Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Malarial parasites
reproduce sexually inside mosquito
reproduce asexually inside human

Fungi
genetically identical spores by asexual reproduction
sexually produced spores to introduce variation and increase chances of survival in case of environmental change

Plants
reproduce sexually(egg cells and pollen) to give seeds
reproduce asexually
strawberries send out runners
daffodils grow identical bulbs
Features of asexual reproduction
only one parent
offspring are genetically identical/clones to parent
No variation
Mitosis
Features of sexual reproduction
Two parents
Offspring are genetically different
Variation
Gametes produced by meiosis
Process of sexual reproduction
Gametes(egg and sperm) with 23 chromosomes fuse together to form a new zygote with 46 chromosomes
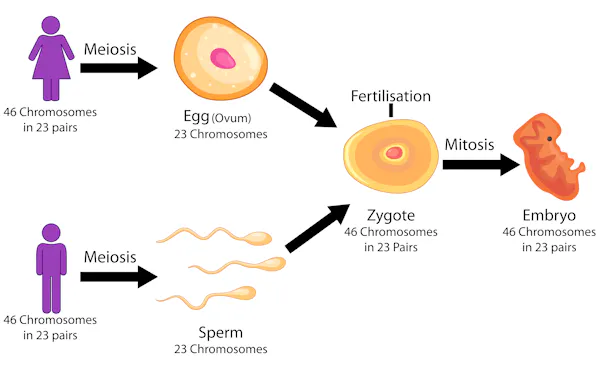
Mitosis
gives genetically identical cells
growth, repair of tissues, and asexual reproduction
Meiosis
gives genetically different cells
producing gametes
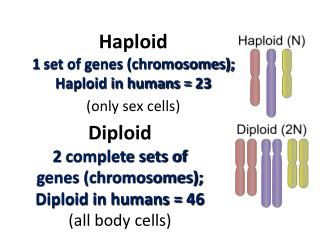
DIPloid vs. HAPloid
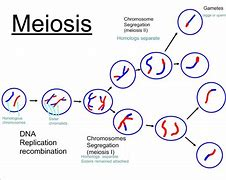
Stages of meiosis
DNA is replicated
The pairs of chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell
The pairs are pulled apart
Two new cells are formed, each with one copy of each chromosome, some form each parent cell
In each cell, the chromosomes line up along the centre again
The arms of the chromosomes are pulled apart
Four gametes are formed which contain half the number of chromosomes
What happens after fertilisation?
cell divides by mitosis
cells differentiate to give rise to specialised cells
Advantages of sexual reproduction
there is variation in the offspring
this increases their chance of survival in case of a change in environment due to variety of alleles
they will survive to reproduce successfully and pass on alleles due to natural selection
Advantages of asexual reproduction
only one parent needed
uses less energy since organisms don’t need to find a mate
faster
identical offspring so favourable in crop production