Testosterone Pharmacology (Dr. Sharma)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Binding of testosterone to ABP maintains local high concentration of testosterone for what
spermatogenesis
testis contains how many higher concentration of testosterone compared to the circulating concentration in plasma
100 times high concentration
circulating levels of what exert negative feedback effect on hypothalamus to decrease GnRH and on pituitary gonadotrophs to decrease LH
testosterone
when high amounts of therapeutic testosterone are administered, it suppresses GnRH and LH.
Low LH levels in turn impair spermatogenesis by decreasing testosterone levels in testis
true about testosterone negative feedback
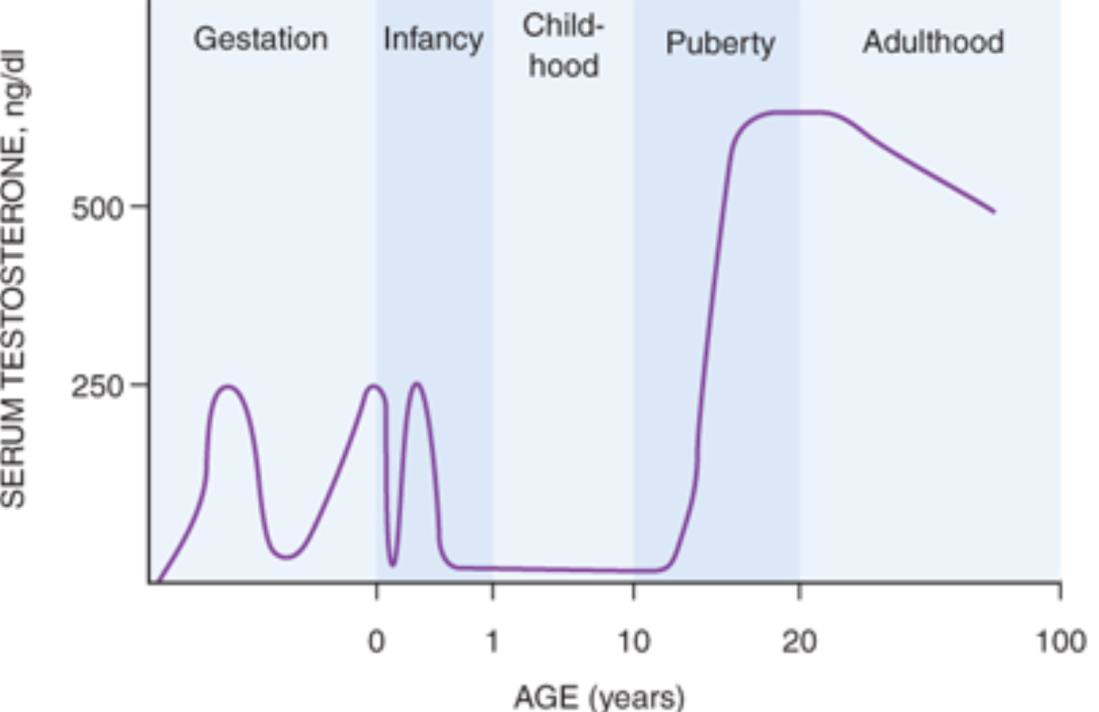
when does testosterone start at
at puberty to 30s
LH is release in the pulses of 2h interval
Peak LH pulse is in the morning
peak testosterone levels at 8AM lowest at 8PM
testosterone variation
physiological effects of testosterone is what
at puberty
during adulthood
during aging
at puberty, the increased level of testosterone causes what
increase in testicle size
growth of male genitali
during adulthood what are the physiological effects of testosterone
maintenance of spermatogenesis
libido
erythropoiesis
male pattern baldness
prostate hyperplasia
low testosterone causes decreased energy, muscle mass, libido, bond density in what
during aging (senescence)
95% testosterone in plasma in bound to proteins
true
65% is bound to b-globulin called what
GBG (gonadal steroid binding globulin)
1)To a more potent derivative dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by enzyme 5α-reductase in skin, prostrate gland, hair follicles and some other tissues
2)To estradiol in bone and adipose tissue by enzyme aromatase (CYP19)
3)To inactive metabolites androsterone and etiocholanolone in liver
testosterone is metabolized
active metabolite of testosterone
dihydrotestosterone
estradiol
Inactive metabolite of testosterone
androsterone and etiocholanolone
receptors for testosterone are called what
androgen receptors
what are present in cytosol of testosterone repsonseive cells and are bound to a repressor heart shock protein
androgen receptor
what has approximately 5 times greater affinity for the androgen receptors than testosterone which makes DHT more potent androgenic steroid at physiologic concentrations
dihydrotestosterone
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY trisomy)
Undescended testicles (Cryptochidism)
Mumps orchitis
Injury to the testicles
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
Drugs (Ketoconazole, Spironolactone, Marijuana)
are etiology of what
małe hypogonadism primary (defect in testeS)
Kallmann syndrome (Abnormal development of the hypothalamus)
Pituitary disorders
Inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis, histiocytosis and tuberculosis)
Hemochromatosis (Excessive iron) and pituitary lesions
HIV/AIDS
Obesity
Late onset hypogonadism due to normal aging (Andropause)
are etoiology of what
małe secondary hypogonadism
Erectile dysfunction
Infertility
Decrease in muscle mass
Gynecomastia
Osteoporosis
Decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit
symptoms what ?
hypogonadism in adulthood
Decreased development of muscle mass
Lack of deepening of the voice
Impaired growth of body hair
Impaired growth of the penis and testicles
Excessive growth of the arms and legs in relation to the trunk of the body
Gynecomastia
symptoms of what
before puberty for hypogonadism
what is rapidly absorbed orally but undergoes extensive first pass metabolism. Thus, very low levels reach the systemic circulation.
testosterone
therapeutic use of testosterone required either what
development of testosterone derivatives that undergo less hepatic metabolism
use routes of administration that bypass first pass metabolism
what is testosterone derivatives for oral administration
17a methyl derivatives
what is the testosterone derivates for parental intramuscular administration
ester derivatives
testosterone derivaties have an alpha methyl group at what carbon
17 carbon position
17a methyl tsetosterone derivates are what
hepatotoxicity
what are the 2 testosterone derivates
17a methyl derivatives
ester derivates
esterification of the hydroxyl group present at what carbon to generate ester derivates
carbon 17
testosterone esters are highly lipophilic and are formulated in oils for intramuscular depot injections for long duration of action
true
which formulation are oily injection containing testosterone ester
intramuscular
the formulation for the following routes contain testosterone except what
Oral: Testosterone undecanoate
Nasal: Spray pump
Subdermal: Pellets
Topical: Gel, Solution
Intramuscular
oral and IM
for testosterone what is at carbon 3
ketone
for testosterone what is on carbon 17
hydroxyl
Self-emulsifying lipoprotein particle formulation
by-passes hepatic metabolism
Jatenzo (oral testosterone undecanoate)
black box warning for what kind of formation in testosterone
topical