Collison Theory + Reaction Rate
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is collision theory?
What are the three points of collision theory?
What is reaction rate?
What are the factors affecting reaction rate?
Temperature
Concentration
Pressure
State of Sub - Division
Catalyst
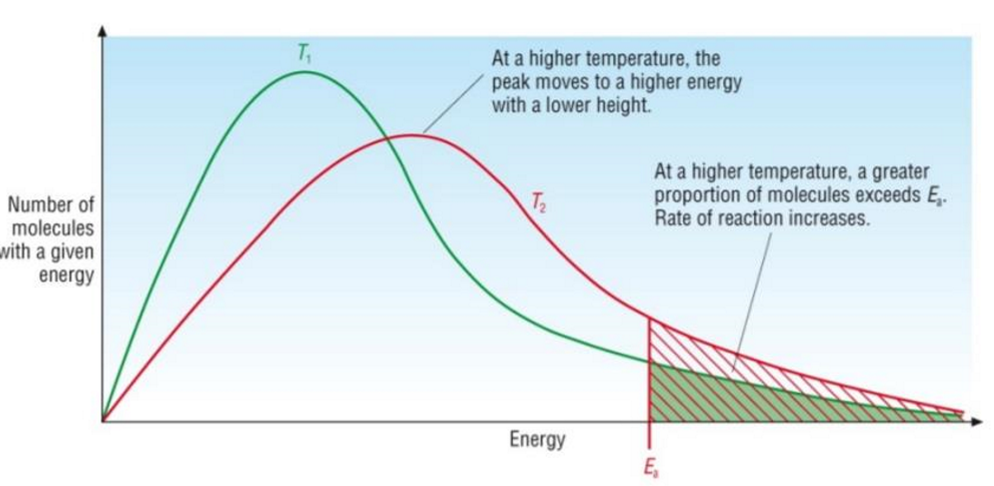
Temperature - Explained
As temp increases, reaction rate increases
A greater proportion of particles have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
Particles have a higher average kinetic energy and move faster, resulting in a higher frequency of collisions, thus resulting in a higher frequency of successful collisions

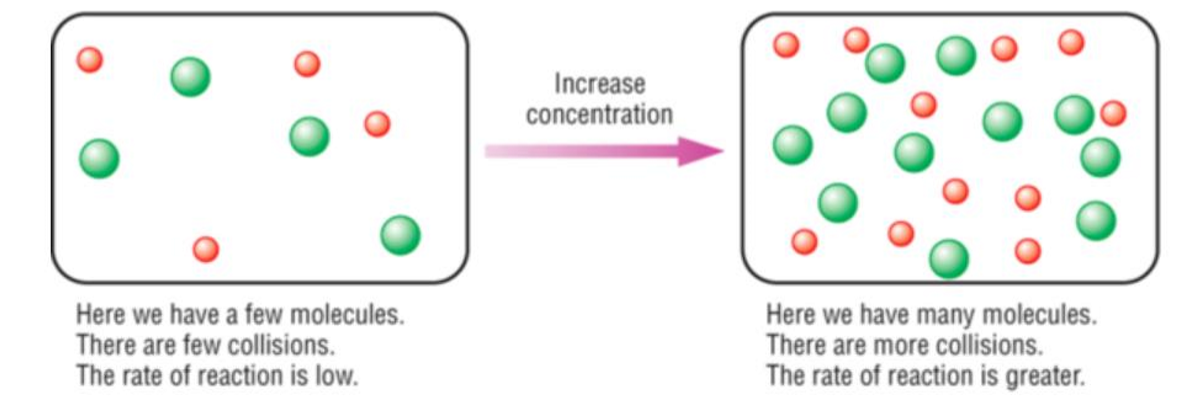
Concentration - Explained
As concentration increases, reaction rate increases
A greater number of particles in a given volume leads to a higher frequency of collisions, thus resulting in a higher frequency of succesful collisions

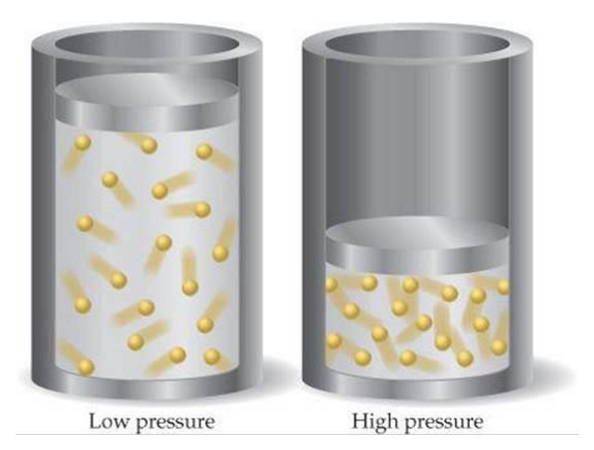
Pressure (Gases Only) - Explained
As pressure increases, rate of reaction increases
Gas Pressure can be increased by:
Adding more gas (volume does not change)
Decreasing the volume
More particles in a given volume leads to a higher frequency of collisions, thus resulting in a higher frequency of successful collisions
Gas pressure is caused when gas particles hit the walls of their container. The more often the particles hit the walls, and the faster they are moving when they do this, the higher the pressure

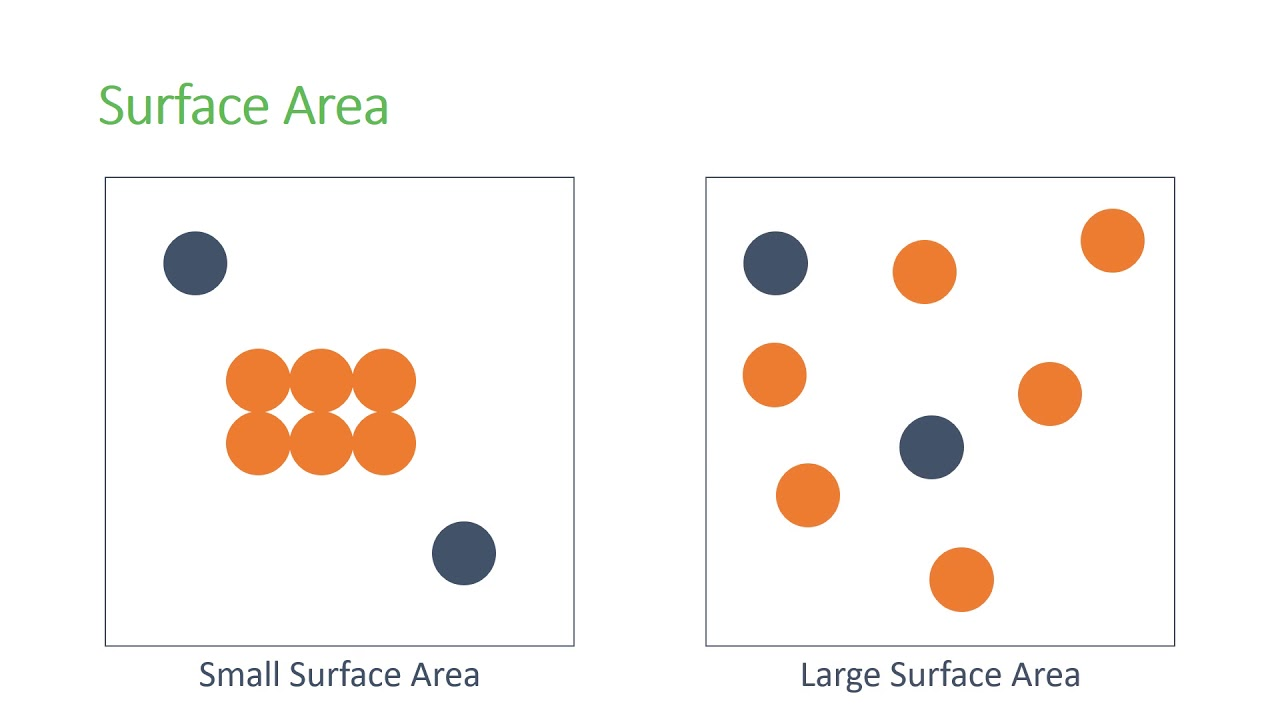
State of Subdivision - Explained
The smaller the particle size, the greater the surface area is for a given mass of particles
The result of an increase in surface area is an increase in the frequency of collisions, therefore increasing chance of successful collisions, and the reaction rate

Catalysts
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of reaction without being consumed or produced
A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
A lower activation energy means more particles have sufficient energy to react; thus, proportion of effective collisions will be higher

