Neurology For Exam 1 (Reduced Version)
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
almost all cranial nerve content was removed
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Where are the ventricles located?
in the subcortex
what many ventricles do we have
4 total
2-lateral
1-thirds that connects the two lateral onces
1-between the cerebellum and the brainsteam
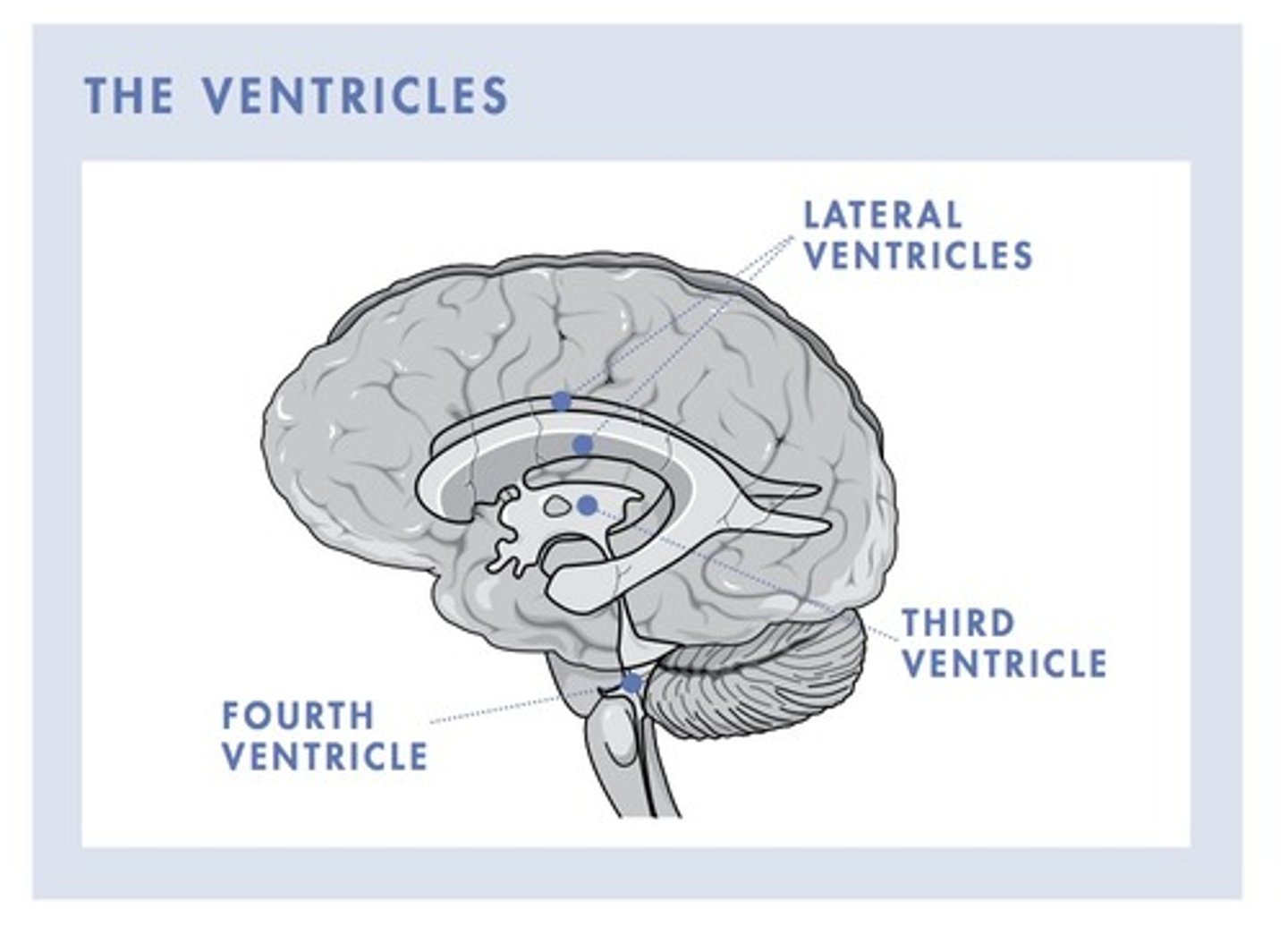
what are ventricles filled with
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Basal ganglia
collection of 5 nuclei that influences movement (does not cause it)
where is the basal ganglia located
deep in the cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem
where does the basal ganglia receive information from
the cortex
direct pathway of basal ganglia
responsible for making all volunary movements
relys on dopamine to excite
basal ganglia is less involved (simplar)
indirect pathway of basal ganglia
responsible for preventing unwanted movements from hindering voluntary movements
relies on dopamine to supress movements
basal ganglia is more involved (complex)
what other structure does the basal ganglia inhibit
thalamus (limits its encouragment of movements)
3 key parts of the limbic system
cingulate gyrus
amygdala
hippocampus
what is the purpose of the limbic system
motivtation, emotional behavor, sexual drive, long term memory formation and retreival
what is the purpose of the cingulate gyrus
connects emotions with actions
Bridge between limbic system to frontal lobe
what is the purpose of the amygdala
fear and anxiety processing center
what is the purpose of the hippocampus
file clerk of memory, filling new inforamtion and retreving old memories, attention, and navigation throughout space
cortical spinal tract
on the top part of the cortex
contralateral
one nerve controls each specific movement
cortical bulbar tract
on the side of the cortex
bilateral
more protective since two nerouns control each thing
where is prodecural memory located
basal ganglia
what disease affects the hippocampus
Alzheimer's
cingulate gyrus
carries the limbic system's informaiton to the prefrontal cortex
what is another name for the cerebellum
little brain
what is the primary job of the cerebellum
smooth and accurate movements
what is the secondary job of the cerebellum
cognition, motor skills, language, attention, and emotional regulation
where is the location of the cerebellum
in the skull base (posterior cranial fossa)
below cerebrum
posterior to the brain stem (by the 4th ventricle)
what does the cerebellum detect
errors in movement
Is the cerebellum ipsilateral or contralateral?
ipsilateral
it has two hemispheres
no crossing over (the left hemisphere controls the left foot)
what are the three steps in the cerebellum motor plan
1) receives the motor plan (input)
2) provided with correct proprioception information from the body (input)
3) carries out adjustments/corrections to the motor plan (output to the cortex)
signs of damage of the cerebellum
ataxia, nystagmus, tremor, dizziness, dysdiadokinesis, dysarthria, dysmetria
causes of cerebellar decline
degenerative diseases, tumor, trauma, stroke
what is the difference between the cerebellum and the basal ganglia
cerebellum: controls ongoing adjustments, revision of the motor plan to achieve a smooth and accurate result
basal ganglia: controls timing and initiation of direct and indirect muscles/movements
what does innervation mean
bringing nervous energy to muscles
contralateral innervation
providing innervation to the opposite side of the body (decussation)
bilateral innervation
providing innervation to both sides of the body
corticospinal tract
decussates in the lower medulla at a location called the pyramids
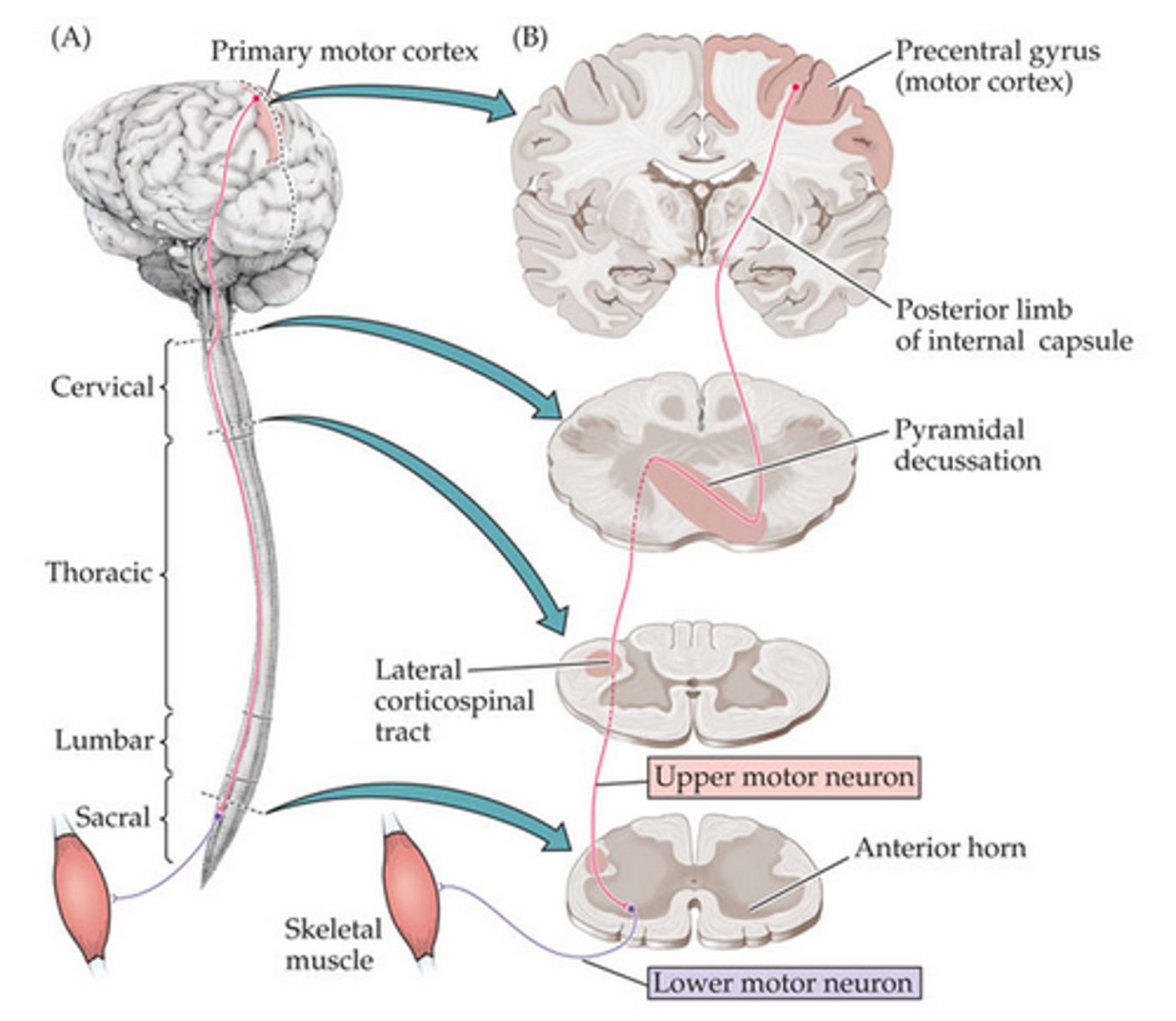
what is the pathway of the cortiocspinal tract
message starts in the specific hemisphere, then it travels on the corticospnal tract until it gets to the medulla where it decussates before going to the spinal cord
then it synapese with a specific motor neuron
corticobulbar tract
decussates just above the point of synapses with a cranical nerve
more complex (redundant than the corticospinal tract)
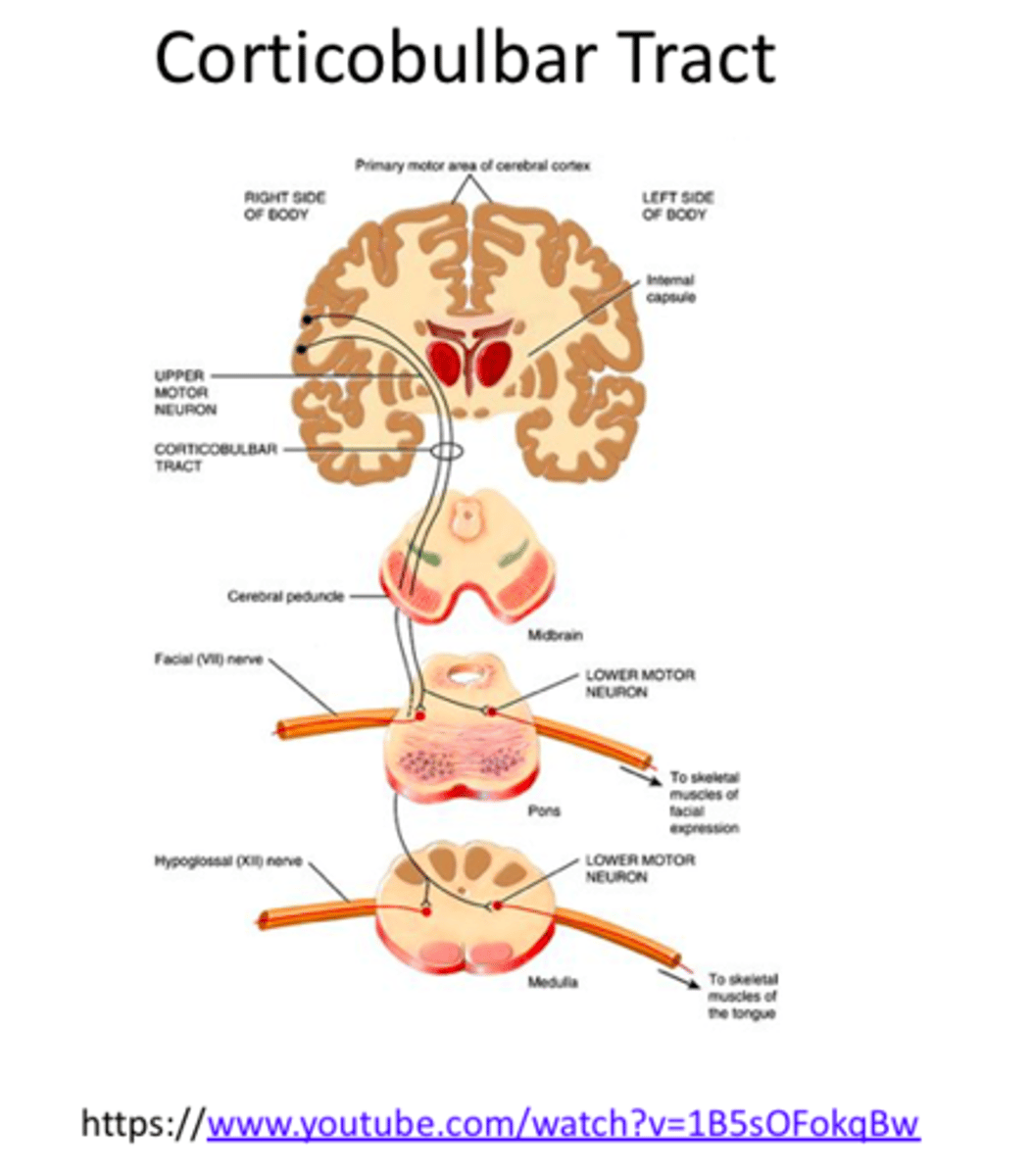
what is the pathway of the corticobulbar tract
lower part of the motor strip enters the specific part of the brainstem, part of the nerve goes left, some goes right (bilateral)
what 4 roles does the brainstem have
1) connects the brain to the body
2) the place where our PNS and CNS connect
3) connect the cerebellum to the rest of the body
4) controls our heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, swallowing, and alertness
Key parts of the midbrain
superior cerebellar peduncles
corticospinal and bulbar tracts
cerebral aquduct
CN III and CN IV
Substantia Nigra
Reticular formation
Key parts of the Pons
Middle cerebellar peduncles
cortiospinal and bulbar tract
CN V, VI, VII, VIII
Recticular formation
Key parts of the Medulla
inferior cerebellar peduncles
corticospinal and bulbar (some) tract
CN IX, X, XI, XII
Pyramids
point of decussation for corticospinal tract
recticular formation
are cranial nerves bilaterally innervatted
yes