Chapter 25: Seedless Plants
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are terrestrial plants mostly descended from?
aquatic plants, mostly green algae
What is desiccation?
drying out
Why do aquatic plants have it "easy"?
No threat of desiccation—they live in water
No need for structural support—water provides support and protects them from UV rays
How are gametes and zygotes protected in aquatic plants?
Gametes are transported through water, and neither is threatened by desiccation
What adaptations were needed for aquatic plants to colonize land?
Dry conditions and UV rays
What are the disadvantages of colonizing terrestrial environments?
threats of desiccation, UV rays, need for structural support, plant reproduction is water-dependent, and zygote is water-dependent
What are the advantages of colonizing terrestrial environments?
sunlight and carbon dioxide is abundant, no competitors for resources, no predators
What strategies did the first terrestrial plants use to survive on land?
live near water and/or colonize humid environments, develop tolerance to desiccation, stayed small, develop mechanisms to protect against UV rays
How did the first terrestrial plants develop their adaptations?
through time and natural selection (genetic variation selected for beneficial traits)
What is the function of sporopollenin and why is it important?
protects spores and pollen from desiccation and degradation, allowing survival outside water
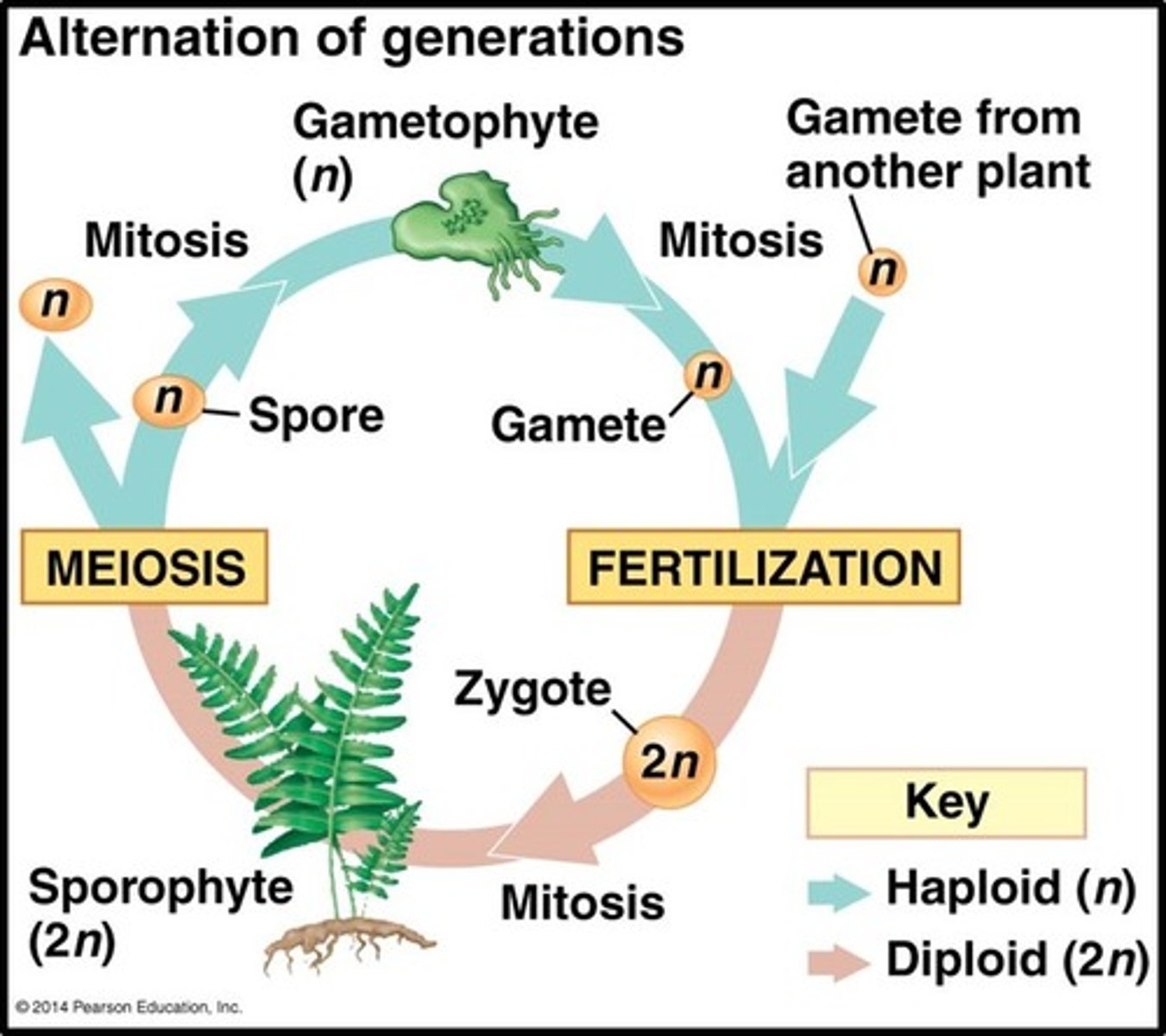
What is the alternation of generations life cycle?
Organisms alternate between multicellular haploid and multicellular diploid stages:
Sporophyte stage—produces spores via meiosis
Gametophyte stage—produces gametes via mitosis
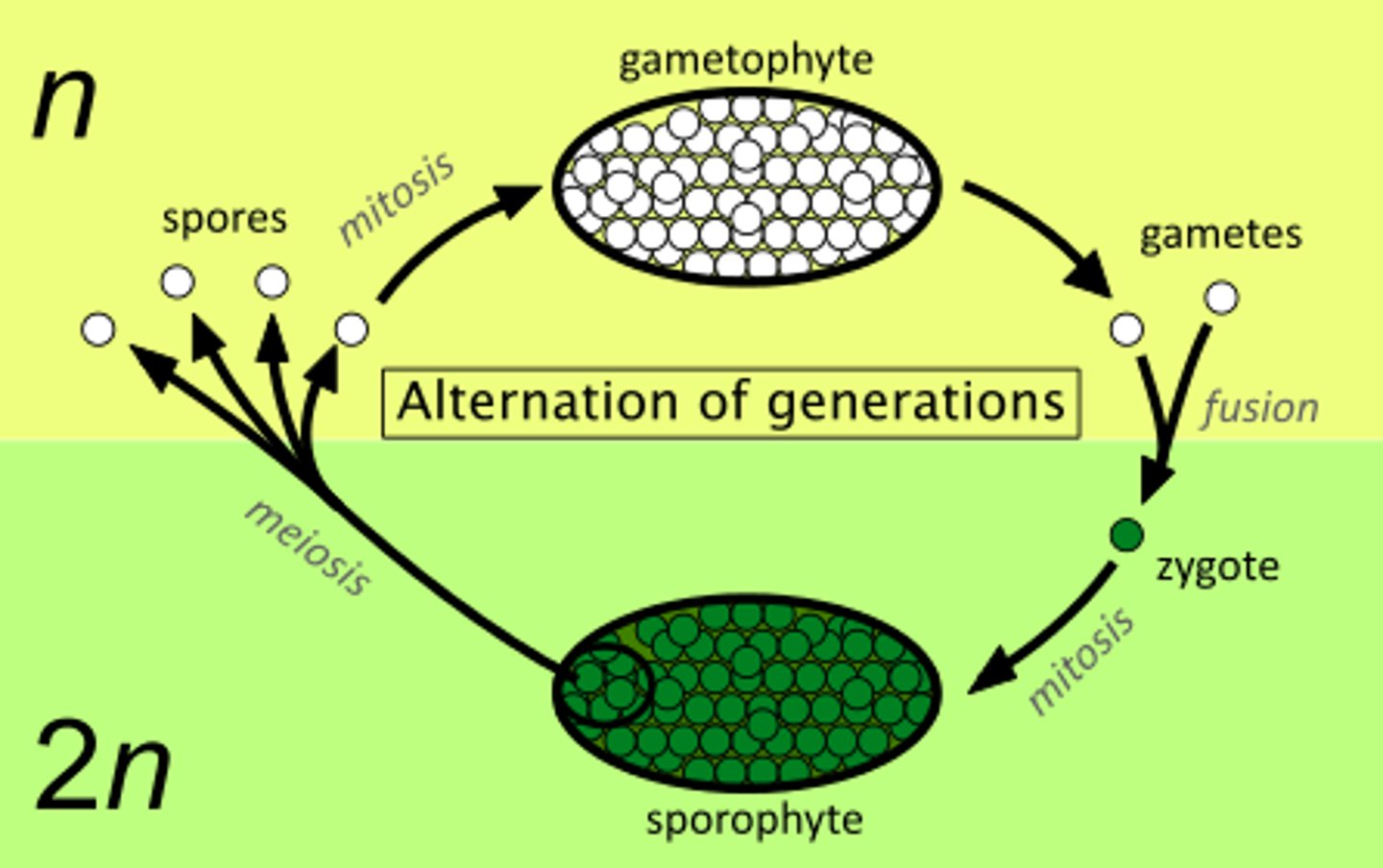
How is alternation of generations different in plants versus humans?
Humans: diploid stage is multicellular body; haploid is unicellular gametes
Plants: both diploid and haploid stages are multicellular
What does the haploid gametophyte stage produce and what occurs?
haploid gametes through mitosis
sperm of one plant fertilized egg of another to create new plant: diploid sporophyte
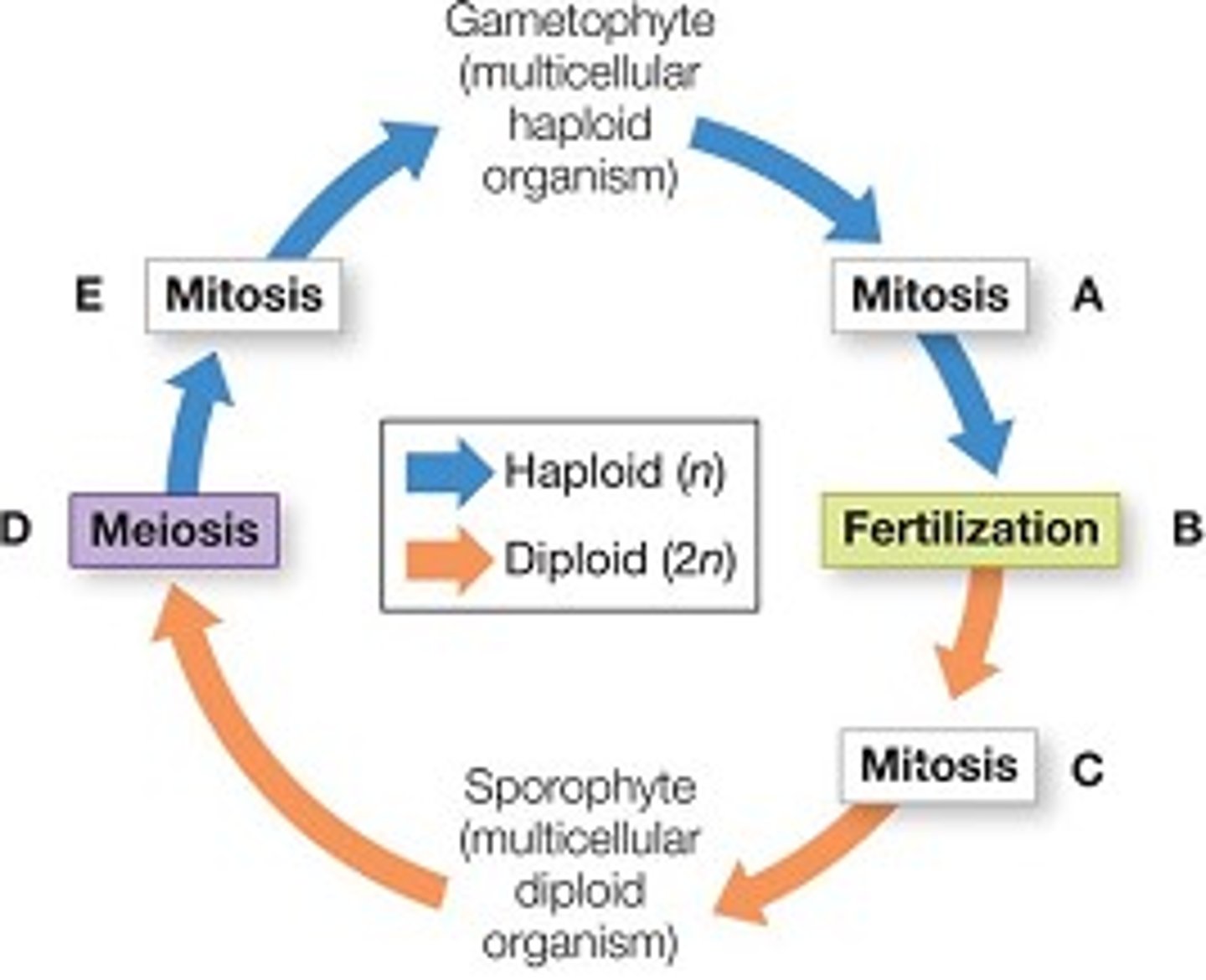
What does the diploid sporophyte stage produce and what occurs?
diploid zygote grows into sporophyte, haploid spores through meiosis
spores germinate into new gametophyte plants
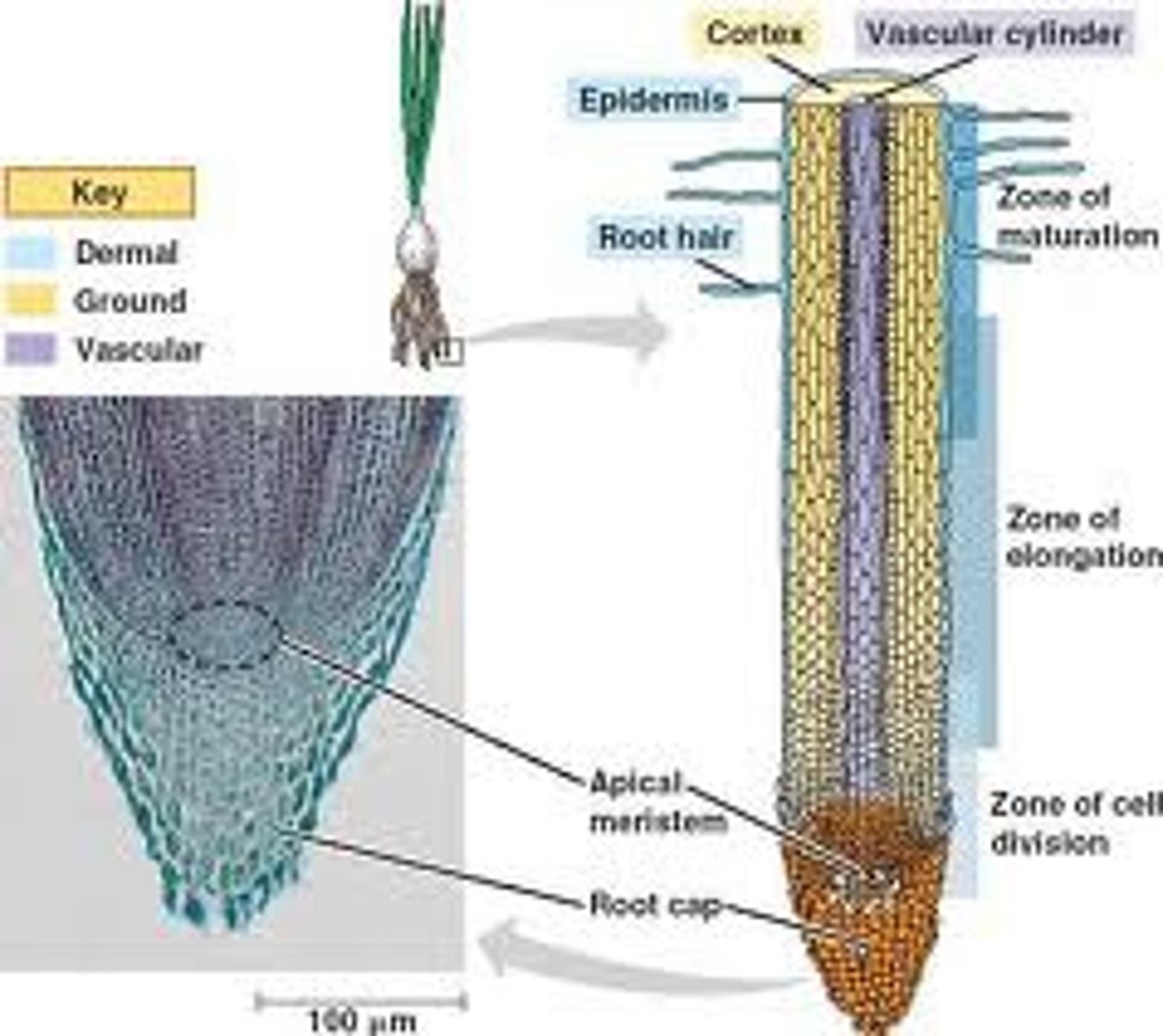
What is the function of apical meristems in roots and shoots?
meristem tissues at root and shoot tips allow vertical growth to help plants access light and resources
What are meristem tissues in plants?
made of undifferentiated cells that can develop into any type of plant cell
What is the function of the shoot apical meristem?
allows upward growth of the shoot, access sunlight
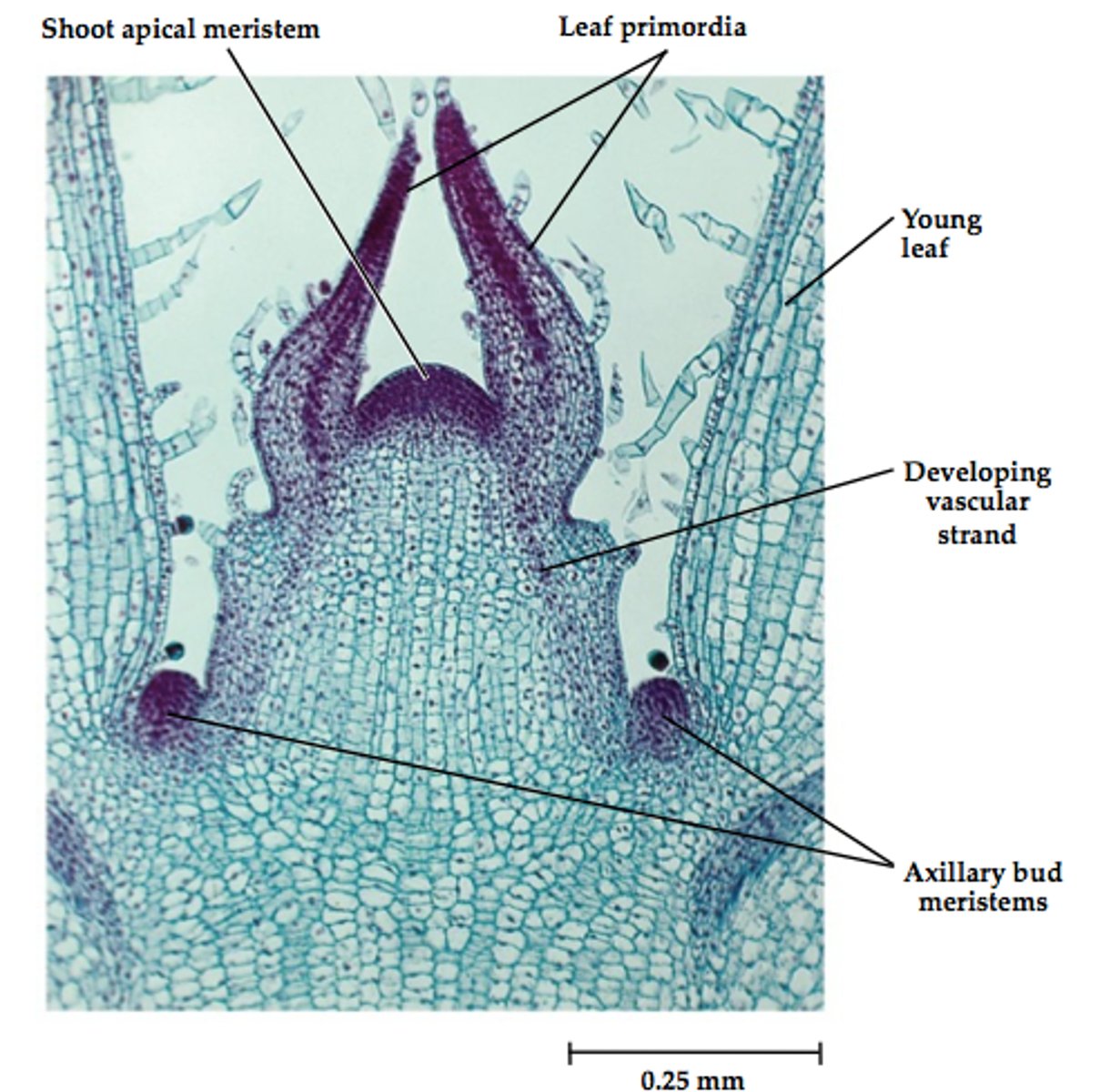
What is the function of the root apical meristem?
allows downward growth of roots, access water and minerals
What is the function of a waxy cuticle on leaves and stems?
prevents desiccation by reducing water loss
What is a waxy cuticle?
epidermal tissue with wax that covers surfaces of leaves and stem
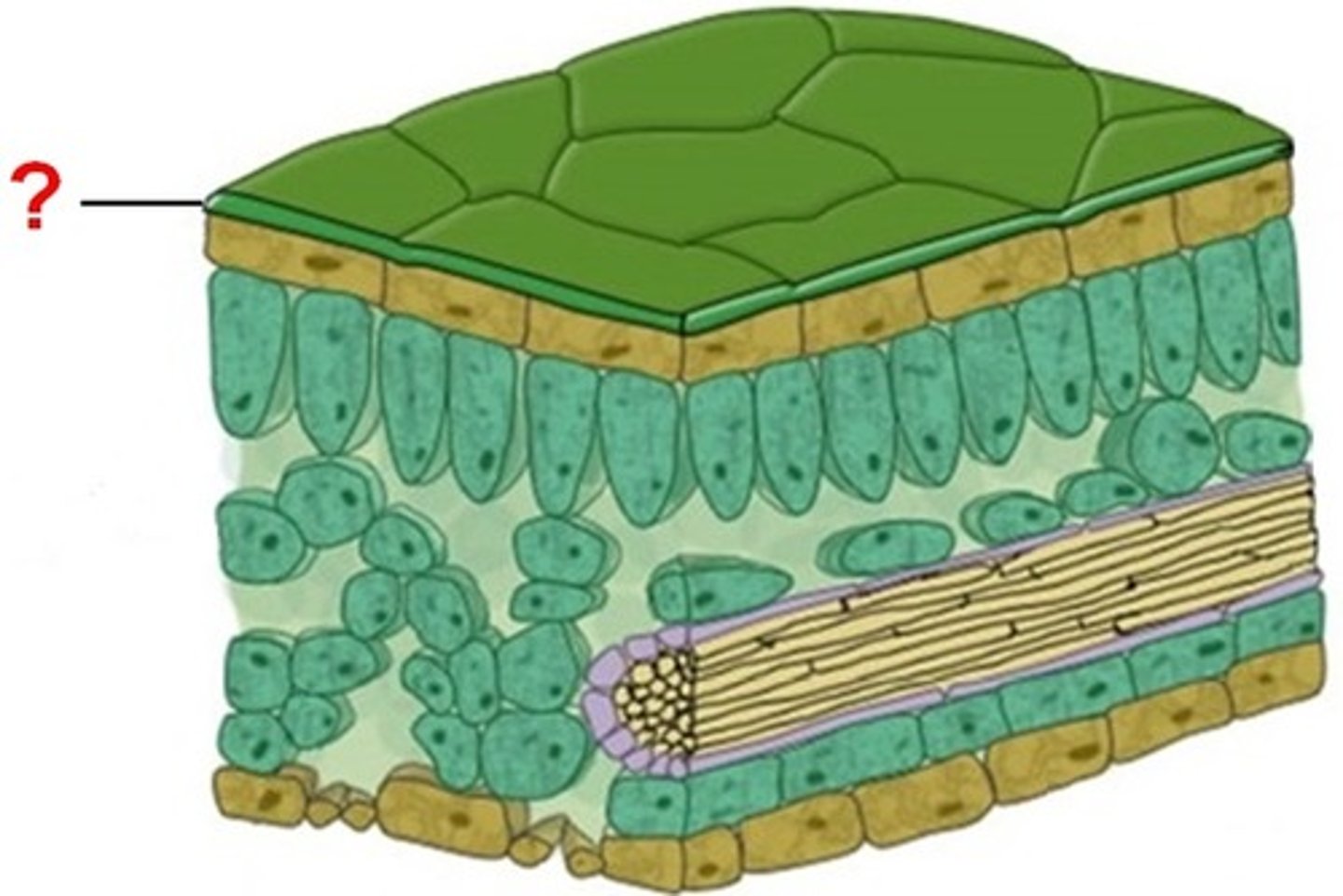
What is the role of lignin in vascular tissues?
structural support, only in vascular plants
What are adaptations that the first terrestrial plants developed?
sporopollenin, alternation of generations life cycle, apical meristems, waxy cuticles, lignin in vascular tissues (nonvascular plants)
What is sporopollenin?
thick cell walls of spores, composed of organic molecules similar to fatty acids and carotenoids
What is the sporophyte in seedless plants?
diploid (2n) stage of the plant, formed after gametes fertilized
How is the sporophyte different in nonvascular seedless plants?
it is dependent on the gametophyte (n) stage for nutrition and support
What are sporangia/sporangium?
produced by the sporophyte, contain sporocytes, where haploid spores are produced via meiosis
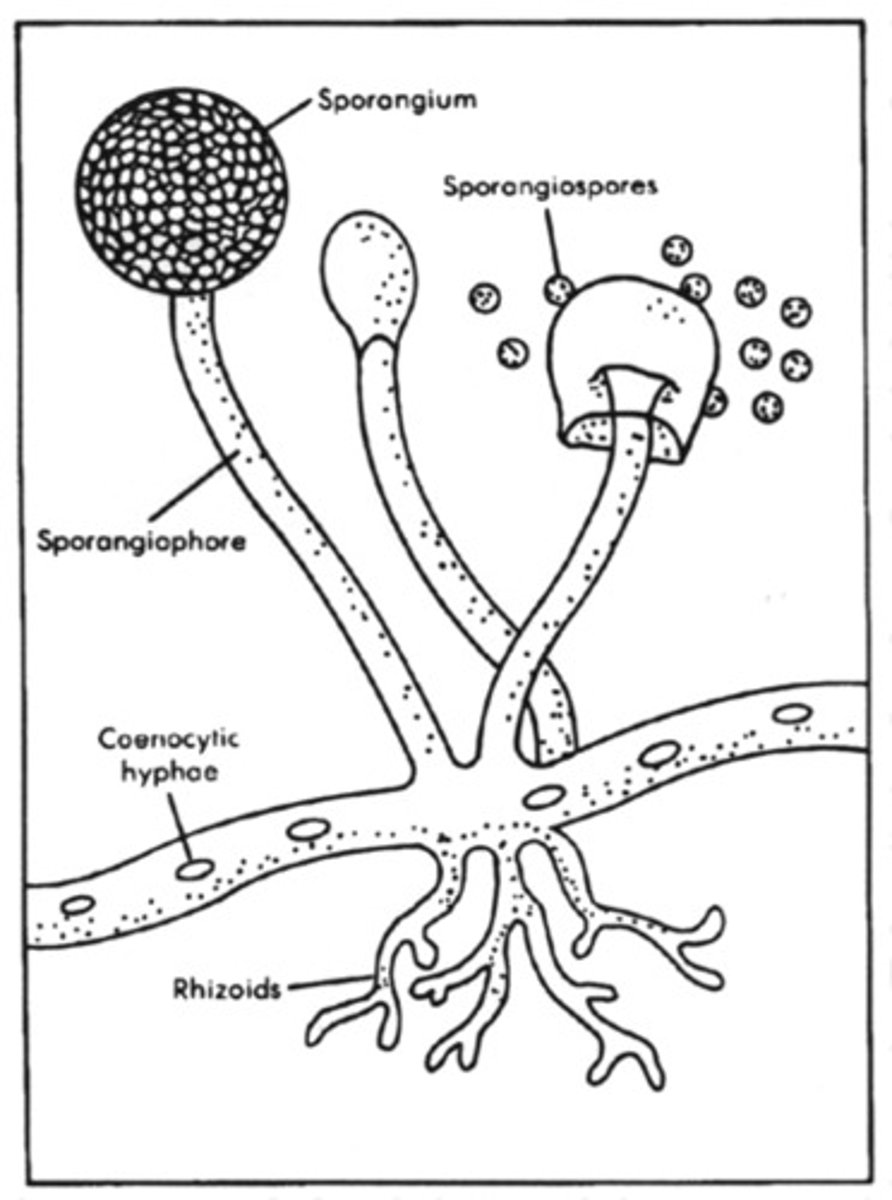
What happens to the spores produced in sporangia?
released from sporangia, disperse, and germinate into new gametophyte plants
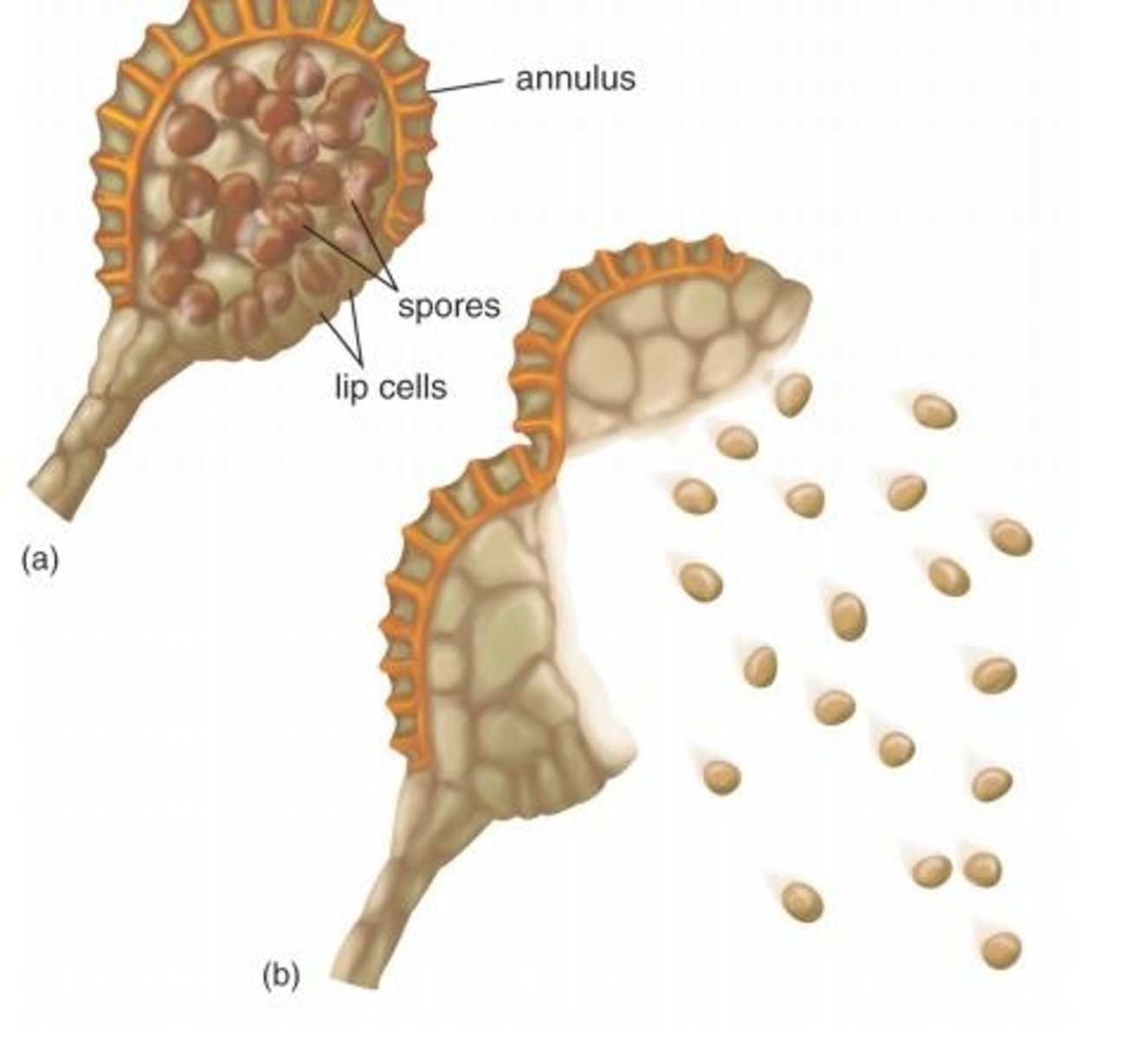
What are homosporous spores?
produce only one type of spore; germinate into a monoecious gametophyte
What is a monoecious gametophyte?
produces both male and female gametes on same plant; typically germinated from homosporous spores
Are all seedless plants homosporous?
most, but not all
What are heterosporous spores?
produces two different types of spores; male and female
What are microspores?
male spores that develop into male gametophytes, produce only male gametes
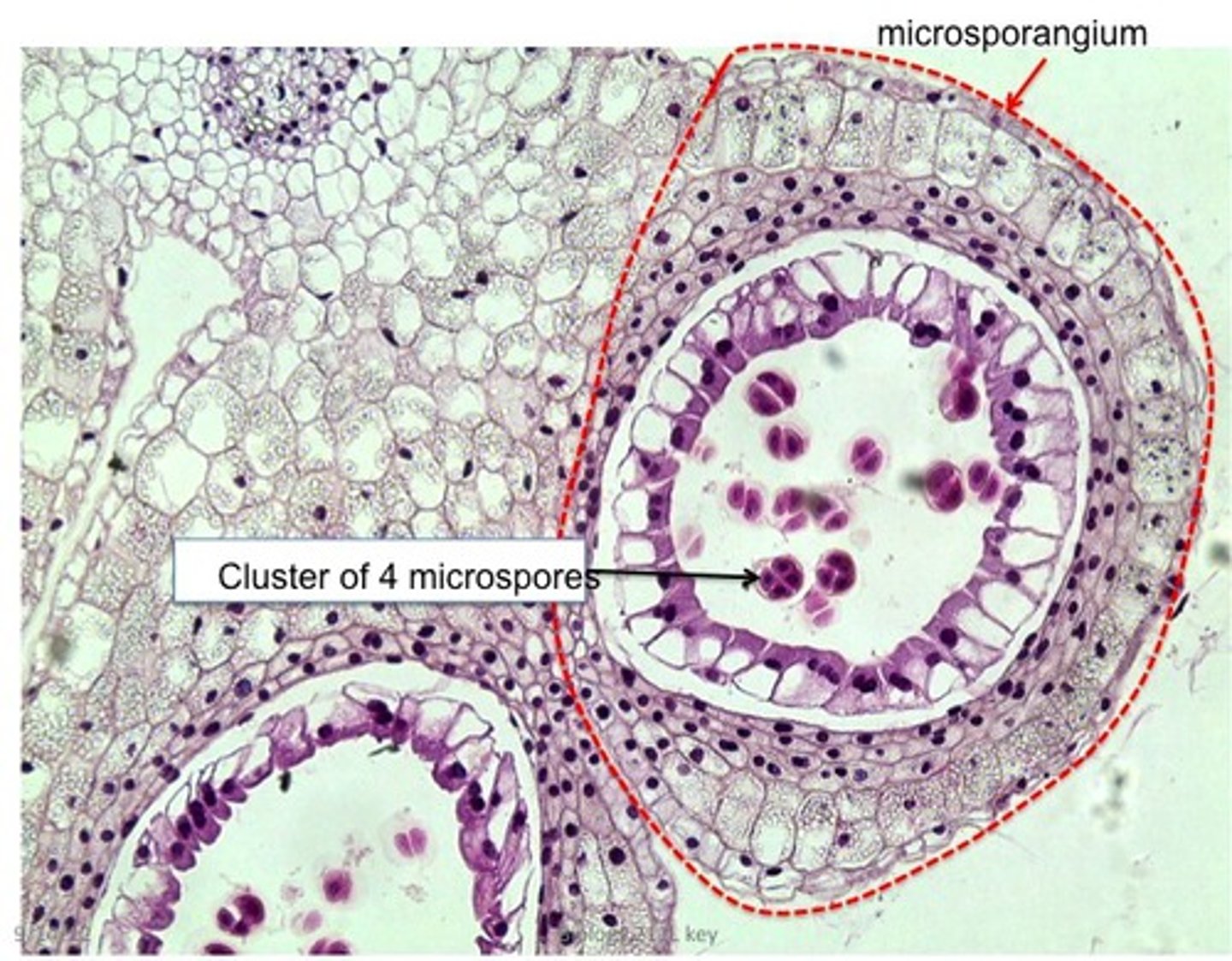
What are megaspores?
female spores that develop into female gametophytes, produce only female gametes
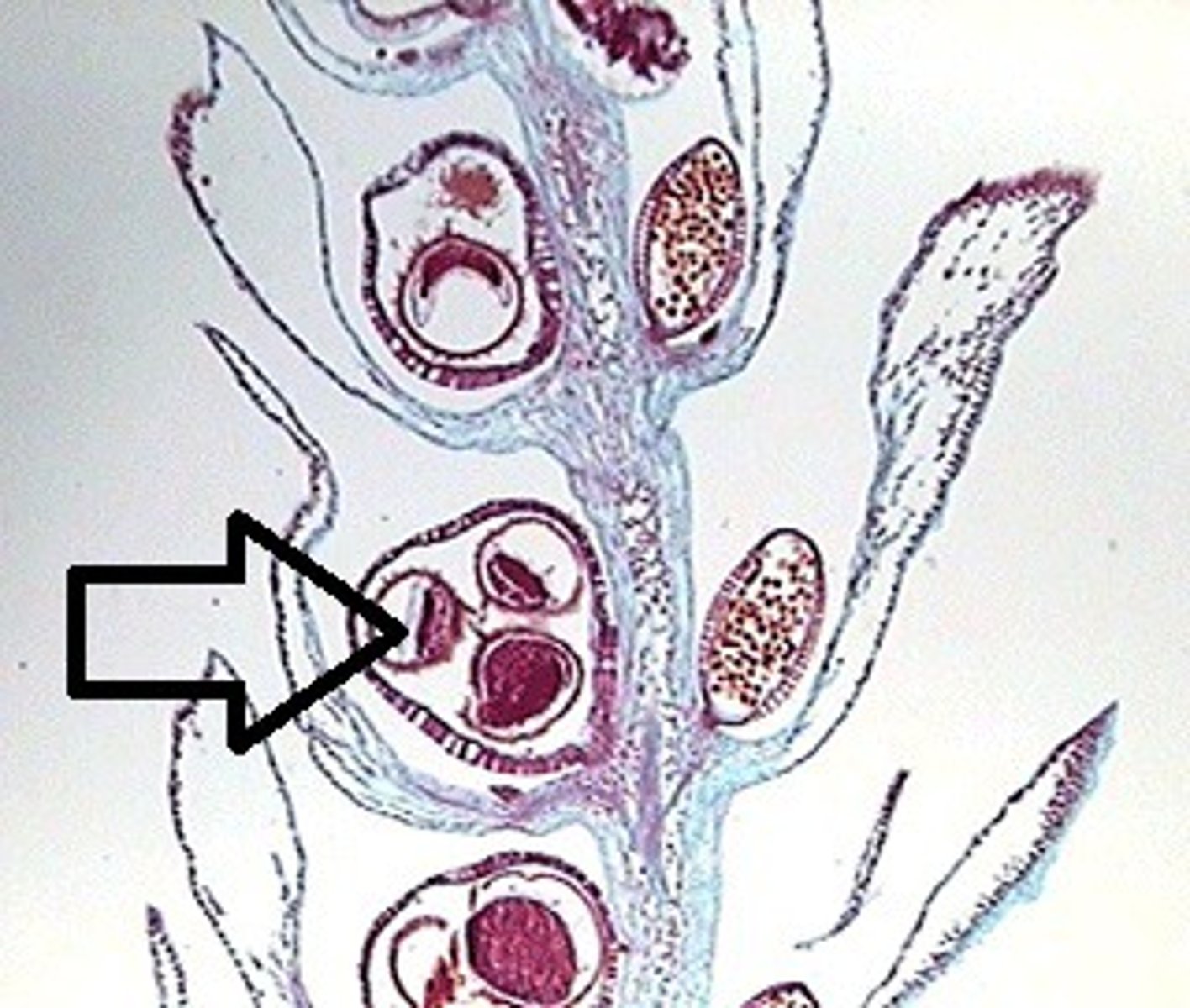
Which plants are heterosporous?
some seedless plants and all seed plants
What is the gametophyte in seedless plants?
the haploid (n) stage that produces gametes through mitosis
What are gametangia?
produced by gametophyte; generates haploid gametes through mitosis
What is an antheridium?
male gametangium that produces sperm, released into water and have flagella to swim
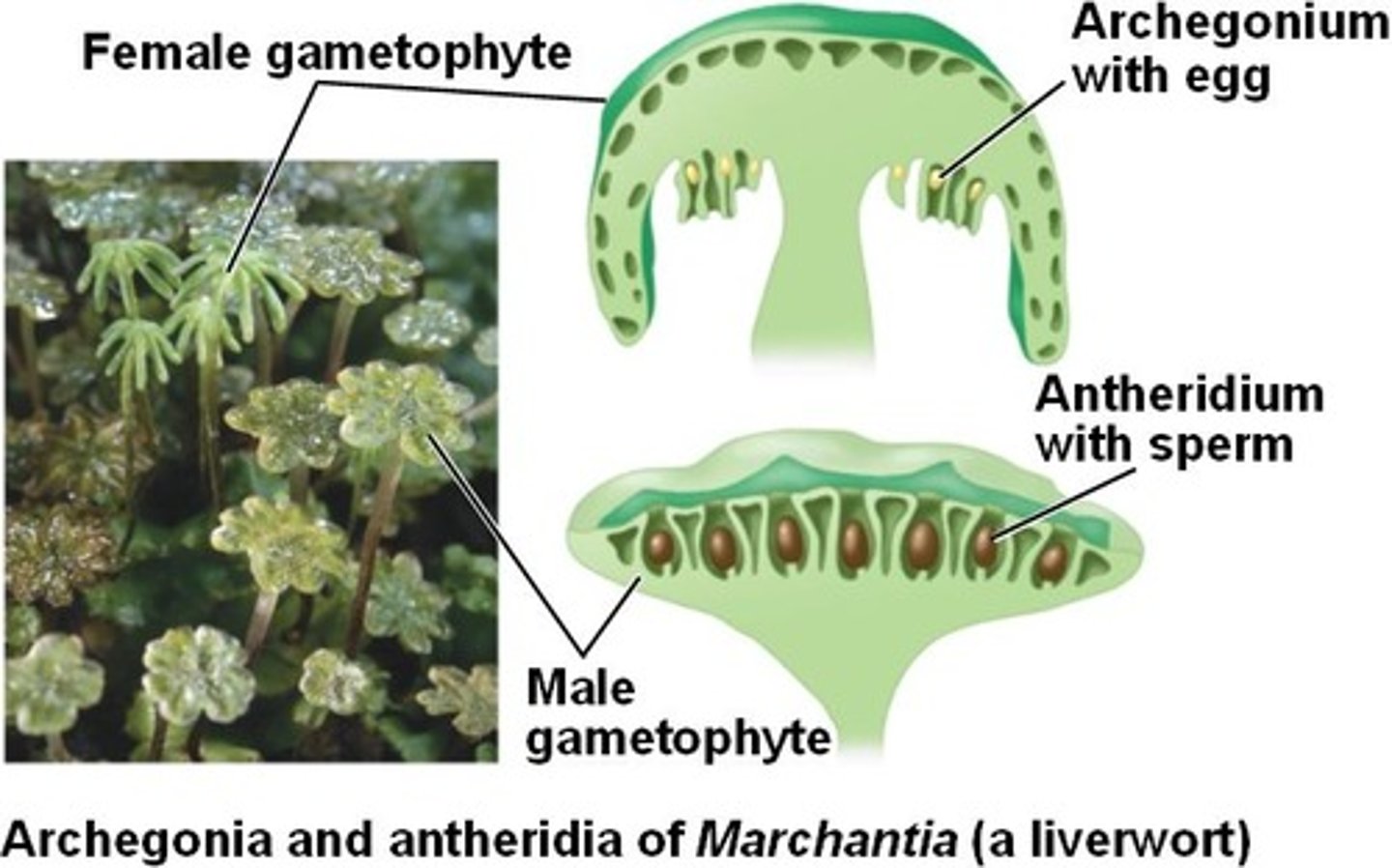
What is an archegonium?
female gametangium that produces eggs
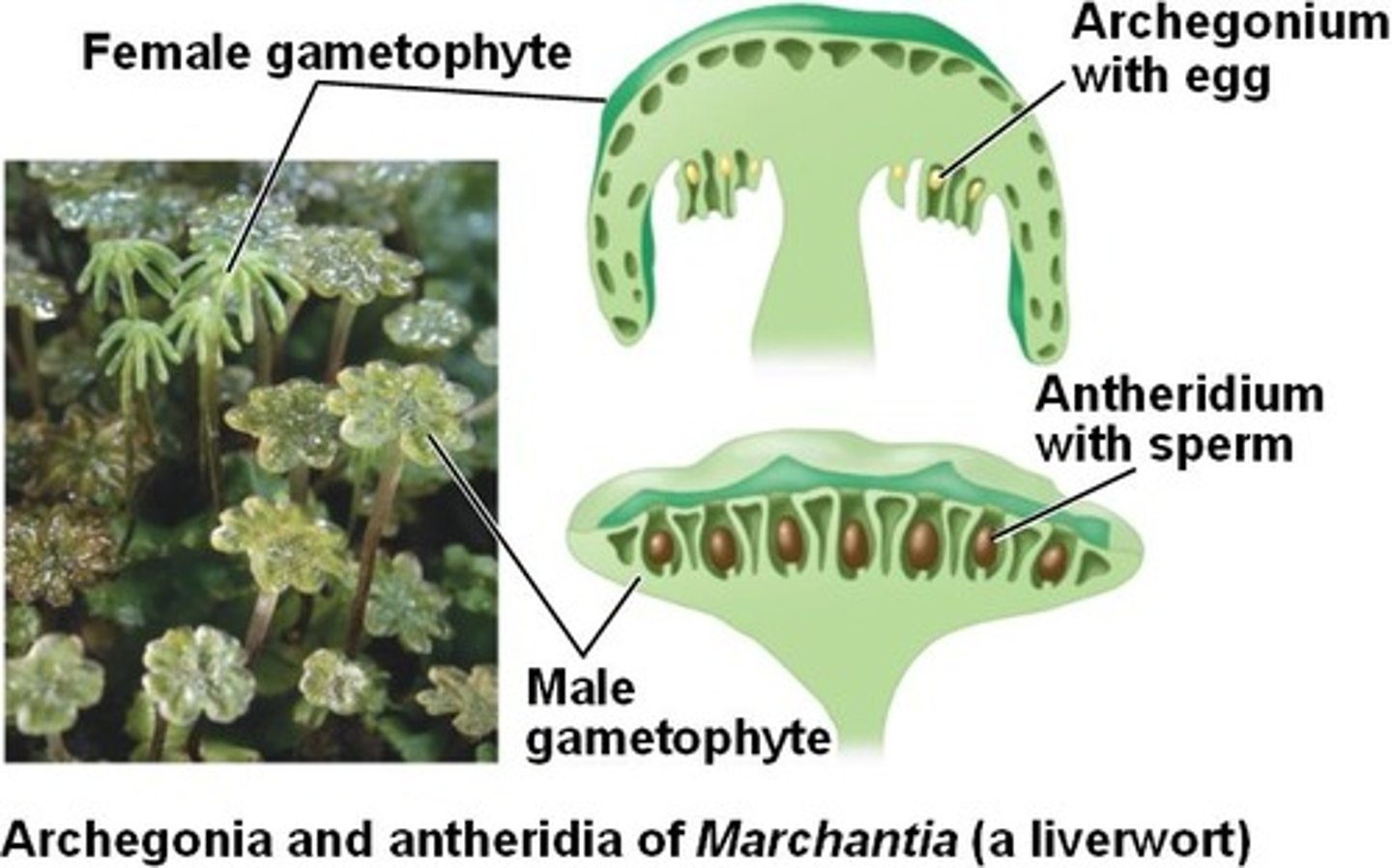
How does fertilization occur in seedless plants?
sperm swim through water from antheridium to archegonium of another gametophyte to fertilize eggs
What occurs after fertilization in seedless plants?
diploid sporophyte develops inside the archegonium
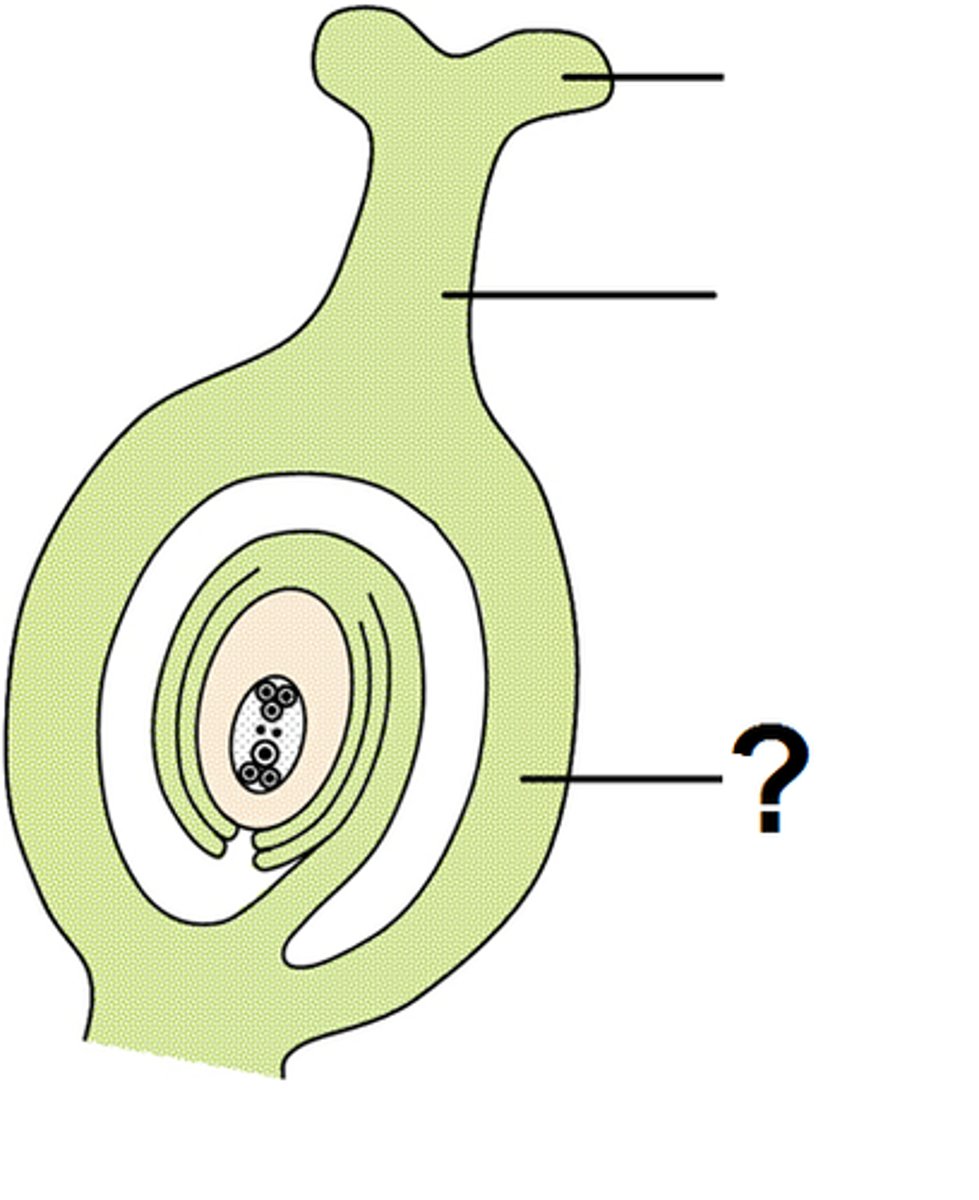
What is a bryophyte?
nonvascular homosporous seedless plant with thallus and rhizoids; no true leaves, stems, or roots; must be small; most similar to earliest terrestrial plants
What are rhizoids?
thread-like structures that anchor nonvascular plants to the ground (mosses and liverworts)
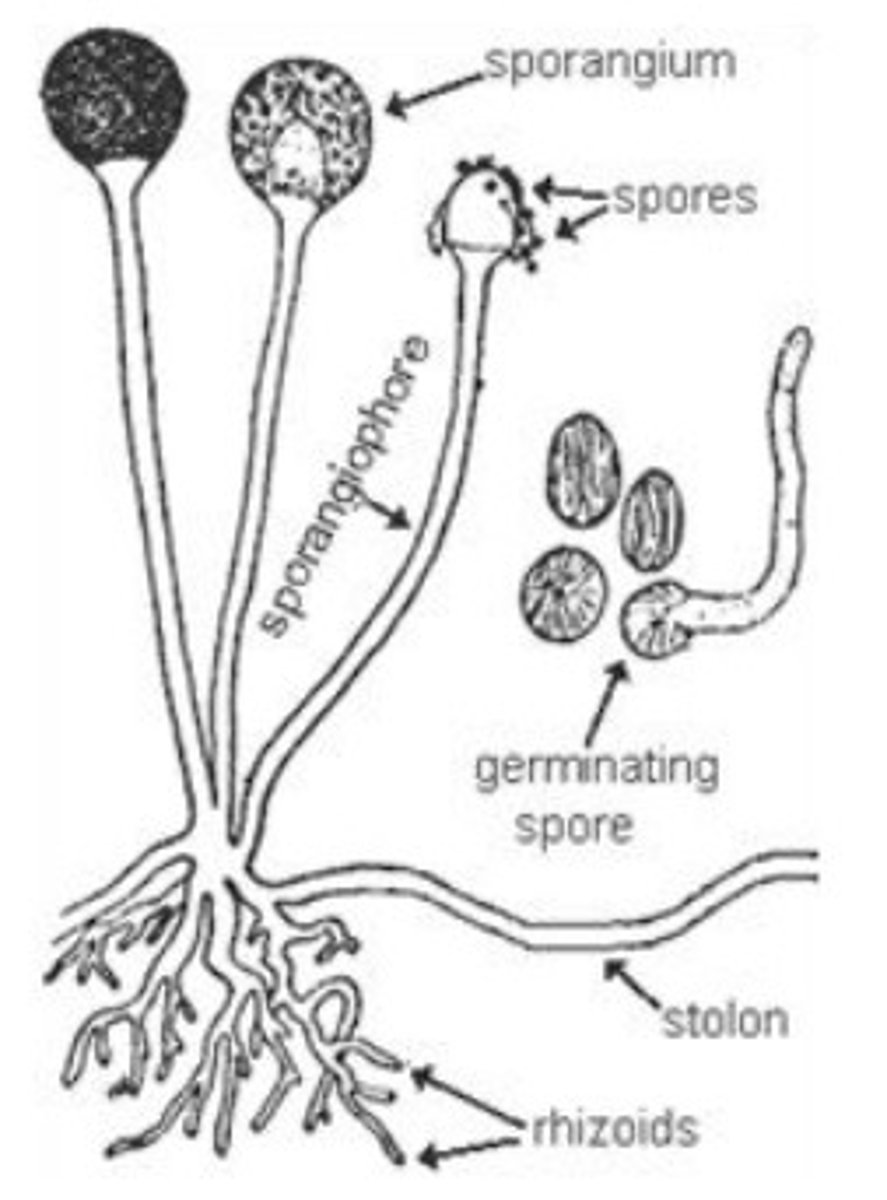
How does a bryophyte reproduce?
spores
Do nonvascular plants/bryophytes have vascular tissue?
No; they lacks conductive tissue to transport water and sugars, so they move via diffusion
Which life stage is dominant in nonvascular plants?
haploid gametophyte (n) stage; diploid sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte
What structures grow from the gametophyte thallus?
gametangia—archegonia (female) and antheridia (male)
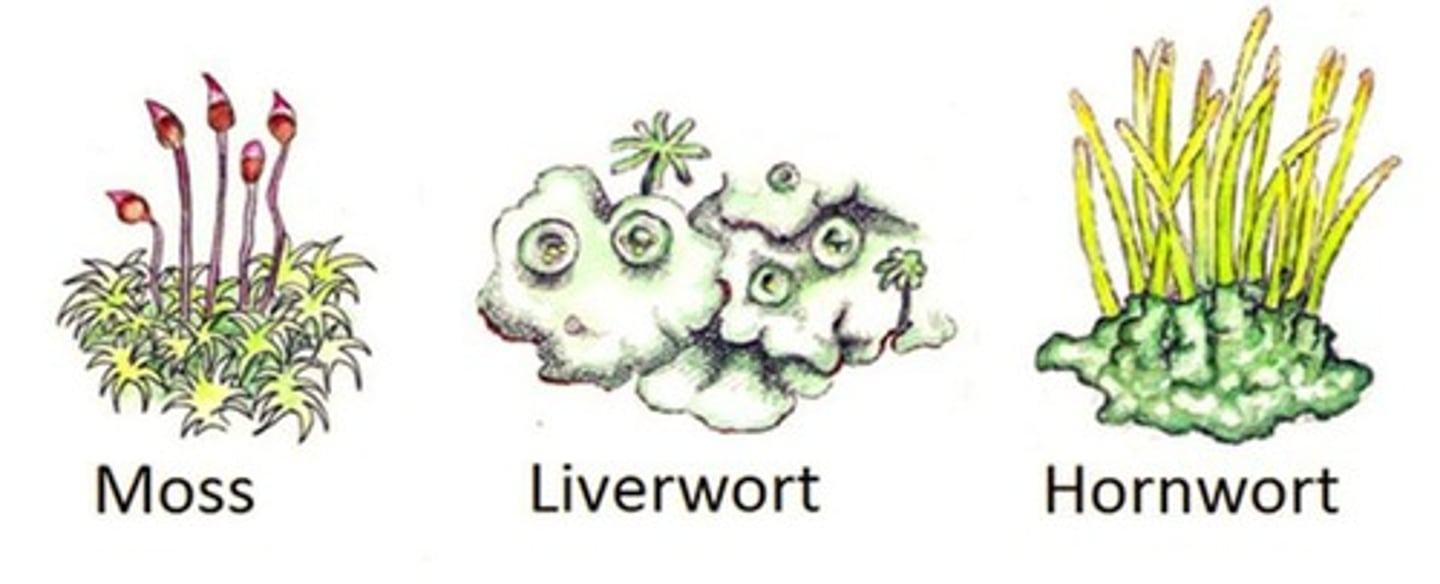
What are the three types of bryophytes?
liverworts, hornworts, mosses
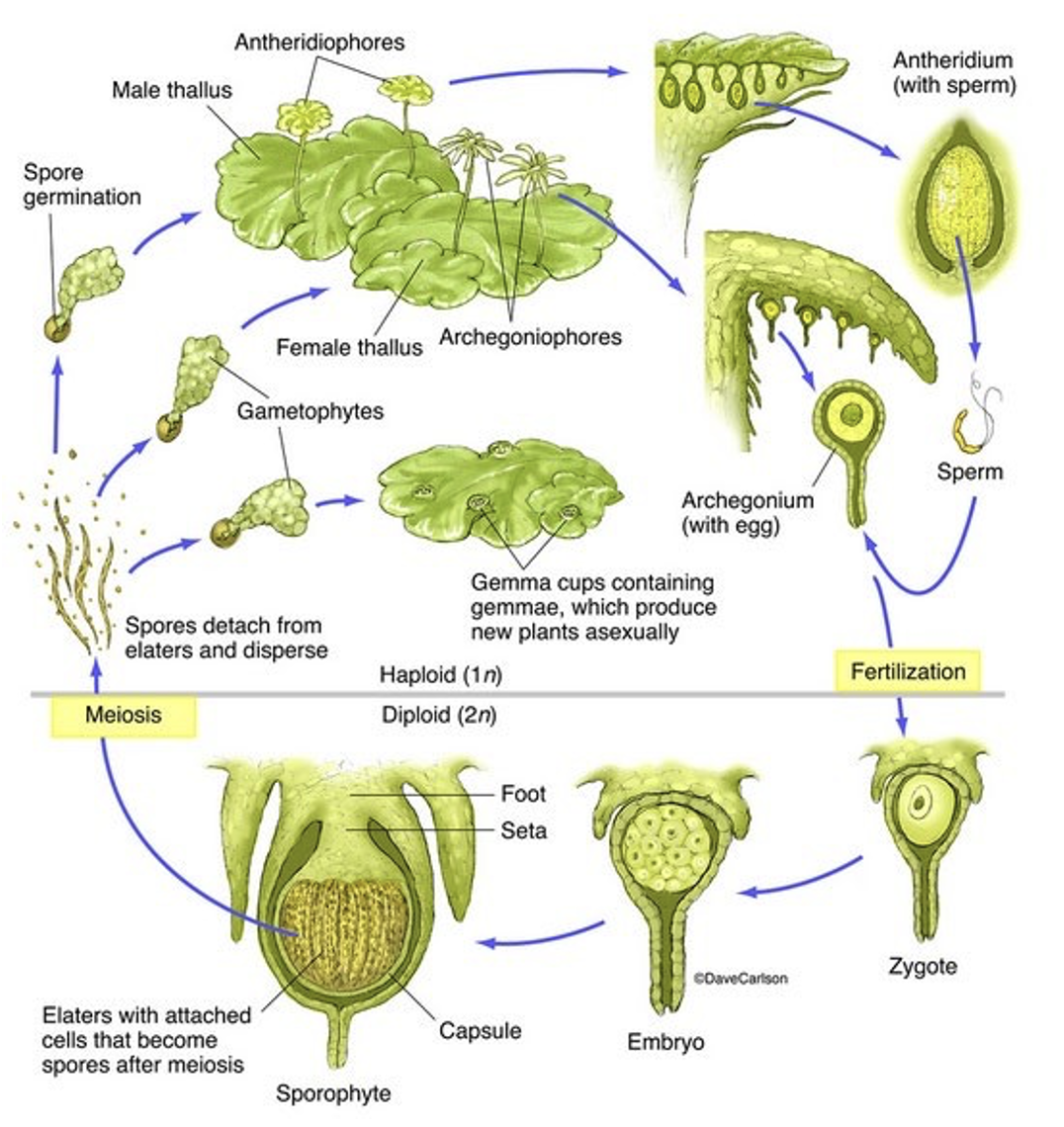
Liverwort life cycle
gametophyte dominant; thalloid or leafy
sporophyte dependent, short-lived
sporangium releases spores
no stomata
Moss life cycle
gametophyte dominant, thallus
sporophyte is horn-life and elongated; grows continuously and lives longest
sporangium releases spores gradually from horn
has stomata
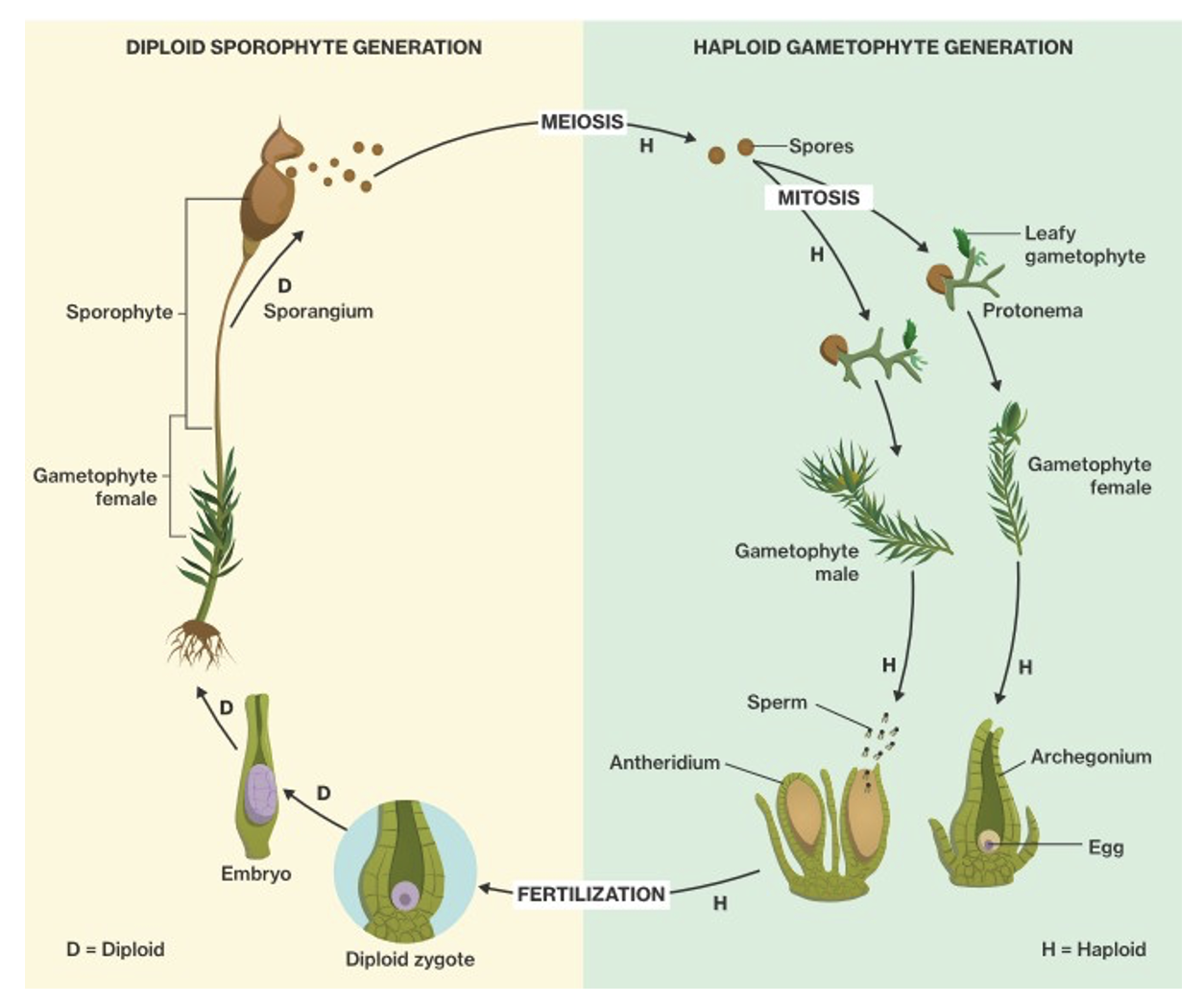
What are vascular seedless plant adaptations?
dominant sporophyte, conductive vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), roots, leaves, sporophylls, lignin in xylem cell walls
Which life stage is dominant in vascular seedless plants?
diploid sporophyte (2n) stage
How is the sporophyte in vascular seedless plants different?
sporophyte is independent of gametophyte, while gametophyte is dependent on the sporophyte
What vascular tissues do vascular seedless plants have?
xylem and phloem
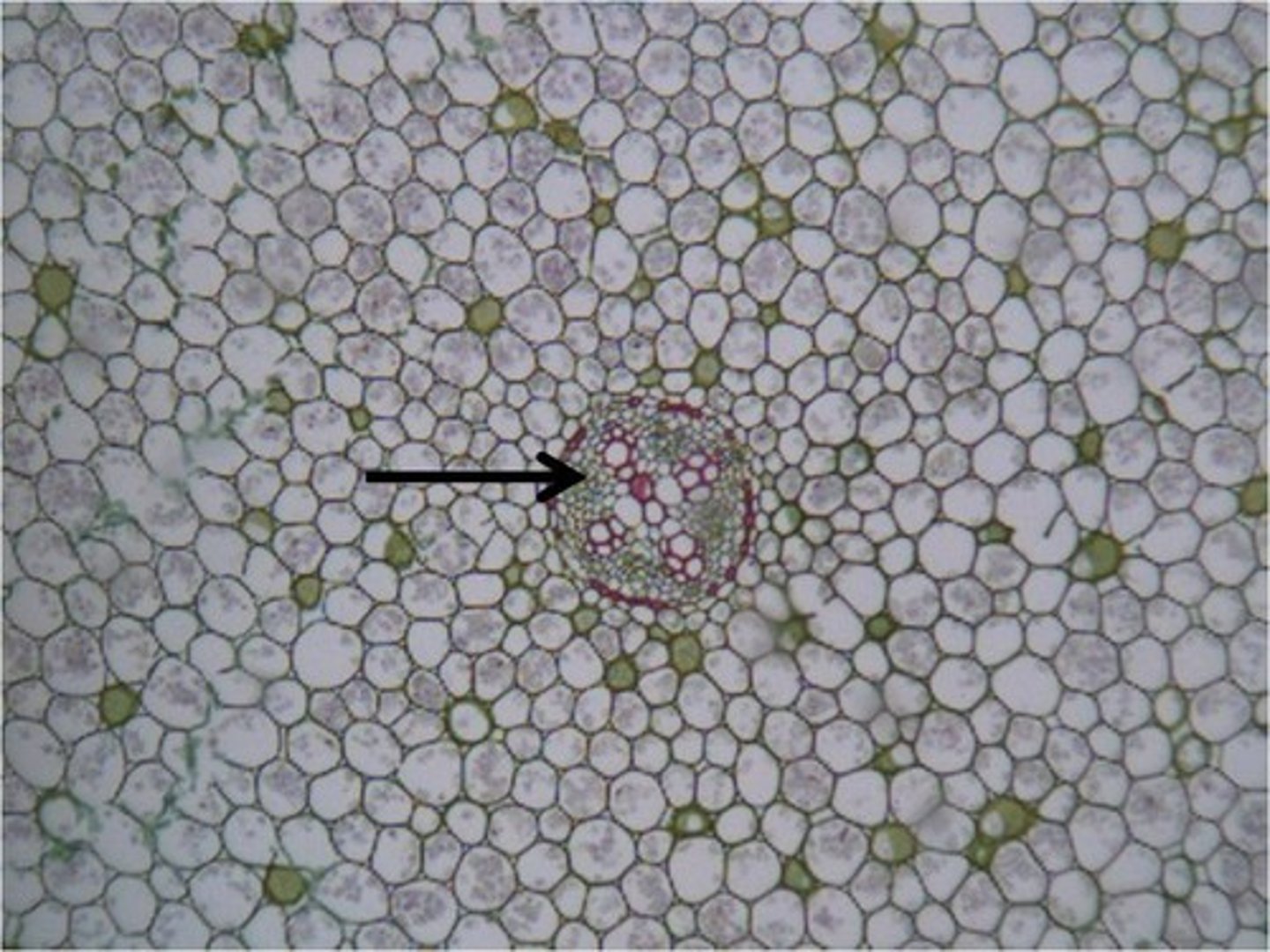
What is a xylem?
tissue that transports water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
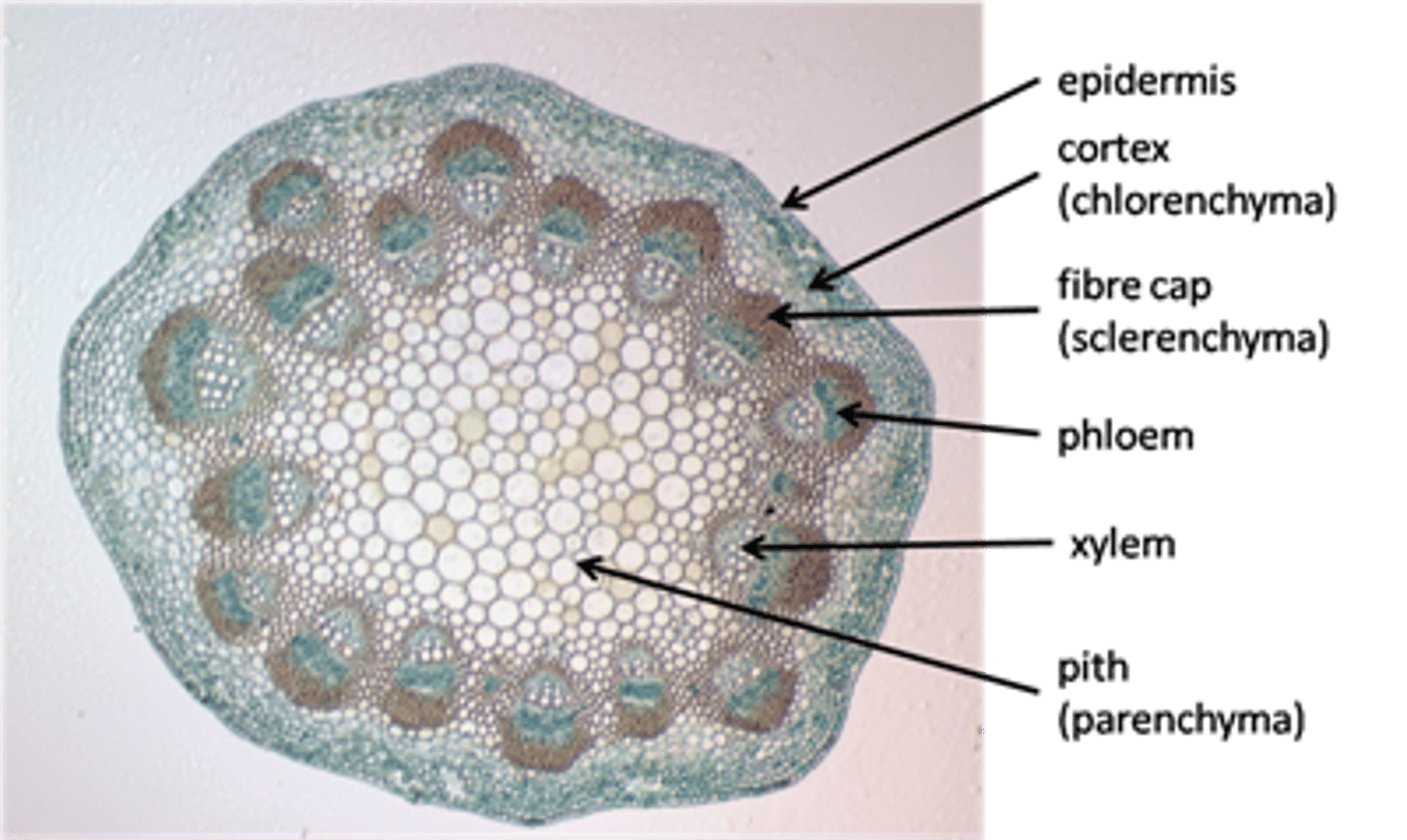
What is a phloem?
tissue that transports dissolved products of photosynthesis in various directions around the plant
What is the role of lignin in vascular plants?
provides strength and structural support in vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) for plants to grow tall
How are roots in vascular plants different from rhizoids in nonvascular plants?
roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from soil
rhizoids help with anchoring only
What is the function of leaves in vascular seedless plants?
increase surface area for greater photosynthetic efficiency
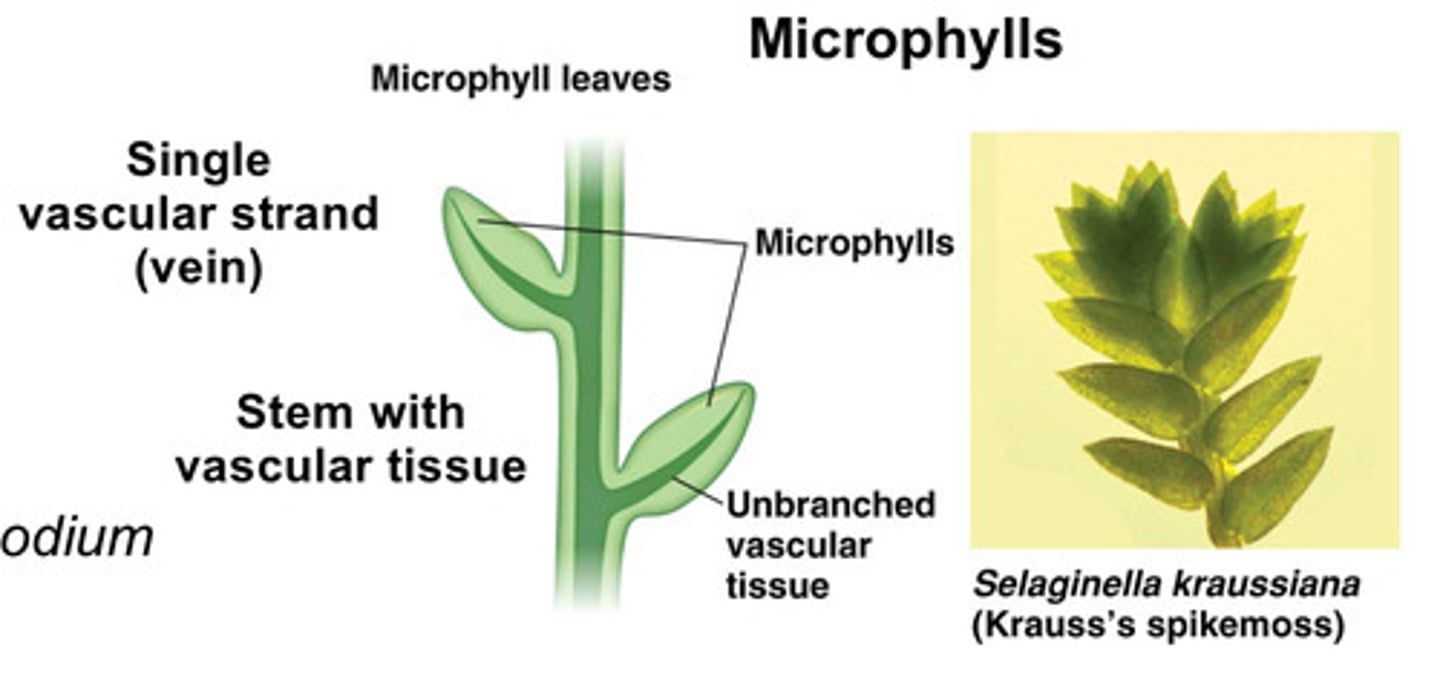
What are microphylls?
small, spine-shaped leaves with single unbranched vascular vein
What are megaphylls?
Larger leaves with branched vascular network
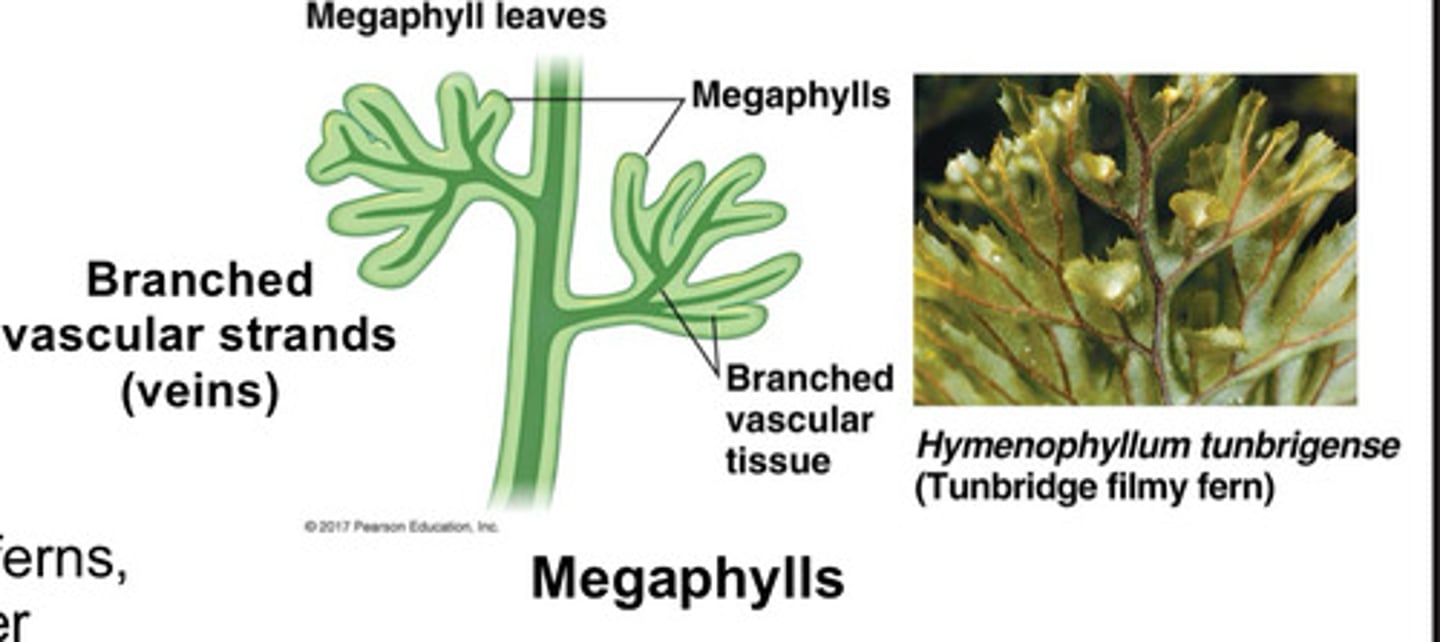
What are sporophylls?
modified leaves that bear sporangia for spore production; sori and strobili
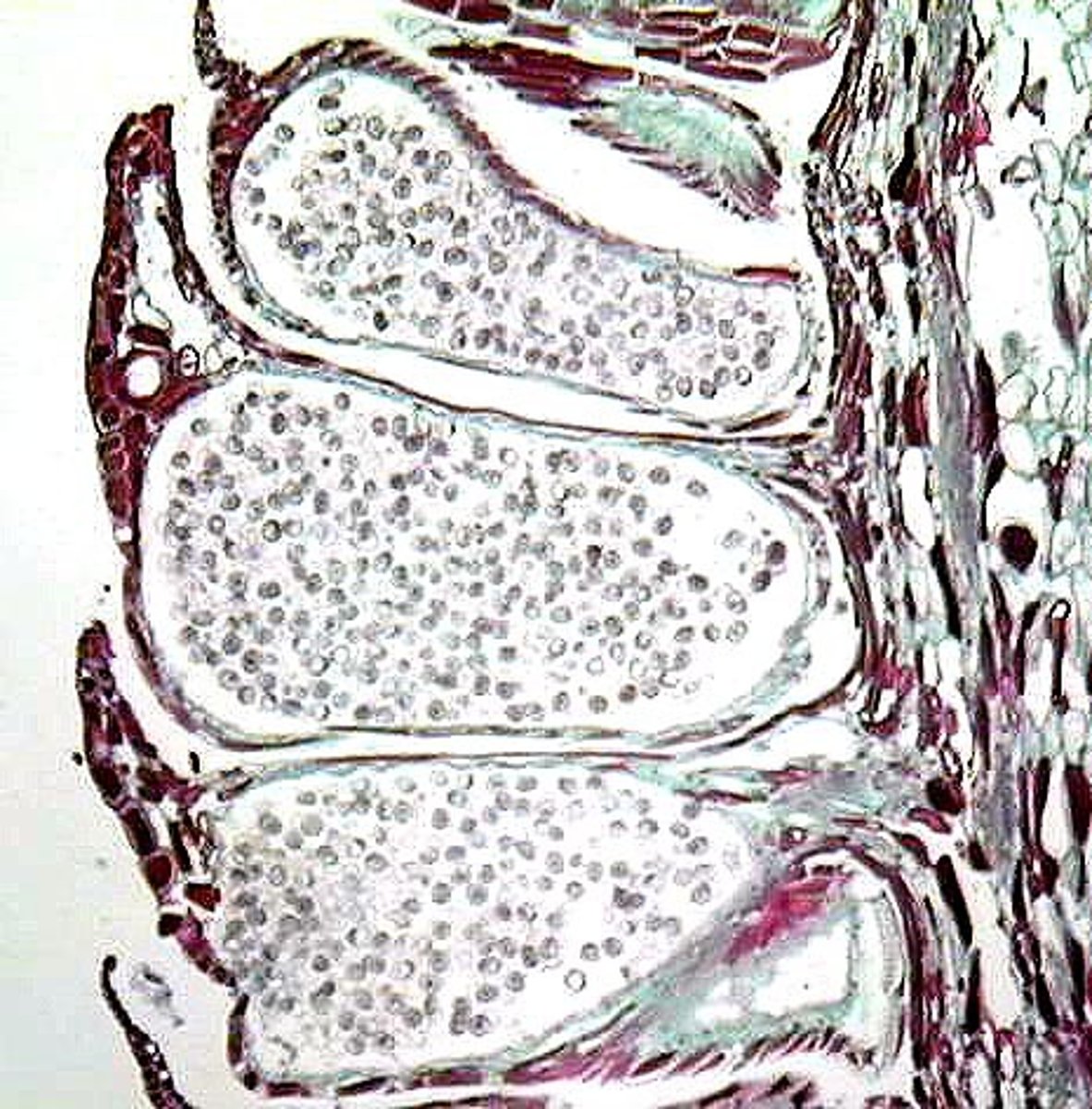
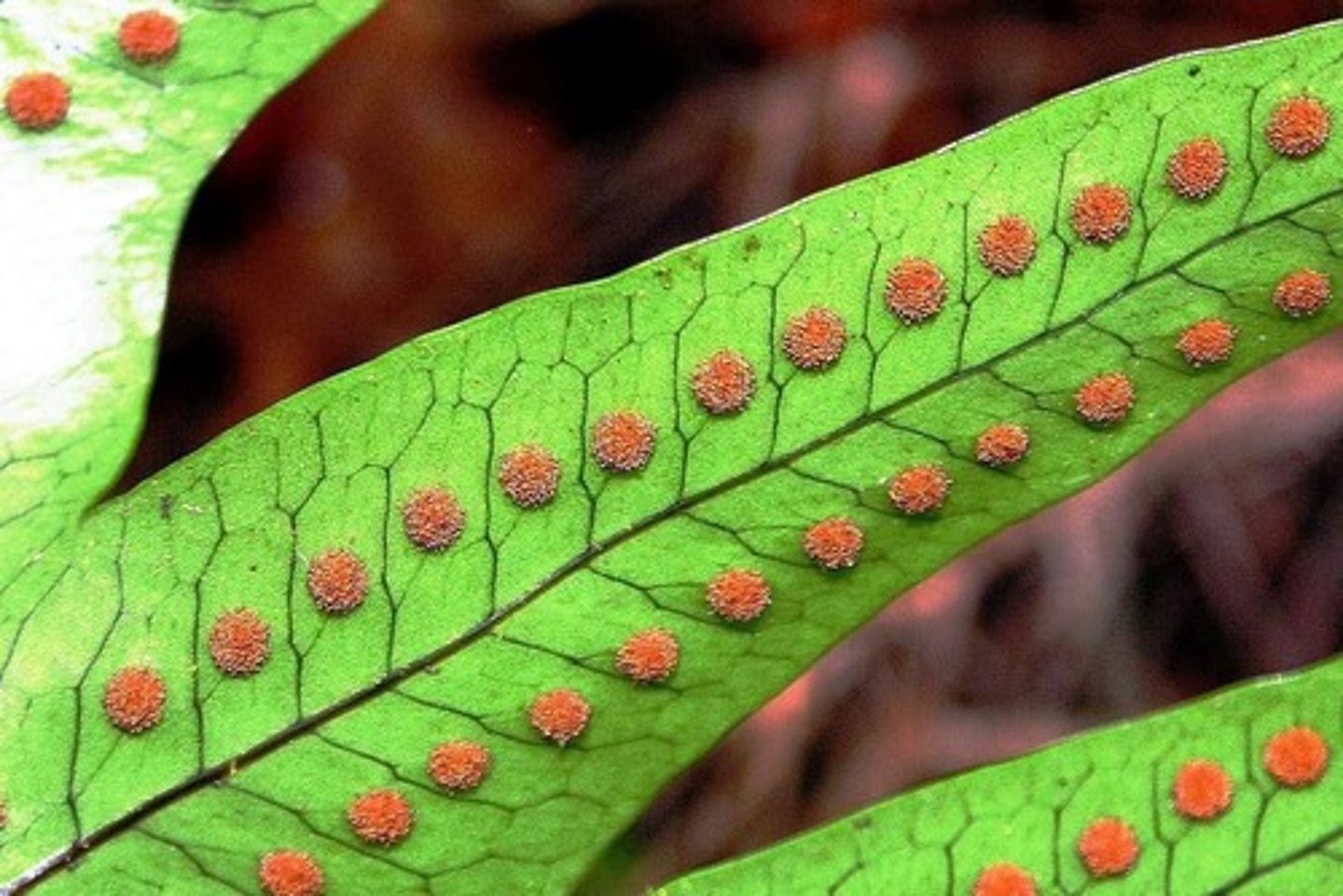
What are sori?
clusters of sporangia on underside of fern sporophyll

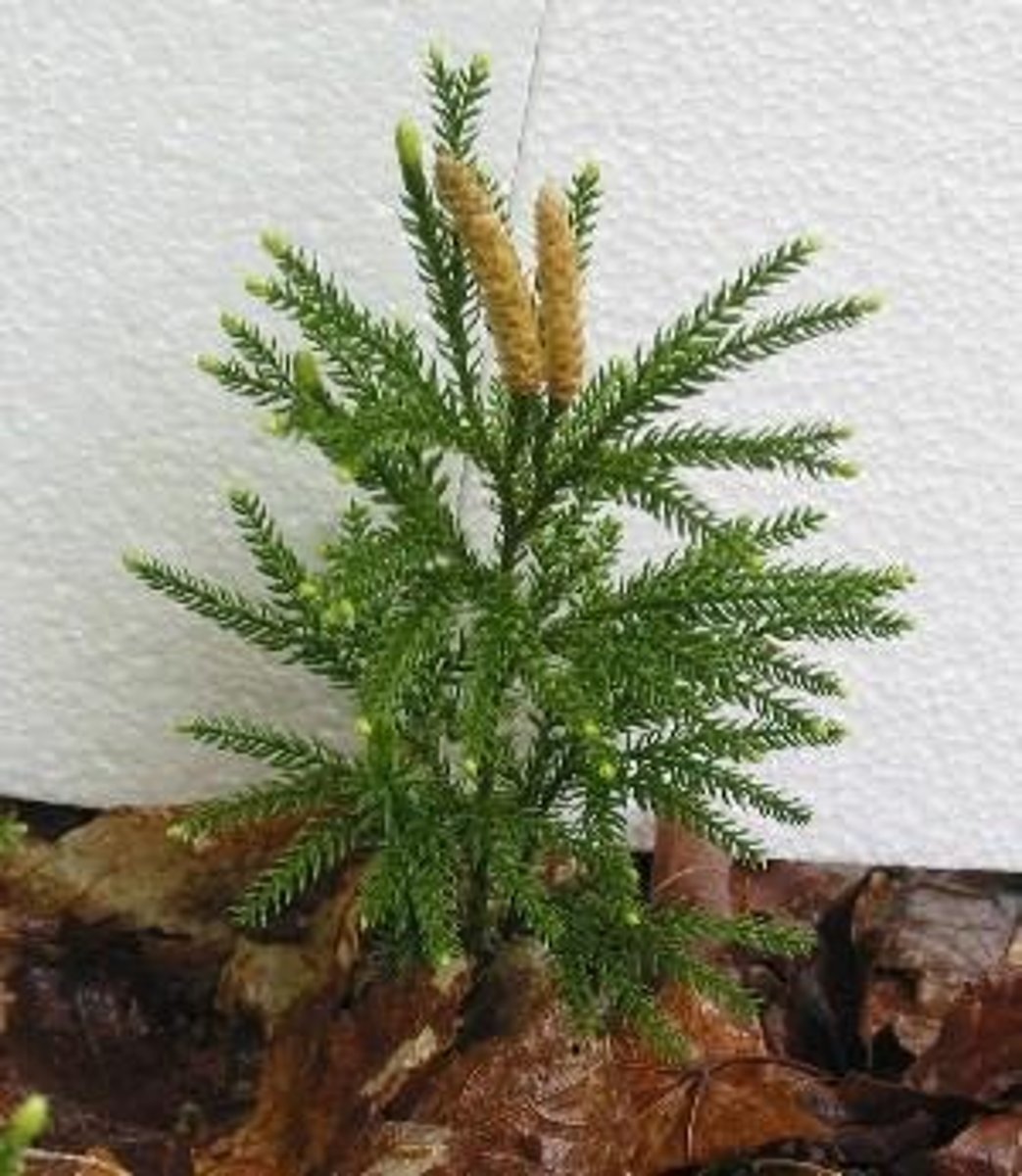
What are strobili?
cone-like structures formed from sporophylls, found in some vascular plants

What is the role of lignin in xylem cell walls?
impermeable to water, giving strength to vascular tissue
What are examples of vascular seedless plants?
lycophyta (moss) and monilophytes (fern)
What is lycopodiophyta?
club mosses, spikemosses, quillworts
What are monilophytes?
ferns, horsetails, whisk ferns
How does the sporophyte develop in vascular seedless plants?
zygote grows into a sporophyte, which is independent and dominant