Core Exam 2 Review
1/178
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
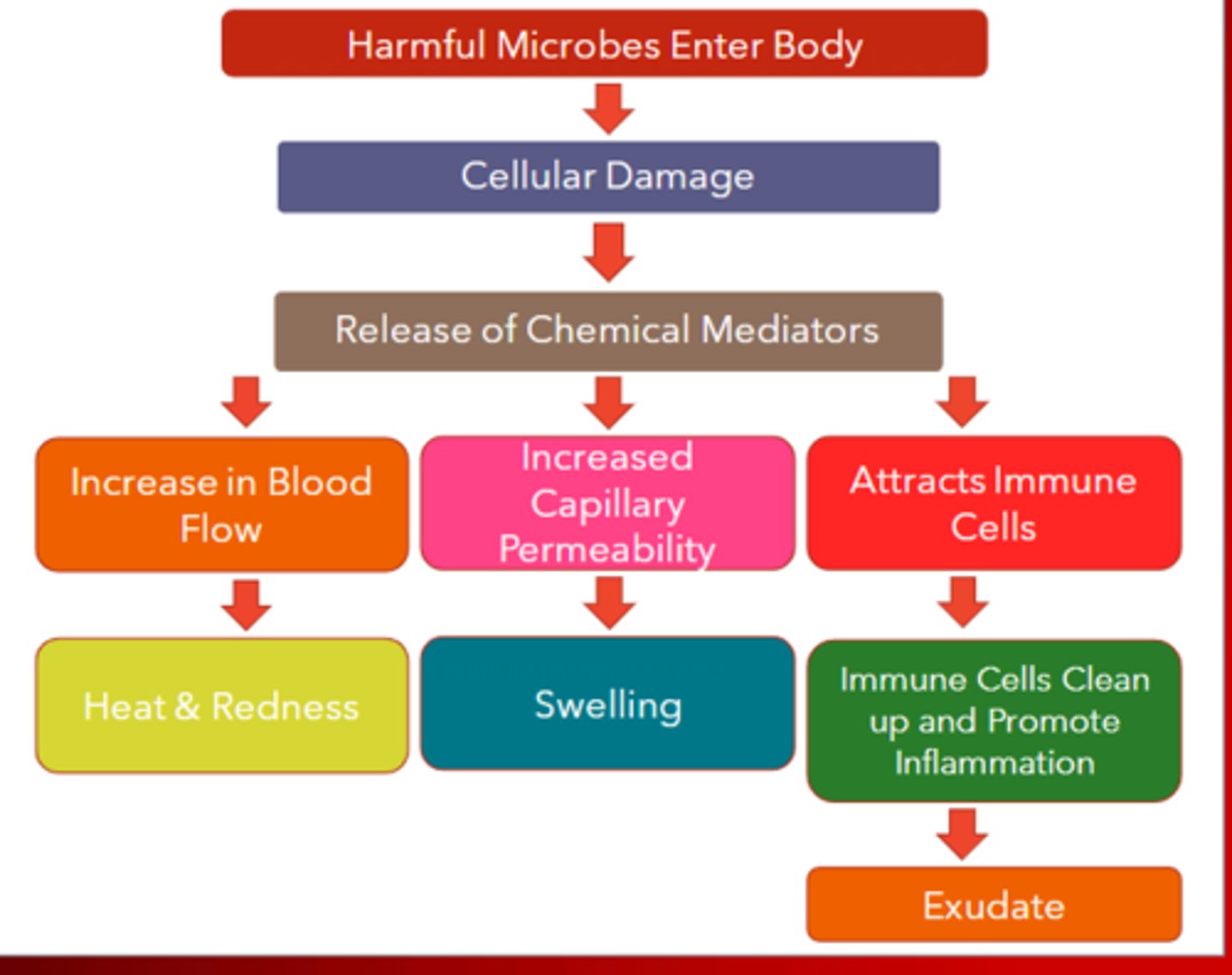
what is inflammation
- an immune response
- the body's response to an injury and illness
- plasma, dissolved substances aid in healing injured tissues
is inflammation every a normal response
yes, all part of the healing process
Give an example of a Nursing Diagnosis indicating inflammation
risk for infection at injury site
can inflammation occur anywhere in the body?
yes, inflammation can occur internally and externally
Vascular cellular responses (First Phase)
- heat and redness due to vasodilation
- increased blood supply (hyperemia) cases swelling and edema
- pain is caused by lack of circulation and nerve ending stimulation by edema
what causes swelling and edema
vascular permeability resulting in swelling, pain, inflammation, and histamine response
Five cardinal signs of inflammation
- Pain
- heat
- redness
- swelling
- loss of function
Second stage of inflammation
exudate production
What is exudate
drainage from injury site
serous exudate
clear, watery, straw colored fluid accompanying mild inflammation
purulent exudate
opaque, milky white, contains potentially necrotic debris (pus) indicates infection
hemorrhagic/ sanguineous exudate
thick, bloody drainage, resulting of infection or injury
Third stage of inflammation
reparative phase
reparative phase includes
regeneration and granulation
what is regeneration
cells begin to repair and replace destroyed cells with identical copies
what is granulation
replacing damaged cells via scar tissues, early stage of scar tissue formation
tissues within the body that have good regenerative capacity
- skin cells, epithelial tissue
- digestive tissue
- respiratory tissue
- lymphoid tissue
- bone marrow tissue
First phase- Tissue injury
release of chemical signals such as histamines
Second phase- dilation and increased leakiness of local blood vessels
migration of phagocytes to the area
Third phase- macrophages and neutrophils consume bacteria and cell debris
tissue heals
examples of inflammation
- edema
- throbbing
- burning
- pain at site
- increased skin temperature
- erythema (redness)
- ecchymosis (bruise)
Rheumatoid arthritis
- autoimmune disease that attacks joints
- causes inflammation
- pain
- heat
- can range from mild to severe
What are you going to educate your patient about preventing inflammation?
- avoid injury
- hand hygiene
- diabetics should take special care for abrasions on neuropathic limbs
- advise adequate risks
- take medications regularly
- hydrate properly
- keep good nutritional goals
RICE
- rest
- ice
- compression
- elevation
what are risk factors related to inflammation?
- family history of rheumatoid arthritis
- age
- adequate rest
- low sodium and low sugar
- high fiber
- omega three and fatty acid needs should be met
- no smoking
- avoid allergens
Genetic predispositions for inflammatory process
- native Americans and Mexicans are at increased risk for gallstones
- family history
- female gender (hormones make women predisposed to RA)
- African Americans are at greater risk for nephritis
IV infiltration
cannula through vessel= fluid flowing into tissues causes edema, nonvesicant fluid
IV extraversion
leaking of vesicant fluid into vascular space, tissue damage
IV infiltration vs IV extravasaion
infiltration= edema, no tissue damage
extravasation= fluids causing tissue damage or necrosis
Phlebitis
- veins swell, red path in tissue
- very painful
- inflammation due to vessel wall injury
- can be caused by catheter placement or IV fluid administration
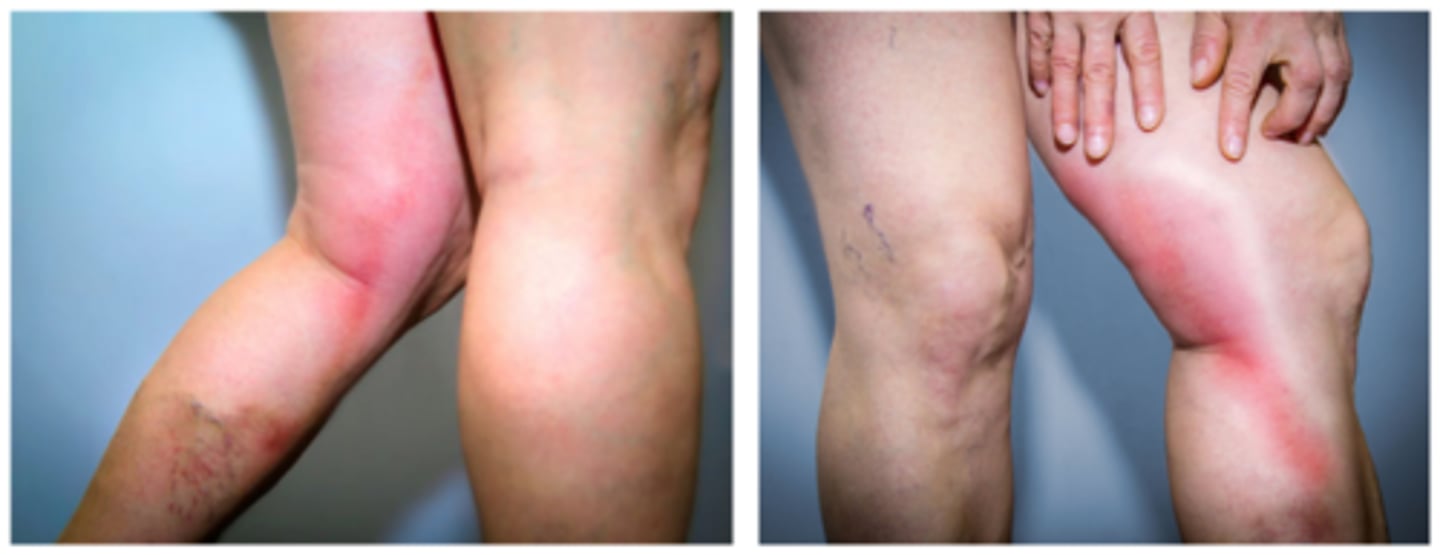
thrombophlebitis
inflammation of a vein due to a blood clot
Cellulitis
diffuse, acute infection of the skin marked by local heat, redness, pain, fever, and swelling
cellulitis priority treatment
stop infusion, elevate extremity,
apply warm compress three to four times a day
s/s of localized inflammation
- pain
- heat
- swelling
- redness
- loss of function
- edema
- can be in any part of the body
S/S of systematic inflammation
- widespread symptoms can cause a variety of symptoms
- temp of 104+
- RR 20+
- alter vitals
5 diagnostic tests for inflammation
- WBC greater than 10,000
- ESR Greater than 20mm/hr
- C reactive protein( less than 2.9)
- CMP/BMP
CMP/BMP
- complete or basic metabolic panels
- assessing for liver and kidney function
- albumin levels
albumin levels can indicate
- high levels= dehydration
- low levels indicate malnutrition, liver or kidney dysfunction, or infections
ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
normal ranges for men are 0-15 and 0-20 for women
what can the patient do for inflammatory process?
RICE, prevent further injury, ice for acute muscular injury, heat for chronic inflammatory conditions
what can the nurse do for inflammation?
ice packs, pt education, repositioning, elevate extremities with pillows
what are medications for inflammation?
NSAIDs, antipyretics, corticosteroids
what are some treatments for inflammation?
allergy shots, avoid triggers
what dietary changes will reduce inflammation?
- reduce salt intake
- avoid triggers
- decease sugar
- increase fiber and protein intake
- know what you are eating
do heat and cold application require an order
- yes, for major and constant application
- for smaller applications like IV upset may vary by facility
orders for application of heat or cold must contain
location on body, specific durations, frequency, temperature parameters
those at higher risk for complications with application of heat or cold
young children due to lack of communication and older adults due to lack of sensation and low adipose tissue
asses heat or cold therapy every
5-10 minutes
pathophysiology of infection
pathogens
underlying pathogen must be determined so we can better treat infection
bacteria example
Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, treated with antibiotics
virus example
herpes zoster/varicella zoster virus , treated with antivirals
parasitic examples
protozoa- malaria
helminths- worms
fungi examples
Candida albicans or yeast infections
prion
causes malformation of protein, affects neuro system and brain
ex- mad cow disease
stages of infection
- incubation
- prodromal
- illness
- convalescence
incubation stage of infection
microorganism has entered body and is begging to manifest non specific signs and symptoms
prodromal stage of infection
more specific symptoms appear that are closely related to disease, organism is rapidly replicating/ multiplying
illness stage of infection
very specific disease presentation, more intense than prodromal stage, peak of illness
convalescence stage of infection
recovery, returning to normal, can take days to months depending on pathogen
nonspecific immunity
skin, mucous, hair, inflammatory response, NO MEMORY
specific immunity
antibody mediated, requires past exposure to antigen, lymphocytes, vaccines, MEMORY
largest risk factor for infection
inadequate hand hygiene and non intact skin
other risk factors for infection
- environment: alcohol, tobacco, malnutrition
- chronic illness
- medications: long term use of steroids, any cancer drugs, weakened immune system
- age: newborns and older adults
- internal: stress, poor nutrition, not immunized, exhaustion, poor hygiene
chain of infection
infectious agent, reservoir, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portal of entry, susceptible host
causative agent
pathogens, Bactria, prion, parasite, fungi
Revisor of infection
- infected thing or person, pathogen breeds and grows here
- can be a human, animal, food, water
portal of exit
- how pathogen leaves revisor
- often same as portal of entry
- skin to skin, respiratory system, GI to GI
Mode of transmission
how bug is spread
- droplet, airborne, vector borne(bugs), vehicle borne( non-living objects)
portal of entry
usually the same as portal of exit
- how pathogen enters susceptible host
susceptible host
the immunocompromised, older adults, neonates, risky behaviors
five classic symptoms of localized infection
- redness
- warmth
- edema
- pain
- loss of function
signs of systemic infection
- fever
- tachycardia
- tachypnea
- hypotension
- fatigue/ malaise
- N/V, anorexia
- enlarged lymph nodes
asepsis
Absence of pathogens
medical asepsis
"clean technique" disinfected but not entirely free from pathogens
surgical asepsis
"sterile technique" total elimination of pathogens
medical asepsis is used
- emptying cathether
- drawing meds (technique is clean, equipment is sterile)
- inserting IV ( skin can never be sterile)
- clean dressing change
surgical asepsis is used
- inserting an indwelling urinary Cath
- surgical procedures
- central line dressing changes
- sterile dressing changes
hand hygiene
- alcohol based disinfectants expect with C diff or soiled hands
- at least 20 seconds of friction / suds
clean from
leas soiled to most soiled
if you suspect something is contaminated/ no longer sterile
throw it out and start again
transmission based precautions are dependent on
mode of pathogen transmission
patients on any form of transmission based precautions are at risk for
social deprivation, isolation, and mental health decline
Standard Precautions
- always in effect
- all bodily fluids(except sweat), open wounds, and mucosal membranes
- hand hygiene
- gloves
- additional personal preferences on protection
airborne precautions
- negative pressure private rooms
- healthcare professionals wear N95 masks and face shield
- client wears surgical mask when outside the room
droplet precautions
- private room or shared room with matching precaution
- surgical mask
- client wears mask when leaving room
contact precautions
- private room or shared room with same precautions
- gloves and gown
reverse/neutropenic precautions
- to protect patent from outside, for immunocompromised pts
- positive and private pressure room
- patient wears mask when outside of room
- no plants in room
- fully cooked food
- RN wears mask when in room
protective environment
- neutropenic precautions
- protects patients from healthcare environment rather than healthcare environment protected from patient
varicella Zoster virus
responsible for
- chicken pox
- herpes zoster/shingles
- pearls
chicken pox
- highly contagious
- prevented with vaccine
- disseminated rash
- childhood illness
- self limiting
- lives in dorsal ganglia( why shingles follows nerve pathway)
- possible reactivation later in life
Herpes Zoster / shingles
- cannot be caught, only reactivated from previous infection( can transmit chickenpox)
- painful rash that follows from dermatomes
- does not pass midline
- treat with antiviral drugs
Pearls
-requires primarily contact precautions( blisters/ dermatomes)
- airborne precautions in severe cases
- no longer contagious once lesions are dry and crusted over
- pregnant women should not care for patients with shingles due to fetal risk
Diseases with transmission based precautions
Measles, TB, Varcilla ( MTV)
mumps is
droplet precautions
Hep B precaution level
standard and bloodborne
C. diff requires
contact precautions
Diagnostics for infection
X-ray, CT, Ultrasound, Biopies
Labs related to infection
- White Blood Cells over
10,000
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- culture and sensitivity
RN care for infection
- follow precautions
- follow appropriate aseptic technique
- appropriate nutrition and hydration