Work, Power and Mechanical Energy
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Work
____ - measure of energy transfer done when a force causes displacement. The unit of work is joule.
Power
____ - rate at which work is done
d. 36 KJ
1. The amount of work a 0.6 KW electric drill can do in 1 min is…
a. 0.6 J
b. 36 J
c. 0.6 KJ
d. 36 KJ
c. equal work was done by the professor and the student
2. A professor who arrived early at school walked up two flights of stairs. Afraid that he will be late, a student had to run up the same flights of stairs. Assuming that they have the same masses, which would have greater work
done?
a. the professor
b. the student
c. equal work was done by the professor and the student
d. no work was done by the professor and the student
b. the student
3. Using the scenario in the previous number, which would have greater power?
a. the professor
b. the student
c. equal power was exerted by the professor and the student
d. no power was exerted by the professor and the student
Torque
___ - a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate The unit of torque is N-m, not Joule since torque is not an energy quantity
d. In a seesaw, the heavier person must be positioned farther from the fulcrum compared to the lighter person positioned on the other side to balance the seesaw.
1. Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Which of the following statements about torque and its application is false?
a. Torque (𝜏) is the cross product of force (𝐹) and moment arm (𝑟).
b. The SI unit of torque is N·m and has dimension: 𝑀𝐿2𝑇−2
c. Doorknobs are placed at the edge of a door rather than at the center to increase the lever arm.
d. In a seesaw, the heavier person must be positioned farther from the fulcrum compared to the lighter person positioned on the other side to balance the seesaw.
b. 1.5 m from the fulcrum
2. A 30-kg boy sits down on one side of a seesaw, 2.0 m from the fulcrum. Where must a 40-kg boy sit on the other side to keep the see-saw balanced?
a. on the fulcrum
b. 1.5 m from the fulcrum
c. 2.0 m from the fulcrum
d. 2.67 m from the fulcrum
Kinetic Energy
____ - is the energy of an object due to its movement - its motion
Potential energy
_____ - is the : energy stored in an object due to its position or arrangement
d. The kinetic energy is minimum at the lowest point of its flight.
1. A body thrown vertically up into the air possesses kinetic energy at the beginning of its flight, but as it rises, it loses kinetic energy and acquires potential energy with respect to the level from which it started. Which of the following is NOT likely to happen?
a. When it reaches the highest point, the kinetic energy has been wholly changed to potential energy.
b. As it falls, its potential energy is again transformed to kinetic energy.
c. The potential energy is maximum at the highest point of its flight.
d. The kinetic energy is minimum at the lowest point of its flight.
d. Total mechanical energy is conserved and is constant at all points
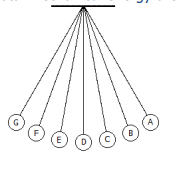
2. In the figure below, in which point is the total mechanical energy the highest?
a. Points A and G
b. Points B and F
c. Point D
d. Total mechanical energy is conserved and is constant at all points
Heat
Thermal energy is aka ___ ?
Thermal Energy (Heat)
____ - is the energy contained within a system that is responsible for its temperature.
Thermodynamics
_____ - deals with how heat is transferred between different systems and how work is done in the process.
Zeroth Law
[Law of Thermodyanmic]
If TA=TB and TB=TC, then TA=TC
(If two objects are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are in equilibrium with each other.)
First Law of Thermodynamic
[Law of Thermodyanmic]
Energy is conserved: ΔEtot=Q+W
(The total energy change of a system is the heat added (Q) plus the work done (W).)
Second Law of Thermodynamic
[Law of Thermodyanmic]
Entropy always tends to increase: ΔS≥0
(Systems naturally move toward disorder over time.)
Third Law of Thermodynamic
[Law of Thermodyanmic]
(It’s impossible to cool a system to absolute zero.)
Convection
____ - is the transfer of heat through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by the molecular motion
Conduction
____ - is the transfer of heat or electricity from one substance to another through direct contact.
Radiation
____ - refer to when the energy is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles
Specific heat (c )
_____ - is the heat required to change a temperature
Latent heat of fusion
______ - is the heat required to change from solid to liquid ( or from liquid to solid)
Latent heat of vaporization
____ - is the heat required to change from liquid to gas (or from gas to liquid)
d. I, II, III, and IV
1. A 100 g copper initially at 950C is put inside an aluminum container with a piece of silver amounting to a mass of 200 grams and with water at 250C. Which of the following statement/s given must be TRUE?
I. The final temperature of the system will be less than 950C.
II. Copper loses heat while silver and water absorbs heat.
III. The temperature of silver and water increases and the temperature of copper decreases.
IV. The temperature of copper, silver, and water will eventually be equal.
a. I and II only
b. I and III only
c. I, II, and III only
d. I, II, III, and IV
a. The metal cools at a temperature less than 1000C
2. A metal initially at 100oC is immersed in lukewarm water. What can be observed from this?
a. The metal cools at a temperature less than 1000C.
b. The water evolves heat to the metal.
c. The water’s temperature will decrease.
d. All of the above.
a. a higher temperature for copper
NOTE:
The specific heat capacity (cc) measures how much energy is needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C.
Copper requires less energy to increase its temperature.
Aluminum requires more energy to increase its temperature by the same amount.
4. Copper has a specific heat of 0.093 𝑐𝑎𝑙 /𝑔∗𝐶° while that of aluminium is 0.22 𝑐𝑎𝑙 /𝑔∗𝐶 ° . Applying the same amount of energy to equal masses (5.0 g of copper and 5.0 g aluminium) will result in:
a. a higher temperature for copper
b. a higher temperature for aluminium
c. the same temperature for each metal
d. unknown results
b. 50oC
5. A 80-gram sample of aluminium, initially at 60oC, is placed in contact with 20 grams of aluminium at 30oC.
Assuming no heat is lost to the surroundings, what is the resulting temperature of the aluminium?
a. 45oC
b. 50oC
c. 90oC
d. 40oC
Pressure
What is constant in Charles law?
Temperature
What is constant in Boyle Law?
Volume
What is constant in Gay-Lussac Law?
d. The average kinetic energy of its molecules increases, and the volume of the gas increases.
1. Which of the following will happen if a sample of gas is heated at constant pressure?
a. The average kinetic energy of its molecules decreases, and the volume of the gas decreases.
b. The average kinetic energy of its molecules increases, and the volume of the gas decreases.
c. The average kinetic energy of its molecules decreases, and the volume of the gas increases.
d. The average kinetic energy of its molecules increases, and the volume of the gas increases.
Increase Temperature
Increase Volume = ____ [increase/decrease] Temperature
Increase Pressure
IncreaseTemperature= ____ [increase/decrease] Pressure
Decrease Pressure
Increase Volume = ____ [increase/decrease] Pressure
d. Decrease two times
2. If the absolute temperature of a gas is doubled and its pressure is quadrupled, then the volume will ___
a. Increase four times
b. Increase two times
c. Decrease four times
d. Decrease two times
a. 200 ℃
3. John is cooking a pot roast for dinner in a pressure cooker. Water will normally boil at a temperature of 373 K
and an atmospheric pressure of 1.01 x 105 Pa. What is the boiling temperature inside the pot, when the pressure is increased to 1.28 x 105 Pa? The pot maintains a constant volume.
a. 200 ℃
b. 20.0 ℃
c. 500 ℃
d. 50.0 ℃