fdasfas
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
1
New cards

Immune System
fd
saf
sdf
as
df
sa
f
asf
s
df
s
f
sad
fsdaf
sdf
s
df
fd
saf
sdf
as
df
sa
f
asf
s
df
s
f
sad
fsdaf
sdf
s
df
1. **Innate Immunity**
* Invertebrates
* Vertebrates
a. Barrier defenses
b. Cellular innate defenses
c. Antimicrobial peptides & proteins
d. Inflammatory response
* Evasion of Innate Immunity
\
2. **Adaptive Immunity**
* Antigens
* B Cells & Antibodies
* T Cells
* B Cell & T Cell Development
a. Generation of B & T Cell Diversity
b. Antigen receptor gene arrangement
c. Origin of self-tolerance
d. Proliferation of B and T cells
e. Immunological memory
\
3. **Infection Defense through Adaptive Immunity**
* Activating adaptive immunity
* Response to extracellular pathogens
a. Activation of B cells
b. Antibody function
* Response to infected host cells
* Immunization
* Active & passive immunity
* Antibodies as tools
* Immune rejection
a. Blood groups
\
4. **Disruptions in Immune System Function**
* Exaggerated, self-directed, and diminished immune responses
a. Allergies
b. Autoimmune diseases
c. Exertion and stress
d. Immunodeficiency diseases
* Evolutionary adaptions of pathogens
a. Antigenic variation
b. Latency
c. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
* Cancer and immunity
2
New cards
Innate Immunity
* Invertebrates
* Vertebrates
a. Barrier defenses
b. Cellular innate defenses
c. Antimicrobial peptides & proteins
d. Inflammatory response
* Evasion of Innate Immunity
* Vertebrates
a. Barrier defenses
b. Cellular innate defenses
c. Antimicrobial peptides & proteins
d. Inflammatory response
* Evasion of Innate Immunity
3
New cards
receptor, defenses
**Innate Immunity**
* Molecular recognition relies on small _____ proteins that bind to molecules/structures that are common in viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens
* Not found in animals
* Binding of an innate immune receptor to a foreign molecule activates internal _____
* Response to a very broad range of pathogens
* Molecular recognition relies on small _____ proteins that bind to molecules/structures that are common in viruses, bacteria, and other pathogens
* Not found in animals
* Binding of an innate immune receptor to a foreign molecule activates internal _____
* Response to a very broad range of pathogens
4
New cards
Pathogen
* a bacterium, fungus, virus, or other disease- causing agent
* the internal environment of an animal offers \n a source of nutrients, a protected setting, and a means of transport to new environments
* the internal environment of an animal offers \n a source of nutrients, a protected setting, and a means of transport to new environments
5
New cards
exoskeletons, chitin, Lysozyme, recognition
**Invertebrates**
* Insects rely on their _______ as a physical barrier from infection
* Composed of ____ (polysaccharide)
* Also lines the intestine to
block infection of pathogens
ingested through food
* ______ in digestive system
breaks down cell walls to
protect insect \n
* Insect immune cells produce ______ proteins
* Each binds to a class of molecule that is common to a broad class of pathogens
* Molecules are components of fungal/bacterial cell walls
* Function as identity tags for pathogen recognition
* Trigger an innate immune response once a bound to a pathogen molecule
* Insects rely on their _______ as a physical barrier from infection
* Composed of ____ (polysaccharide)
* Also lines the intestine to
block infection of pathogens
ingested through food
* ______ in digestive system
breaks down cell walls to
protect insect \n
* Insect immune cells produce ______ proteins
* Each binds to a class of molecule that is common to a broad class of pathogens
* Molecules are components of fungal/bacterial cell walls
* Function as identity tags for pathogen recognition
* Trigger an innate immune response once a bound to a pathogen molecule
6
New cards
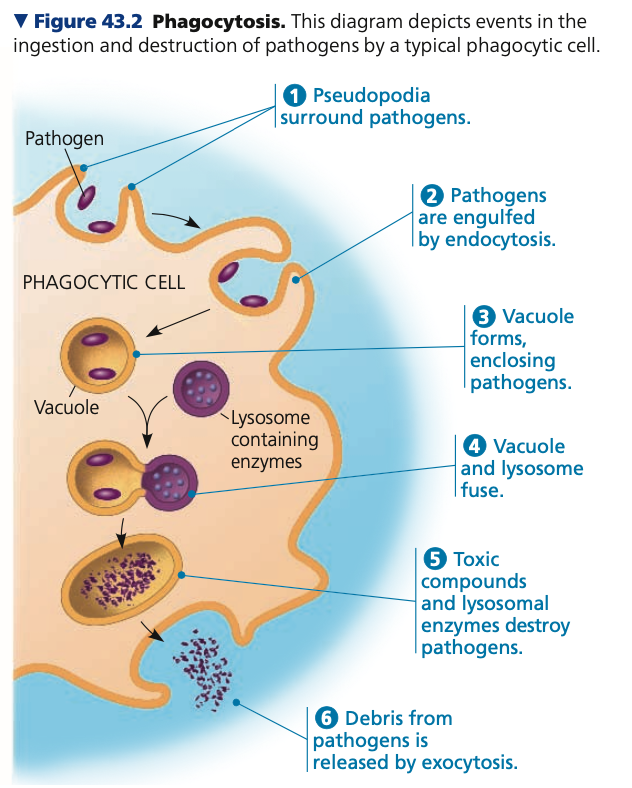
Phagocytize, peptides
**Hemocytes**
* Major immune cells of insects ______ microorganisms
* Ex. entrap Plasmodium
* Release antimicrobial ______
* Circulate body to inactivate/kill fungi and bacteria through disruption of cell membrane
* Major immune cells of insects ______ microorganisms
* Ex. entrap Plasmodium
* Release antimicrobial ______
* Circulate body to inactivate/kill fungi and bacteria through disruption of cell membrane
7
New cards
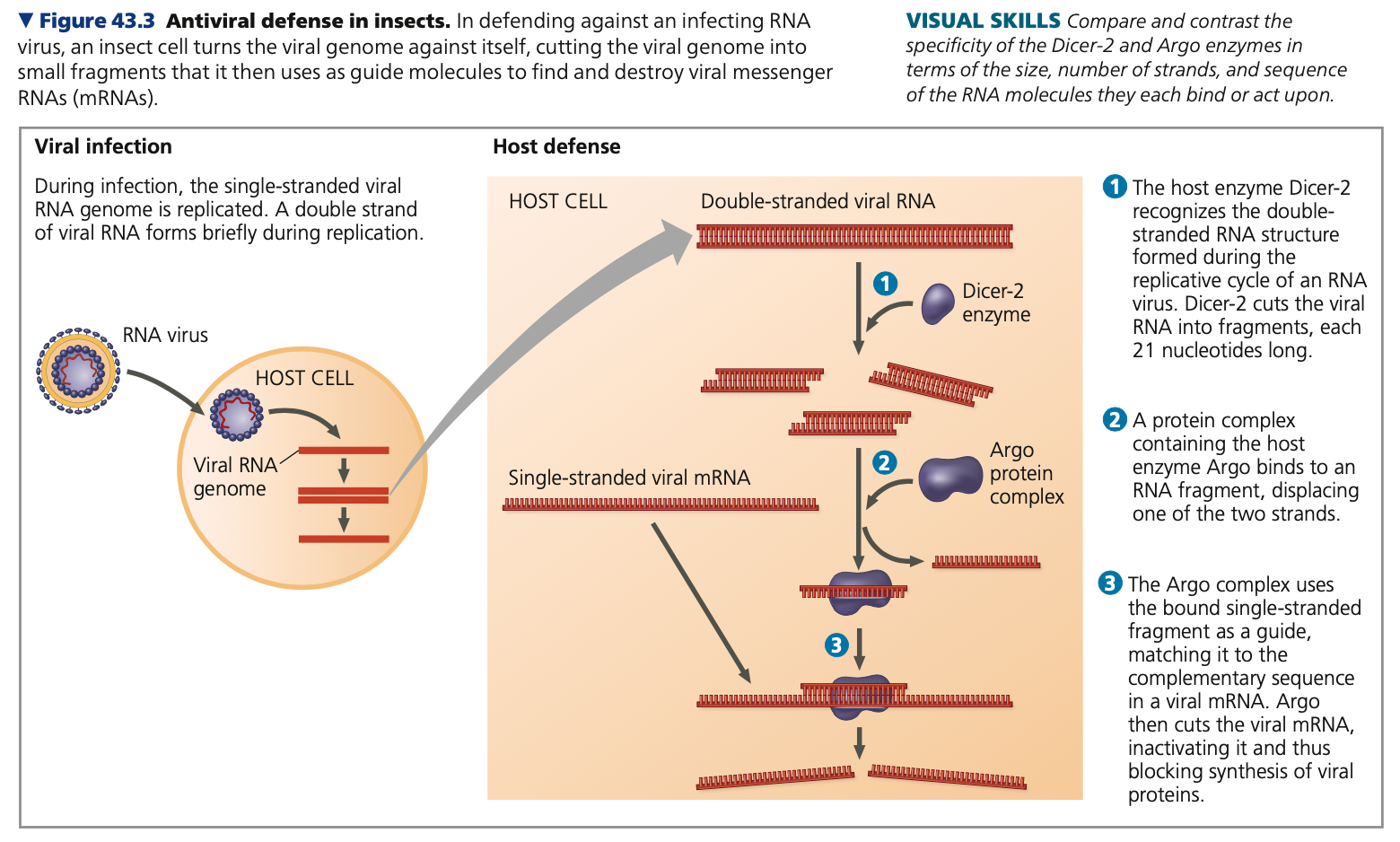
Toll, fungal, double
**Invertebrates**
* Specific reactions for specific pathogens
* Ex. Fungal cell wall molecules bind to the transmembrane receptor ____
* Toll activates production and secretion of antimicrobial peptides that specifically kill ___ cells
* Mammalian cells use receptor proteins similar to Toll
* Defense against viruses
* Viral genome consists of a single strand of RNA
* As it replicates in host cells, RNA becomes the template strand for the synthesis of ____-stranded RNA
* Animals DO NOT produce double stranded RNA, thus triggering an immune response
* Specific reactions for specific pathogens
* Ex. Fungal cell wall molecules bind to the transmembrane receptor ____
* Toll activates production and secretion of antimicrobial peptides that specifically kill ___ cells
* Mammalian cells use receptor proteins similar to Toll
* Defense against viruses
* Viral genome consists of a single strand of RNA
* As it replicates in host cells, RNA becomes the template strand for the synthesis of ____-stranded RNA
* Animals DO NOT produce double stranded RNA, thus triggering an immune response
8
New cards
Vertebrates
a. Barrier defenses
b. Cellular innate defenses
c. Antimicrobial peptides & proteins
d. Inflammatory response
b. Cellular innate defenses
c. Antimicrobial peptides & proteins
d. Inflammatory response
9
New cards
adaptive
**Vertebrates**
* Coexist with _____ immunity
* Mostly focused on mammals
* Coexist with _____ immunity
* Mostly focused on mammals
10
New cards
mucus, Ciliated, epithelia
**Barrier Defenses**
* Block entry of pathogens
1. **Mucous membranes**
* Line digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
* Produce ____
* Viscous fluid that traps pathogens and other particles
* Airway
* ______ cells sweep mucus and entrapped particles upwards to prevent infection of lungs
* Saliva, tears, and mucus secretions
* Bathe exposed _____
* Provide washing action that inhibits colonization by fungi and bacteria
2. **Skin**
* Block entry of pathogens
1. **Mucous membranes**
* Line digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
* Produce ____
* Viscous fluid that traps pathogens and other particles
* Airway
* ______ cells sweep mucus and entrapped particles upwards to prevent infection of lungs
* Saliva, tears, and mucus secretions
* Bathe exposed _____
* Provide washing action that inhibits colonization by fungi and bacteria
2. **Skin**
11
New cards
Lysozyme, walls, 2, Oil, sweat, 3, 5
**Barrier Defenses**
3. **Body secretions**
* Create hostile environment for pathogens
* _____ (tears, saliva, mucus secretions)
* Destroys cell ___ of bacteria in eye openings and upper respiratory tract
* Acidic environment of stomach
* Swallowed pathogens in food and water must contend with pH _ acid
* Kills most pathogens before entry to the small intestine
* _____ and__ ___
* Gives human skin a pH of _ to _
* Acidic enough to prevent bacterial growth
3. **Body secretions**
* Create hostile environment for pathogens
* _____ (tears, saliva, mucus secretions)
* Destroys cell ___ of bacteria in eye openings and upper respiratory tract
* Acidic environment of stomach
* Swallowed pathogens in food and water must contend with pH _ acid
* Kills most pathogens before entry to the small intestine
* _____ and__ ___
* Gives human skin a pH of _ to _
* Acidic enough to prevent bacterial growth
12
New cards
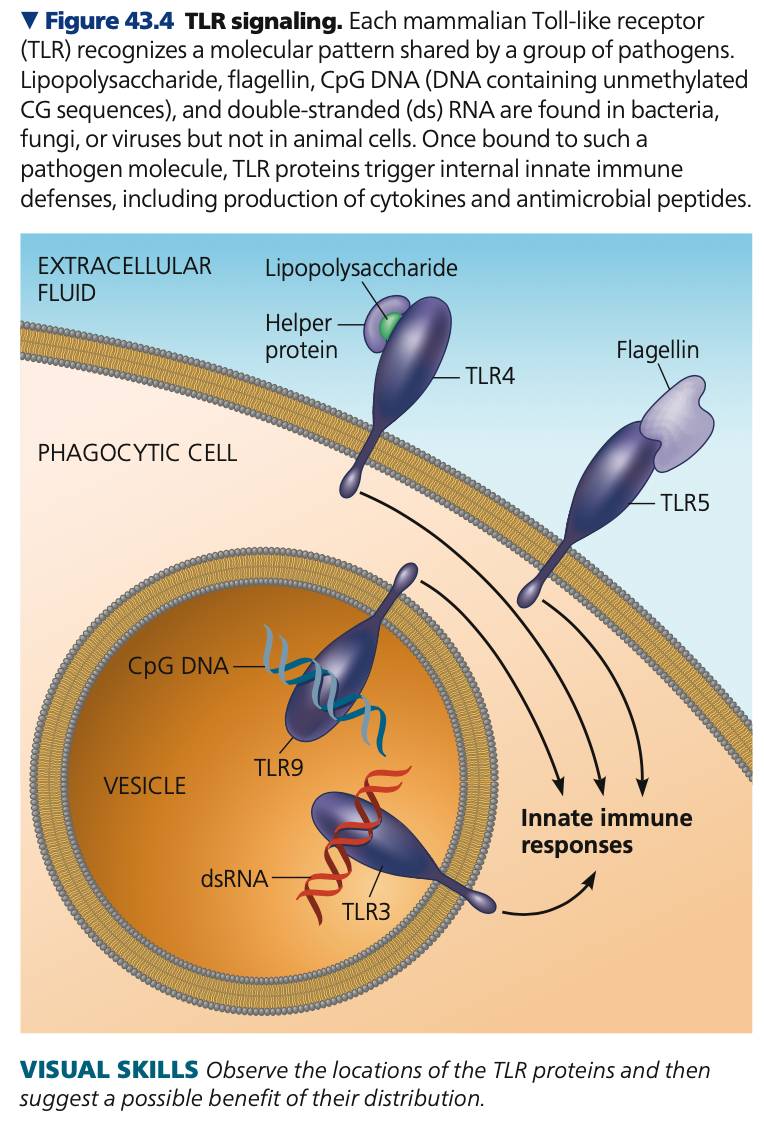
detecting, devouring, destroying, TLR3, RNA, TLR4, lipopolysaccharides, TLR5, flagellin
**Cellular innate defenses**
* Innate immune cells are dedicated to _____, _____, and _____ (3Ds) pathogens \n
1. **Toll-like receptors (TLR)**
* Mammalian receptor similar to the Toll receptor in insects
* TLR proteins produce signals that initiate specific responses to specific microorganisms
* **Mechanism of TLRs**
* Each TLR protein binds to fragments of molecules specific to a pathogen
* __ (inner surface of vesicles formed by endocytosis) → binds to double-stranded ____
* ___ (immune cell plasma membranes) → binds to ______
* ____ → recognizes ____
* Innate immune cells are dedicated to _____, _____, and _____ (3Ds) pathogens \n
1. **Toll-like receptors (TLR)**
* Mammalian receptor similar to the Toll receptor in insects
* TLR proteins produce signals that initiate specific responses to specific microorganisms
* **Mechanism of TLRs**
* Each TLR protein binds to fragments of molecules specific to a pathogen
* __ (inner surface of vesicles formed by endocytosis) → binds to double-stranded ____
* ___ (immune cell plasma membranes) → binds to ______
* ____ → recognizes ____
13
New cards
**Phagocytic,** signals, Larger, spleen
**Cellular innate defenses**
2. **______ cells**
* **Neutrophils**
* Circulate in the blood
* Attracted by ____ from infected tissue
* Engulf and destroy pathogens
* **Macrophages**
* Big eaters
* ____ than neutrophils
* May migrate or reside permanently in places that are more likely to encounter pathogens
* Ex. found in the ____ (pathogens in blood are often trapped here)
2. **______ cells**
* **Neutrophils**
* Circulate in the blood
* Attracted by ____ from infected tissue
* Engulf and destroy pathogens
* **Macrophages**
* Big eaters
* ____ than neutrophils
* May migrate or reside permanently in places that are more likely to encounter pathogens
* Ex. found in the ____ (pathogens in blood are often trapped here)
14
New cards
Dendritic, skin, Eosinophils
**Cellular innate defenses**
3. ______ cells
* Populate tissues that contact the environment (e.g. ___)
* Stimulate adaptive immunity & engulf
* Ex. _______
* Important in defense against multicellular invaders (parasitic worm)
* Discharge destructive enzymes
3. ______ cells
* Populate tissues that contact the environment (e.g. ___)
* Stimulate adaptive immunity & engulf
* Ex. _______
* Important in defense against multicellular invaders (parasitic worm)
* Discharge destructive enzymes
15
New cards
surface, chemicals
**Cellular innate defenses**
4. **Natural killer cells**
* Circulate through the body
* Detect abnormal array of _____ protein characteristics
* Present in virus-infected and cancerous cells
* Do NOT engulf
* Release _____ that lead to cell death
4. **Natural killer cells**
* Circulate through the body
* Detect abnormal array of _____ protein characteristics
* Present in virus-infected and cancerous cells
* Do NOT engulf
* Release _____ that lead to cell death
16
New cards
connective
**Cellular innate defenses**
5. **Mast cells**
* found in _____ tissue and make key contributions to the inflammatory response, described next, as well as to allergies, discussed later.
5. **Mast cells**
* found in _____ tissue and make key contributions to the inflammatory response, described next, as well as to allergies, discussed later.
17
New cards
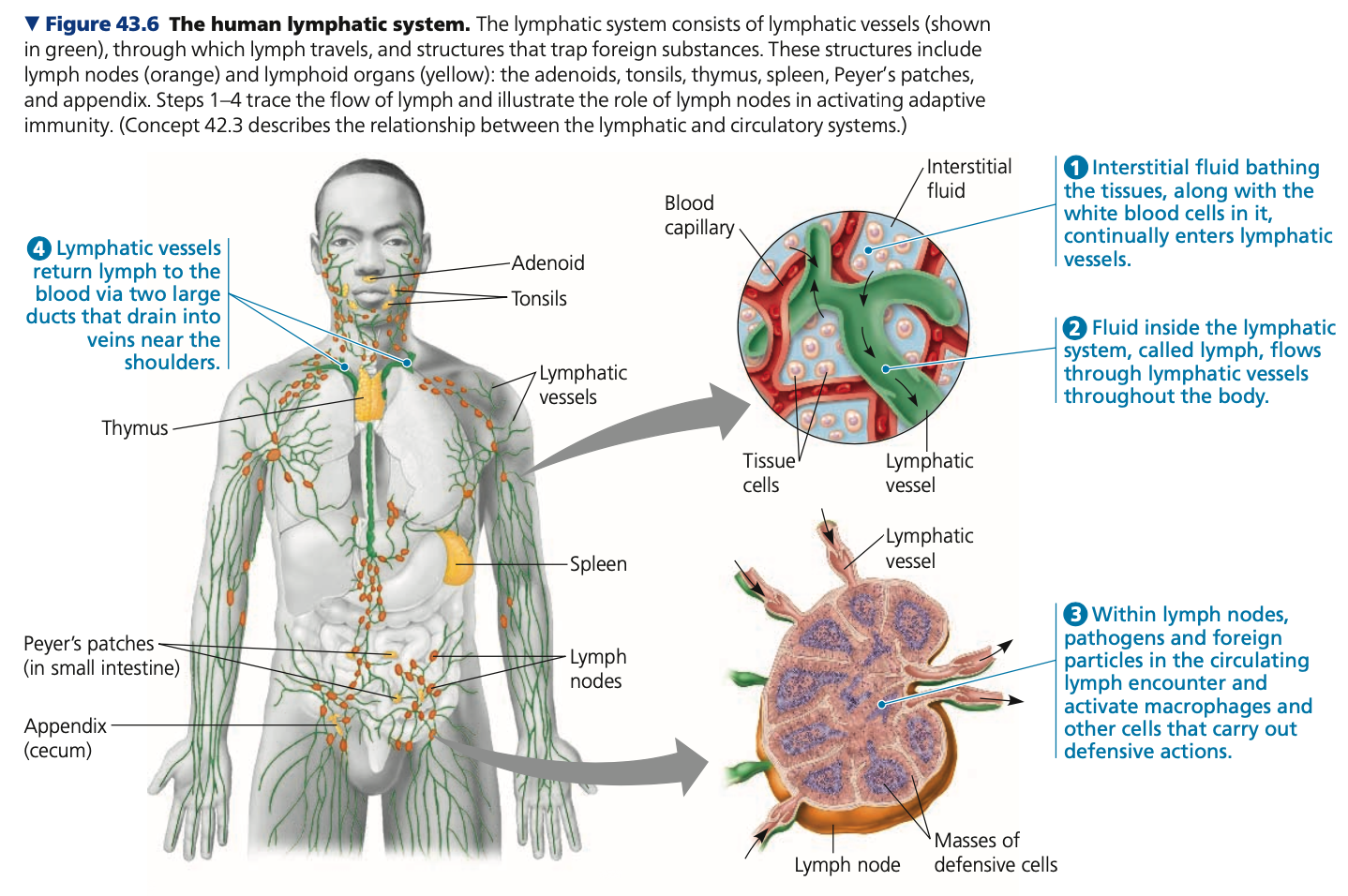
lymphatic, Macrophages, Dendritic, adaptive
**Cellular innate defenses**
* Involve the _______ system
* Distributes lymph throughout the body
* ______ → lymph nodes
* Engulf pathogens in lymph from interstitial fluid
* _____ cells → migrate to lymph nodes after interaction with pathogens
* Interact with other immune cells to stimulate _____ immunity
* Involve the _______ system
* Distributes lymph throughout the body
* ______ → lymph nodes
* Engulf pathogens in lymph from interstitial fluid
* _____ cells → migrate to lymph nodes after interaction with pathogens
* Interact with other immune cells to stimulate _____ immunity
18
New cards
membrane
**Antimicrobial peptides & proteins**
* Result of pathogen recognition
* Peptides may damage broad groups of
pathogens
* Disrupt ______ integrity
* Similar to insect immune response
* Result of pathogen recognition
* Peptides may damage broad groups of
pathogens
* Disrupt ______ integrity
* Similar to insect immune response
19
New cards
Proteins, replication, WBC, recombinant
**Interferons**
* _____ that interfere with viral infections
* Secreted by virus-infected cells
* Induces nearby uninfected cells to produce substances that inhibit viral _____
* Limit cell-to-cell spread of viruses; controls infections like influenza and colds
* Some ___s secrete a different interferon
* Activate macrophages and enhance phagocytic ability
* Pharma companies use _____ DNA tech to mass-produce interferons to treat viral infections (ex. Hepatitis C)
* _____ that interfere with viral infections
* Secreted by virus-infected cells
* Induces nearby uninfected cells to produce substances that inhibit viral _____
* Limit cell-to-cell spread of viruses; controls infections like influenza and colds
* Some ___s secrete a different interferon
* Activate macrophages and enhance phagocytic ability
* Pharma companies use _____ DNA tech to mass-produce interferons to treat viral infections (ex. Hepatitis C)
20
New cards
**Complement, 30,** lysis
**_______ system**
* Consists of roughly __ proteins in blood plasma
* Circulate in an inactive state
* Activated by substances on surfaces of pathogens
* Results in a cascade of biochemical reactions
* Leads to ___ of invading cells
* Functions in immune response
* Consists of roughly __ proteins in blood plasma
* Circulate in an inactive state
* Activated by substances on surfaces of pathogens
* Results in a cascade of biochemical reactions
* Leads to ___ of invading cells
* Functions in immune response
21
New cards
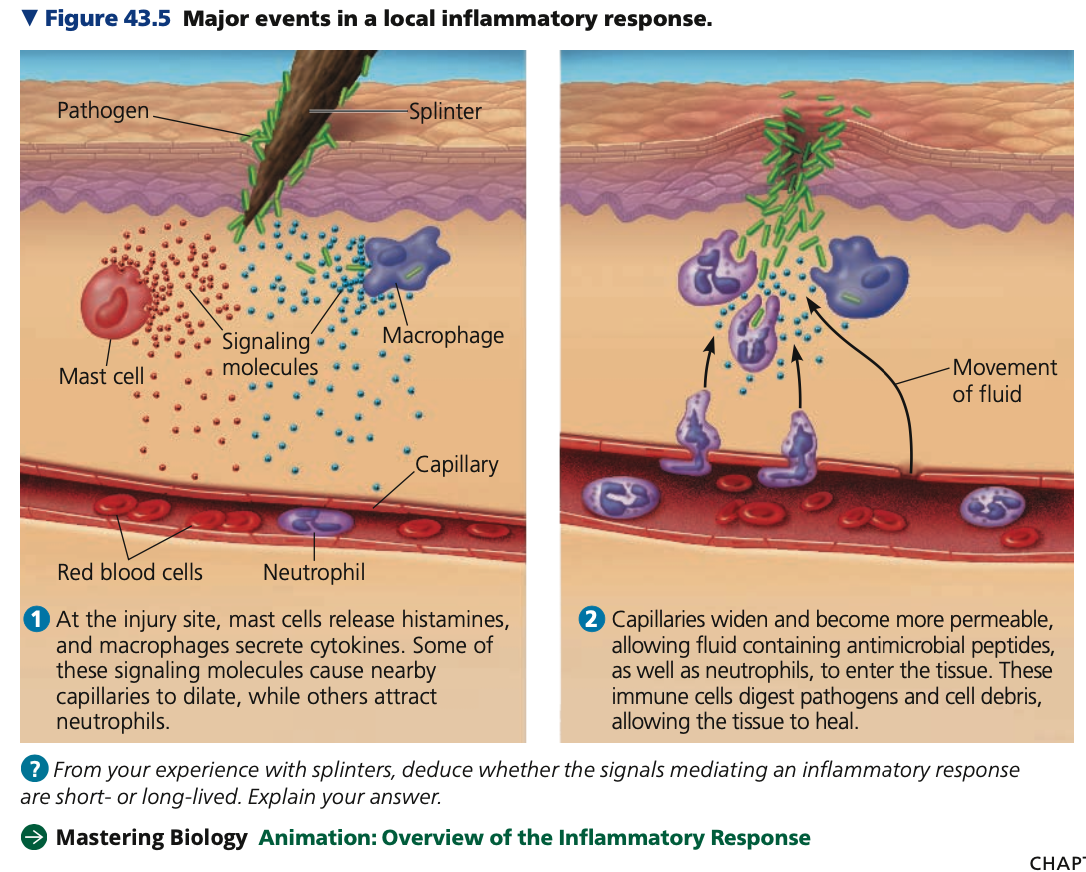
**cytokines, neutrophils, Mast, histamine,** dilate, increase
**Inflammatory response**
* Set of events triggered by signaling molecules released upon injury/infection
* **Mechanism**
1. **Activated macrophages release ______**
* Signaling molecules that recruit _____ to site of injury/infection
2. **_____ cells release ______**
* Release signaling molecule histamine at sites of damage
* Triggers nearby blood vessels to ____ and become more permeable
* Results in _____ of local blood supply, which produces the redness and increased skin temperature in the area
* Set of events triggered by signaling molecules released upon injury/infection
* **Mechanism**
1. **Activated macrophages release ______**
* Signaling molecules that recruit _____ to site of injury/infection
2. **_____ cells release ______**
* Release signaling molecule histamine at sites of damage
* Triggers nearby blood vessels to ____ and become more permeable
* Results in _____ of local blood supply, which produces the redness and increased skin temperature in the area
22
New cards
Cycles, complement, phagocytic, peptides, pus
**Inflammation**
* ___of cell signaling and response transform site of injury/infection
* Activated _______ proteins promote further release of histamine
* Attracts more ______ cells
* Enhanced blood flow delivers antimicrobial _____
* Results in accumulation of __
* A fluid rich in white blood cells, dead pathogens and debris from damaged tissue
* ___of cell signaling and response transform site of injury/infection
* Activated _______ proteins promote further release of histamine
* Attracts more ______ cells
* Enhanced blood flow delivers antimicrobial _____
* Results in accumulation of __
* A fluid rich in white blood cells, dead pathogens and debris from damaged tissue
23
New cards
**Inflammatory response**
1. Local inflammatory response
2. Systemic inflammatory response
24
New cards
Local inflammatory response
* Minor injuries and infections
25
New cards
marrow, fever, higher
**Systemic inflammatory response**
* Larger injuries/infections
* Injured cells and tissues stimulate release of additional neutrophils from bone ______
* In severe infections (ex. Meningitis or appendicitis)
* White blood cell concentration increases rapidly in a few hours
* May involve a ___
* Substances released by macrophages may reset body’s thermostat to a _____ temperature
* Underlying mechanism is still under debate
* May enhance phagocytosis
* Speeds up chemical reactions → accelerate tissue repair
* Larger injuries/infections
* Injured cells and tissues stimulate release of additional neutrophils from bone ______
* In severe infections (ex. Meningitis or appendicitis)
* White blood cell concentration increases rapidly in a few hours
* May involve a ___
* Substances released by macrophages may reset body’s thermostat to a _____ temperature
* Underlying mechanism is still under debate
* May enhance phagocytosis
* Speeds up chemical reactions → accelerate tissue repair
26
New cards
septic, **Chronic, Crohn’s,** colitis
**Inflammatory response**
* **Bacterial infections**
* May induce an overwhelming systemic inflammatory response
* Leads to ____ shock
* Very high fever, low blood pressure, poor blood flow through capillaries
* Occurs most often in the very old and very young
* **____ inflammation**
* Ex. ___ disease, ulcerative ___
* Unregulated inflammatory response disrupts function
* Ex. intestinal function
* **Bacterial infections**
* May induce an overwhelming systemic inflammatory response
* Leads to ____ shock
* Very high fever, low blood pressure, poor blood flow through capillaries
* Occurs most often in the very old and very young
* **____ inflammation**
* Ex. ___ disease, ulcerative ___
* Unregulated inflammatory response disrupts function
* Ex. intestinal function
27
New cards
capsule, Streptococcus, breakdown, Myobacterium
**Evasion of Innate Immunity**
* Adaptations
* Outer _____ of certain bacteria
* interferes with molecular reception and phagocytosis
* Ex. _______ pneumoniae causes pneumonia and meningitis
* Resistance to _____ after being engulfed
* Ex. _______ tuberculosis grows and reproduces within host cells to hide from immune defenses → causes tuberculosis
* Adaptations
* Outer _____ of certain bacteria
* interferes with molecular reception and phagocytosis
* Ex. _______ pneumoniae causes pneumonia and meningitis
* Resistance to _____ after being engulfed
* Ex. _______ tuberculosis grows and reproduces within host cells to hide from immune defenses → causes tuberculosis
28
New cards
Adaptive immunity
* Antigens
* B Cells & Antibodies
* T Cells
* B Cell & T Cell Development
a. Generation of B & T Cell Diversity
b. Antigen receptor gene arrangement
c. Origin of self-tolerance
d. Proliferation of B and T cells
e. Immunological memory
* B Cells & Antibodies
* T Cells
* B Cell & T Cell Development
a. Generation of B & T Cell Diversity
b. Antigen receptor gene arrangement
c. Origin of self-tolerance
d. Proliferation of B and T cells
e. Immunological memory
29
New cards
vertebrates, Specific, slower
**Adaptive immunity**
* Unique to ______ (AKA acquired immune response)
* Molecular recognition relies on many different receptors
* Recongizes a specific part of a specific molecule on a specific pathogen
* _____ response
* Activated by innate immune system
* Develops ____
* Enhanced by previous exposure to pathogen
* Unique to ______ (AKA acquired immune response)
* Molecular recognition relies on many different receptors
* Recongizes a specific part of a specific molecule on a specific pathogen
* _____ response
* Activated by innate immune system
* Develops ____
* Enhanced by previous exposure to pathogen
30
New cards
lymphocytes, stem, thymus, T, marrow, B, killer
**Adaptive immunity**
* Relies on T cells and B cells
* Types of white blood cells called ______
* Originate in the ___ cells in bone marrow
* Some migrate to the ____ (organ in thoracic cavity above heart) → T cells
* Some mature in the ____ → _ cells
* Other lymphocytes become natural ___ cells
* Relies on T cells and B cells
* Types of white blood cells called ______
* Originate in the ___ cells in bone marrow
* Some migrate to the ____ (organ in thoracic cavity above heart) → T cells
* Some mature in the ____ → _ cells
* Other lymphocytes become natural ___ cells
31
New cards
**receptor,** Lymphocytes, 100K
**Antigens**
* Any substance that elicits a response from B or T cells
* Recognition occurs when a B or T cell binds to an antigen
* Bacterial or viral protein
* Recognition occurs through binding to an **antigen _____** which binds to a specific part of the pathogen
* Immune cells produce different antigen receptors
* ______ produce one variety only
* All antigen receptors made by one B
or T cells are identical
* Infection triggers activation of B and
T cells with receptors specific for parts
of the pathogen
* A single B or T cell has about ____
receptors on its surface
* Any substance that elicits a response from B or T cells
* Recognition occurs when a B or T cell binds to an antigen
* Bacterial or viral protein
* Recognition occurs through binding to an **antigen _____** which binds to a specific part of the pathogen
* Immune cells produce different antigen receptors
* ______ produce one variety only
* All antigen receptors made by one B
or T cells are identical
* Infection triggers activation of B and
T cells with receptors specific for parts
of the pathogen
* A single B or T cell has about ____
receptors on its surface
32
New cards
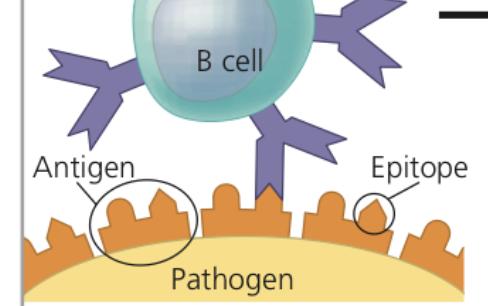
antigen, specificity
**Epitope**
* Small and accessible portion of an _____ that binds to an antigen receptor
* Ex. a group of amino acids in a particular protein
* A single antigen has multiple epitopes which bind to a receptor with different ______
* Each B or T cell displays specificity for a particular epitope
* Because receptors produced by one B or T cell are identical
* Small and accessible portion of an _____ that binds to an antigen receptor
* Ex. a group of amino acids in a particular protein
* A single antigen has multiple epitopes which bind to a receptor with different ______
* Each B or T cell displays specificity for a particular epitope
* Because receptors produced by one B or T cell are identical
33
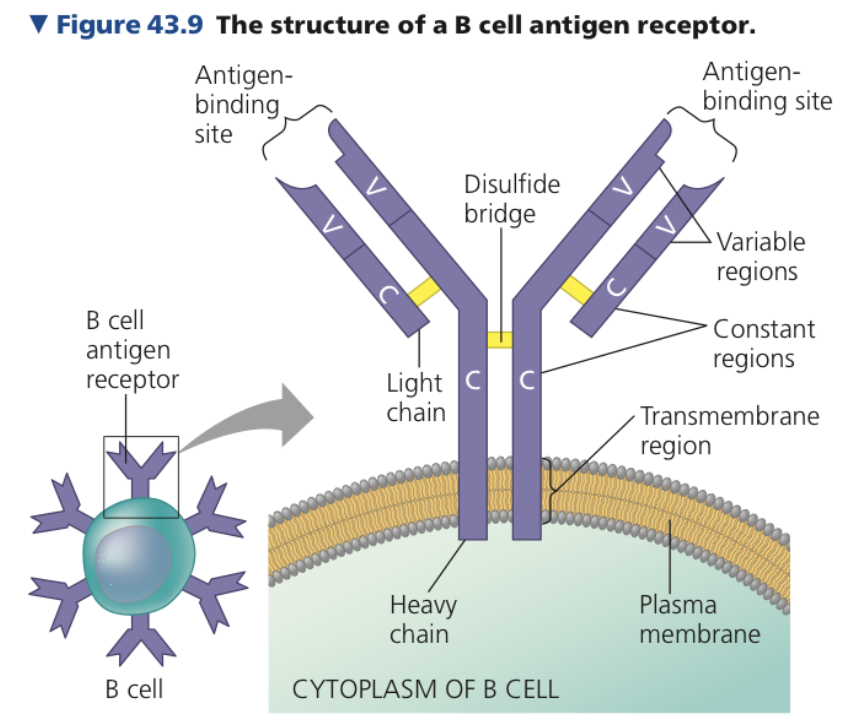
New cards
Y, 4, Disulfide, **Constant, Variable**
**B Cells & Antibodies**
* Antigen receptor in B cell
* _-shaped protein
* _ polypeptide chains
* Two identical heavy chains
* Two identical light chains
* ____ bridges link the chains together
\
1. **_____ (C) Region**
* Region in light/heavy chains where amino acids have little variation among receptors on different B cells
* On heavy chains
* Contains a transmembrane region
* Anchors receptor to membrane
\
2. **_____ (V) Region**
* Amino acid sequence varies extensively from one B cell to another
* Parts of heavy and light chain V regions form an asymmetrical binding site for an antigen
* Each B cell antigen has two identical antigen-binding sites
* Antigen receptor in B cell
* _-shaped protein
* _ polypeptide chains
* Two identical heavy chains
* Two identical light chains
* ____ bridges link the chains together
\
1. **_____ (C) Region**
* Region in light/heavy chains where amino acids have little variation among receptors on different B cells
* On heavy chains
* Contains a transmembrane region
* Anchors receptor to membrane
\
2. **_____ (V) Region**
* Amino acid sequence varies extensively from one B cell to another
* Parts of heavy and light chain V regions form an asymmetrical binding site for an antigen
* Each B cell antigen has two identical antigen-binding sites
34
New cards
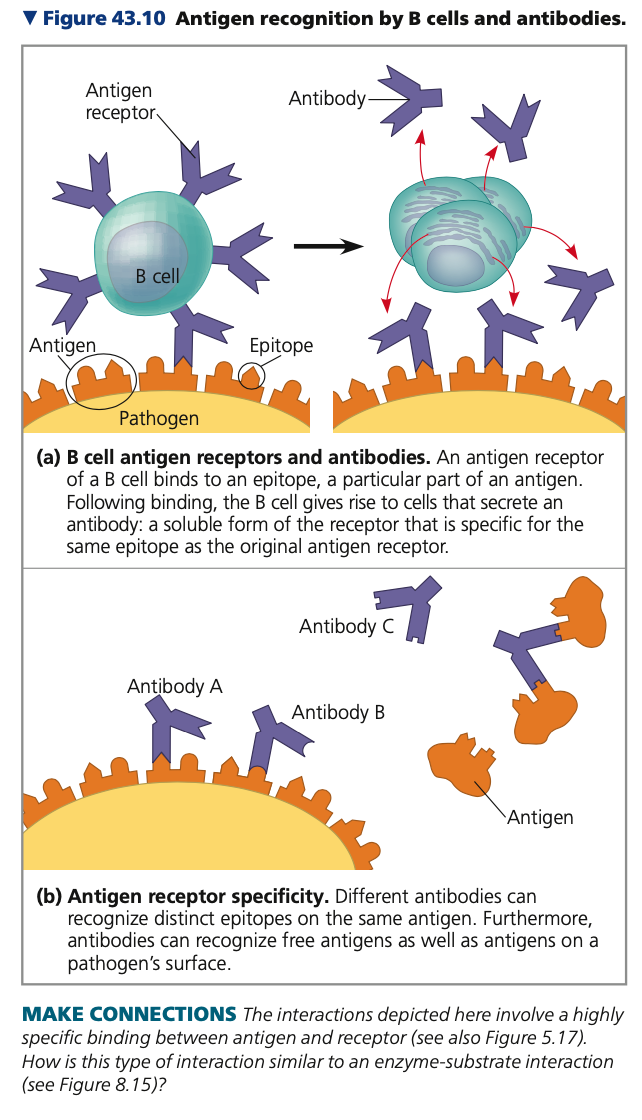
soluble, anchor, noncovalent, amino
**B Cells & Antibodies**
* **B**i**nding of B cell antigen**
* Early step in B cell activation
* Leads to formation of cells that secrete a _____ form of the receptor
* Antibody (e.g., immunoglobulin or Ig)
* **Antibodies**
* Have same Y-shaped structure
* Lack a membrane _____
* Provide direct defense against pathogens in body fluids
* **Lock-and-key fit**
* Antigen-binding site of a membrane-bound receptor or antibody has a unique shape
* Fits a specific epitope
* Stable interaction
* Many ______ bonds between epitope and surface of binding site
* Differences in ___ acid sequence enable binding to be highly specific
* B cell antigen receptors and antibodies bind to antigens in blood and lymph
* **B**i**nding of B cell antigen**
* Early step in B cell activation
* Leads to formation of cells that secrete a _____ form of the receptor
* Antibody (e.g., immunoglobulin or Ig)
* **Antibodies**
* Have same Y-shaped structure
* Lack a membrane _____
* Provide direct defense against pathogens in body fluids
* **Lock-and-key fit**
* Antigen-binding site of a membrane-bound receptor or antibody has a unique shape
* Fits a specific epitope
* Stable interaction
* Many ______ bonds between epitope and surface of binding site
* Differences in ___ acid sequence enable binding to be highly specific
* B cell antigen receptors and antibodies bind to antigens in blood and lymph
35
New cards
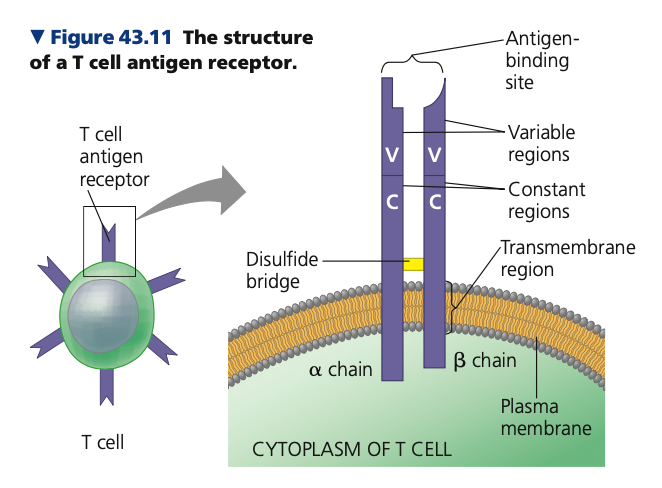
polypeptide, anchor
**T Cells**
* Antigen receptor in T cell
* Two different ______ chains
* α chain
* β chain
* Near the base, there is a transmembrane region to ____ the molecule to the cell
\
1. **Variable (V) region**
* Outer tip of molecule
* At the end of the chains
* Forms the antigen-binding site
\
2. **Constant (C) region**
* Rest of the receptor
* Antigen receptor in T cell
* Two different ______ chains
* α chain
* β chain
* Near the base, there is a transmembrane region to ____ the molecule to the cell
\
1. **Variable (V) region**
* Outer tip of molecule
* At the end of the chains
* Forms the antigen-binding site
\
2. **Constant (C) region**
* Rest of the receptor
36
New cards
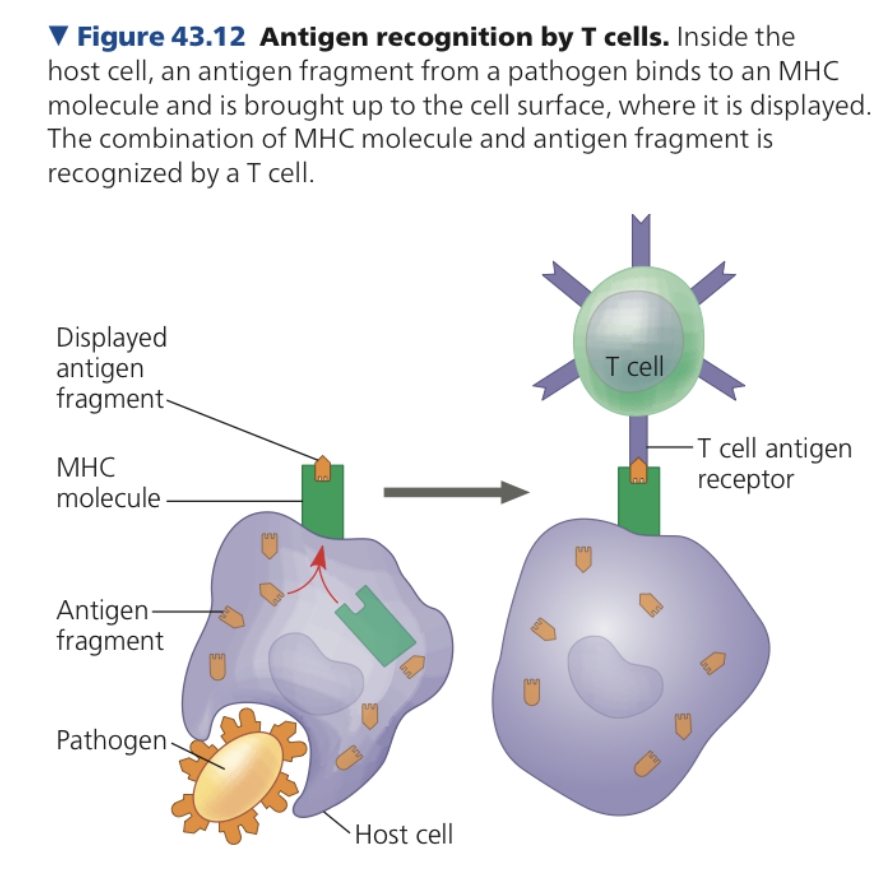
**histocompatibility,** Enzymes
**T Cells**
* Bind to fragments of antigens that are displayed on a host cell’s surface
* **Major _______ complex (MHC) molecule**
* Host protein that displays antigen fragment on cell surface
* Essential for antigen recognition by T cells
* Display of protein antigens
* Occurs when
* a pathogen infects a cell of animal host
* Immune cell engulfs pathogen proteins/whole pathogen
* Inside animal cell
* ____ cleave antigen into antigen fragments binds to MHC molecule
* Bind to fragments of antigens that are displayed on a host cell’s surface
* **Major _______ complex (MHC) molecule**
* Host protein that displays antigen fragment on cell surface
* Essential for antigen recognition by T cells
* Display of protein antigens
* Occurs when
* a pathogen infects a cell of animal host
* Immune cell engulfs pathogen proteins/whole pathogen
* Inside animal cell
* ____ cleave antigen into antigen fragments binds to MHC molecule
37
New cards
**presentation,** foreign
**Antigen ________**
* Display of antigen fragment in an exposed groove of the MHC protein
* Advertises that the host cell contains a ____ substance
* If it encounters a T cell with the right specificity, the T cell receptor can bind to both antigen fragment and MHC molecule
* Triggers adaptive immunity
* Display of antigen fragment in an exposed groove of the MHC protein
* Advertises that the host cell contains a ____ substance
* If it encounters a T cell with the right specificity, the T cell receptor can bind to both antigen fragment and MHC molecule
* Triggers adaptive immunity
38
New cards
B Cell & T Cell Development
a. Generation of B & T Cell Diversity
b. Antigen receptor gene arrangement
c. Origin of self-tolerance
d. Proliferation of B and T cells
e. Immunological memory
b. Antigen receptor gene arrangement
c. Origin of self-tolerance
d. Proliferation of B and T cells
e. Immunological memory
39
New cards
lymphocytes, Self, activation, memory
**B Cell & T Cell Development**
* Four major characteristics of adaptive immunity
1. Repertoire of _______ and receptors enables detection of antigens and pathogens that have never been encountered
2. ___-tolerance → lack of reactivity against own cells
3. Cell proliferation triggered by _____ greatly increases number of B and T cells specific for an antigen
4. Stronger and more rapid response to antigens encountered previously → immunological _____
* Four major characteristics of adaptive immunity
1. Repertoire of _______ and receptors enables detection of antigens and pathogens that have never been encountered
2. ___-tolerance → lack of reactivity against own cells
3. Cell proliferation triggered by _____ greatly increases number of B and T cells specific for an antigen
4. Stronger and more rapid response to antigens encountered previously → immunological _____
40
New cards
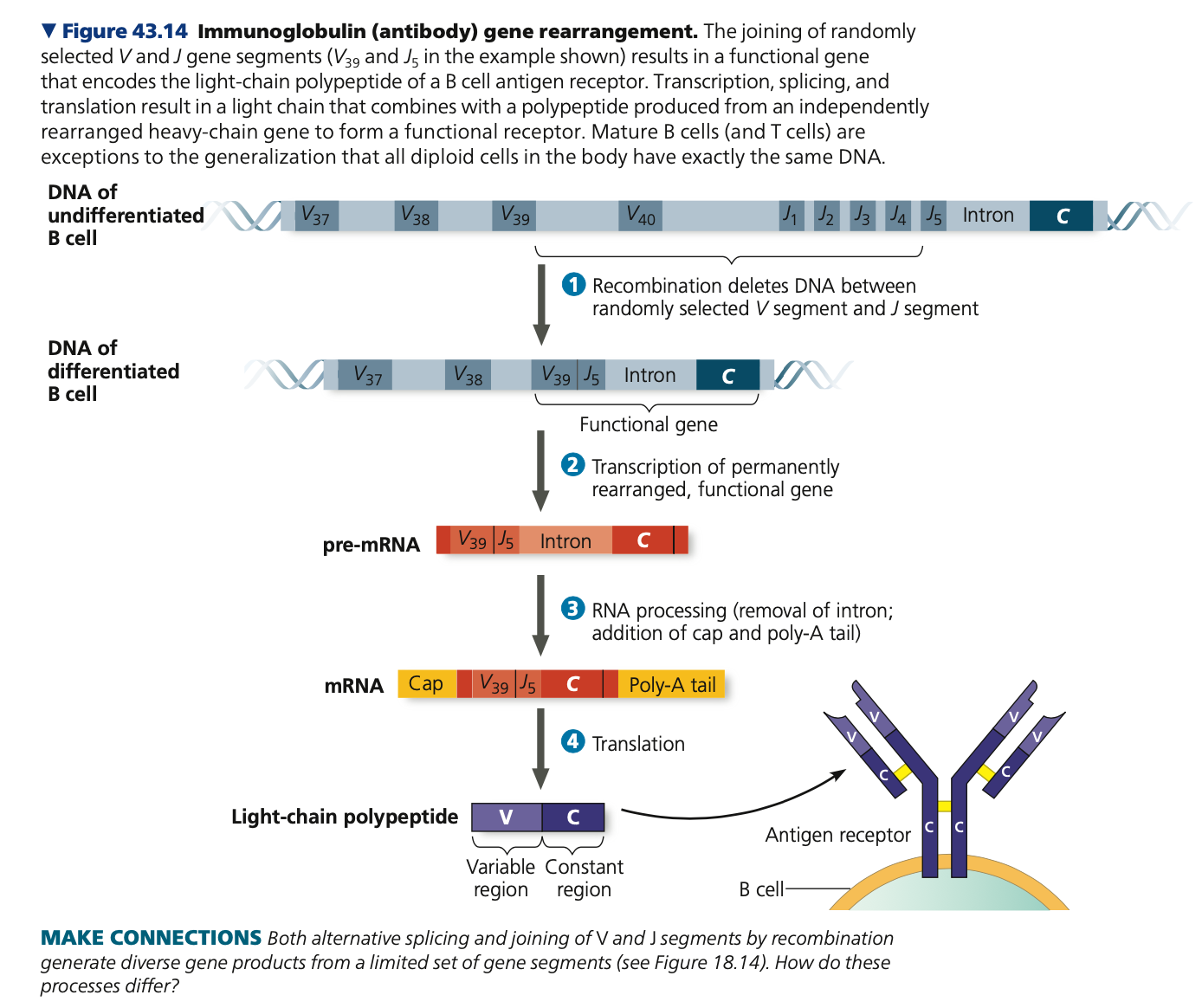
**Immunoglobulin,** light, Joining, 200, heavy
**Generation of B & T Cell Diversity**
* More than 1 million types of B cell receptors
* 10 million types of T cell receptors
* 20,000 protein-coding genes
* How are there so many different types of
receptors?
* Combining different variable elements
* Immune system can assemble millions of different receptors from a small collection of parts
* **_________ (Ig) gene**
* Codes for ___ chain of B cell antigen receptors and immunoglobulins
* Receptor light chain has 3 parts
* Variable region
* Variable (V) segment
* _____ (J) segment
* Constant region
* Constant (C) segment
* Light chain gene contains
* 1 C segment
* 40 V segments
* 5 J segments
* Alternative copies of V and J segments are arrayed along the gene in a series
* Functional gene is built from one copy of each gene
* Pieces can be combined ___ different ways (40 V x 5 J x 1 C)
* Number of ____ chain combinations is even greater
* All B and T cell antigen receptor genes undergo similar transformations
* More than 1 million types of B cell receptors
* 10 million types of T cell receptors
* 20,000 protein-coding genes
* How are there so many different types of
receptors?
* Combining different variable elements
* Immune system can assemble millions of different receptors from a small collection of parts
* **_________ (Ig) gene**
* Codes for ___ chain of B cell antigen receptors and immunoglobulins
* Receptor light chain has 3 parts
* Variable region
* Variable (V) segment
* _____ (J) segment
* Constant region
* Constant (C) segment
* Light chain gene contains
* 1 C segment
* 40 V segments
* 5 J segments
* Alternative copies of V and J segments are arrayed along the gene in a series
* Functional gene is built from one copy of each gene
* Pieces can be combined ___ different ways (40 V x 5 J x 1 C)
* Number of ____ chain combinations is even greater
* All B and T cell antigen receptor genes undergo similar transformations
41
New cards
recombinase, V, J, randomly
**Antigen receptor gene arrangement**
* Assembly of a functioning Ig gene
* Requires rearranging the DNA
* Early B cell development
* Enzyme _______ links one light-chain V gene segment to one J gene segment
* Recombination event eliminated long DNA between V and J gene
* Forms single exon that is part __ and part __
* Recombinase acts ______
* Links any of the 40 V segments to any of the 5 J segments
* Heavy chains undergo similar rearrangement
* Assembly of a functioning Ig gene
* Requires rearranging the DNA
* Early B cell development
* Enzyme _______ links one light-chain V gene segment to one J gene segment
* Recombination event eliminated long DNA between V and J gene
* Forms single exon that is part __ and part __
* Recombinase acts ______
* Links any of the 40 V segments to any of the 5 J segments
* Heavy chains undergo similar rearrangement
42
New cards
one, receptors, binding, Mutations
**Antigen receptor gene arrangement**
* Only ___ allele each from the light-chain and heavy-chain are rearranged
* Rearrangements are permanent and are passed onto daughter cells
* After rearrangement, antigen ______ can be synthesized
* Rearranged genes are transcribed
* Transcripts are processed for translation
* Light chain and heavy chain assemble together to form a receptor
* Randomly rearranged heavy and light chains form different antigen-_____ sites
* In the total population of B cells in the body
* Number of combinations is as high as 3.5 x 10^6
* _____ in the VJ recombination add more variation
* Only ___ allele each from the light-chain and heavy-chain are rearranged
* Rearrangements are permanent and are passed onto daughter cells
* After rearrangement, antigen ______ can be synthesized
* Rearranged genes are transcribed
* Transcripts are processed for translation
* Light chain and heavy chain assemble together to form a receptor
* Randomly rearranged heavy and light chains form different antigen-_____ sites
* In the total population of B cells in the body
* Number of combinations is as high as 3.5 x 10^6
* _____ in the VJ recombination add more variation
43
New cards
own, apoptosis, mature
**Origin of self-tolerance**
* Antigen receptor genes are randomly rearranged
* Some immature lymphocytes produce receptors specific for epitopes on the ___ organism’s molecules
* If not eliminated, immune system would attack body’s own cells
* As lymphocytes mature
* Tested for self-reactivity
* Destroyed by ______
* Rendered nonfunctional
* Immune system lacks _____ cells that are able to react against its own components
* This is called self-tolerance
* Antigen receptor genes are randomly rearranged
* Some immature lymphocytes produce receptors specific for epitopes on the ___ organism’s molecules
* If not eliminated, immune system would attack body’s own cells
* As lymphocytes mature
* Tested for self-reactivity
* Destroyed by ______
* Rendered nonfunctional
* Immune system lacks _____ cells that are able to react against its own components
* This is called self-tolerance
44
New cards
divisions, **clone,** effector
**Proliferation of B and T cells**
* Only a tiny fraction of antigen receptors are specific to a given epitope
* Antigen is presented to a steady stream of lymphocytes in the lymph nodes
* Continues until a match is made
* Successful match initiates events that activate the lymphocyte bearing the receptor
* Once activated
* B or T cell undergoes multiple cell ______
* Each activated cell proliferates as a **___** (identical to original)
* May become ____ cells which take effect immediately against antigen/pathogen producing the antigen
* Only a tiny fraction of antigen receptors are specific to a given epitope
* Antigen is presented to a steady stream of lymphocytes in the lymph nodes
* Continues until a match is made
* Successful match initiates events that activate the lymphocyte bearing the receptor
* Once activated
* B or T cell undergoes multiple cell ______
* Each activated cell proliferates as a **___** (identical to original)
* May become ____ cells which take effect immediately against antigen/pathogen producing the antigen
45
New cards
Plasma, Helper, Cytotoxic, Memory
**Proliferation of B and T cells**
* In B cells
* Effector forms
* ____ cells
* Secrete antibodies
* In T cells
* Effector forms
* ____ T cells
* _____ T cells
* ____ cells
* Long-lived cells which give rise to effector cells if the same antigen is encountered later on
* Clonal selection
* In B cells
* Effector forms
* ____ cells
* Secrete antibodies
* In T cells
* Effector forms
* ____ T cells
* _____ T cells
* ____ cells
* Long-lived cells which give rise to effector cells if the same antigen is encountered later on
* Clonal selection
46
New cards
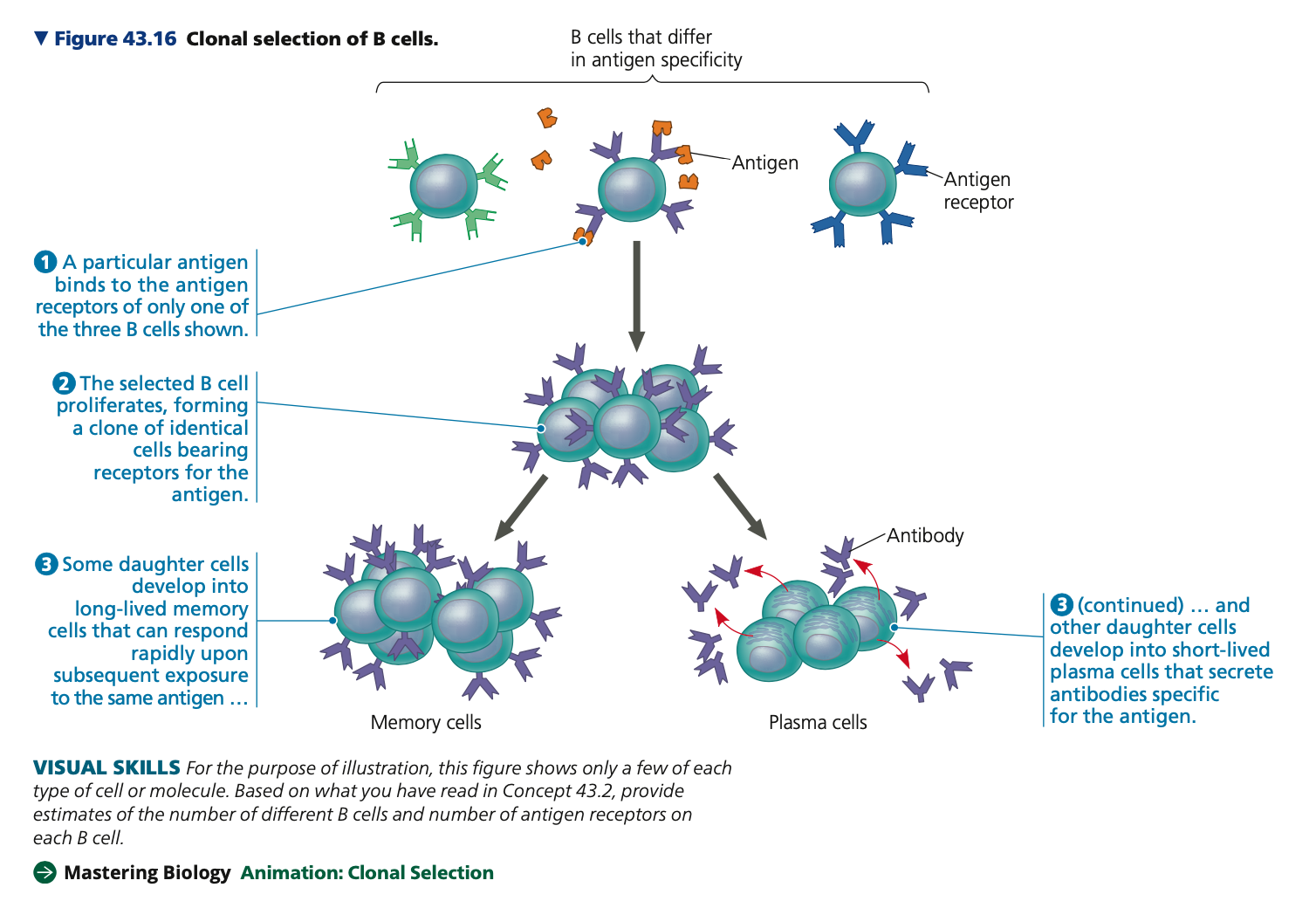
**Clonal selection**
➔ An encounter with an antigen selects which lymphocyte will divide to produce a clonal population of thousands of cells for a specific epitope
47
New cards
long, Speed, strength, duration
**Immunological memory**
* Responsible for ___-term protection that a prior infection provides
* Ex. chicken pox
* Noted by Greek historian Thucydides
* Individuals who had recovered from the plague could safely care for those who were sick/dying
* Prior exposure to antigen increases:
* _____
* ______
* ______
Of the immune response
1. Primary immune response
2. Secondary immune response
* Responsible for ___-term protection that a prior infection provides
* Ex. chicken pox
* Noted by Greek historian Thucydides
* Individuals who had recovered from the plague could safely care for those who were sick/dying
* Prior exposure to antigen increases:
* _____
* ______
* ______
Of the immune response
1. Primary immune response
2. Secondary immune response
48
New cards
10
1. **Primary immune response**
* Produced by effector cells formed by clones after initial exposure to antigen
* Peaks __-17 days after exposure
49
New cards
2, decades
2. **Secondary immune response**
* Produced if the same antigen is encountered again
* Peaks after _-7 days (faster)
* Greater magnitude, more prolonged
* Relies on reservoir of B and T memory cells generated upon initial exposure to antigen
* Long-lived cells provide bases for immunological memory
* Can span _____
* Second exposure to an antigen allows memory cells to enable rapid formation of clones
50
New cards
Infection Defense through Adaptive Immunity
* Activating adaptive immunity
* Response to extracellular pathogens
a. Activation of B cells
b. Antibody function
* Response to infected host cells
* Immunization
* Active & passive immunity
* Antibodies as tools
* Immune rejection
a. Blood groups
* Response to extracellular pathogens
a. Activation of B cells
b. Antibody function
* Response to infected host cells
* Immunization
* Active & passive immunity
* Antibodies as tools
* Immune rejection
a. Blood groups
51
New cards
Antibodies, lymph
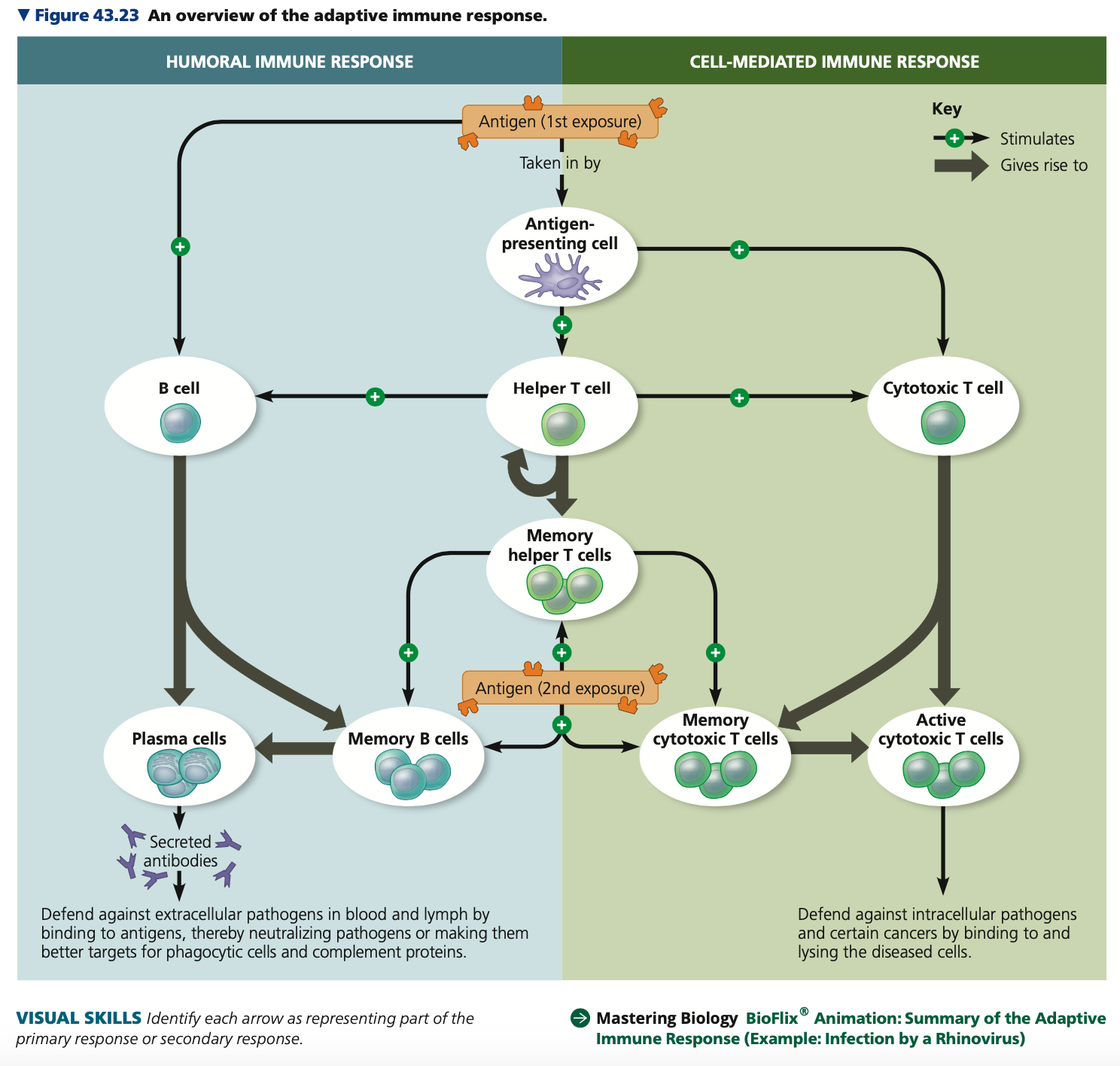
1. **Humoral immune response**
* ______ are secreted by effector cells to neutralize or eliminate toxins and pathogens
* Protects blood plasma and ____
52
New cards
Cytotoxic
2. **Cell-mediated immune response**
* ______ T cells destroy infected host cells
* Depends on direct action
\
* Both humoral and cell-mediated immunity can include primary or secondary immune responses
53
New cards
**presenting,** MHC, signature
**Activating adaptive immunity**
* **Helper T cell**
* Activates humoral and cell-mediated immune responses under two conditions:
1. An antigen that binds specifically to the
receptor of the helper T cell must be present
2. The antigen must be displayed on the surface
of an **antigen-_____ cell**
1. Can be a dendritic cell, macrophage,
or B cell
\
* Antigen-presenting cells vs. infected cells
* Both can display foreign antigens on surface, but:
* Only antigen-presenting cells have both class I and class II ___ molecules
* Most body cells have only class I MHC molecules
* Class II molecules provide a molecular _____ that allows an antigen-presenting cell to be recognized
* Helper T cells stimulate humoral and cell-mediated immunity
* **Helper T cell**
* Activates humoral and cell-mediated immune responses under two conditions:
1. An antigen that binds specifically to the
receptor of the helper T cell must be present
2. The antigen must be displayed on the surface
of an **antigen-_____ cell**
1. Can be a dendritic cell, macrophage,
or B cell
\
* Antigen-presenting cells vs. infected cells
* Both can display foreign antigens on surface, but:
* Only antigen-presenting cells have both class I and class II ___ molecules
* Most body cells have only class I MHC molecules
* Class II molecules provide a molecular _____ that allows an antigen-presenting cell to be recognized
* Helper T cells stimulate humoral and cell-mediated immunity
54
New cards
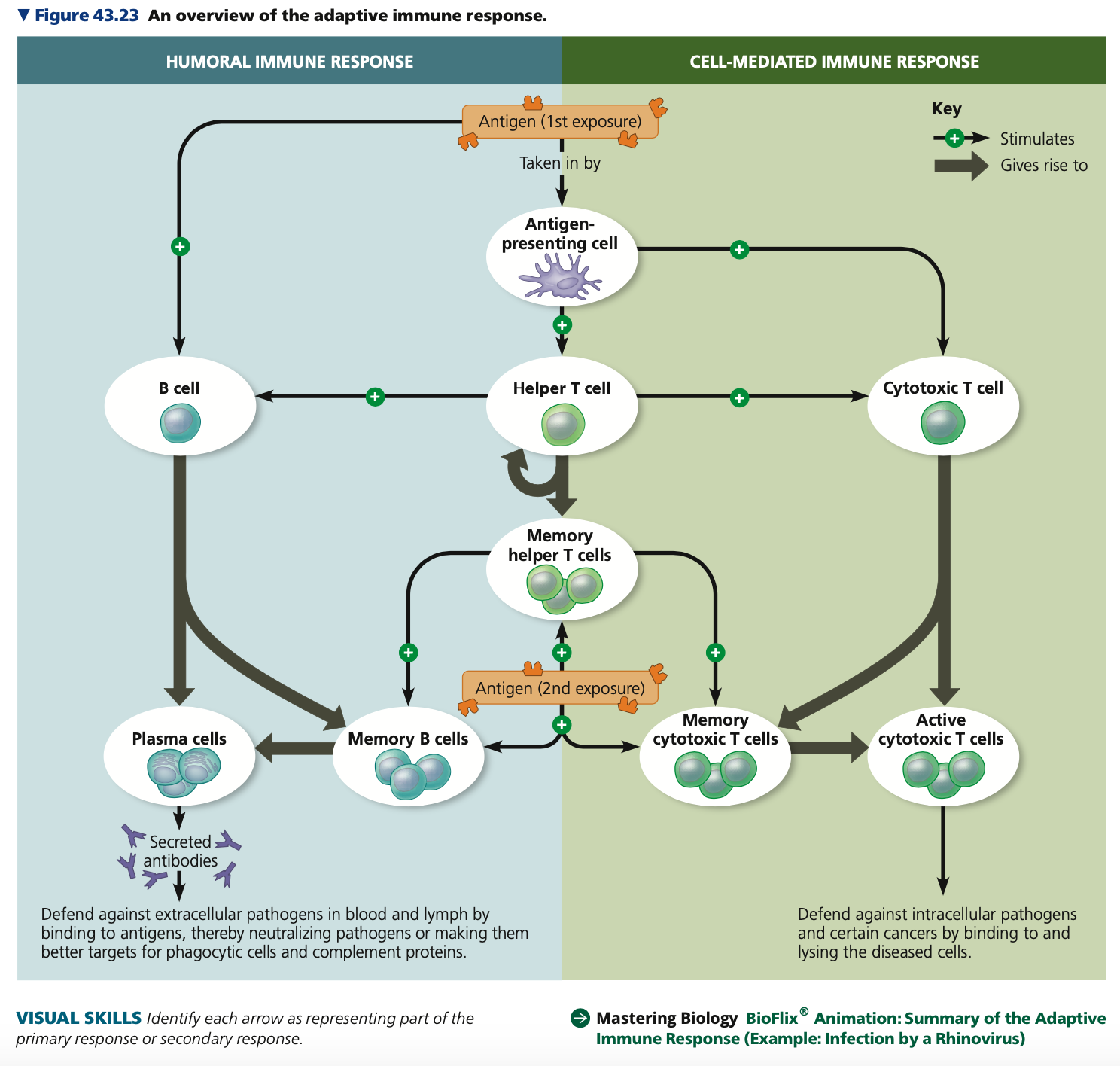
II, receptor, **CD4**
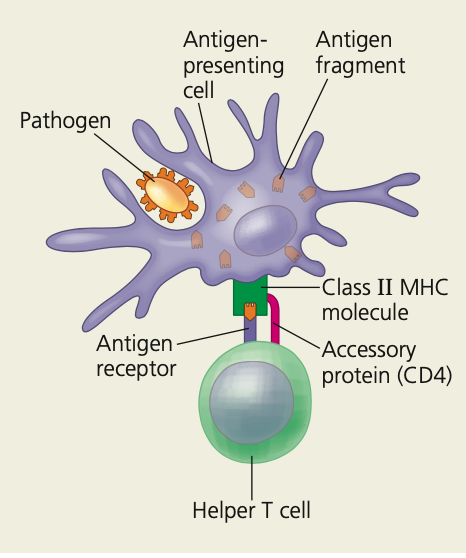
**The central role of helper T cells in humoral and cell-mediated immune responses.**
\
1. An antigen-presenting cell engulfs a pathogen, and degrades it
2. Antigen fragments complexed with Class _ MHC molecules are displayed on the cell surface
3. Antigen _____ on the surface of the helper T cell binds to the fragment-MHC complex
4. **___**, an accessory protein on the helper T cell surface binds to the class II MHC molecule
\
1. An antigen-presenting cell engulfs a pathogen, and degrades it
2. Antigen fragments complexed with Class _ MHC molecules are displayed on the cell surface
3. Antigen _____ on the surface of the helper T cell binds to the fragment-MHC complex
4. **___**, an accessory protein on the helper T cell surface binds to the class II MHC molecule
55
New cards
cytokine, proliferates
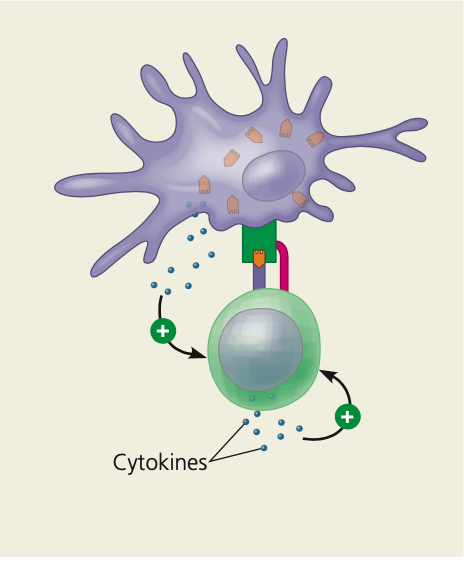
**The central role of helper T cells in humoral and cell-mediated immune responses.**
\
5. Binding of the helper T cell promotes ____ secretion by the antigen-presenting cell
6. These cytokines interact with cytokines from the helper T cell itself, activating the helper T cell
7. The activated helper ______
\
5. Binding of the helper T cell promotes ____ secretion by the antigen-presenting cell
6. These cytokines interact with cytokines from the helper T cell itself, activating the helper T cell
7. The activated helper ______
56
New cards
same, cytotoxic
**The central role of helper T cells in humoral and cell-mediated immune responses.**
\
8. All clones have receptors for the ____ antigen and secrete other cytokines
9. These cytokines help activate B cells and _____ T cells with the same antigen specificity
\
8. All clones have receptors for the ____ antigen and secrete other cytokines
9. These cytokines help activate B cells and _____ T cells with the same antigen specificity
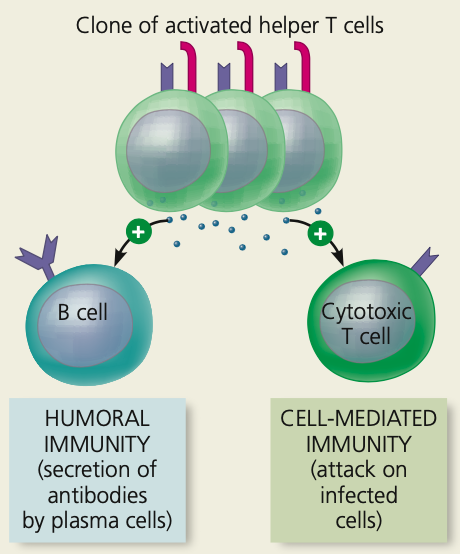
57
New cards
Humoral, B
**Response to extracellular pathogens**
* _____ immune response is characterized by secretion of antibodies by _ cells
a. Activation of B cells
b. Antibody function
* _____ immune response is characterized by secretion of antibodies by _ cells
a. Activation of B cells
b. Antibody function
58
New cards
Macrophage, dendritic, B, II, differentiates, memory, plasma
**Activation of B cells**
1. ___ __or__ ____cell activates helper T cell (see process above)
2. Helper T cell activates a __ cell
1. B cell with receptors for the same
epitope internalize the antigen
2. An antigen fragment is displayed on
the B cell surface in complex with a
class __ MHC molecule
3. An activated helper T cell binds to the complex and activates the B cell
3. B cell ______ into antibody-secreting plasma
1. The activated B cell proliferates
2. It differentiates into _____ B cells
and antibody-secreting ____ cells
3. Antibodies secreted by plasma cells
are specific to the same antigen that first initiated the response
1. ___ __or__ ____cell activates helper T cell (see process above)
2. Helper T cell activates a __ cell
1. B cell with receptors for the same
epitope internalize the antigen
2. An antigen fragment is displayed on
the B cell surface in complex with a
class __ MHC molecule
3. An activated helper T cell binds to the complex and activates the B cell
3. B cell ______ into antibody-secreting plasma
1. The activated B cell proliferates
2. It differentiates into _____ B cells
and antibody-secreting ____ cells
3. Antibodies secreted by plasma cells
are specific to the same antigen that first initiated the response
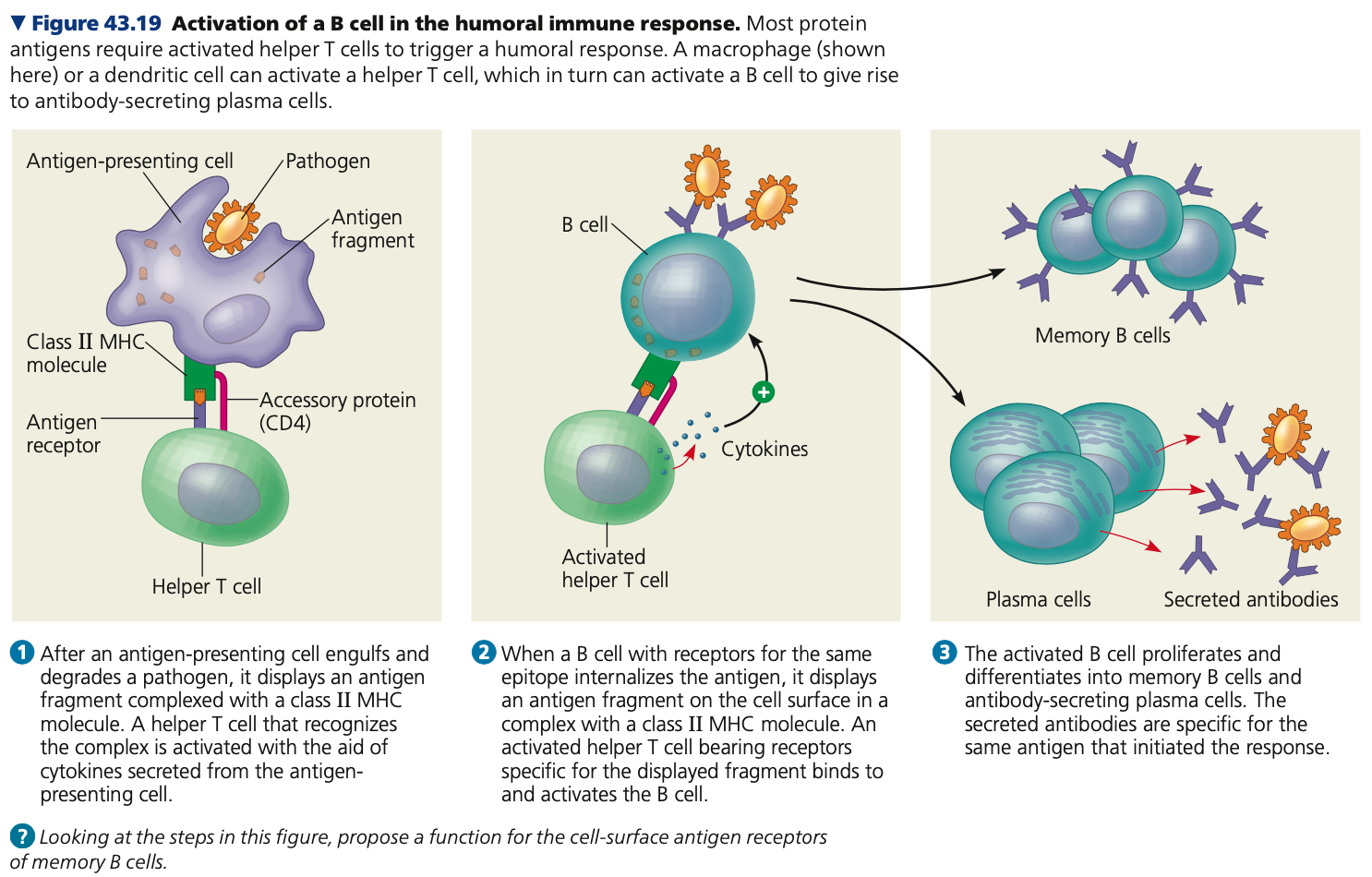
59
New cards
activity, mark
**Antibody function**
* Do not directly kill pathogens
* When antibodies bind to antigens, they interfere with pathogenic ____ or ____ pathogens for inactivation or destruction
1. **Neutralization**
2. **Opsonization**
* Do not directly kill pathogens
* When antibodies bind to antigens, they interfere with pathogenic ____ or ____ pathogens for inactivation or destruction
1. **Neutralization**
2. **Opsonization**
60
New cards
bind
1. **Neutralization**
* When antibodies ___ to proteins on the surface of a virus
* Bound antibodies prevent viral infection, neutralizing the virus
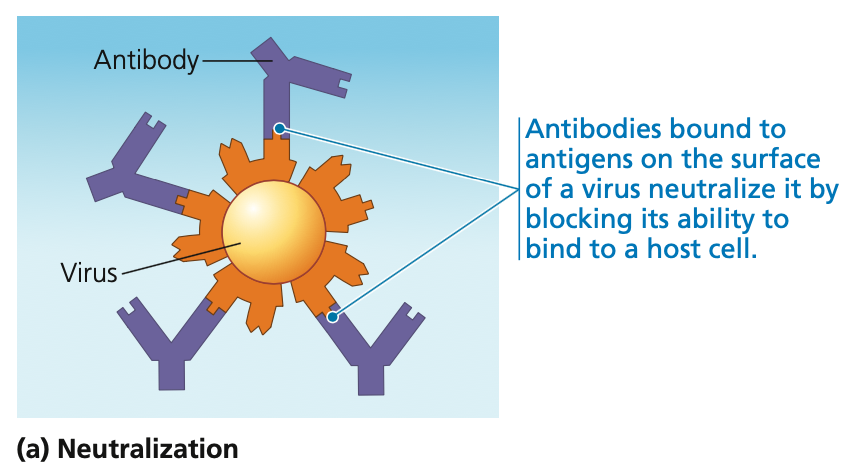
61
New cards
phagocytosis
2. **Opsonization**
* Antibodies promote ______ by presenting a recognized structure to macrophages or neutrophils
* With the other antigen-binding site, antibodies directly facilitate phagocytosis by aggregating bacterial cells, viruses, and other foreign substances
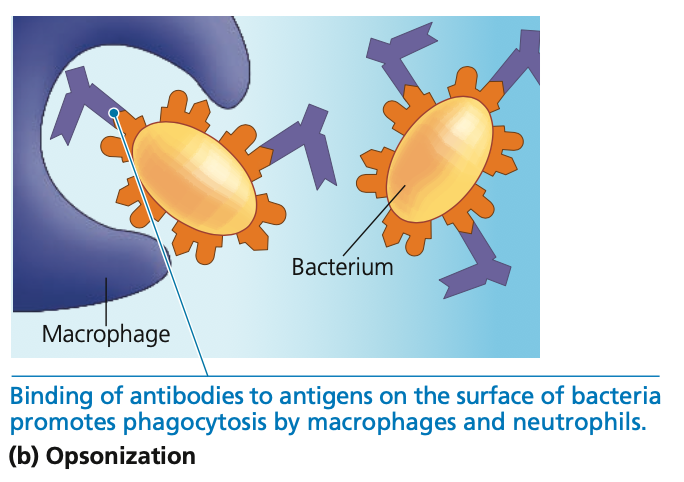
62
New cards
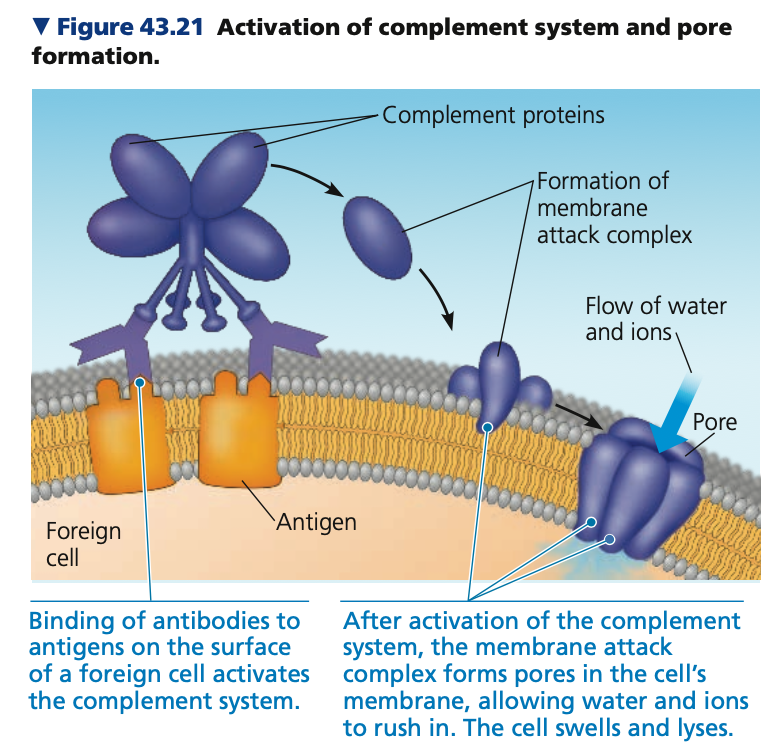
proteins, complement, bacteria, attack, pores,
**Antibody function**
* Antibodies work together with ___ of the ____ system
* Proteins that add to the effectiveness of antibody-directed attacks on _____
1. Complement protein binds to an antigen-antibody complex on a foreign cell, forming a **membrane _____ complex**
2. The membrane attack complex forms ___ in the cell membrane, allowing water and ions to rush in
3. The cell swells and _____
* Antibodies work together with ___ of the ____ system
* Proteins that add to the effectiveness of antibody-directed attacks on _____
1. Complement protein binds to an antigen-antibody complex on a foreign cell, forming a **membrane _____ complex**
2. The membrane attack complex forms ___ in the cell membrane, allowing water and ions to rush in
3. The cell swells and _____
63
New cards
natural, apoptosis, 5, heavy, C, IgD
**Antibody function**
* Antibodies can cause death of infected body cells
* The presence of bound antibodies at
the cell surface can recruit ______
killer cells
* Natural killer cells release proteins that cause the infected cell to undergo _____
* B cells can express _ classes of
immunoglobulin: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM
* Each has an identical
antigen-binding specificity, but:
* A distinct ____-chain _ region
* __ is exclusively membrane bound, but other classes have soluble forms (e.g. antibodies in blood, tears, breast milk)
* Antibodies can cause death of infected body cells
* The presence of bound antibodies at
the cell surface can recruit ______
killer cells
* Natural killer cells release proteins that cause the infected cell to undergo _____
* B cells can express _ classes of
immunoglobulin: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM
* Each has an identical
antigen-binding specificity, but:
* A distinct ____-chain _ region
* __ is exclusively membrane bound, but other classes have soluble forms (e.g. antibodies in blood, tears, breast milk)
64
New cards
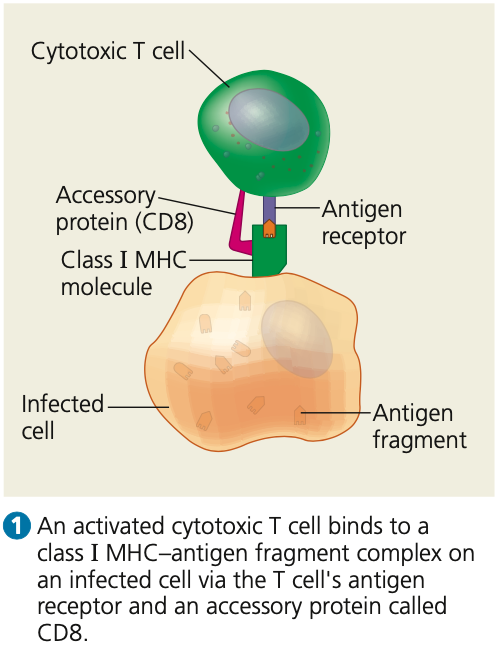
proteins, cytotoxic, I, **CD8**
**Response to infected host cells**
* In cell-mediated immune response, cytotoxic T cells use toxic _____ to kill cells infected by viruses or other intracellular pathogens before pathogens fully mature
\
1. An activated _____ T cell binds to a class _ MHC-antigen fragment complex
2. **___**, an accessory protein, binds to the class I MHC molecule
* In cell-mediated immune response, cytotoxic T cells use toxic _____ to kill cells infected by viruses or other intracellular pathogens before pathogens fully mature
\
1. An activated _____ T cell binds to a class _ MHC-antigen fragment complex
2. **___**, an accessory protein, binds to the class I MHC molecule
65
New cards
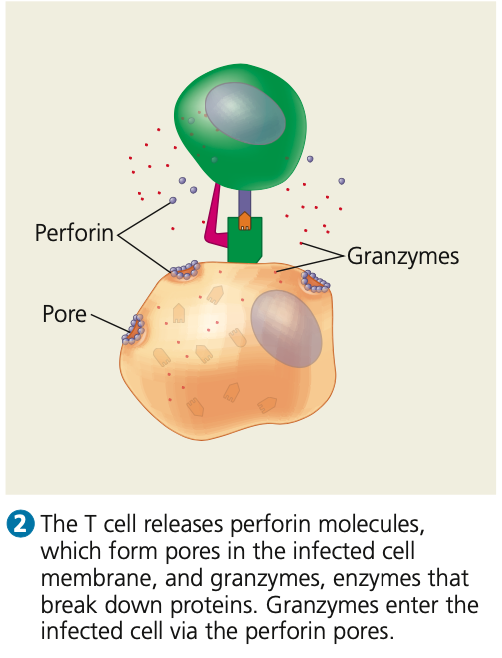
perforin, granzymes
**Response to infected host cells**
\
3. The T cell secretes **____ molecules**, which form pores in the infected cell membrane, and:
4. Secretes **_____**, enzymes that break
down proteins
5. Granzymes enter the infected cell via the
perforin pores
\
3. The T cell secretes **____ molecules**, which form pores in the infected cell membrane, and:
4. Secretes **_____**, enzymes that break
down proteins
5. Granzymes enter the infected cell via the
perforin pores
66
New cards
apoptosis, released
**Response to infected host cells**
\
6. Granzymes initiate _____, causing fragmentation of nucleus and cytoplasm, and eventual cell death
7. The cytotoxic T cell is _____, allowing it to attack other infected cells
\
6. Granzymes initiate _____, causing fragmentation of nucleus and cytoplasm, and eventual cell death
7. The cytotoxic T cell is _____, allowing it to attack other infected cells
67
New cards
**vaccination,** Jenner, Inactivated, weakened, genes
**Immunization**
* Use of artificially-introduced antigens to generate an adaptive immune response and memory cell formation
* Also called **_______**
\
* First documented immunization: Edward ____, 1796
* Mild cowpox virus used to induce adaptive immunity against dangerous smallpox virus
* Vaccines used today may be made from:
* _____ bacterial toxins
* Killed or _____ pathogens
* ___ encoding microbial proteins
* Vaccination has been successful in:
* Eradicating smallpox
* Reducing polio and measles
incidence
* Use of artificially-introduced antigens to generate an adaptive immune response and memory cell formation
* Also called **_______**
\
* First documented immunization: Edward ____, 1796
* Mild cowpox virus used to induce adaptive immunity against dangerous smallpox virus
* Vaccines used today may be made from:
* _____ bacterial toxins
* Killed or _____ pathogens
* ___ encoding microbial proteins
* Vaccination has been successful in:
* Eradicating smallpox
* Reducing polio and measles
incidence
68
New cards
response
1. **Active immunity**
* Defenses that arise when a pathogen infection or immunization prompts an immune _____
69
New cards
IgA
2. **Passive immunity**
* Antibodies in recipient are produced
by another individual
* E.g. ___ antibodies in breast milk are passed from mother to fetus
* Provide immunity in infant’s digestive tract while infant’s immune system develops
70
New cards
antivenin
**Artificial passive immunization**
* Antibodies from an immune animal are injected into a nonimmune animal
* E.g. Humans bitten by venomous snakes are treated with _____
* Serum from sheep or horses that have been immunized against snake venom
* Antibodies from an immune animal are injected into a nonimmune animal
* E.g. Humans bitten by venomous snakes are treated with _____
* Serum from sheep or horses that have been immunized against snake venom
71
New cards
**Monoclonal, B,** chorionic, gonadotropin
**Antibodies as tools**
* **______ antibodies**
* Antibodies produced from a single clone of _ cells grown in culture
* are used in medical diagnosis and treatment
* E.g. Home pregnancy kits use monoclonal antibodies to detect human ___ _______ (hCG), which is produced as soon as an embryo implants in the uterus
* Also used for cancers
* **______ antibodies**
* Antibodies produced from a single clone of _ cells grown in culture
* are used in medical diagnosis and treatment
* E.g. Home pregnancy kits use monoclonal antibodies to detect human ___ _______ (hCG), which is produced as soon as an embryo implants in the uterus
* Also used for cancers
72
New cards
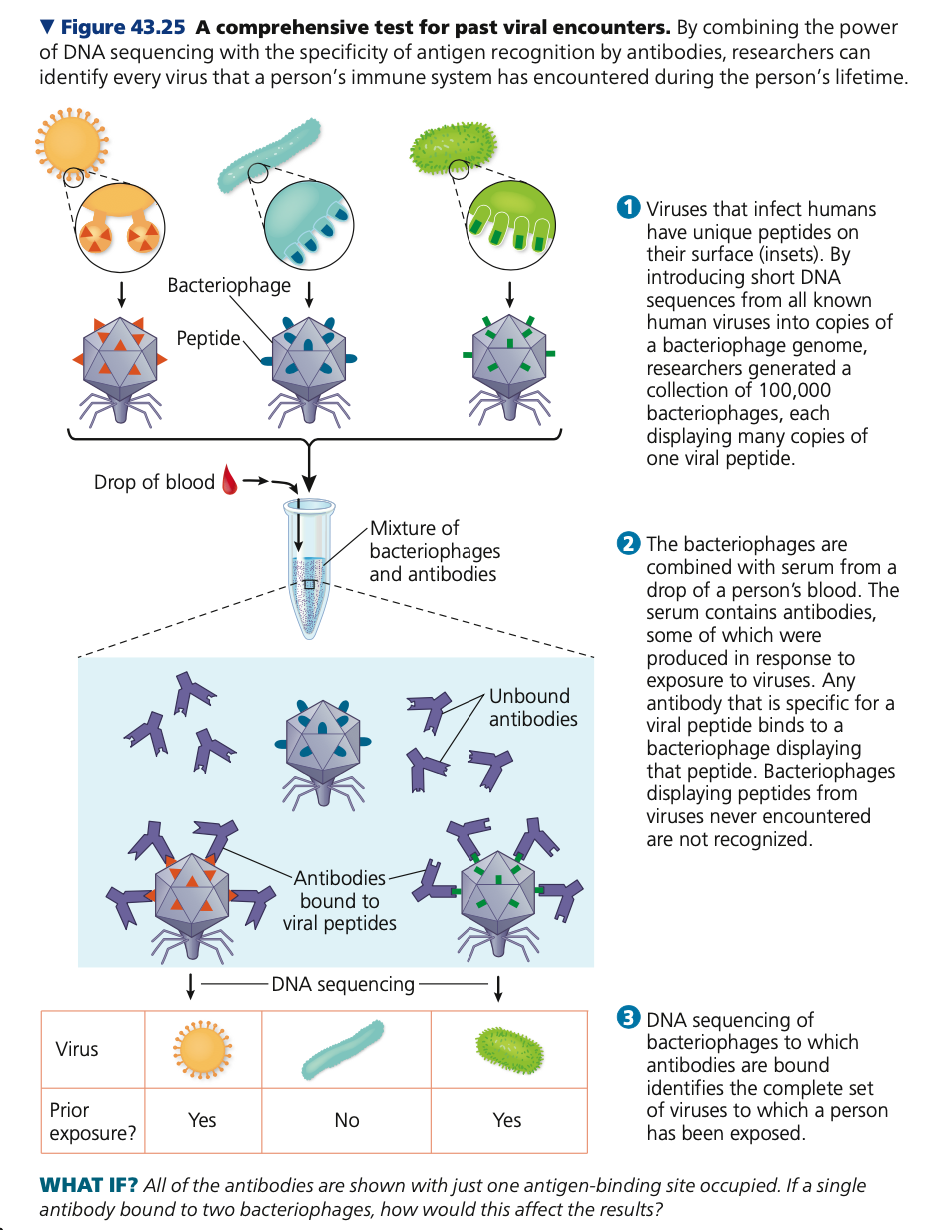
**insets,** bacteriophage, antibodies, bound
**Antibodies as tools**
* A single drop of blood can be used to identify
every virus that a person has encountered
\
1. Viruses that infect humans have unique peptides (**____**) on their surface
2. Short DNA sequences from all known human viruses were introduced into copies of a ________ genome
3. This generated a collection of 100,000 bacteriophages, each displaying many copies of one viral peptide
4. Bacteriophages were combined with serum from a drop of the person’s blood
5. The serum contains ______, some produced in response to virus exposure
6. Any antibody specific to a peptide binds to bacteriophage displaying that peptide
7. DNA of bacteriophages _____ to antibodies is sequenced, and set of viruses person has been exposed to identified
* A single drop of blood can be used to identify
every virus that a person has encountered
\
1. Viruses that infect humans have unique peptides (**____**) on their surface
2. Short DNA sequences from all known human viruses were introduced into copies of a ________ genome
3. This generated a collection of 100,000 bacteriophages, each displaying many copies of one viral peptide
4. Bacteriophages were combined with serum from a drop of the person’s blood
5. The serum contains ______, some produced in response to virus exposure
6. Any antibody specific to a peptide binds to bacteriophage displaying that peptide
7. DNA of bacteriophages _____ to antibodies is sequenced, and set of viruses person has been exposed to identified
73
New cards
MHC, alleles, proteins, immunosuppressants
**Immune rejection**
* Cells from another person can be recognized as foreign and attacked by immune defenses
* Rejection caused by ___ molecules
* MHC proteins are expressed from
different MHC
* Each MGC gene has more than 100
different versions (_____)
* MHC _____ on cell surfaces are
likely to differ between two people,
except identical twins
* Preventing rejection
* Surgeons use donor tissue bearing MHC molecules matching those of the recipient as closely as possible
* Recipient takes _________
* Cells from another person can be recognized as foreign and attacked by immune defenses
* Rejection caused by ___ molecules
* MHC proteins are expressed from
different MHC
* Each MGC gene has more than 100
different versions (_____)
* MHC _____ on cell surfaces are
likely to differ between two people,
except identical twins
* Preventing rejection
* Surgeons use donor tissue bearing MHC molecules matching those of the recipient as closely as possible
* Recipient takes _________
74
New cards
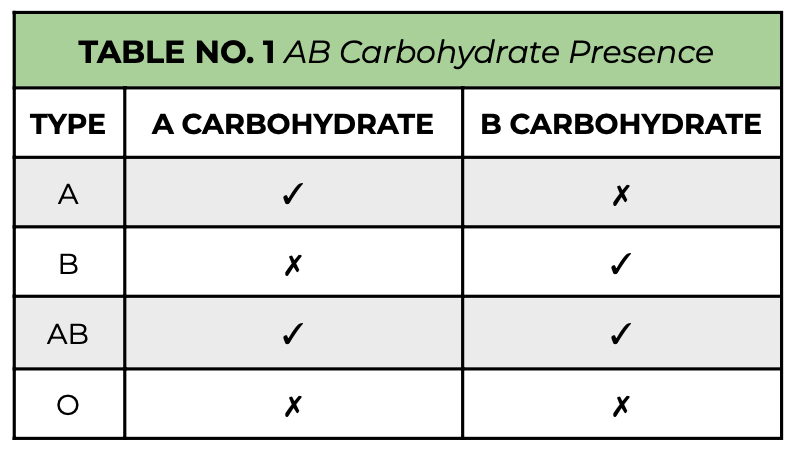
glycoproteins, bacteria, own, O
**Blood groups**
* Recipient can recognize _______ on blood cell surface as foreign, so ABO groups must be taken into account
* People are frequently exposed to ____ that have epitopes similar to carbohydrates on blood cells
* E.g. A person with type A blood will make antibodies against a bacterial epitope similar to a B carbohydrate, and:
* These antibodies react to B carbohydrates upon transfusion
* That person does not make antibodies against the bacterial epitope similar to the A carbohydrate because:
* Lymphocytes do not react with body’s ___ cells
* Type __ people cannot receive any other blood type because they have antibodies against A and B carbohydrates, but can donate to any other blood type
* Recipient can recognize _______ on blood cell surface as foreign, so ABO groups must be taken into account
* People are frequently exposed to ____ that have epitopes similar to carbohydrates on blood cells
* E.g. A person with type A blood will make antibodies against a bacterial epitope similar to a B carbohydrate, and:
* These antibodies react to B carbohydrates upon transfusion
* That person does not make antibodies against the bacterial epitope similar to the A carbohydrate because:
* Lymphocytes do not react with body’s ___ cells
* Type __ people cannot receive any other blood type because they have antibodies against A and B carbohydrates, but can donate to any other blood type
75
New cards
**Disruptions in Immune System Function**
* Exaggerated, self-directed, and diminished immune responses
a. Allergies
b. Autoimmune diseases
c. Exertion and stress
d. Immunodeficiency diseases
* Evolutionary adaptions of pathogens
a. Antigenic variation
b. Latency
c. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
* Cancer and immunity
a. Allergies
b. Autoimmune diseases
c. Exertion and stress
d. Immunodeficiency diseases
* Evolutionary adaptions of pathogens
a. Antigenic variation
b. Latency
c. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
* Cancer and immunity
76
New cards
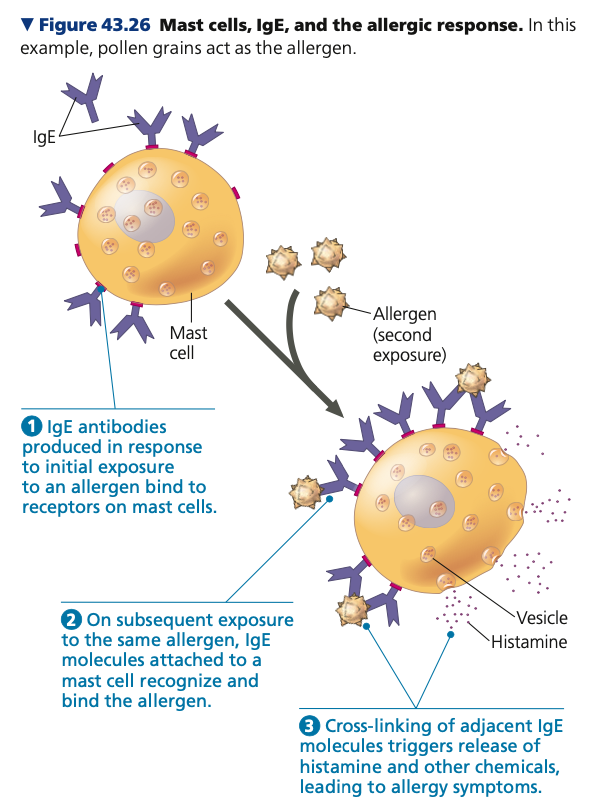
allergens, IgE, Plasma, mast, histamine
**Allergies**
* Exaggerated (hypersensitive) responses to antigens called ______
* Most commonly involve ___ class antibodies
* Process of hay fever
1. _____ cells secrete IgE antibodies specific for antibodies on the surface of pollen grains
1. Some IgE antibodies are bound by their base to mast cells in connective tissues
2. Pollen grains that enter the body attach to
IgE antibodies
3. Adjacent IgE molecules are cross-linked, inducing the ____cell to release ____ and other inflammatory chemicals
4. These chemicals bring about allergy symptoms (e.g. sneezing, runny nose, teary eyes, smooth muscle contractions that inhibit breathing)
* Exaggerated (hypersensitive) responses to antigens called ______
* Most commonly involve ___ class antibodies
* Process of hay fever
1. _____ cells secrete IgE antibodies specific for antibodies on the surface of pollen grains
1. Some IgE antibodies are bound by their base to mast cells in connective tissues
2. Pollen grains that enter the body attach to
IgE antibodies
3. Adjacent IgE molecules are cross-linked, inducing the ____cell to release ____ and other inflammatory chemicals
4. These chemicals bring about allergy symptoms (e.g. sneezing, runny nose, teary eyes, smooth muscle contractions that inhibit breathing)
77
New cards
Antihistamines
Block histamine receptors, diminishing allergy symptoms
78
New cards
**Anaphylactic shock**
* Life-threatening reaction caused by an acute allergic response
* Happens when inflammatory
chemicals trigger **bronchial constriction** and **dilation of peripheral blood vessels**
* This results in a drop in blood pressure and an inability to breathe
* Happens when inflammatory
chemicals trigger **bronchial constriction** and **dilation of peripheral blood vessels**
* This results in a drop in blood pressure and an inability to breathe
79
New cards
**Epinephrine autoinjector (EpiPen)**
* Carried by people with severe allergies
* Counteracts allergic response by **constricting peripheral blood vessels**, **reducing swelling in the throat,** and relaxing muscles in **lungs**
* Counteracts allergic response by **constricting peripheral blood vessels**, **reducing swelling in the throat,** and relaxing muscles in **lungs**
80
New cards
tolerance, lupus, beta, Myelin
**Autoimmune disease**
* Immune system is active against particular molecules of the body
* Loss of self-_______
* E.g. systemic ___ erythematosus (lupus)
* Immune system generates antibodies against histones and DNA released by normal breakdown of body cells
* Causes skin rashes, fever, arthritis, and kidney dysfunction
* Other targets include:
* Pancreas ____ cells (type 1 diabetes)
* ____ sheaths (multiple sclerosis)
* Immune system is active against particular molecules of the body
* Loss of self-_______
* E.g. systemic ___ erythematosus (lupus)
* Immune system generates antibodies against histones and DNA released by normal breakdown of body cells
* Causes skin rashes, fever, arthritis, and kidney dysfunction
* Other targets include:
* Pancreas ____ cells (type 1 diabetes)
* ____ sheaths (multiple sclerosis)
81
New cards
\
Heredity, gender, environment
Heredity, gender, environment
* Susceptibility to autoimmune diseases is influenced by:
1. _____
* Same family → increased susceptibility
2. _____
* Many diseases affect females more often
* E.g. women are 9x more likely than men to have lupus
3. Environment
1. _____
* Same family → increased susceptibility
2. _____
* Many diseases affect females more often
* E.g. women are 9x more likely than men to have lupus
3. Environment
82
New cards
**Tregs,** self
**Regulatory T cells (___)**
* Specialized T cells that modulate immune system activity and prevent response to ___-antigens
* Focus of research on autoimmune disorders
* Specialized T cells that modulate immune system activity and prevent response to ___-antigens
* Focus of research on autoimmune disorders