Physiology Lecture #6 [Neuronal Signaling and Synaptic Transmission]
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Dendrites
Are fine extensions from the cell body of a neuron
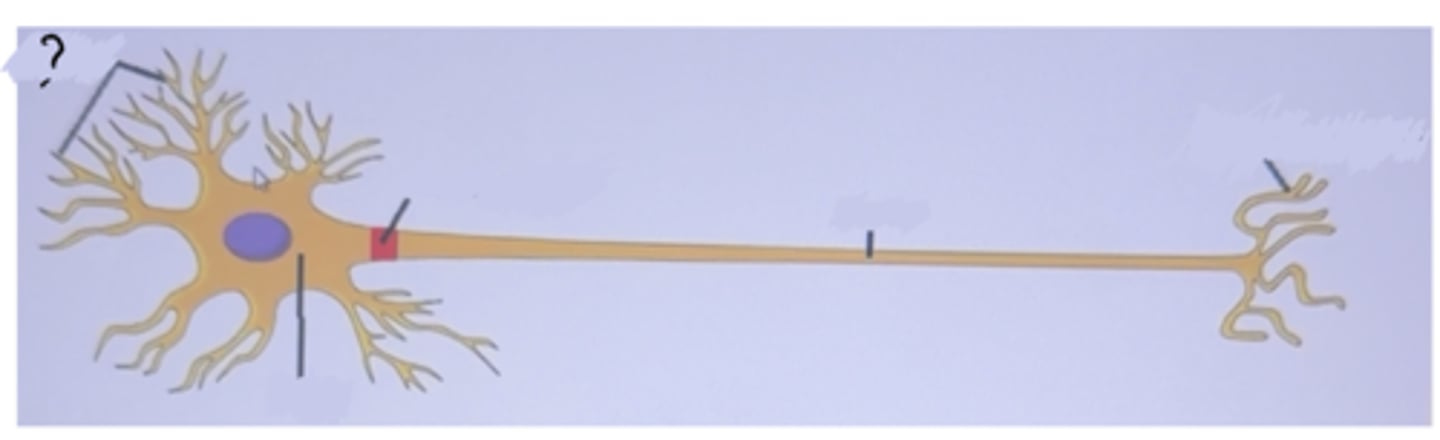

Soma
The cell body where all protein synthesis takes place in a neuron
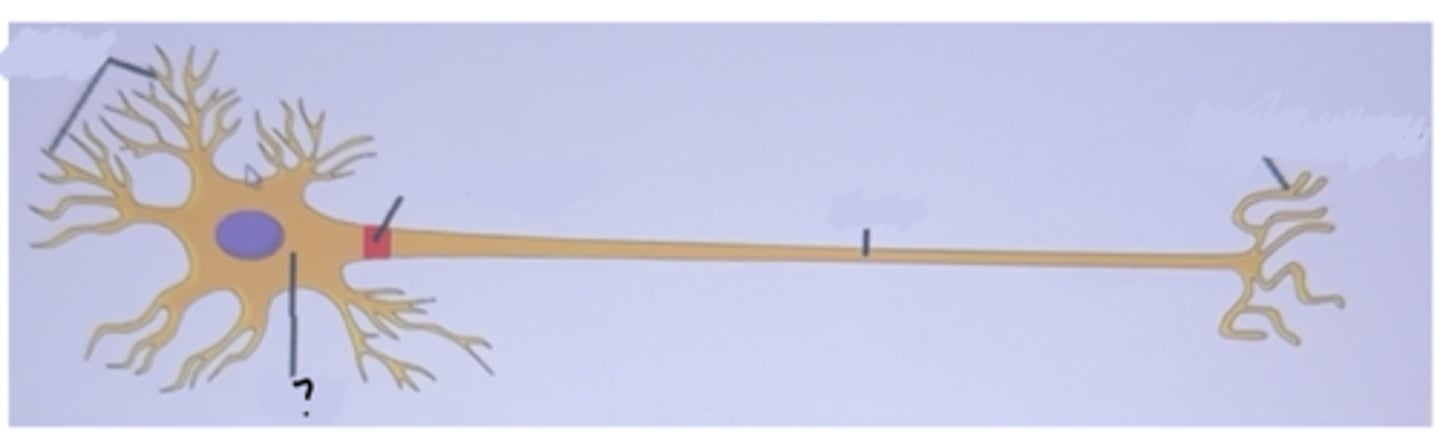
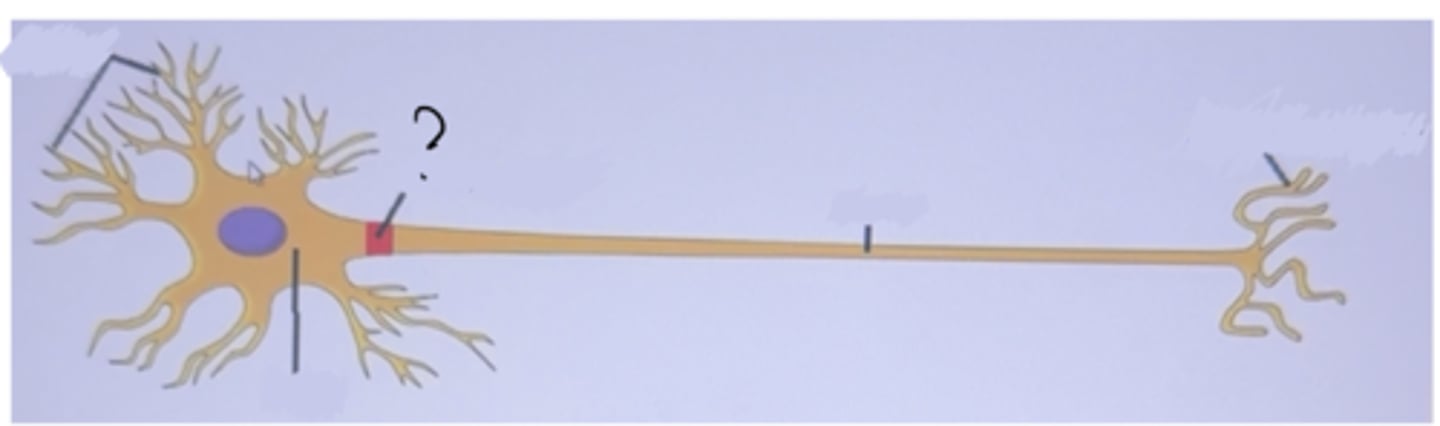
Axon hillock
The first part of the axon
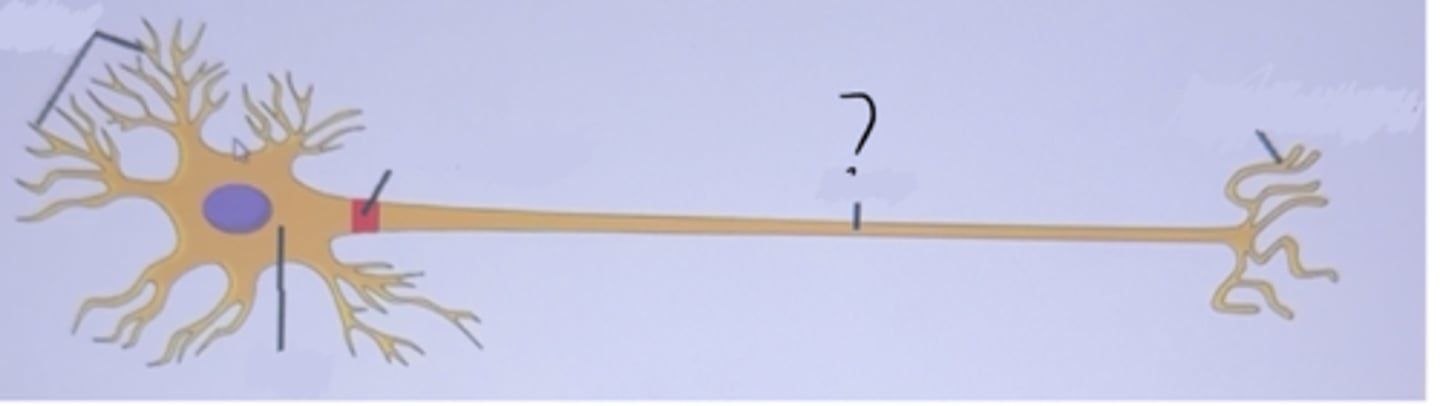
Axon
is a long extension of the soma

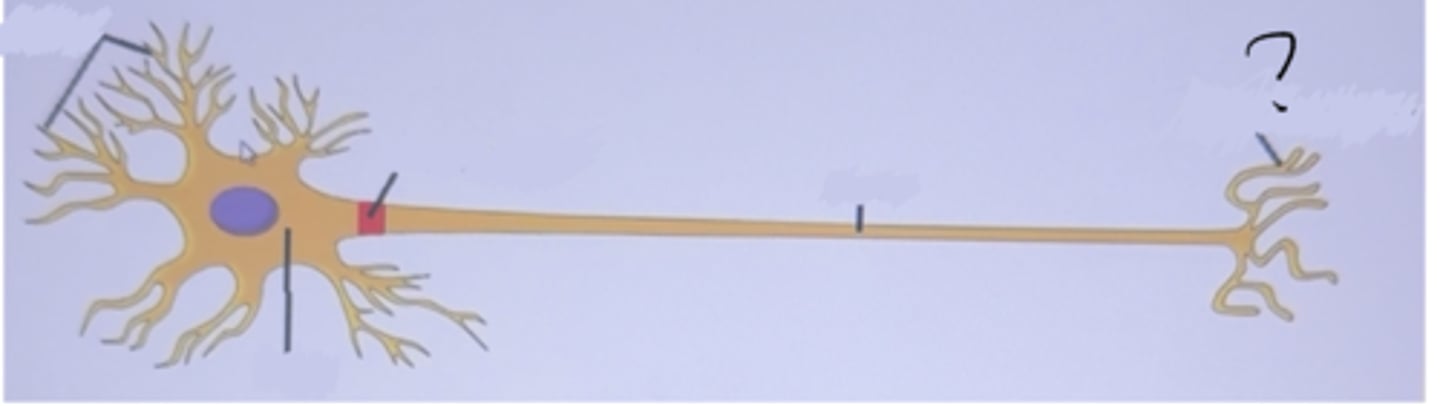
Axon terminals
The end part of a neuron

VGNaC
The axon hillock is rich in ______ and integrates received information
terminal field
Axon conducts action potentials to the
other cells
Axon terminals send information to
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP)
If an input to a neuron causes a depolarization it is called an
- Make it easier to excite neurons
- Influx of cations (or Efflux of anions)
EPSP function (general)
Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP)
If an input to a neuron causes a hyperpolarization it is called an
- Make it harder to excite neurons
- Influx of anions (Efflux of cations)
IPSP function (general)
depolarization (often due to opening of cation selective ligand gated channels eg. nAChR, Glutamate)
EPSP's can add up to give you a larger
hyperpolarization (often due to opening of anion selective gated channels eg. GABA and Glycine)
IPSP's can add up to give you a larger
Threshold is reached
All inputs to a neuron that make it to the axon hillock are summed and determine if
VGNaC, action potential
If threshold is reached then sufficient numbers of _______ will open and generate an _____
Axon hillock
All inputs add up along the path to the
an action potential is generated
If inputs depolarize the axon hillock sufficiently then
EPSPs and IPSPs
The response of postsynaptic cells is derived from the sum of the _____ and _____ from all of its synapses
action potential, postsynaptic cell
When the sum of these events causes a depolarization beyond the threshold potential a(n) _______ is generated in the ________
depolarize
When the action potential reaches the terminals it will ____ the terminals
whatever cell they are connected to
The depolarized axon terminals will then pass the signal on to
- Directly electrically (electrical synapses)
- By releases of a neurotransmitter (chemical synapses)
The signal can be passed on to the next cells by one of two ways:
transmit information
Electrical synapses are very fast to
fidelity (accuracy)
- A stimulatory signal is stimulatory on second cell
- An inhibitory signal is inhibitory on second cell
The electrical synapses has high
Bidirectional
- information transfer can occur in both directions
Electrical synapses are
Voltage gated Ca channels to open.
When a depolarization signal reaches the end it causes
leads to an influx of Ca ions into the cytoplasm
The opening of Ca channels...
Conformational changes into the proteins (SNARE) coating vesicles causing the vesicles (filled with NT) to fuse with the membrane in the post synaptic space
The influx of Ca ions in the cytoplasm ends up triggering
to enter the post synaptic cleft and activate a ligand gated channel in the post synaptic neuron
The fusion of the Vesicles with the post synaptic membrane allows for the NT
slower
Because of the lengthy process of the chemical synapses this makes them much ___ than electrical synapses
synapse
Neurotransmitters (NT) need to be cleared from the _____ to terminate the signal from 1 neuron to the other
After opening, they inactivate in the sustained presence of stimulus
- NT clearance helps them "reset" for the next signal relay steps
Ligand gated ion channels mediating synaptic transmission desensitize i.e....
- Passive diffusion (float away)
- Enzymatic removal (AchE)
- Secondary active transport
3 ways neurotransmitters are cleared from the synapse
SSRIs inhibit serotonin transporter (SERT) which typically brings serotonin back into the presynaptic membrane to be repackaged and reused. By keeping it in the synaptic junction, serotonin will have extended effects since it is not being taken back up by secondary transporter (SERT)
How do SSRIs (antidepressants) work in the clearance of serotonin?
Glutamate in the synapse is transported into glial cells by Glutamine synthetase, where it will be converted to Glutamine, then released back into the synapse. Then Glutamine can be brought back into the presynaptic terminal
Glutamate clearance mechanism
Glial cells pick up and break down GABA via GABA transporter
Presynaptic terminal can also bring GABA back into the cell and break it down (coupled with Na flow into the presynaptic vesicle)
GABA and Glycine clearance mechanism
Neurotransmitter
Secondary active transporters in synaptic vesicles mediate ______ loading
vesicular ATPases
Proton gradient in vesicles is established via
Na
Neurotransmitter transporters are usually ___ coupled
Cl+/Cl- antiporters
ATPases
CIC channels
vesicular transport is driven by ____ or membrane potential gradients established by vesicular _____ or ____ _____
Multi-step
The process of fusion of synaptic vesicles to membrane is a ____ process