Sensory Receptive Fields, Somatosensory & Auditory Pathways, and Pain Processing in Neuroscience
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a receptive field in sensory neurons?
The part of the environment (stimulus type) that a receptor responds to.
What type of stimulus does a somatosensory receptive field respond to?
Touch stimuli, such as feeling on the skin.
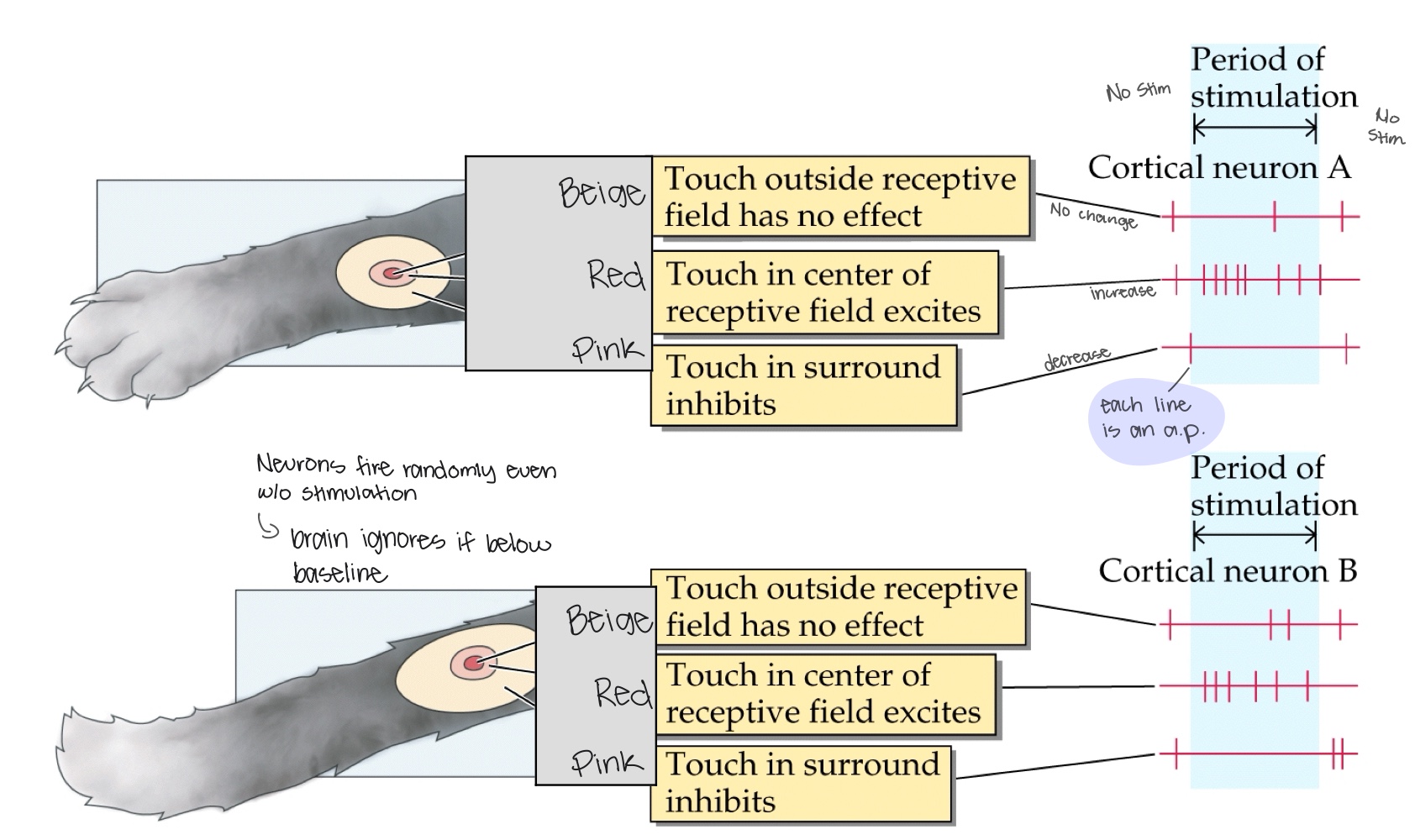
What is the role of the excitatory center and inhibitory surround in receptive fields?
The center will cause an increase in action potentials while the surrounding area will decrease (can be the reverse)
What are the two pathways that carry sensory information from the skin to the brain?
1. Dorsal column system - carries touch information. 2. Anterolateral system - carries pain and temperature information.
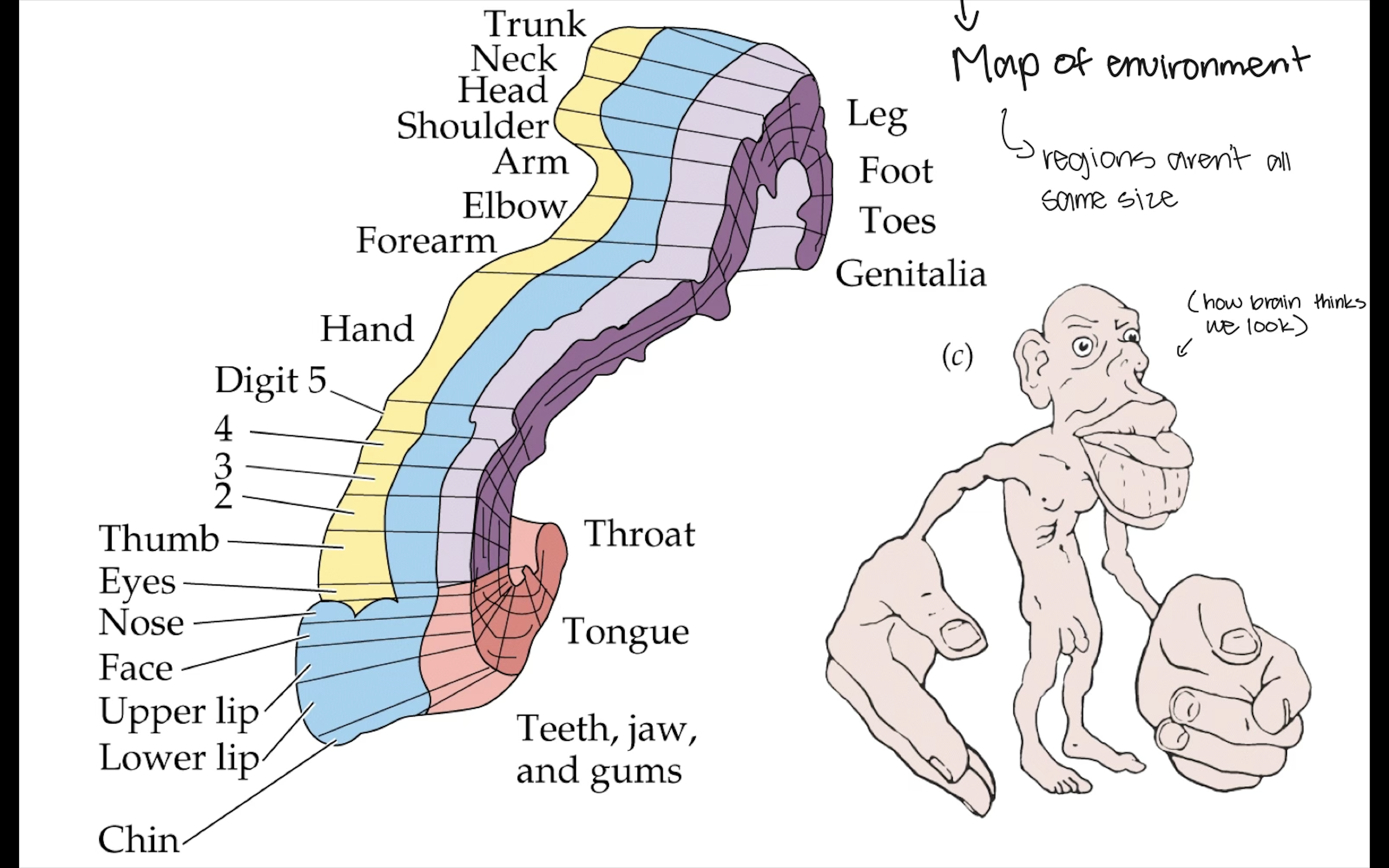
How are brain cells arranged according to the body plan?
They are arranged in a map of the environment, with regions not all being the same size.
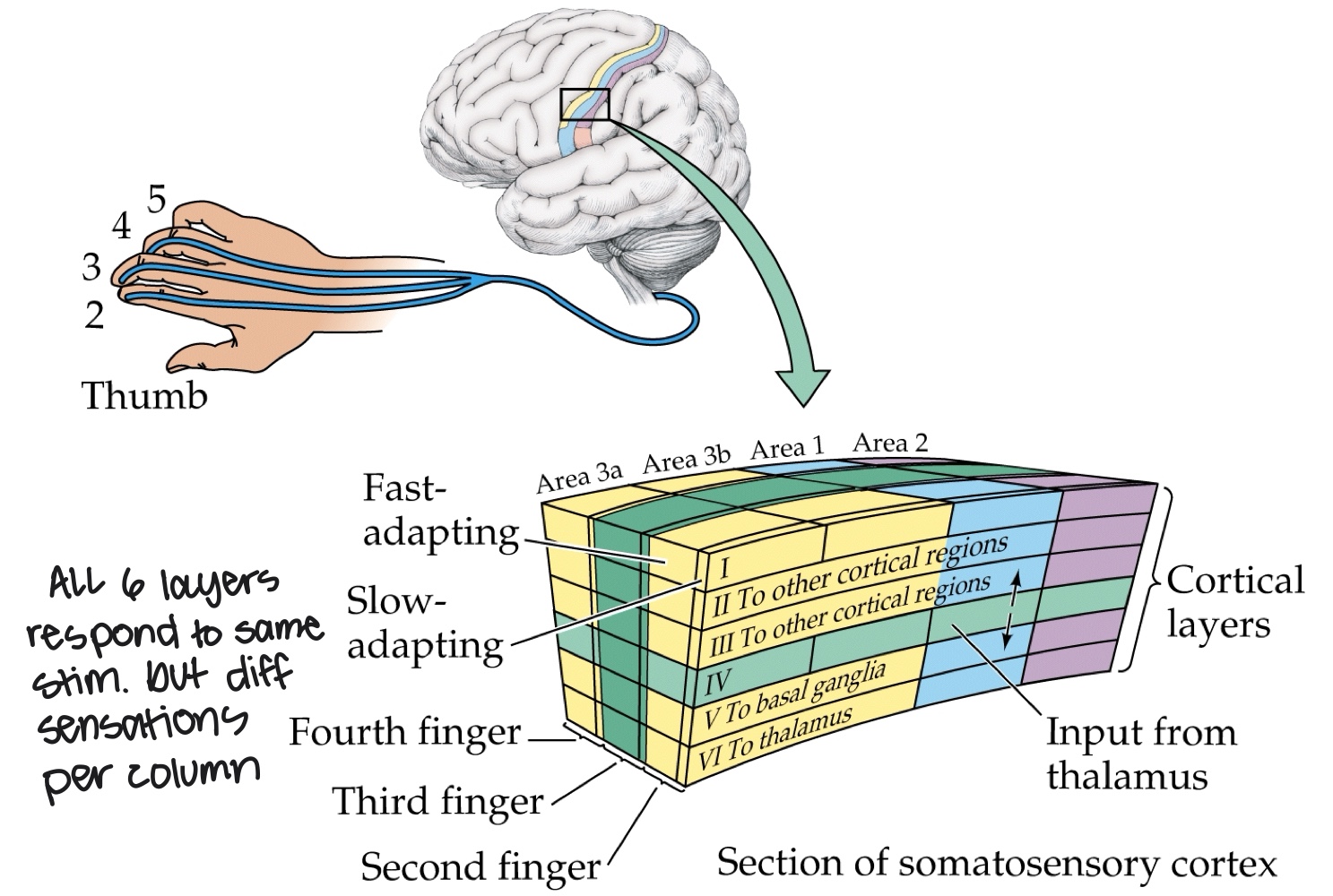
What are cortical columns?
Each cortical cell has a precise receptive field and only responds to one sensation.
What is the function of pain in the body?
Pain indicates tissue damage and serves an adaptive purpose
What are the characteristics of A-delta fibers?
They have a large diameter, are myelinated, and have a high threshold that can only transmit intense pain.
What are C fibers and their role in pain perception?
C fibers are thin, unmyelinated fibers that transmit longer-lasting, dull ache pain.
What is neuropathic pain?
Pain due to inappropriate signaling of pain by neurons, often associated with nerve damage rather than tissue damage.
What is phantom limb pain?
The continued perception of pain in a limb that is no longer present.
What is the role of the cingulate cortex in pain?
It integrates pain infor
What is the function of the external ear?
To capture, focus, and filter sound through the pinna and ear canal
What are the major parts of the middle ear?
It concentrates sound through the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes).
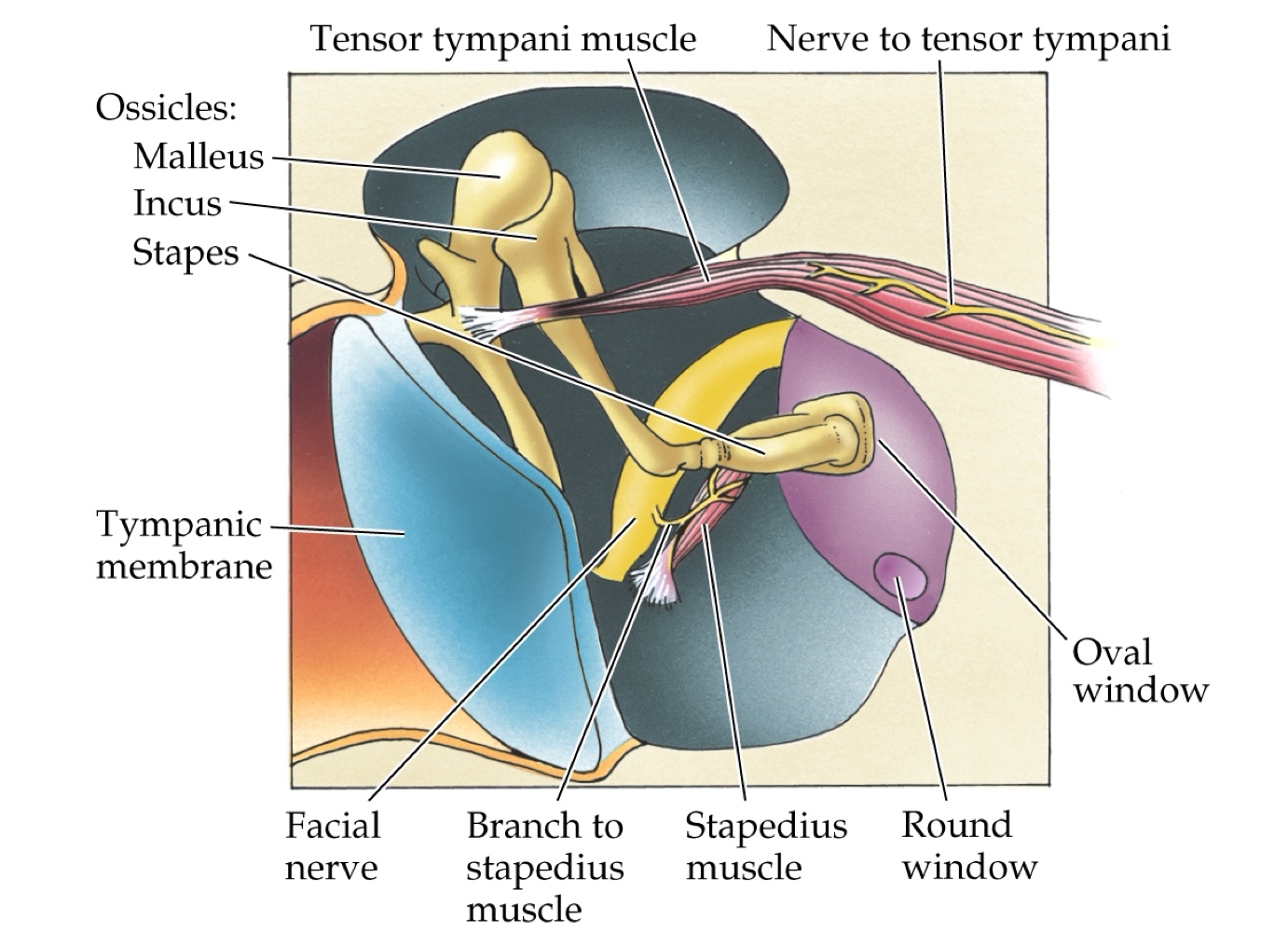
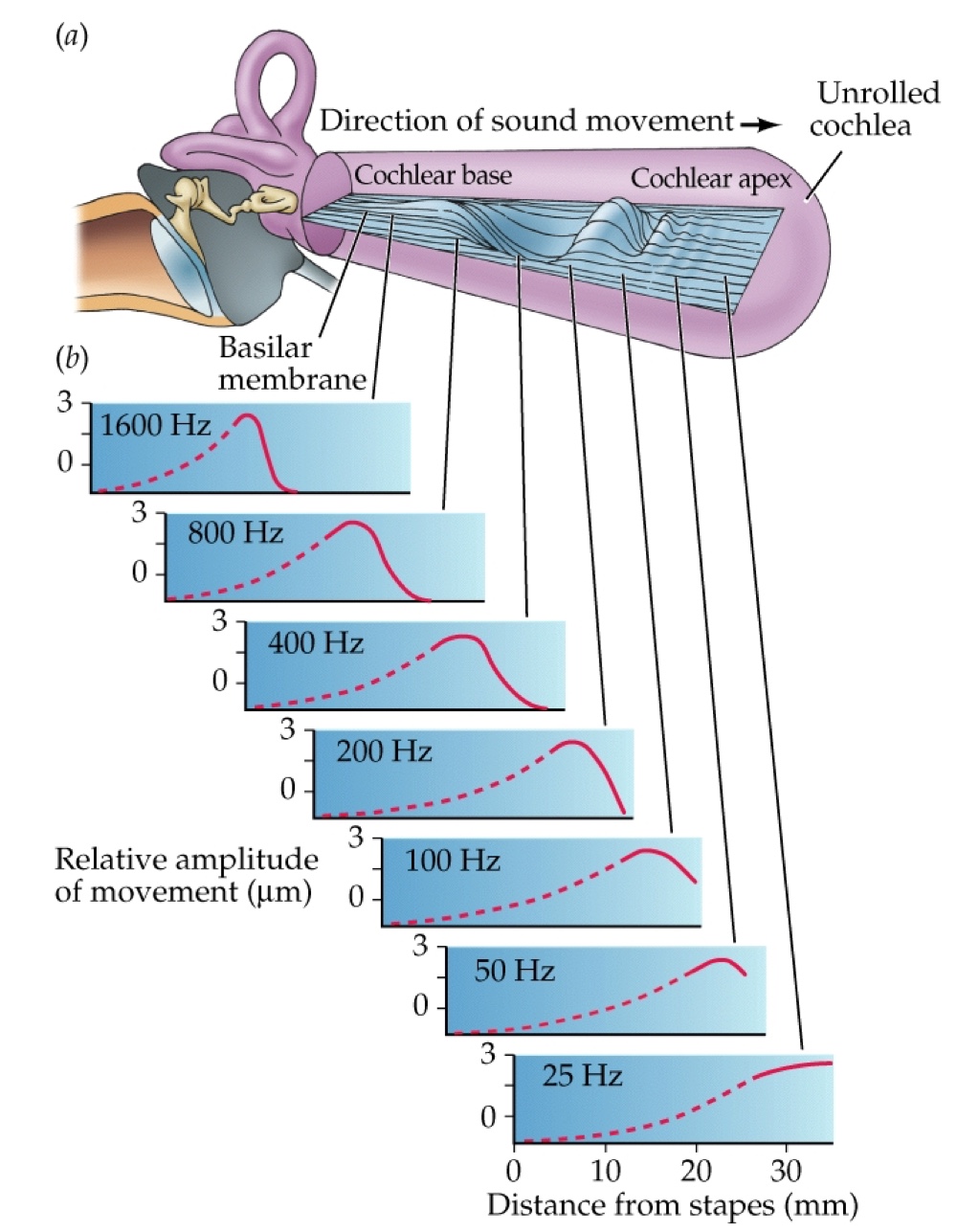
What is the role of the cochlea in the inner ear?
It is the auditory portion that contains fluid-filled canals and transduces sound.
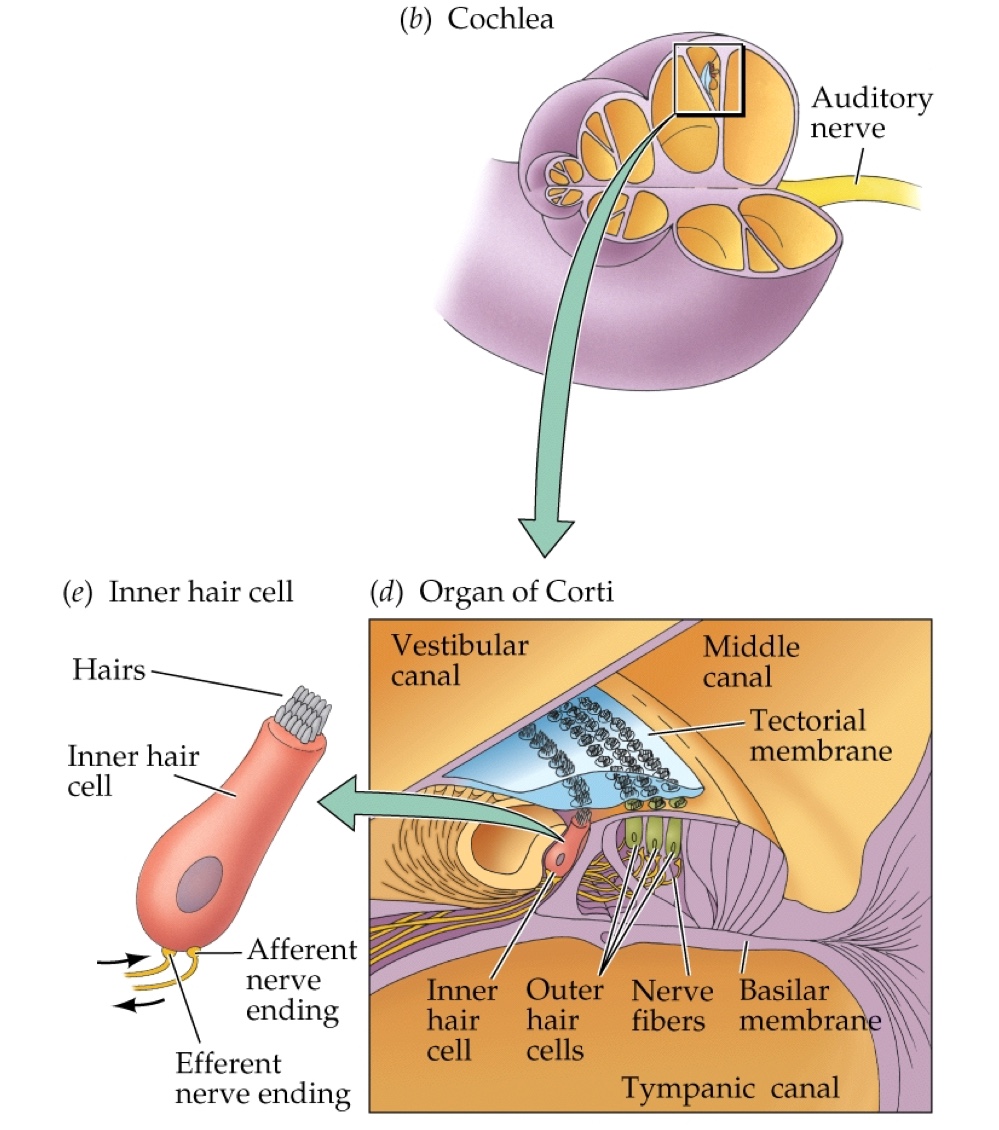
What is the organ of Corti?
The structure in the cochlea that contains hair cells that transmit acoustic stimuli
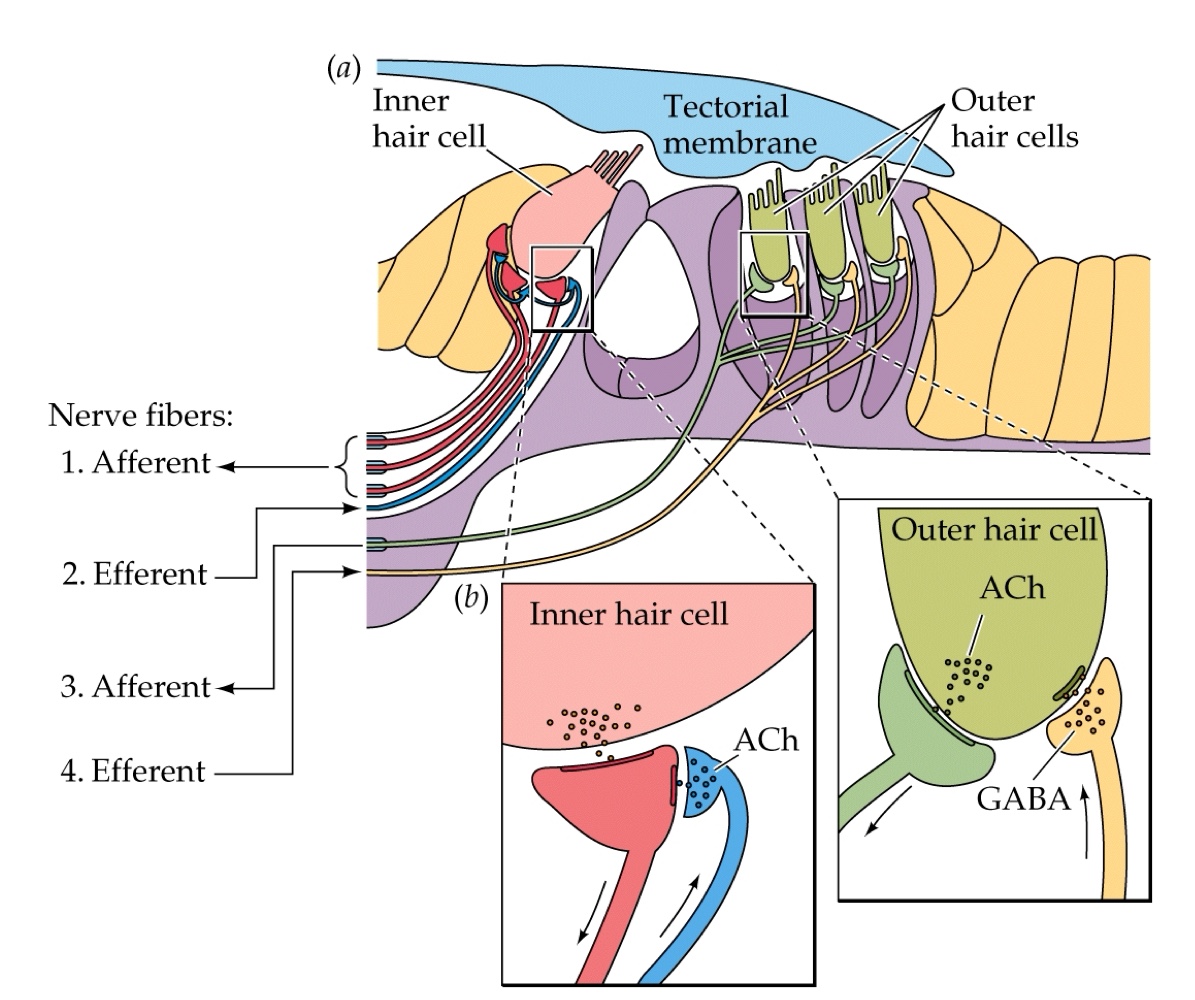
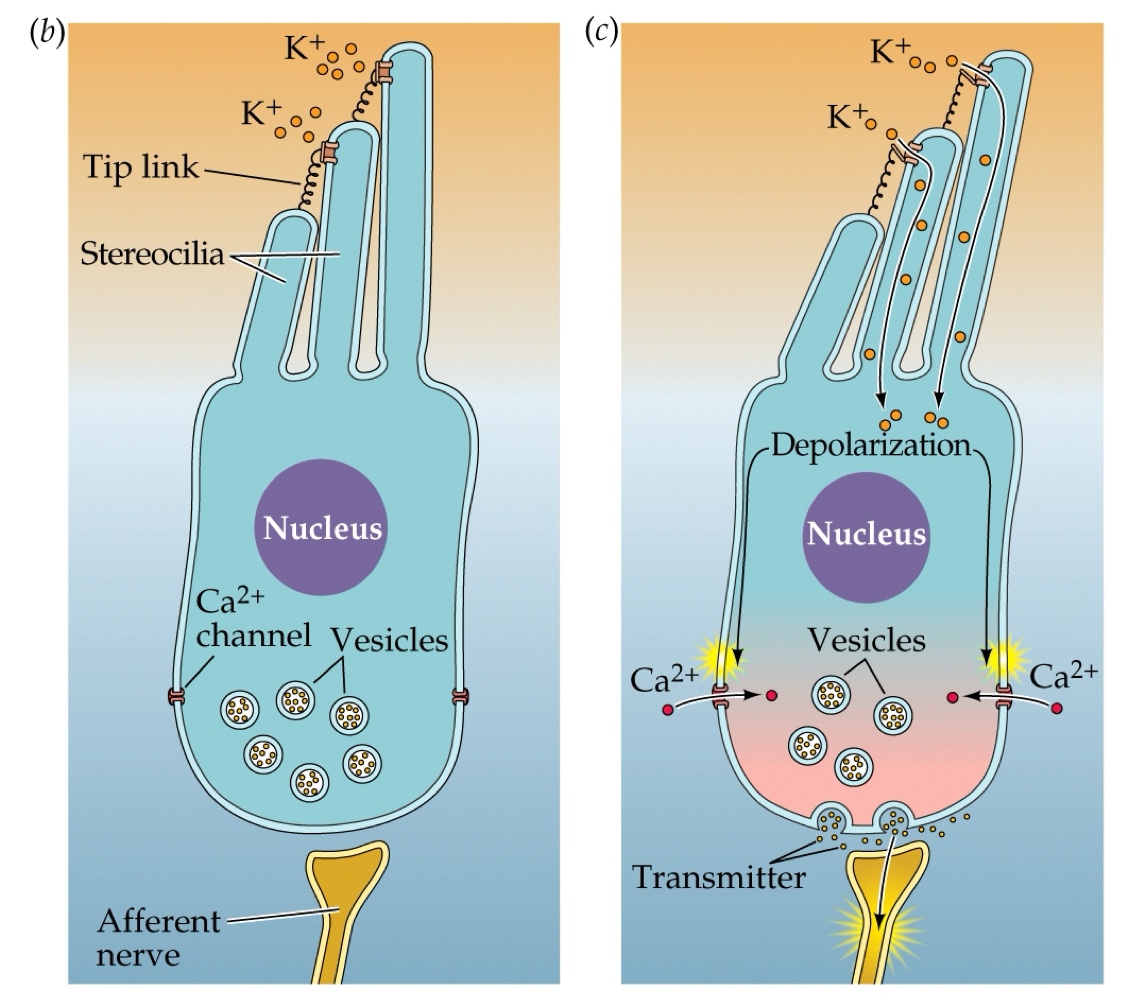
What happens when stiff stereocilia on hair cells bend?
They open ion channels, leading to depolarization of the hair cell as K+ rushes in → voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and synaptic vessicles fuse cause an NT release
What is tonotopic organization in the auditory system?
An orderly map where adjacent frequencies are represented next to each other in the CNS.
How do we localize sound using both ears?
By detecting differences in sound intensity and arrival time at each ear.
What are binaural cues?
Cues that help in localizing sound based on differences in stimuli that reach each ear.
What is the function of the tympanic membrane?
To vibrate in response to sound waves, transmitting vibrations to the ossicles.
What are the two types of differences used in binaural hearing?
Intensity differences (volume) and latency differences (arrival time).
What are the first steps of sound conduction?
Sound waves enter the pinna and ear canal, vibrating the tympanic membrane. The vibrations pass along the ossicles (bones) to the oval window, causing the basilar membrane to vibrate.