GEP-NETs, MEN, Paraneoplastic syndromes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (GEP-NETS)
neuro endocrine tumors that arise from the stomach, intestines, or pancreas
unresectable or metastatic
65% of GEP-NETs are
MEN 1 (most typical), Von Hippel-Lindau disease,
GEP-NETs are associated with which genetic disorders
glucagon
A cells of the pancreas (20%) secrete
insulin
B cells of the pancreas (70%) secrete
somatostatin
D cells of the pancreas (5%) secrete
gastrin
G cells of the pancreas secrete
Insulinoma (B cell adenomas)
What is the most common functional type of GEP-NET that is characterized by the hypersecretion of insulin that is unresponsive to hypoglycemia?
Plasma glucose under 40, Serum insulin 6+ microunit/mL, elevated C peptide, Low beta-hydroxybutyrate
Describe the laboratory findings of Insulinomas
Helical CT (sensitivity 79%), MRI w/ gadolinium (sensitivity 85%), Endoscopic U/S (95% sensitivity)
Ways to diagnose and find insulinomas
surgical resections
Treatment of choice for insulinomas
Gastrinomas
A tumor usually located in the pancreas or duodenum that excretes gastrin leading to excessive stomach acid
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Gastrinomas are associated with ____________________ which is characterized by gastric acid secretion hypersecretion and aggressive, refractory peptic ulceration.
50%
What percentage of gastrinomas are malignant?
mulitple/refractory peptic ulcers, ulcers distal to duodenum, multiple peptic ulcers, relatives with MEN
Red flags for gastrinomas
Glucagonomas
Which type of GEP-NET is usually malignant with metastasis characteized by high levels of glucagon, weight loss, diarrhea, nausea, DM symptoms, and necrolyptic malignant erythema
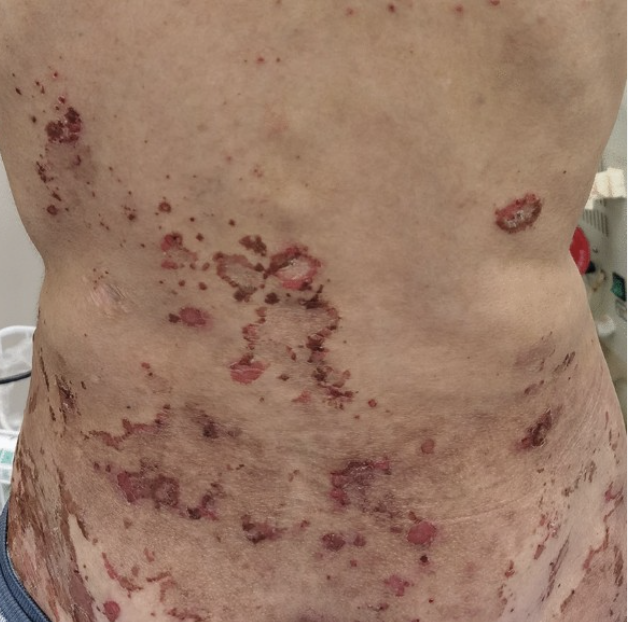
Mass effect
Nonfunctional tumors produce symptoms based on the
somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS)
What type of imaging detects NET (75% sensitivity) by measuring octreotide (somatostatin mimic) uptake?
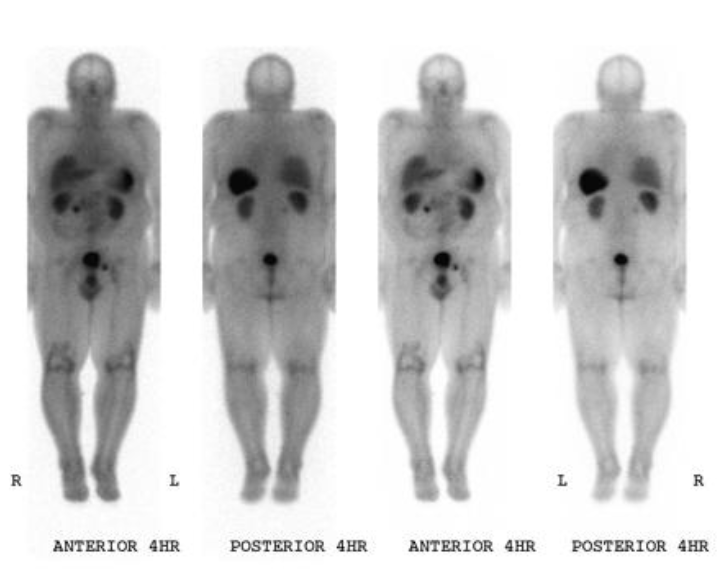
surgical resection
Treatment for GEP-NETs?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MED)
An autosomal dominant disorder that causes predisposition to the development of tumors in at least two endocrine glands
Pituitary adenoma, Facial angiofibromas, collagenomas, parathyroid tumors, insulinomas, gastrinomas
Tumors common with MEN 1
hyperparathyroidism, medullary thyroid cancer, pheo
Tumors common with MEN 2 (2A)
Medullary thyroid cancer, pheo, marfanoid phenotype, mucosal neuromas, intestinal ganglioneuromas, skeletal abnoramilites, delayed puberty
Tumors common with MEN 3 (2B)

parathyroid, pancreatic neuroendrocrine, pituitary, adrenocortical adenoma, thyroid adenoma, renal, testicular, neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma
Tumors common with MEN 4
Hyperparathyroidism (treat with surgical resection)
What is normally the 1st sign of MEN 1 (Wermer Syndrome)
Enteropancreatic tumors (gastrinomas, insulinomas, glucagonomas, somatostatinomas)
70% of MEN 1 patients have __________________
aggressive macroadenomas (secrete prolactin, GH, ACTH, non-secretory)
29% of of MEN 1 patients present with
Prophylactic total thyroidectomy by age 6 for 2A and 6 month for 2B
What is recommended for patients MEN 2A (Sipple Syndrome) or MEN 3 with medullary thyroid cancer?
Different gene mutation
What is different about MEN 4 when compared to MEN 1
Paraneoplastic syndrome
Symptoms and physical findings due to the remote effects of a neoplasm that are NOT related to direct invasion, obstruction, mass effect, or metastasis
Hormones and cytokines secreted by the tumor OR in a immune response against the tumor
What mediated paraneoplastic syndromes?
fever (release of endogenous pyrogens)
What is a common initial presentation of paraneoplastic syndromes
Lung (Small cell), breast, ovarian, liver, leukemias, lymphomas, stomach, pancreas, neuroendocrine
Which cancers commonly cause some paraneoplastic syndromes
Small cell lung (15%), Nonsmall cell lung (1%)
Which cancers may produce SIADH
managing hyponatremia, starting chemo
SIADH from a paraneoplastic syndrome is treated by
squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, multiple myeloma, kidney
Cancers that commonly cause hypercalcemia as a paraneoplastic syndrome
PTHrP, calcitriol, osteoclast activating factors
What might tumors secrete to cause hypercalcemia as a paraneoplastic syndrome
insulinomas, hepatocellular carcinoma
What types of cancer may cause hypoglycemia as a paraneoplastic syndrome
Overproduction of IGF-2 to stimulate glucose utilization
Why can hepatocellular carcinoma cause hypoglycemia
Ectopic production of ACTH, SCLC
What may cause Cushing Syndrome as a paraneoplastic syndrome
treat underlying cancer
For a majority of paraneoplastic syndromes, what is our treatment plan?