Polymers and giant covalent structures
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a polymer?
Long chains of repeating units
What’s bonds do polymers have?
Covalent bonds
How do you draw a repeating unit?
The repeating unit drawn in brackets
subscript value of n for how many times its repeated
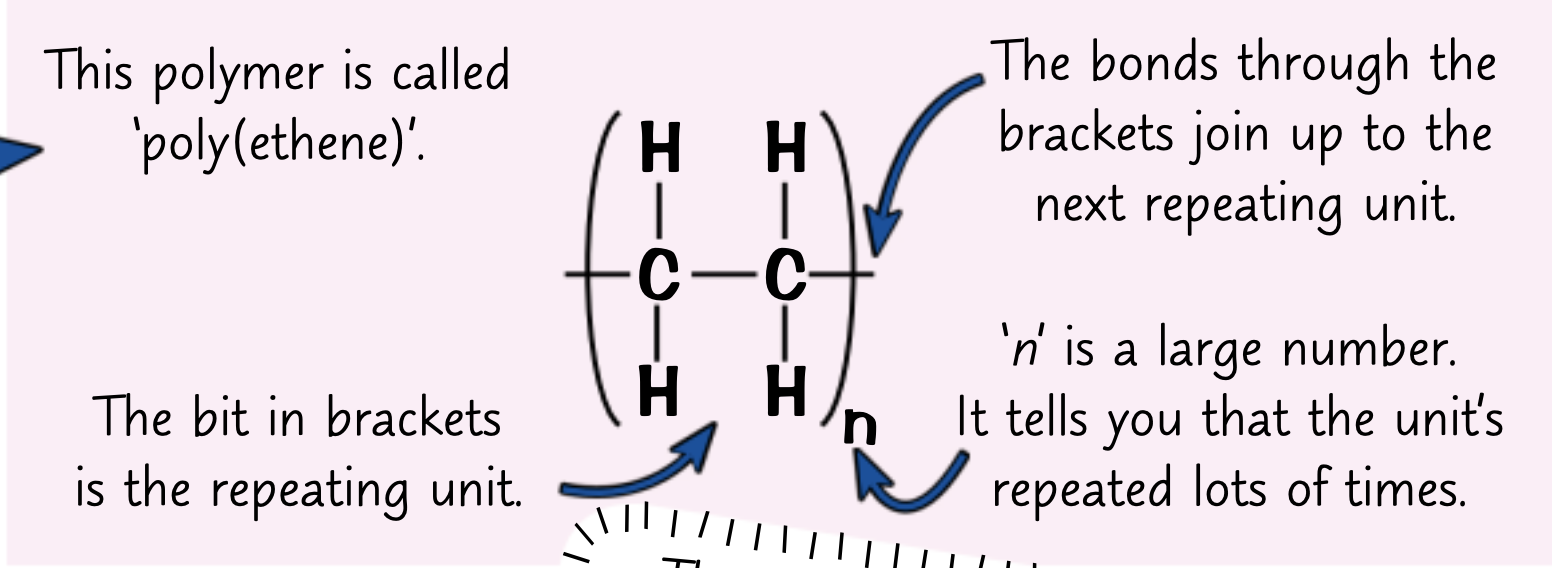
How do you get the molecular formula from a repeating unit of a polymer?
Write down the molecular formula of the repeating unit in brackets and put an n on the outside (C2H4)n
Why are most polymers a solid at room temperature?
The intermolecular forces between the polymer molecules are larger than between simple covalent molecules, so more energy is needed to break them
Why are the boiling points of polymers lower than ionic or giant molecular compounds?
The intermolecular forces are still weaker than ionic or covalent bonds.
What are giant covalent structures called?
Macromolecules
How are molecules bonded I giant covalent structures?
all the atoms are bonded together by strong covalent bonds
Do giant covalent structures have a low or high boiling or melting point and why?
Very high because a lot of energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds
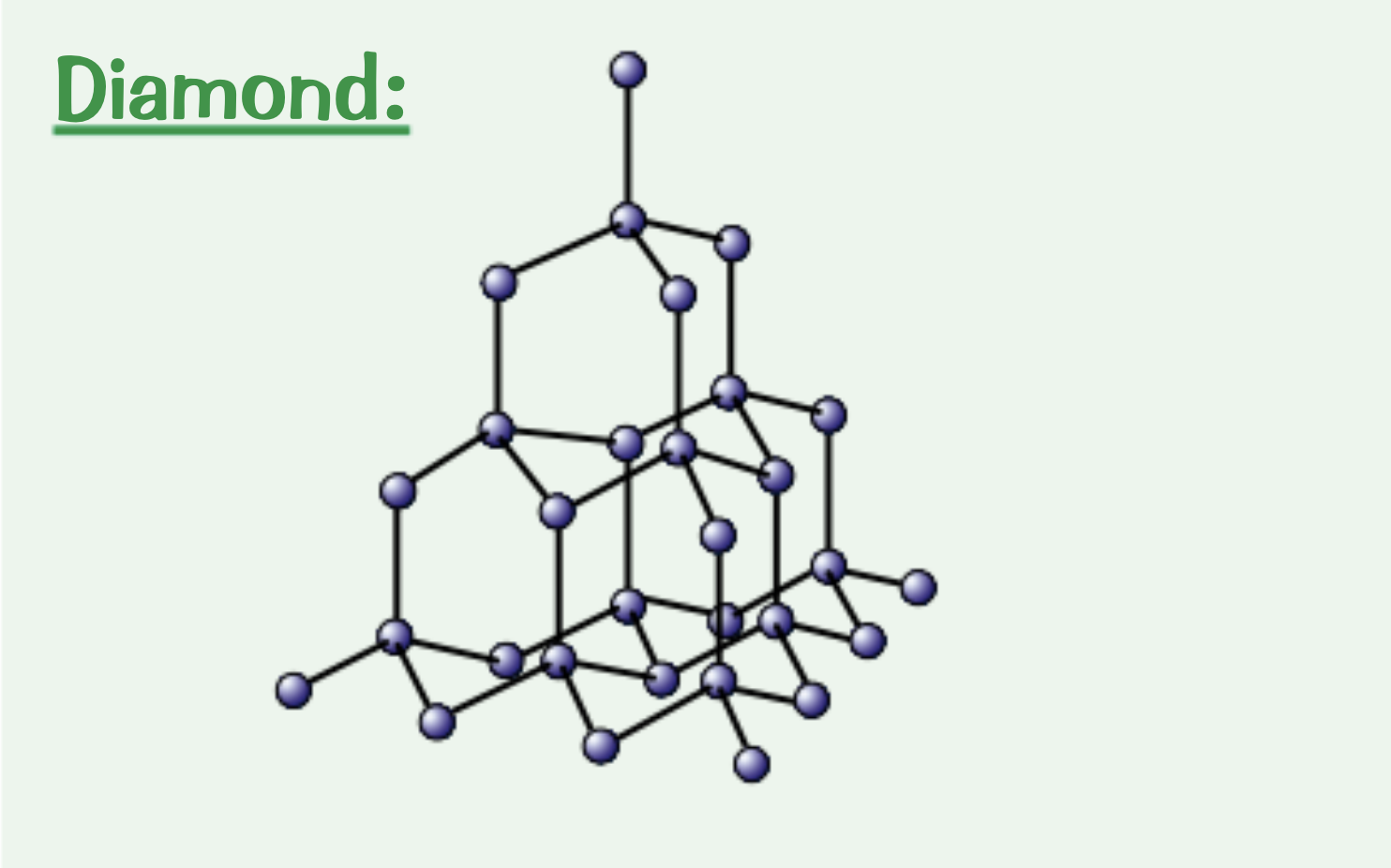
Explain the structure of diamond.
Each carbon atoms forms four covalent bonds in a very rigid giant covalent structure
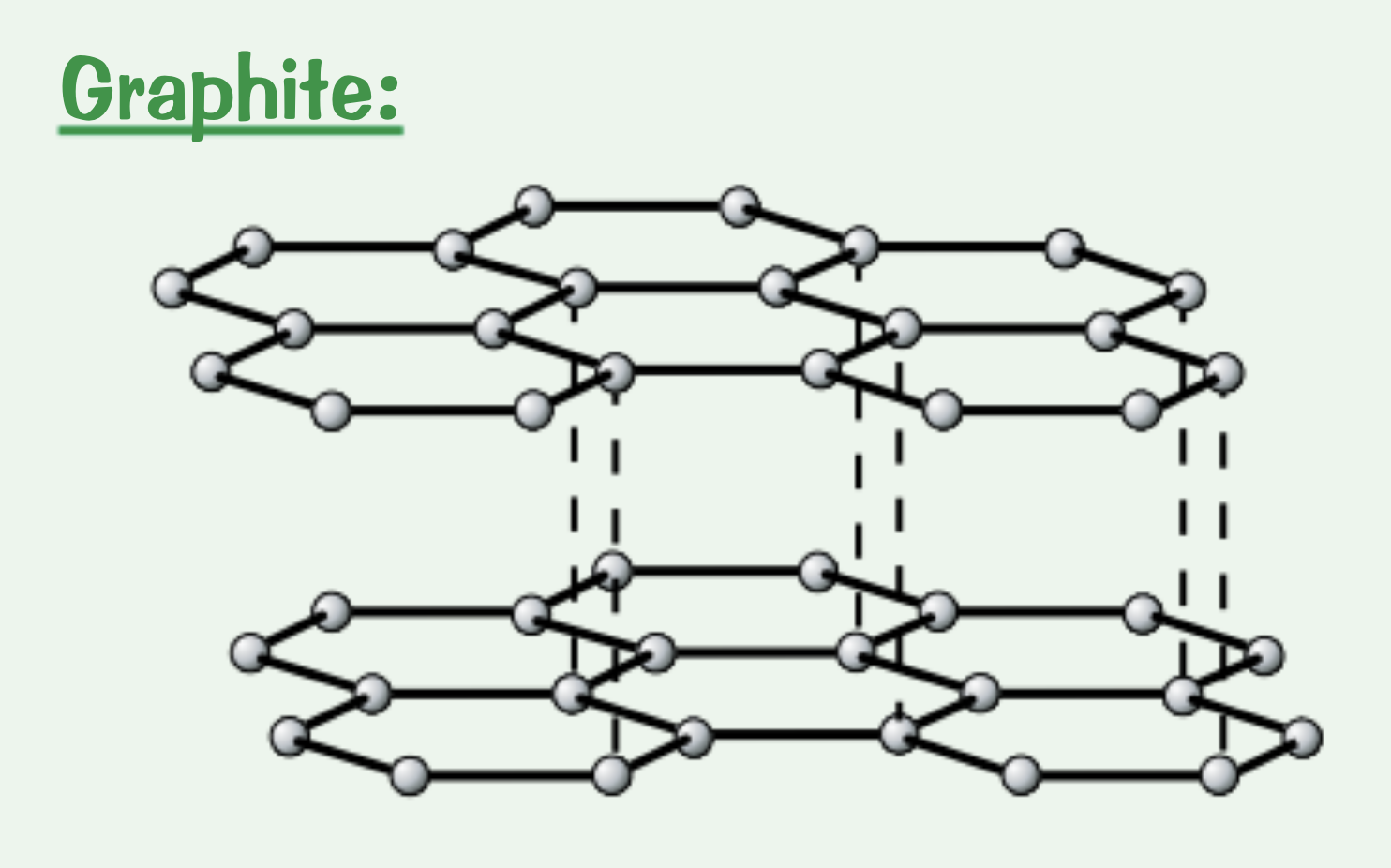
Explain the structure of graphite.
Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds to create layers of hexagons. Each carbon atom also has one delocalised electron
What is sand made of?
Silicon dioxide
Each grain of sand is one giant structure of silicon and oxygen