EOS midterm II (mod 4,5,6)
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
what is Eustatic change??
sea level change that is measured all over the world
Three meain points of the Eutastic change
1) Amount of water in the world ocean can change
2) Changes in the size of the container
3) Thermal expansion-contraction of water
Eutastic is global or non global?
global
Static change?
sea level change that is measure locally
its more about the continent
name the 3 main points of Static change
1) Tectonic motion can affect the height and shape of the coast
2) Plates converging can cause uplift
3) Plates weighed down by ice during a glacial period can slowly rise as ice melts
eutastic sea level is ____ due to _____ of water
rising, warming
Compare coast, beach, shoreline
Coast: the water moves from ocean to inland. The land along the edge of the body of water
Beach: accumulation of sediment
Shoreline: where water meets landerosio
erosional vs depositional coast
erosional coast: shaped by land removal and are typically rocky/rugged
depositional coasts: built up by land creation through sediment accumulation and are characterizes by beaches and spits
what is erosion?
deposition of wave energy. Its the process where natural forces move earth materials like soil and rock from one location to another
erosion is caused by….
the concentration of wave energy on headlands
what causes deposition?
the reduced wave energy reaching shore in bays
reefs ____ small islands from ____ ____
shield, water energy
erosion will be more significant in the…..
headlands
erosion vs deposition plus examples
erosion: earth material being worn away. example: river carrying down mud, wind creating rock formations in desserts
deposition: the transported materials (sediments) are dopped or settled in a new location building up new landforms. examples: sand dunes, delta
selective erosion?
the process by which certain components of a surface are removes by erosion more quickly than others, altering the surface composition
name the erosional coastal features common headlands (4)
sea cliff, marine terraces, arch, stacks
sediments are classified by …..
size, sorting and rounding
pebbles >granules>courase sand
spretd rocks are….
similar sizes
The ____ the particle, the _____ slower it settles out of suspension
smaller, slowe
Rocks are _____ the farther away from the _____
bigger, ocean
name the 5 types of beaches
coastal plain, barrier island, tombolo, pocket beach, sand spitn
name the 4 types of shore from the beach profile
Back shore, foreshores, nearshore, offshore
explain what happens with sediment in april, june, august, september, december, feberuary and april
April: its summer, so sediment is low
June: less wave energy, transport sediment to the beach but dont have enough energy to take it back. slope of beach is gradual
August: beach is shallower, sand is accumulating, same as in june
September: when sand reaches its maximum, larger and more energetic waves due to storms
December: high energy waves, they take sediment off the beach
February: very steep aspect, take sediment offshore
April: very low sediment inventory
Conclusion: summer has low energy waves and low sediment and in winter w ehave high energy waves that take away the sediment.
Talk about the two types of waves and the breakers
Constructive and destructive waves
spilling (no steep), plunging (steep) , surging (very steep)
what are beach cusps
repeating, crescent shaped indentation form on beaches due to wave action
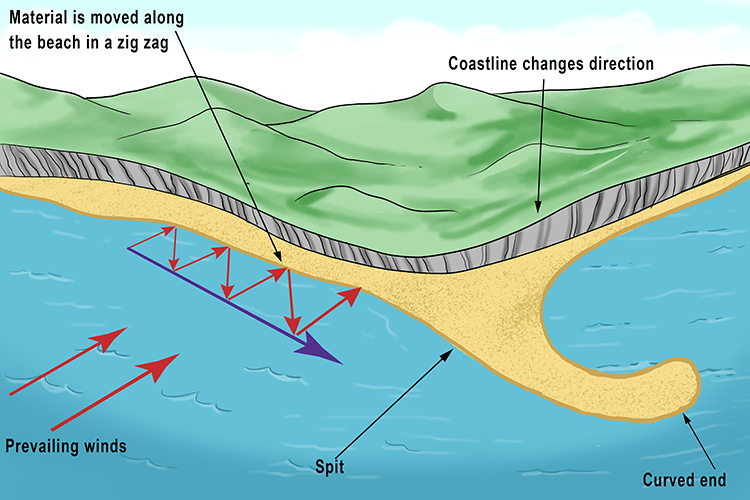
longshore current?
coastal current that flows parallel to the shoreline and within the surf zone
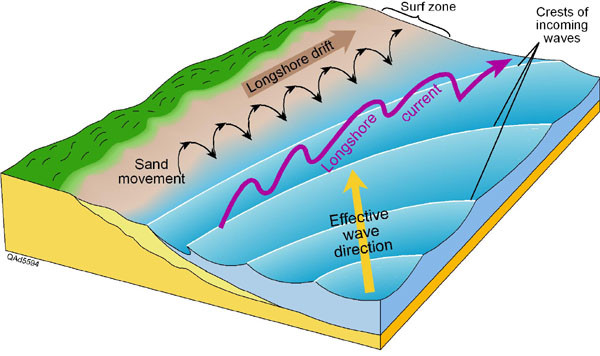
longshore drift?
the process of sediment being transported by waves along a coast parallel to the shoreline
rip currents?
a powerful, narrow channel of water that flows quickly away from the shore. swim parallel to the beach to survive
coastal circulation cells?
localizes oceanographic or littoral systems that move sediment and water along the coast
depositional coastal features?
longsore current bay, sand spit, bay mouth area, tombolo, inlet, barrier islan, sea island
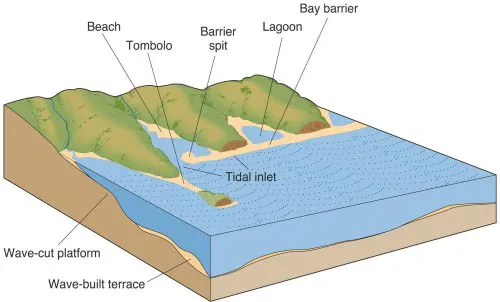
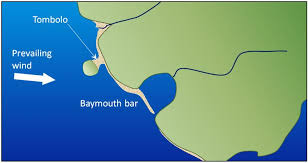
how does a tombolo form?
wave refraction: the island is the obstruction for the waves
longshore drift: the refracted waves, arriving at an angle, push sediment along the coastline
deposition: sediment carried by the longshore drift accumulate on the sheltered area behind the island, building up a connection
connection: the end
How are spits formed:
by sediments transported in the longshore current
they end with a hook
bay mouth bars
water is low energy
a sandbar that extends across the mouth of a bay, partially or completely enclosing it
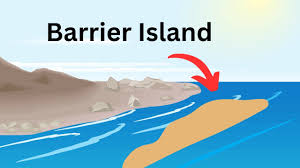
barrier islands?
narrow sand bar, coastal protection
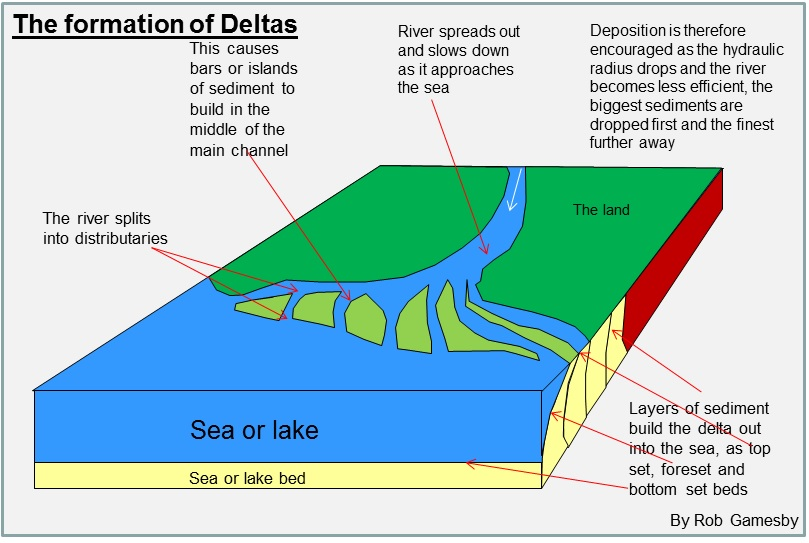
deltas?
how do humans impact how sand moves in coastal cells
dam rivers to generate electricity and get fresh water
build groins to trap sediment along the coast
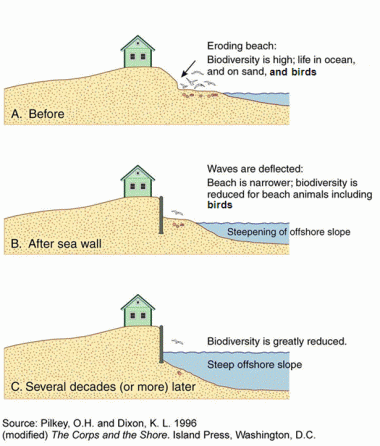
groins and jettie and seawalls?
groins: accumulate sediments
jetties: allow access to harbours for boats
seawalls: attempt of homeowners to shield the shore in front of their dwellings from wave energy
Ediz hook problem
The Ediz Hook problem refers to the erosion and degradation of a sand spit in Port Angeles, Washington, caused by reduced sediment supply from the Elwha River and the construction of shoreline armoring. This erosion threatens the spit itself, which protects the harbor, and the facilities on it, including a U.S. Coast Guard station, necessitating costly repair and nourishment projects.
Dams: The construction of dams on the Elwha River drastically cut the amount of sand and gravel flowing downstream.
Shoreline armoring: The building of rock walls and other structures along the updrift (western) coastline, intended to stop erosion there, also blocks sediment from naturally reaching Ediz Hook.
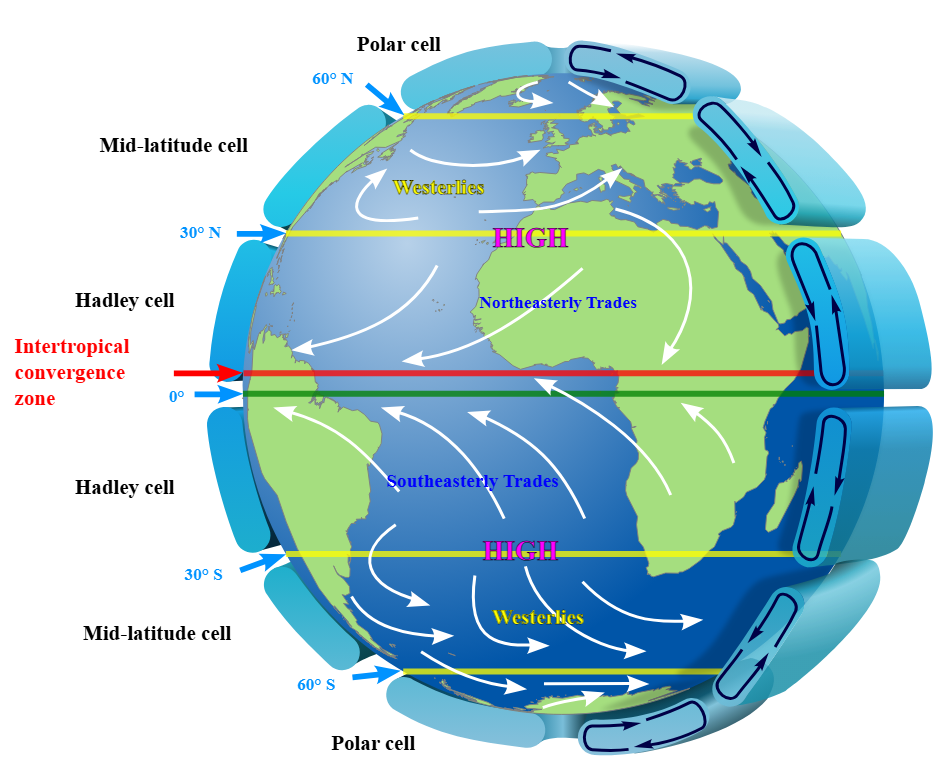
Where would you expect the air to be rising?
the equator, but its actually sinking
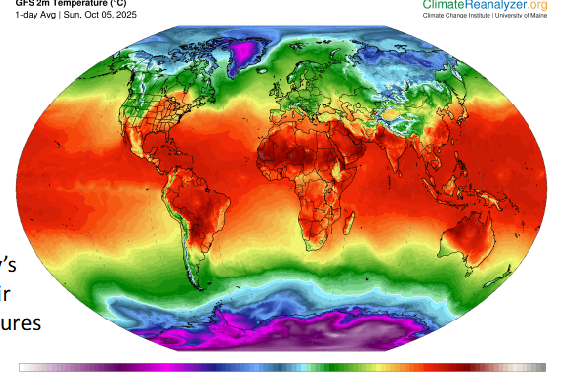
Where would you expect air to be rising? What do we expect'?
tropics are warm, so air rise while the poles are cold so it has a sinking air
we expect there to be circulation cells, but they only happen in smaller scales
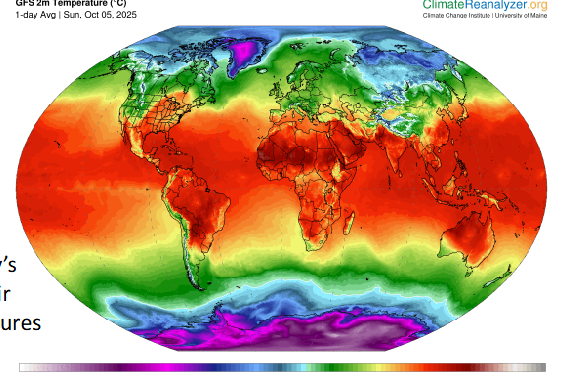
Actually,,,, how many circulation cells are there
3 in each hemisphere, 6 in total
Coriolis force? say the one sentence that describes what it does
this matter at a larger scale
Right on the north
left on the south
Its the apparent force to describe motion in a moving reference frame
Explain the example of buses
the ball will behave the same if the bus moves or not.
If you shoot the ball outside, the ball misses your friend
if your friend is also in another bus, the ball will still miss your friend
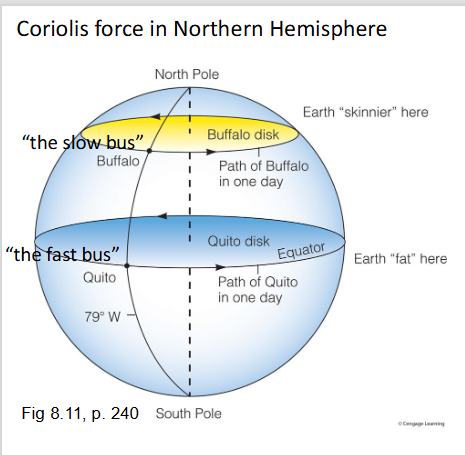
Coriolis force in Northern hemisphere
The slow bus is on the north
the fast bus is at the bottom
right on top
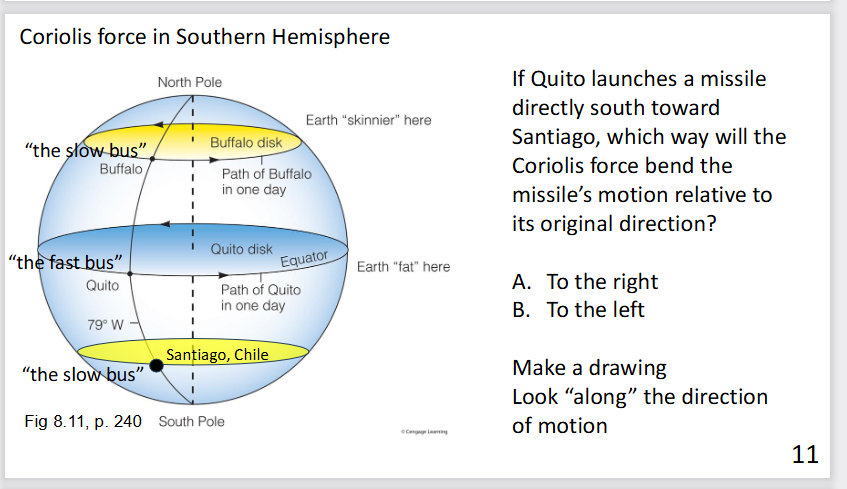
Coriolis force in the Southern hemisphere
left on south
Which way do the coriolis force bend the wind towards
R in N
L in S
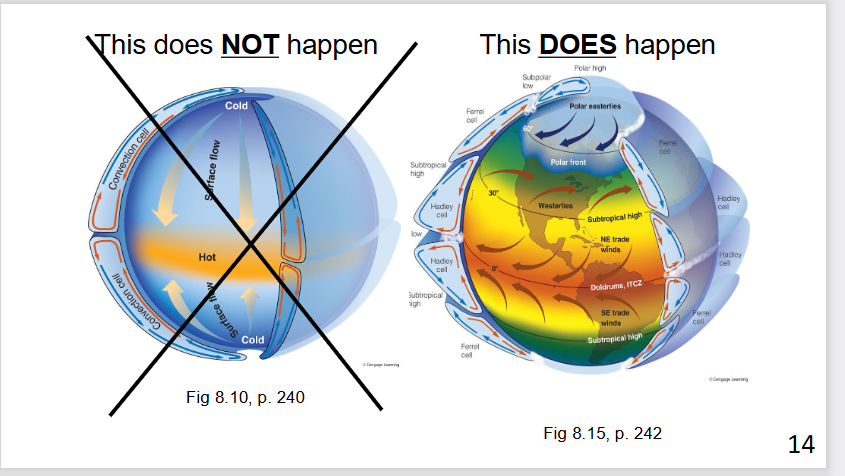
explain what happens here
air paths must bend and it cannot move directly form poles to equator
coriolis force prevents single circulation cell in each hemisphere, instead it has 6 cells
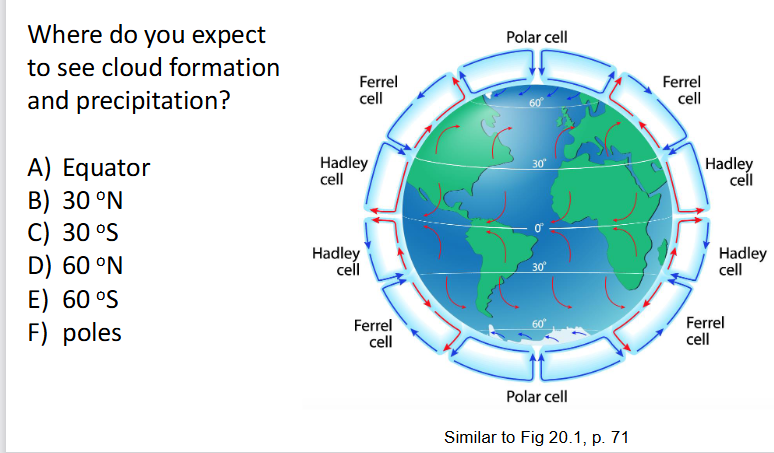
answer: A, D, E, F
Clouds tend to form where air is _____. And usually we see a band of clouds near the____ where ___ air is rising
rising, equator, hot
Relative humidity _______ in sinking air, explains to some extent the desserts
decreases
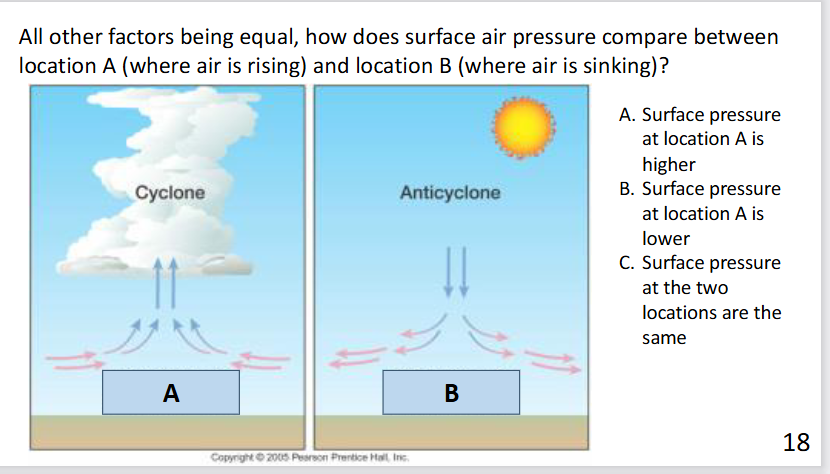
answer: B
Rising air (air sucked off surface) has lower air pressure
Sinking air (air stuffed on surface) has higher air pressure
What is the atmospheric pressure difference:
pressure gradient force is what drives air to move
Lower atmospheric pressure is at the equator, higher atmospheric pressure at poles
pressure gradient force formula:
pressure change / distance
Larger pressure gradients drive faster wind
When you are near ground, _____ becomes important
friction
Surface winds?
wind direction is tilted towrd low pressure zone compared to upper atmosphere
4 key ideas of winds
rising at equator
6 cieculation cells
identify low and high pressure zones
surf wind direction
hurricane and cyclone
hurricane: big pressure gradient
cyclone: low pressure at centre

A
anticyclone:
higer pressure at centre
air is sinking in centre

A
STG, SPG, ACC
subtropical gyre
subpolar gyre
antarctic circumpolar current
what is a gyre:
a large system of rotating ocean currents that form a circular motion driven by winds and the earths rotation
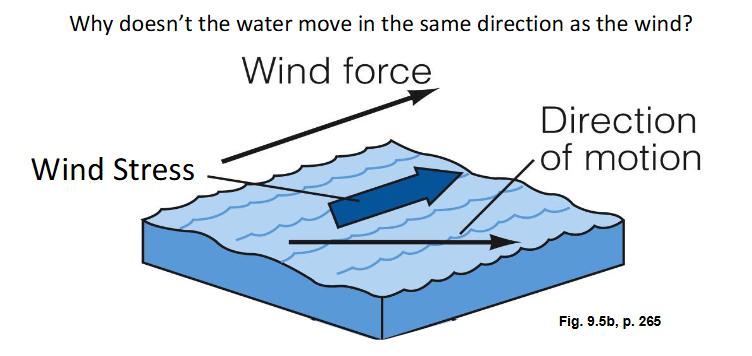
because the coriolis force deflects water to right of wind in NH and to the left of wind in SH
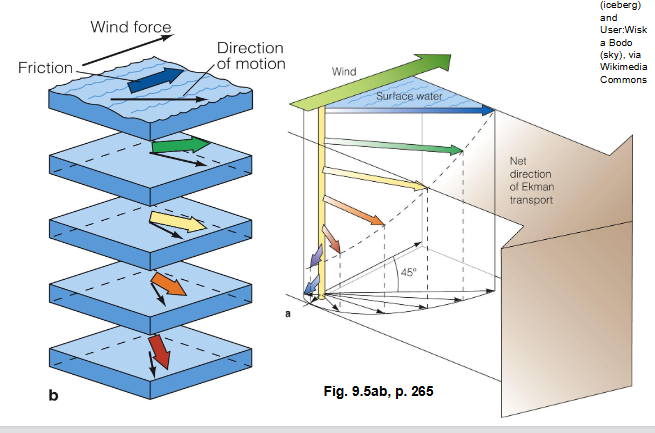
What is the ekman trasnport in the NH
surface water has a net movement of 90 degrees to the right of the wind direction
marine photosynthetic organism why are they important?
base of marine food chin
half of oxygen of the planet every year
some provide a habitat
consume CO2
Phytoplakton?
plankton that photosynthesizes
marine plankton?
organism that is carried by the movement of water
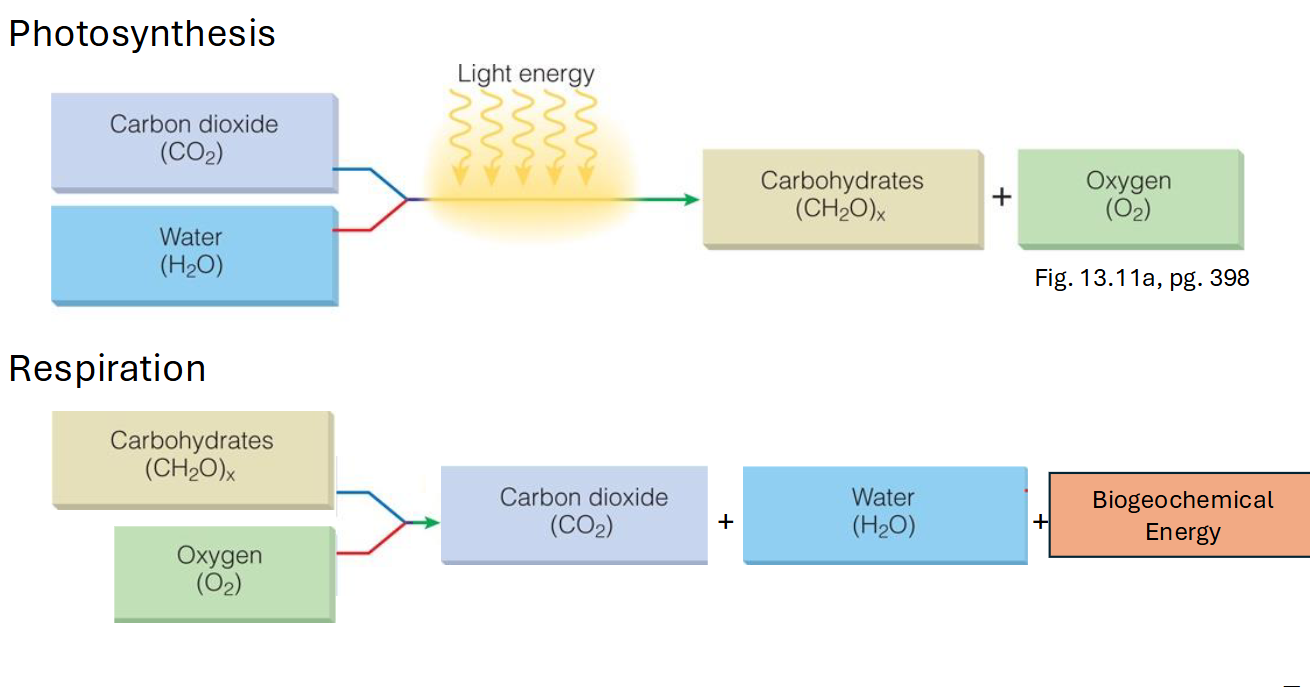
photosynthesizes, how does it work?
produces energy containing molecules (sugars) and oxygen (by product)
converts light energy into chemical energy through a two-stage process: light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
name two ways of producing energy:
photosynthesizes and respoiration
What organisms are made of biomolecules? what do they contain?
lipids, nucleic acid, carbohydrates, proteins
they all contain C, H, O
what is primary production? and what does it require?
creation of organic matter from inorganic compounds, through photosynthesis.
it requires “nutrients“, Nitrate and Phosphorus
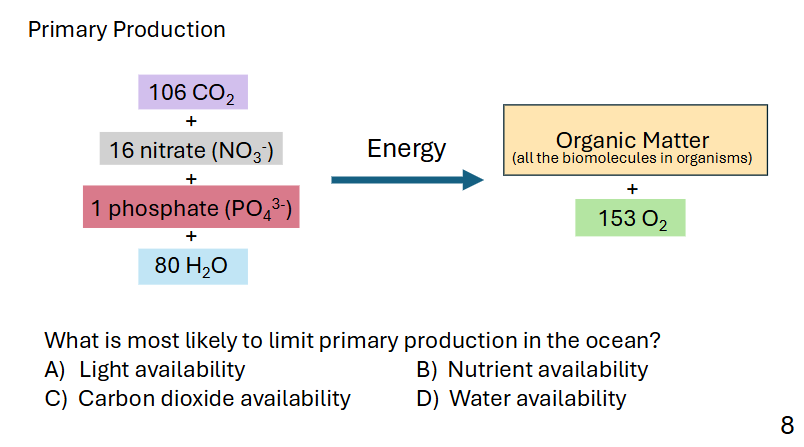
what is a limiting factor?
an environmental factor that lacking can slow or stop productivity
A,B
the tropics have _____ ______ availability
constant light
Relationships between light and depth of water
Less light reaches a higher depth
What does surface water do?
absorbs light and is heated up
euphotic zone?
depth with enough light for primary production to exceed respiration
primary production:only in the euophotic zone
respiration: both euphotic zone and deeep water
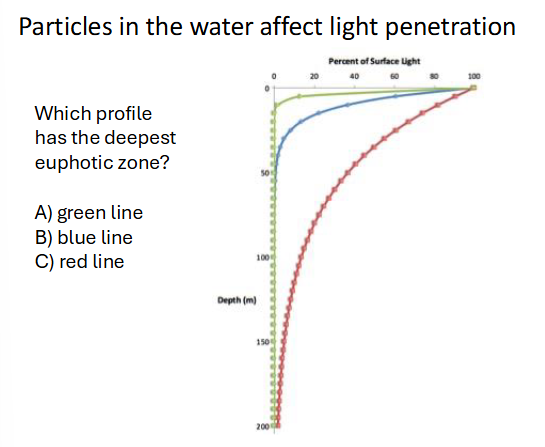
C
red wavelengths…
blue wavelengths…
red: is absorved in the surface cuz it had longer wavelengths
blue: penetrate farthest
photosynthesize pigments absorbs specific wavelengths of light including short wavelengths that penetrate deeply
adaptations to prevent sinking in phytoplankton
spines increase drag
flagella allows weak swimming
low density vacuoles
pump heavy salt ions in and out of the cell
mixed layer?
were there is turbulance and mixes the water
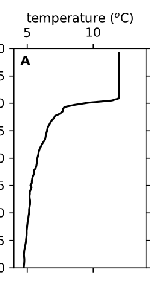
take the table in consideration, explain what you see
at the top the water is in a mized layer, mixing due to turbulance
in the chart change, that is a sharp change in density (the pycnocline)
deeper layers of water stay in the same depth
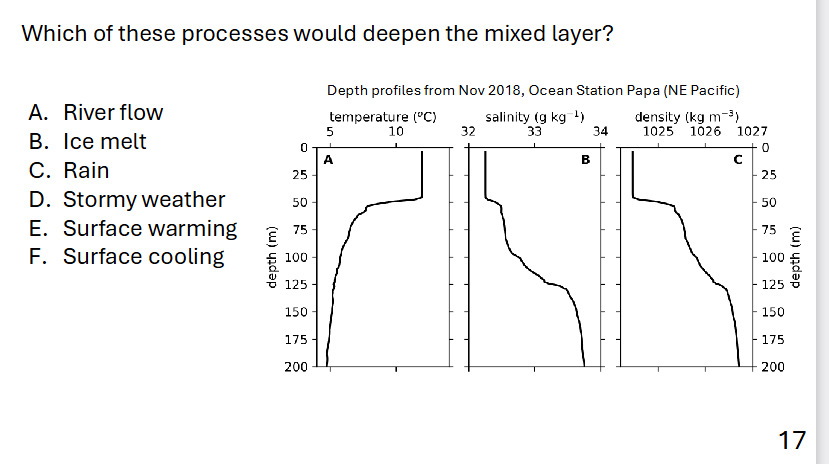
A, B, D, F
Processes that deepend mixed layers?
Processes that should mixed layers?
high wind and cooling winter
surface warming, rain, river, ice melt
at higher latituds in winter, we have low light availability because of (2) in the summer?
Low surface radiation
Deeper mixed layer
its the opposite in summer
Respiration?
consumes organic matter and oxygen. produces CO2, nutrients and energy
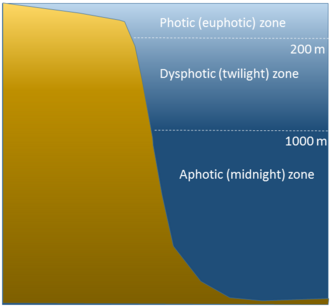
Euphotic zone? deeper (darker) zone?
primary reproduction and respiration
respiration only
Dead plankton and fecal matter are _____ and _____
dense and sink
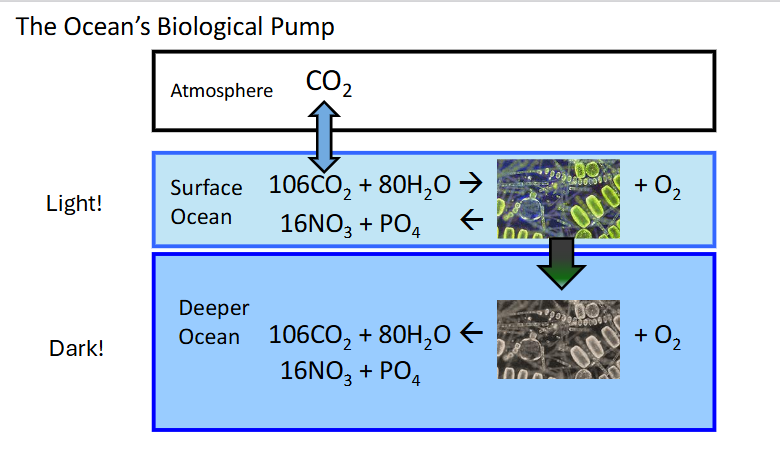
sinking organic matter brings….
carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous to depper ocean
mixing and upwelling can transport nutrients back to _____
euhpotic zone, upper zone
what is source and sink?
source: process that adds a substance
sink: process that consumes/removes a substance
shore, coast, eustatic change?
shore: place wher eocean mets land
coast: refers to the largers zone affected by the processes that occur at this boundary
eustatic: variations in sea level that can measured all over the world ocean
Long term change in sea levels (3 factors)
3 of these factors are due to eustatic change
The amount of water in the world ocean can vary
The water itself may occupy more or less volume as its temperature changes
the volume of the oceans container may vary over long time frames
local sea changes (2)
Tectonic motions can change the heights and shape of coast
Wind and currents, storm, el niño can force water against the shore or draw it away
erosional coasts vs depositional coasts
erosional: remove coastal materials
depositional: rate of sediment accumulation
high energy coast vs low energy coast
high energy coast: frequent large waves
low energy coast: unfrequent large waves
erosional coasts features: (5)
sea cliffs
sea caves
sea arches
sea stacks
wave cut platform
headlands vs bays
wave energy is focused into headlands and away from bays
what s a beach
is a zone of loose particles that covers part or all of a shore
longshore drift? what is it and by what is it driven’
its the movements of sediment (sand) along the coast, driven by wave action