molecule, placing more electronegative elements in terminal positions and the less electronegative elements (other than hydrogen) in the central position.
Calculate total # of electrons.
Distribute electrons, giving octets to as many atoms as possible, beginning with bonding pairs, then lone pairs to terminal atoms, then lone pairs to central atom.
If any atom lacks an octet, form double or triple bonds as necessary until all atoms have octets.
How do you calculate the formal charge of an atom?
Formal charge = number of valence electrons - (number of “nonbonding” electrons + ½ number of bonding electrons)
How do you choose the most stable resonance structure, a.k.a. the “ground-state” structure, a.k.a. the major resonance contributor?
Avoid high formal charges and charge separation.
Place negative charges only on more electronegative elements.
What are the rules for assigning oxidation numbers for these?
Free elements.
Monoatomic ion.
Neutral molecule.
Polyatomic ion.
Oxygen.
Oxygen in peroxides.
Hydrogen.
Hydrogen when bound to metals in binary compounds.
Fluorine.
Halogens when combined with oxygen.
Free element: each atom equal to 0.
Monoatomic ion: equal to charge on ion.
Neutral molecule: sum of oxidation numbers must be zero.
Polyatomic ion: sum of oxidation numbers must be equal to net charge of ion.
Oxygen: -2
Oxygen in peroxides: -1.
Hydrogen: +1
Hydrogen when bound to metals in binary compounds: -1.
Fluorine: -1 in all of its compounds.
Halogens when combined with oxygen: (+)ive oxidation number.
What are the generalities for assigning oxidation numbers for these?
Metallic element and nonmetallic elements.
Highest oxidation numbers.
Transition metals.
Metallic elements have only positive oxidation numbers, whereas nonmetallic elements may have either positive or negative oxidation numbers.
The highest oxidation number a representative element can have is its group number in the periodic table.
The transition metals usually have several possible oxidation numbers.
What’s the difference and similarity between oxidation numbers and formal charges?
Formal charge assumes equal sharing.
Oxidation state assumes complete electron transfer based on electronegativity.
Both ways to assign charges to atoms.
How do you predict molecular geometries?
Draw Lewis structure.
Determine total number of electron groups around central atom.
Determine number of bonding groups and number of lone pairs around central atom.
Determine geometry.
What are the steps to determining the point group of a molecule?
Draw Lewis structure.
Determine molecular geometry.
Use decision tree.
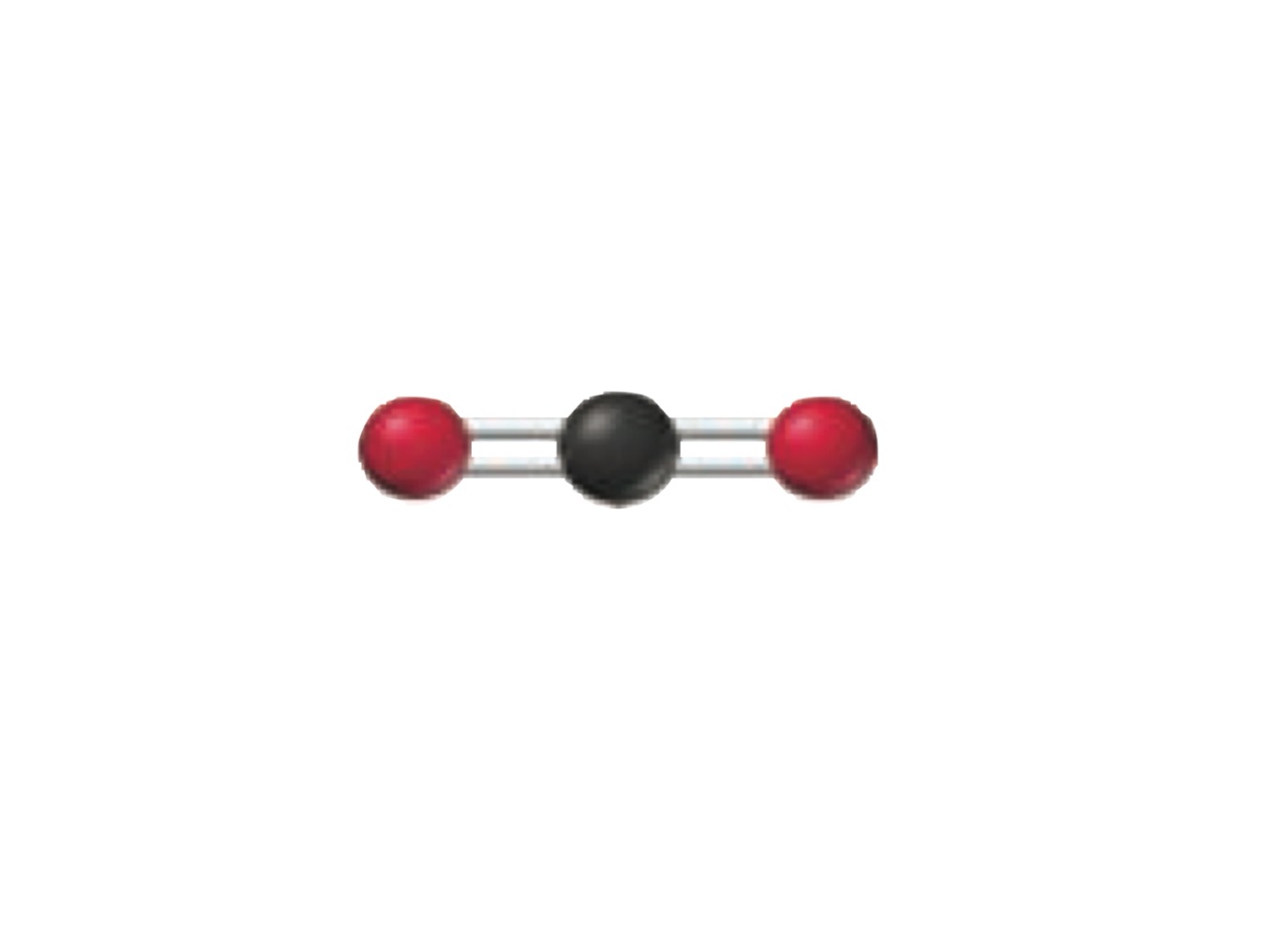
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
2 electron groups.
2 bonding groups.
0 lone pairs.
Linear.
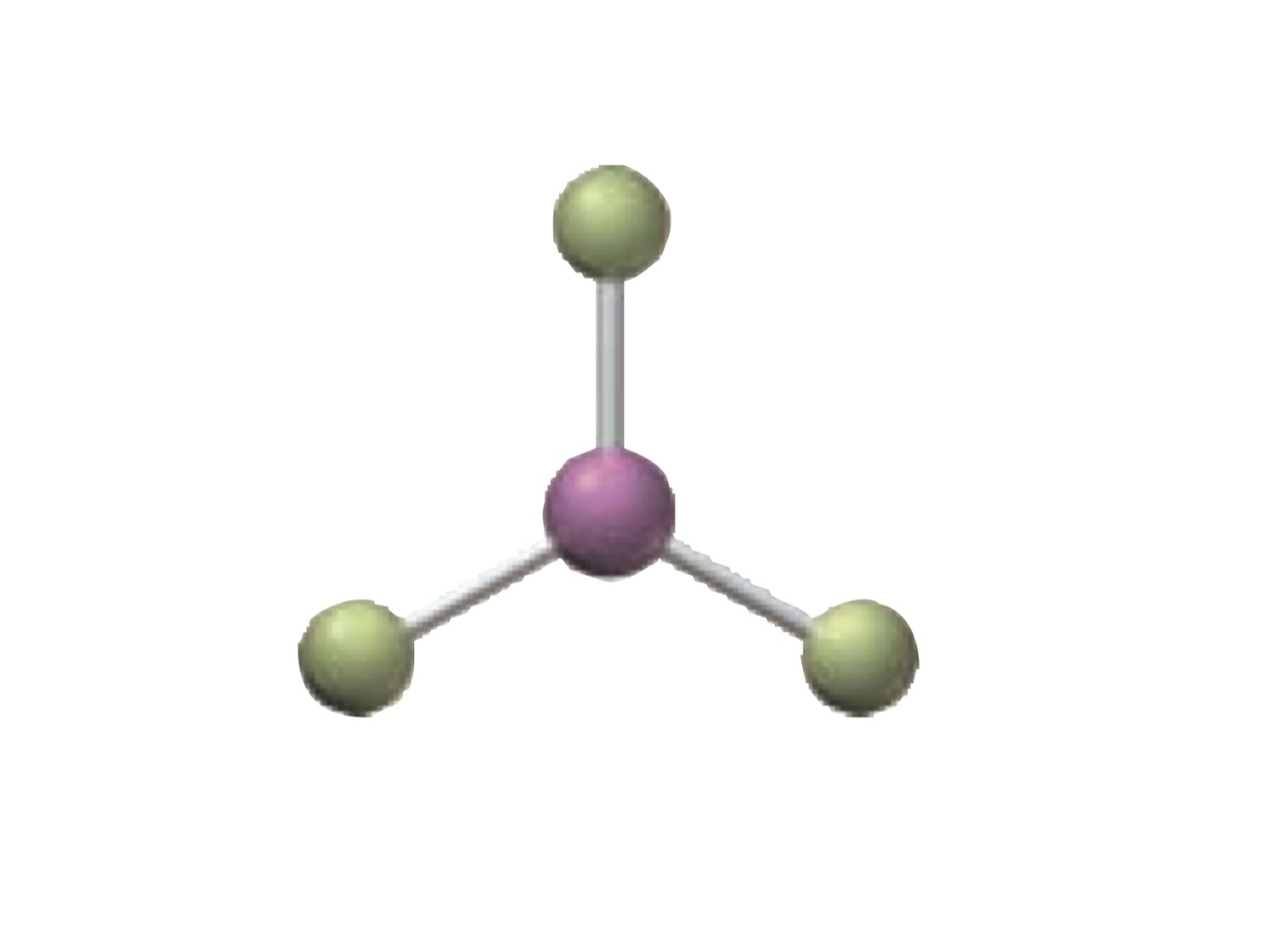
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
3 electron groups.
3 bonding groups.
0 lone pairs.
Trigonal planar.
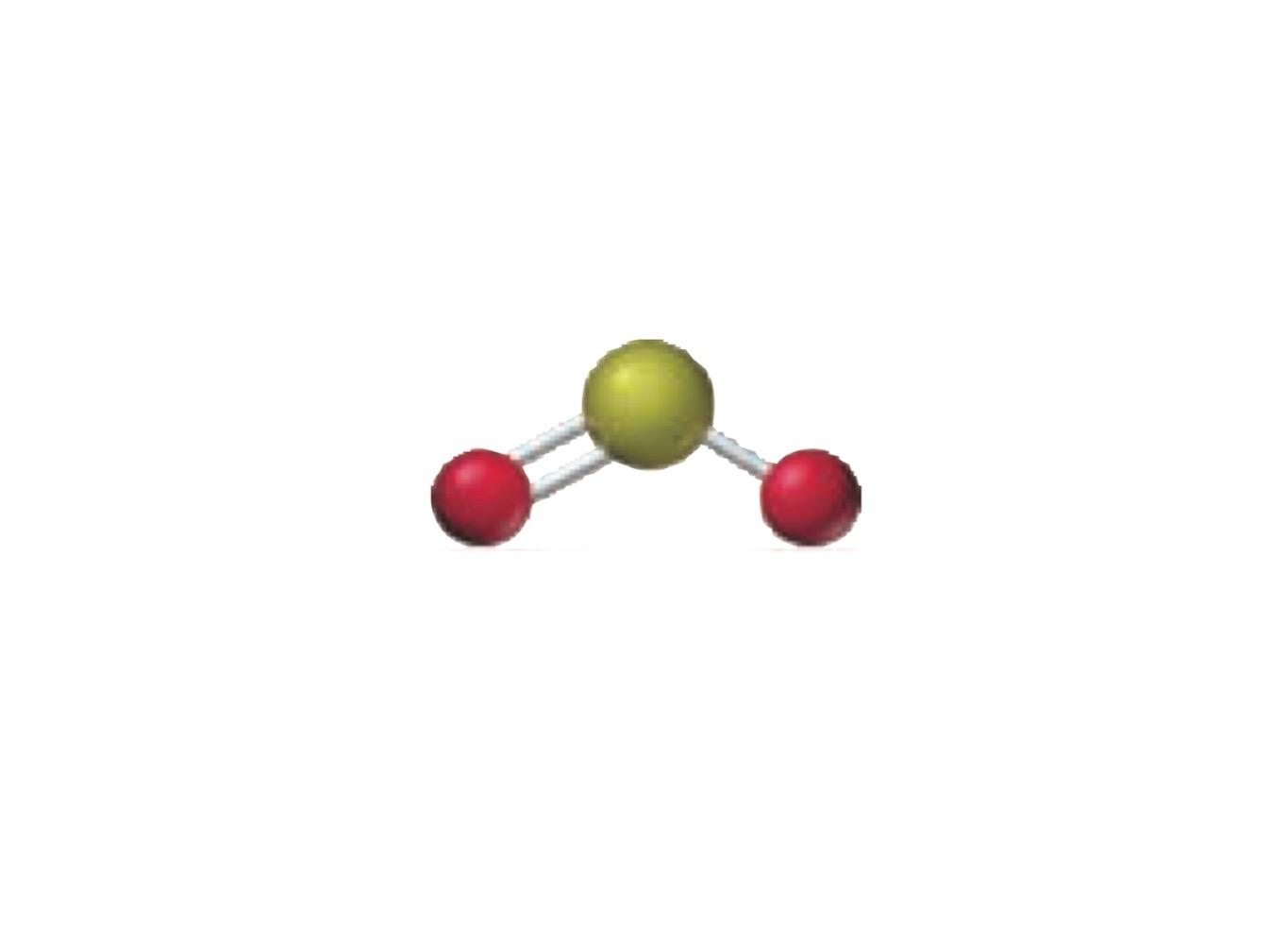
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
3 electron groups.
2 bonding groups.
1 lone pairs.
Bent.
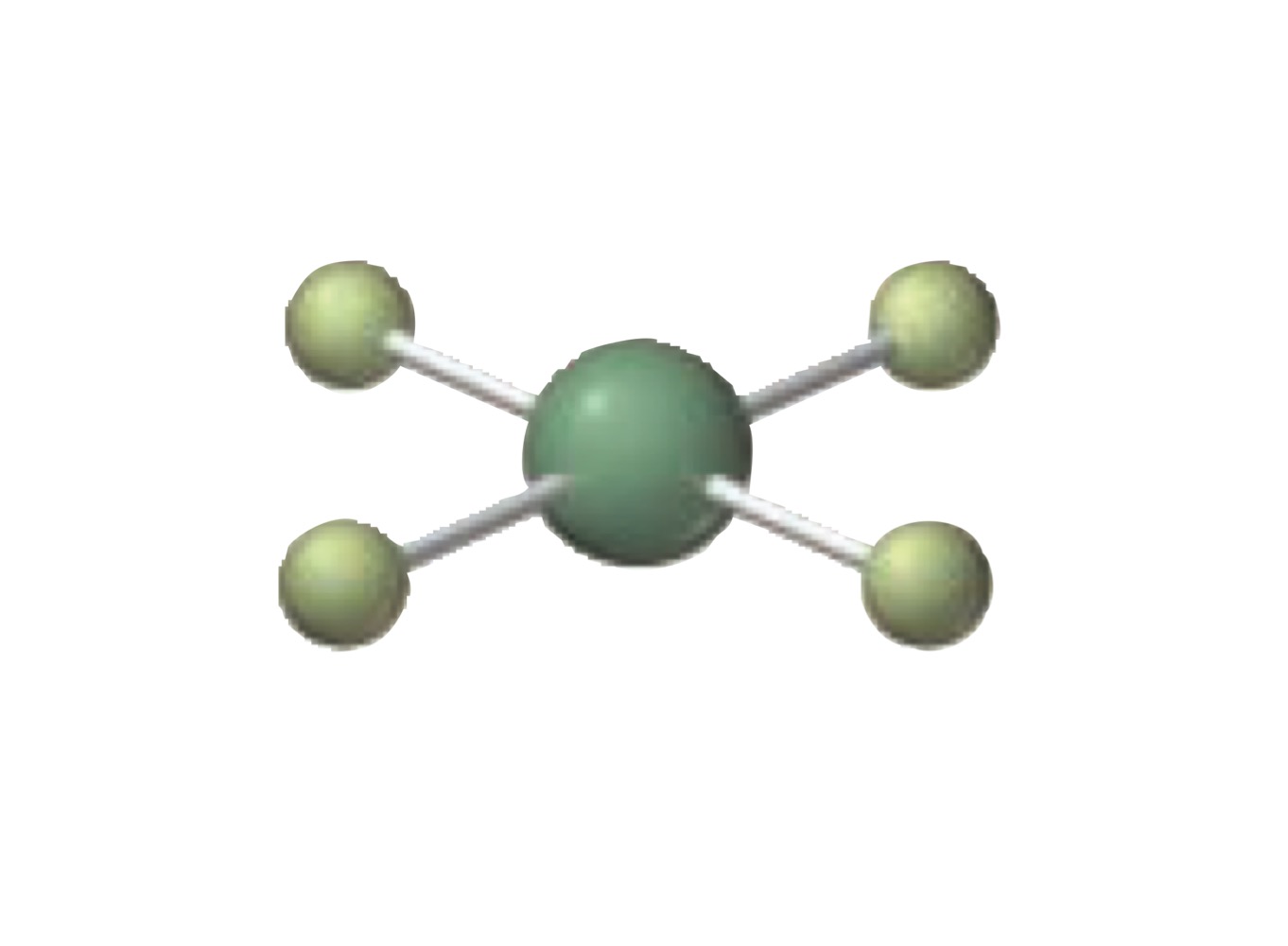
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
4 electron groups.
4 bonding groups.
0 lone pairs.
Tetrahedral.
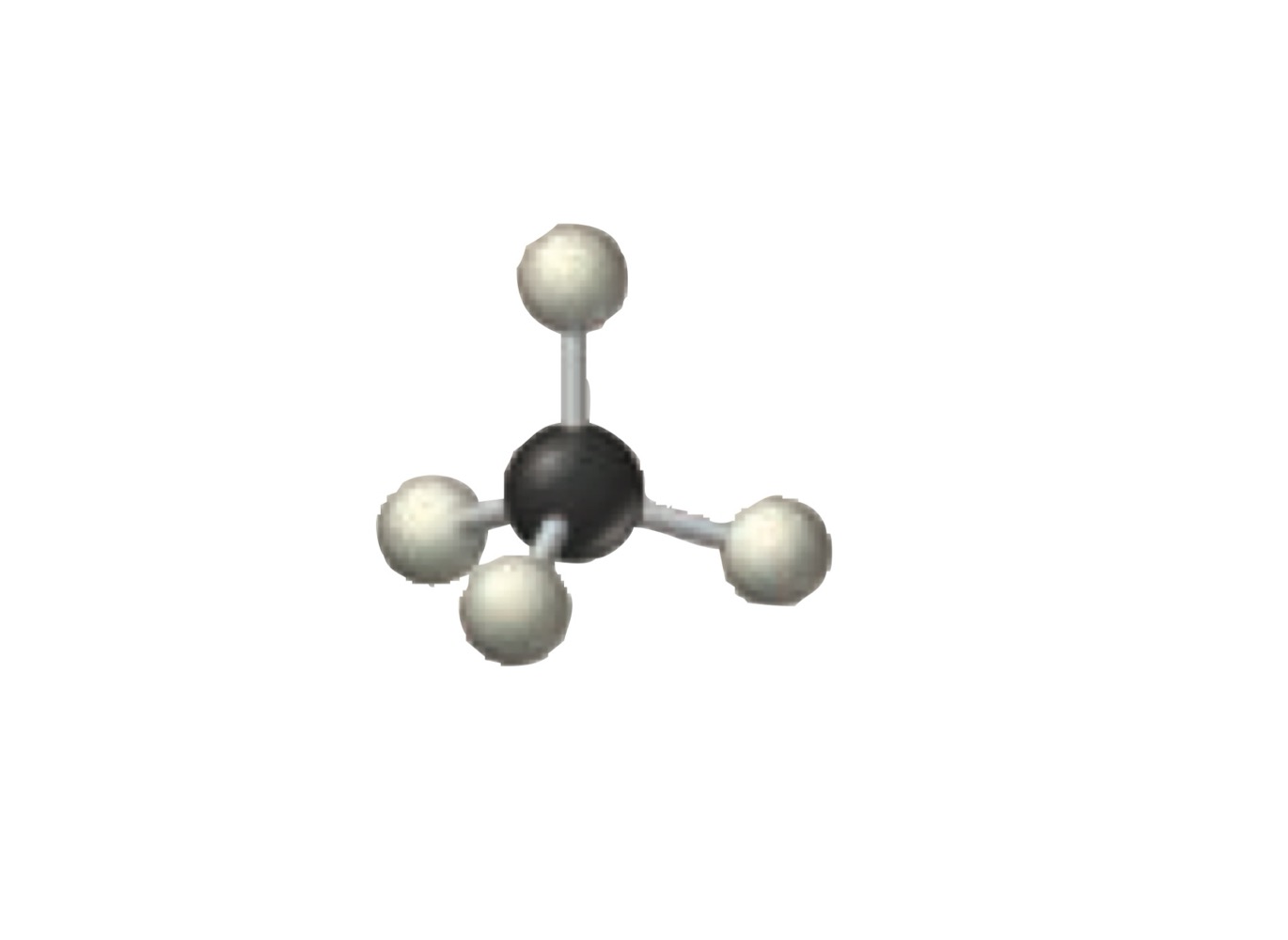
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
4 electron groups.
3 bonding groups.
1 lone pairs.
Trigonal pyramidal.
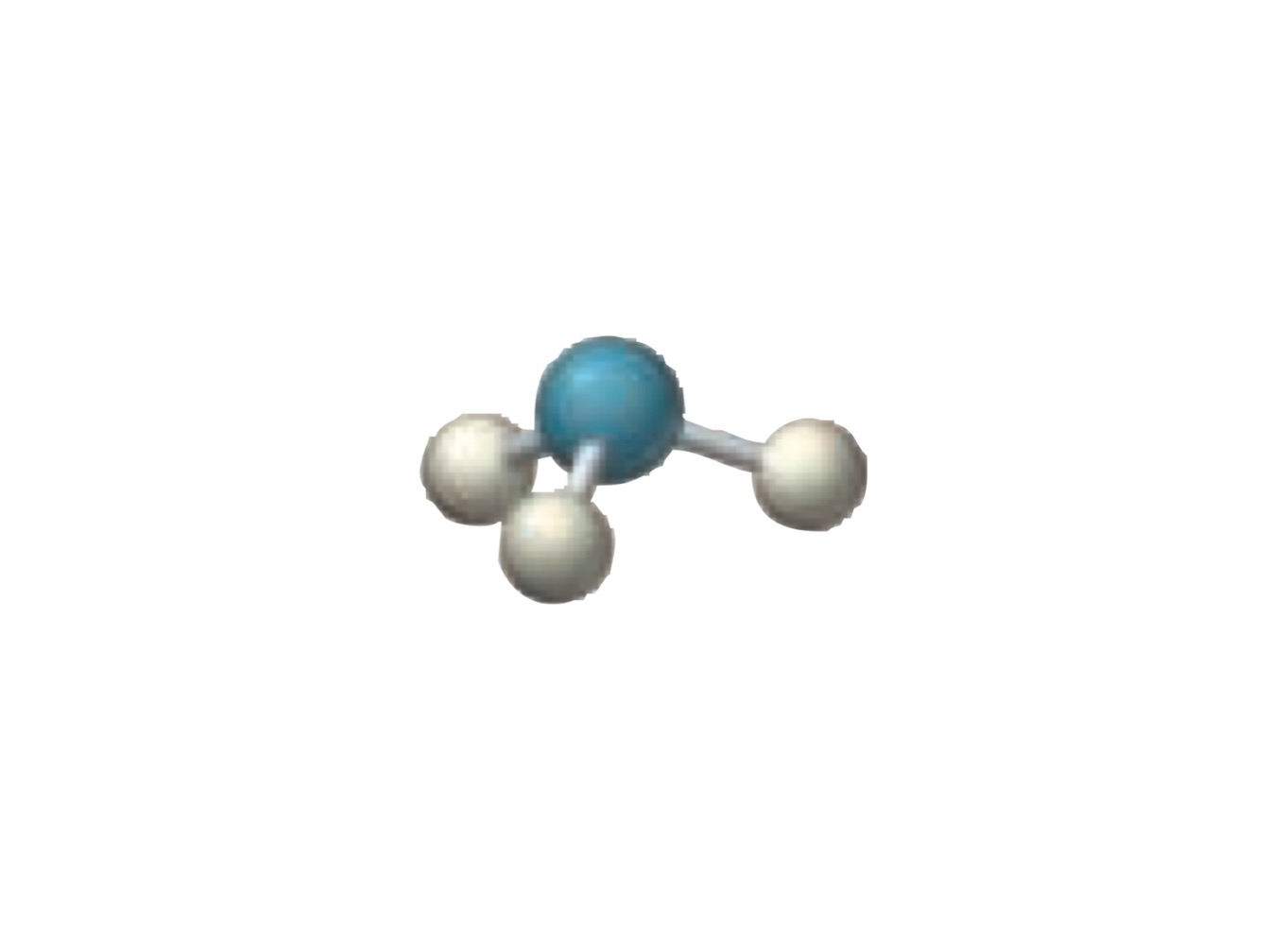
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
4 electron groups.
2 bonding groups.
2 lone pairs.
Bent.
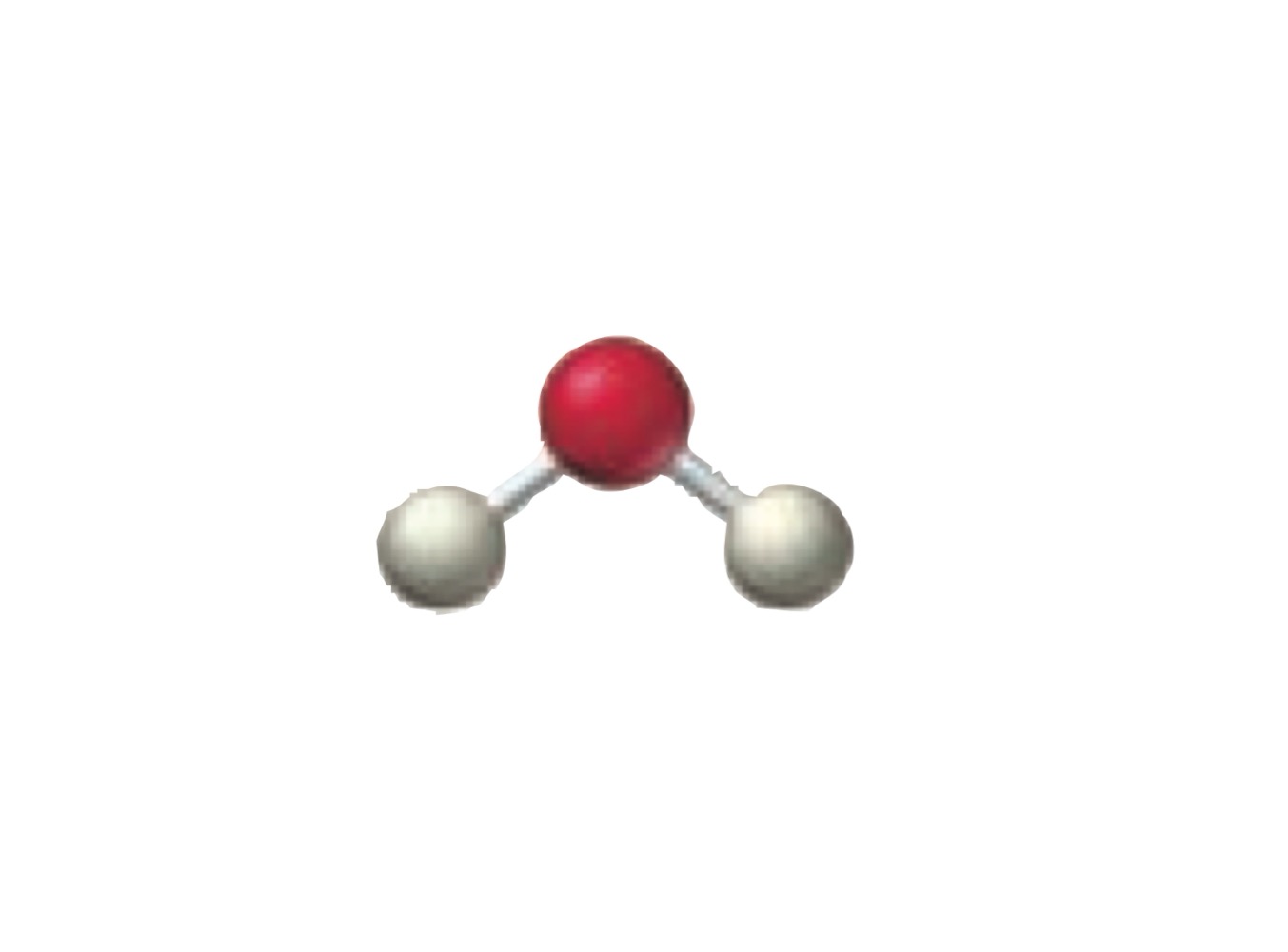
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
5 electron groups.
5 bonding groups.
0 lone pairs.
Trigonal bipyramidal.
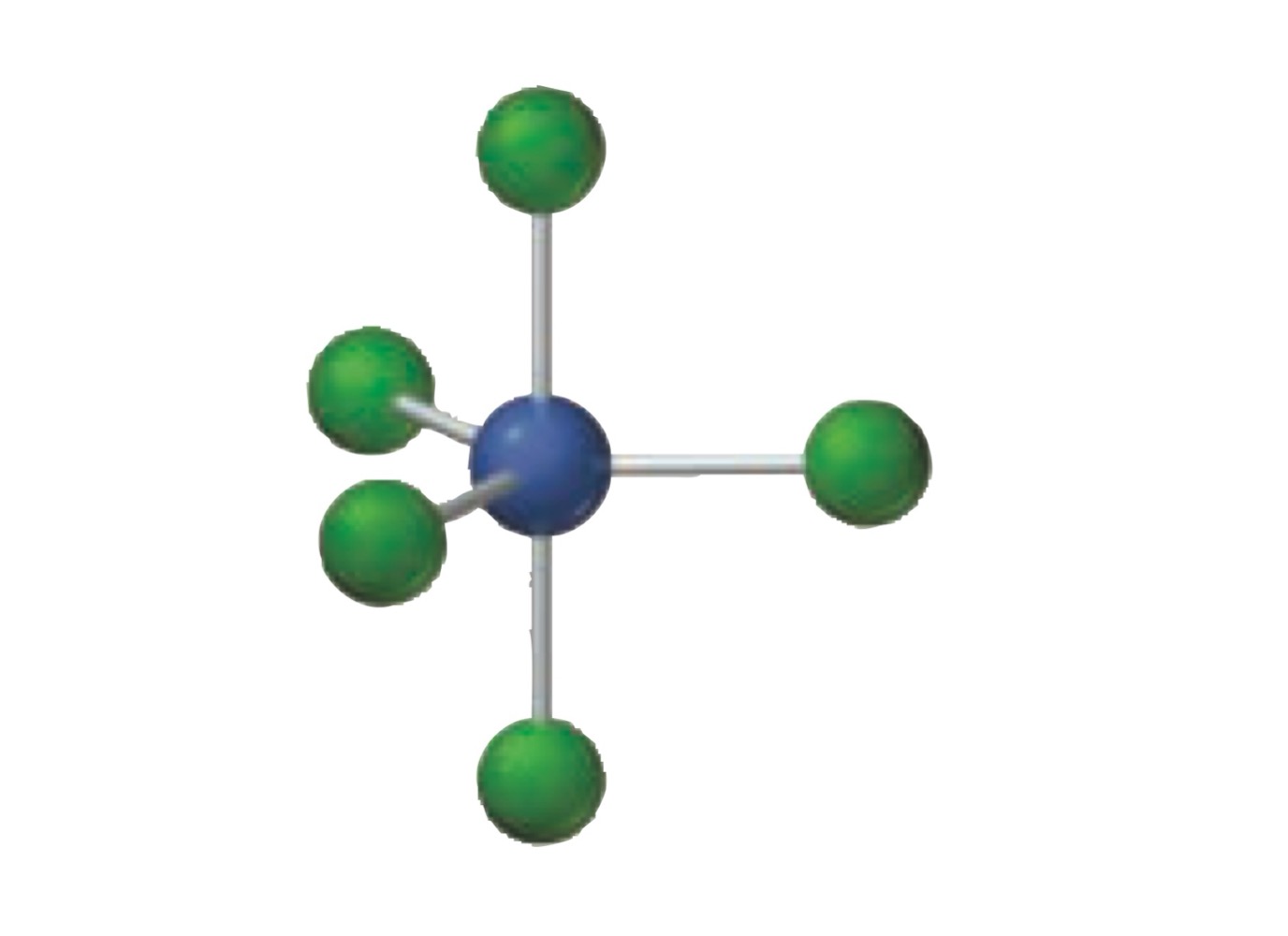
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
5 electron groups.
4 bonding groups.
1 lone pairs.
Seesaw.
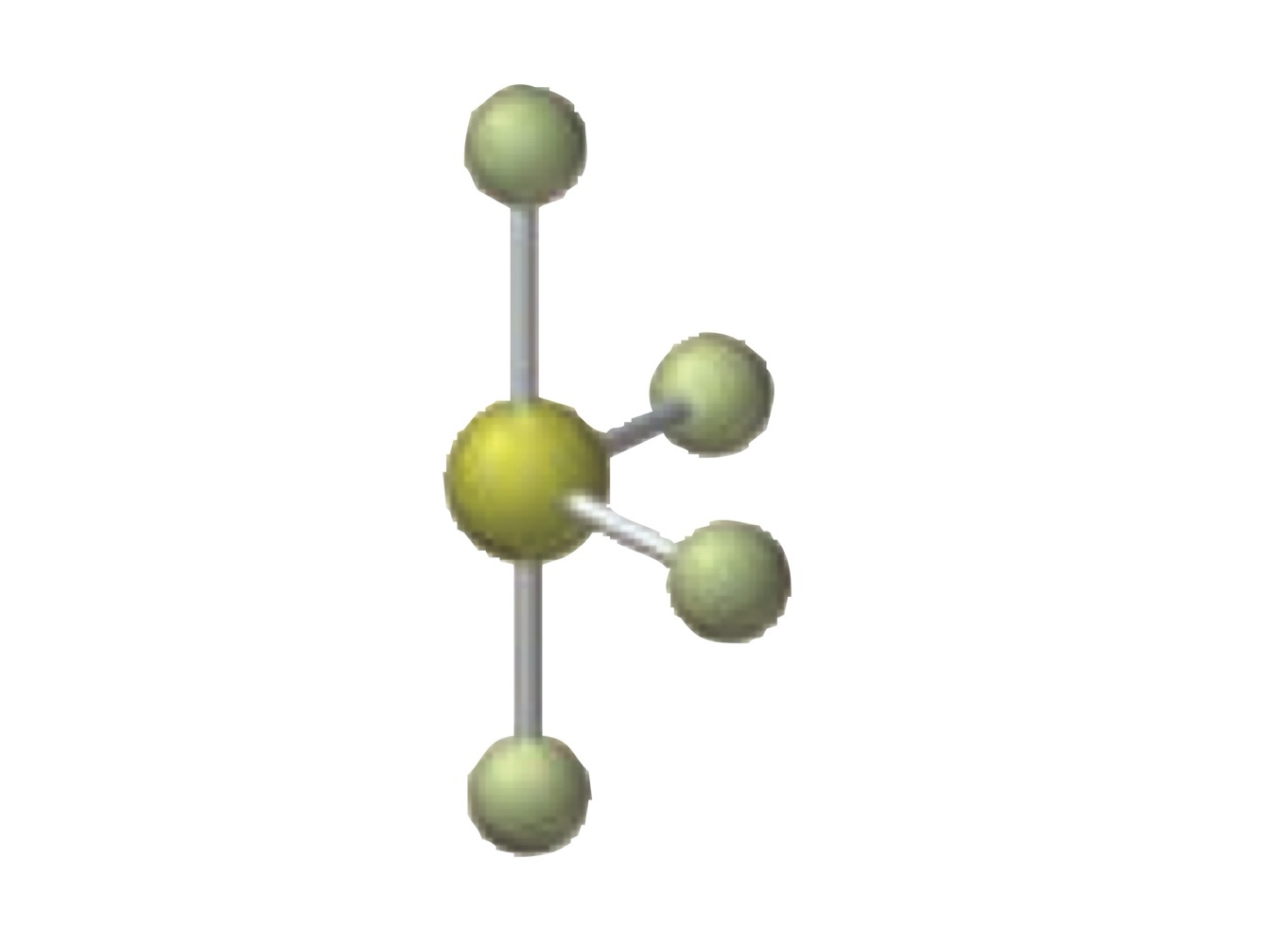
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
5 electron groups.
3 bonding groups.
2 lone pairs.
T-shaped.
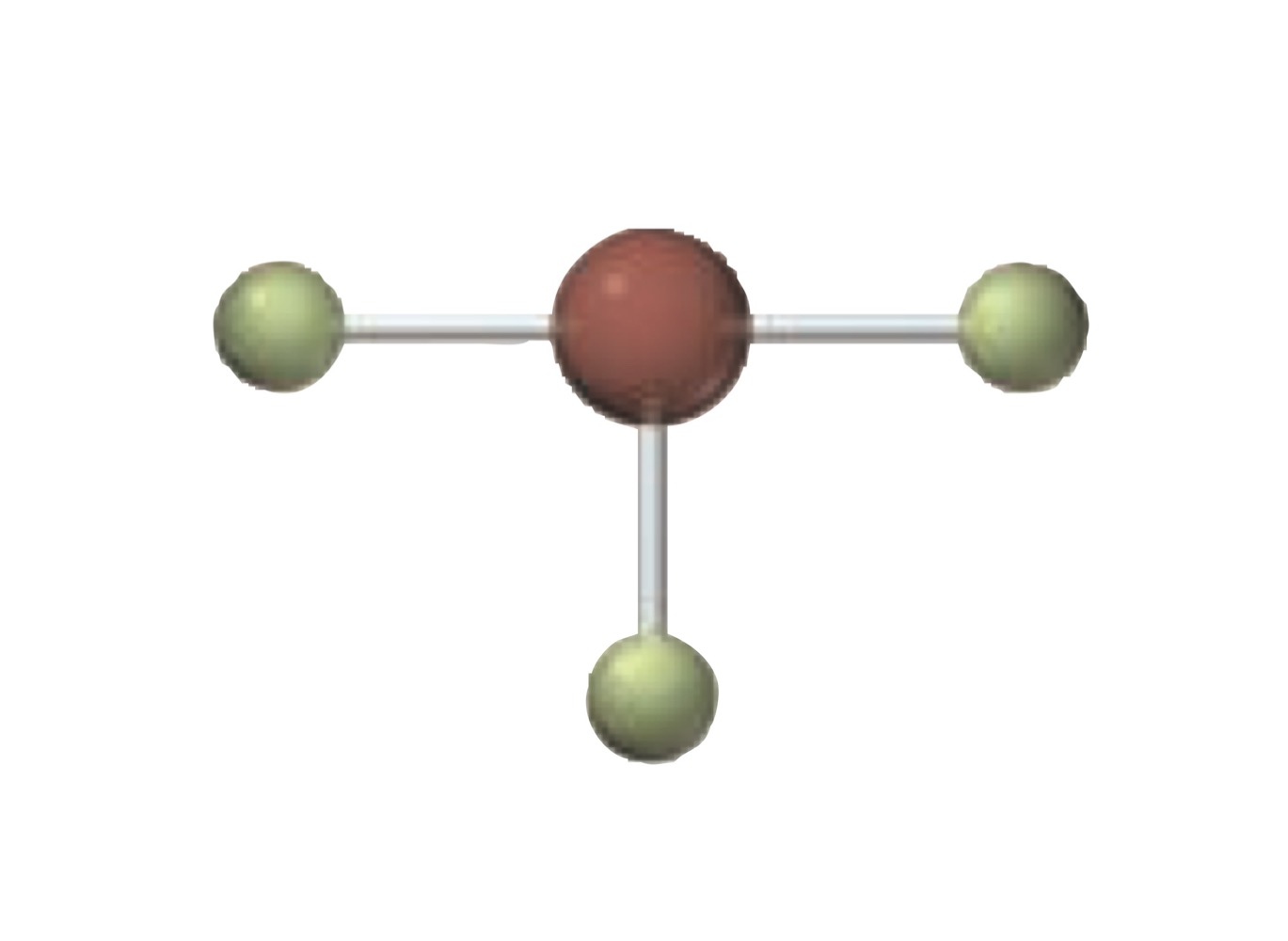
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
5 electron groups.
2 bonding groups.
3 lone pairs.
Linear.
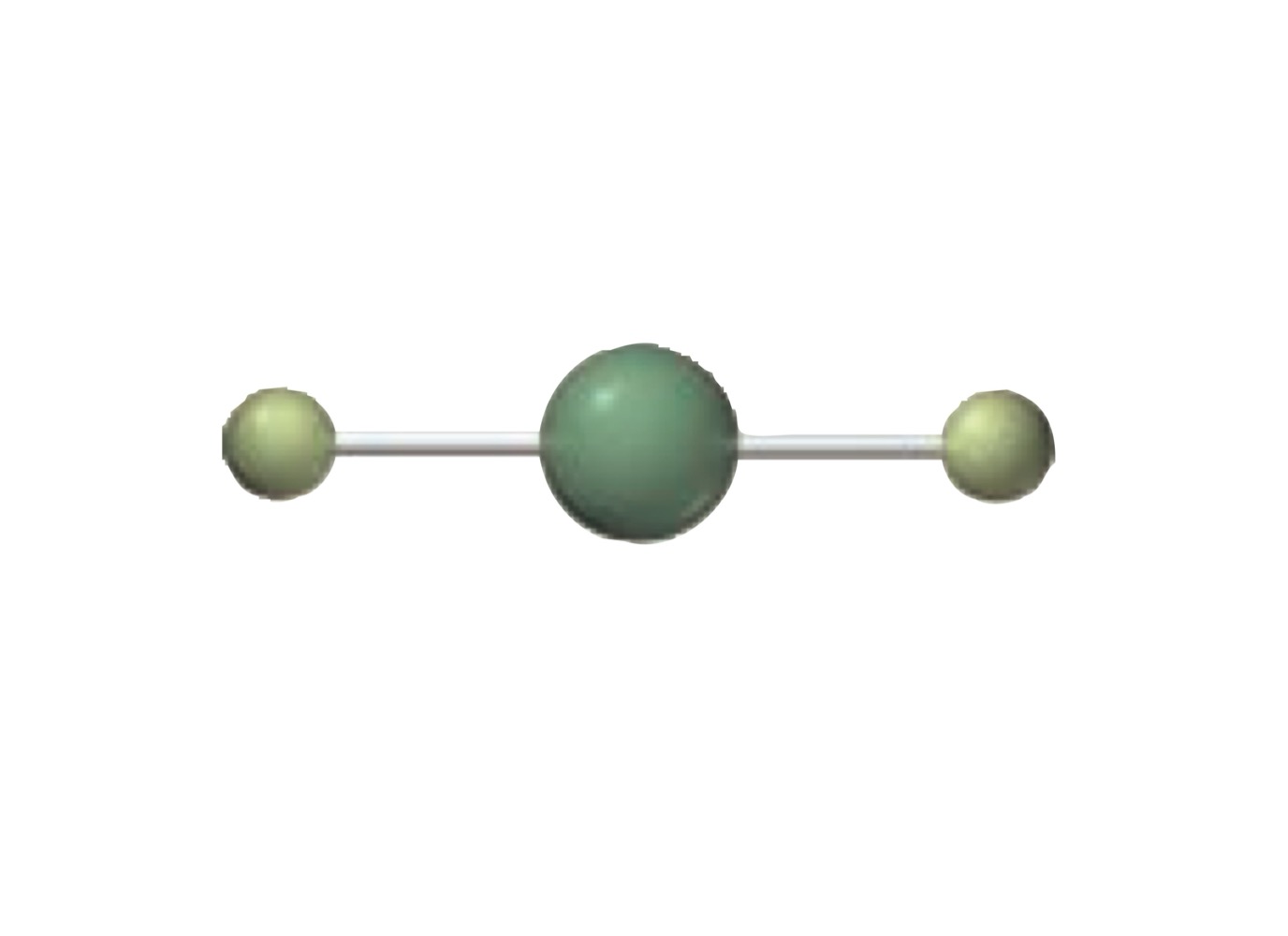
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
6 electron groups.
6 bonding groups.
0 lone pairs.
Octahedral.
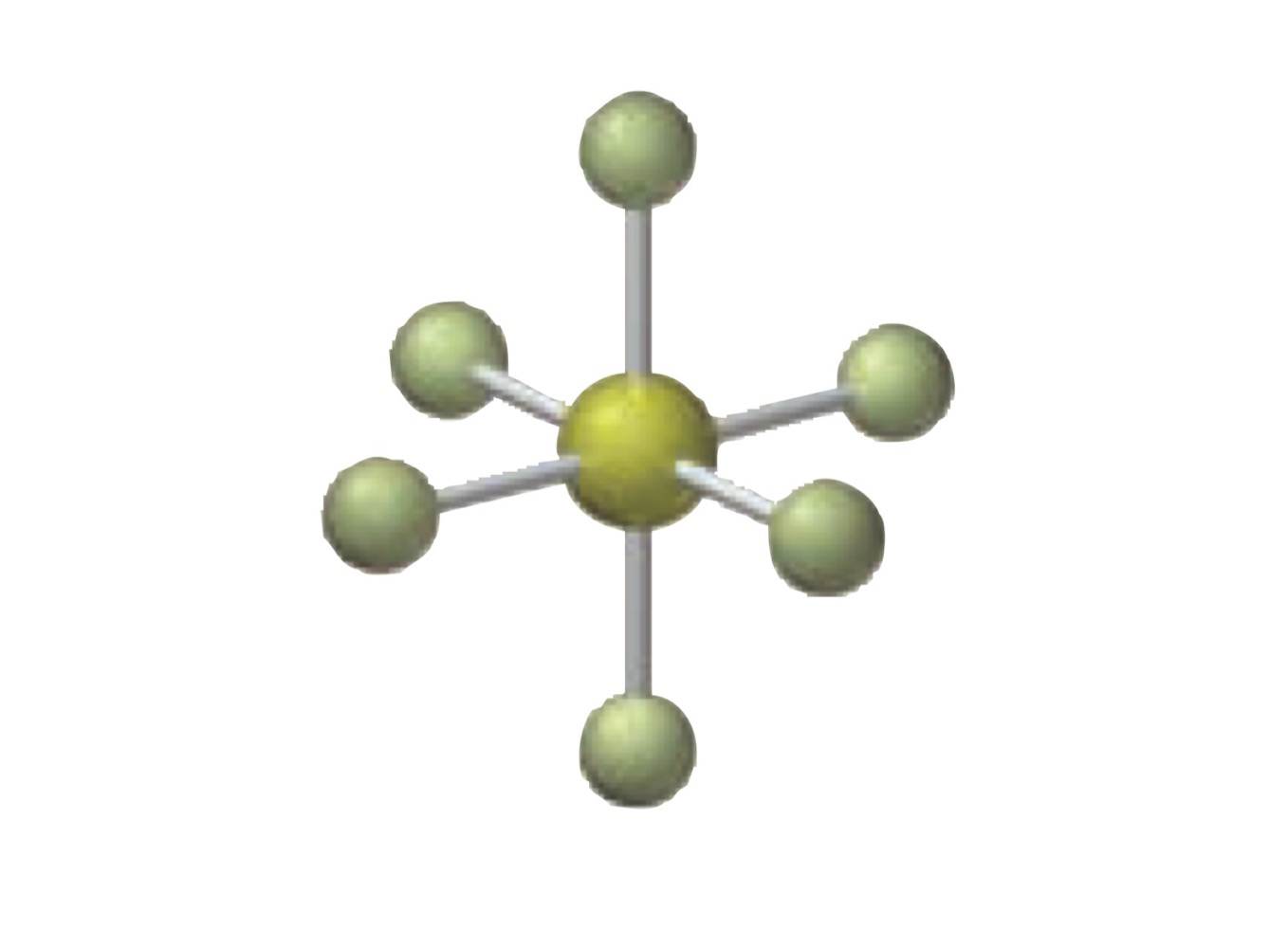
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
6 electron groups.
5 bonding groups.
1 lone pairs.
Square pyramidal.
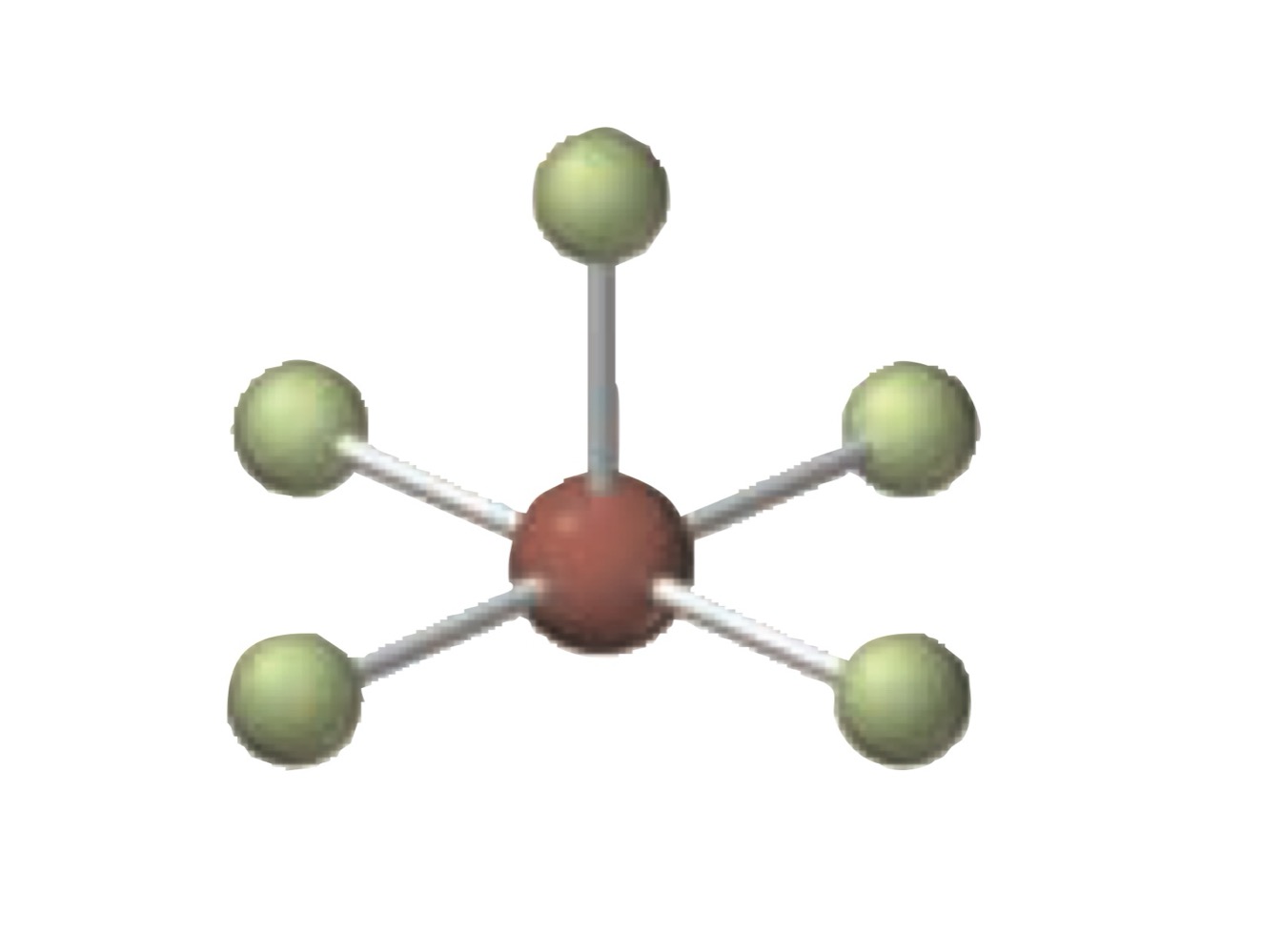
What is the molecular geometry of a molecule with the following?
6 electron groups.
4 bonding groups.
2 lone pairs.
Square planar.