Economics Exam Revision
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microeconomics, Macroeconomics & Globalization
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Definition of economics
The study of society’s optimal use of scarce resources (land, labour capital)
Needs
Things necessary for survival
Wants
things that are desired but not essential
Economic resources
land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship skills
Land
natural resources (water, soil, trees)
Labour
human resources (employees)
Capital
man-made resources (machinery)
Entrepreneurship Skills
skill and talent to combine the other resources (factory owner)
Opportunity cost
The cost forgone of the next best option when the best option is selected
Objective of consumers
to maximise their own economics welfare (satisfaction or utility)
Objective of firms
to maximise their profits
Objective of government
to maximise the welfare of their citizens
Types of economic systems
traditional, capitalism, planned, mixed
Traditional economic system
self-sufficient, barter, exchange of goods and services
Capitalism economic system
people are free to choose the way they will allocate their resources to gain the highest return
Planned economic system
decisions in regard to resource allocation are made by a central planning agency (e.g. Cuba)
Mixed
some elements of both planned a capitalist (e.g. China)
Basic economic questions
How will it be produced?
What will be produced?
For whom will it be produced for?
Definition of market
Where goods and services are bought and sold at prices negotiated between the buyer and seller. Markets attempt to solve the economic problem by allocating scarce resources to meet wants.
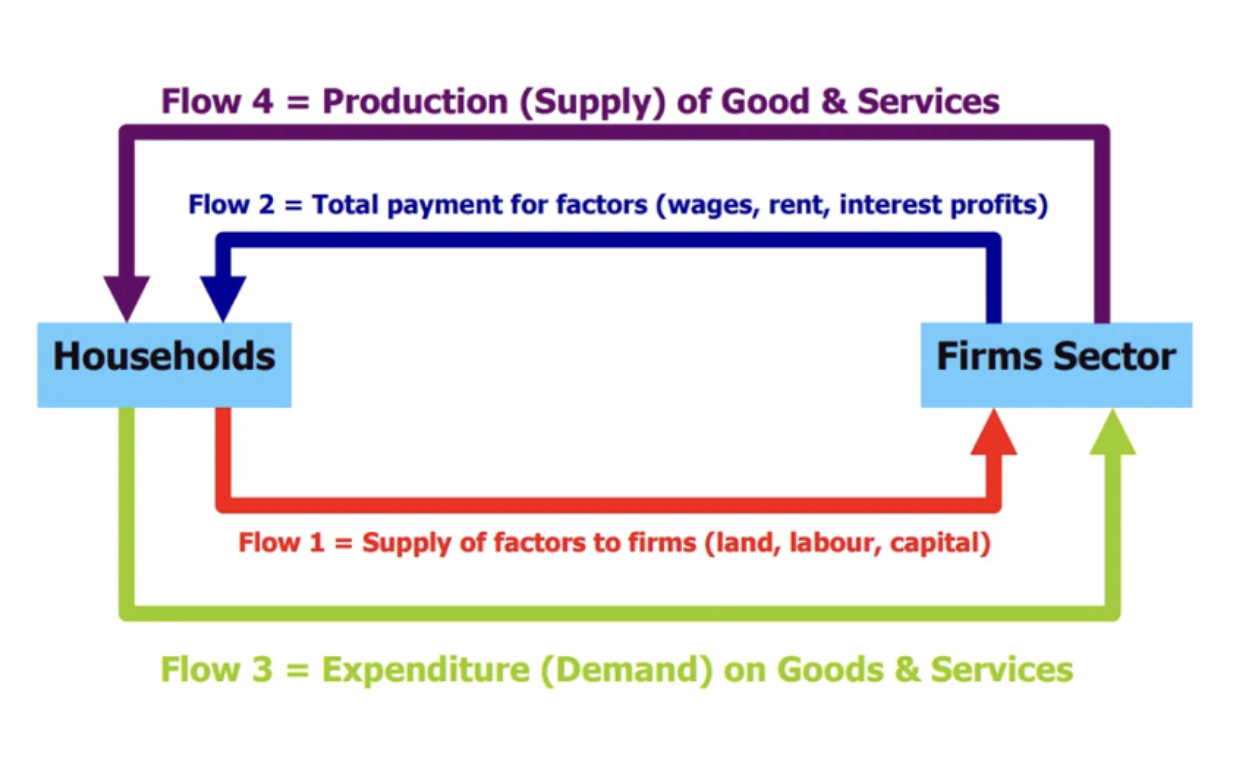
Circular flow of income
Assumption of perfect competition
All people act in a rational manner to maximise their standard of living
There are many buyers in the market, and there are many sellers
Products can only be distinguished by price
Buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge of the market
Resources are perfectly interchangeable
There is no government intervention
The law of demand
As price decreases, demand increases
Definition of demand
Demand refers to the consumer's willingness and ability to purchase a good or service at a given price over a given time.
The law of supply
As prices increase, supply will increase
Definition of supply
Supply refers to the quantity of goods/services
Intersection of supply and demand
The intersection of the demand and supply is equilibrium. This is where the supply is equal to the demand. Surplus is when the price is above the equilibrium price. Shortage is when the price is below the equilibrium price.
Non price factors of demand
taste, preference, fashion
Non price factors of supply
producers preference, level of technology, seasonal influence
Price factors of supply
price of other goods, taxes, cost of production
Price factors of demand
price of substitute goods, price of compliments, income
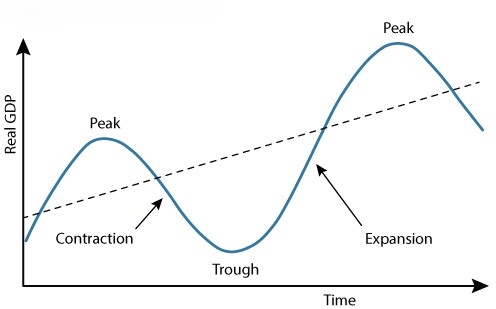
Shift left of the curve
Contraction
Shift right of the curve
Expansion
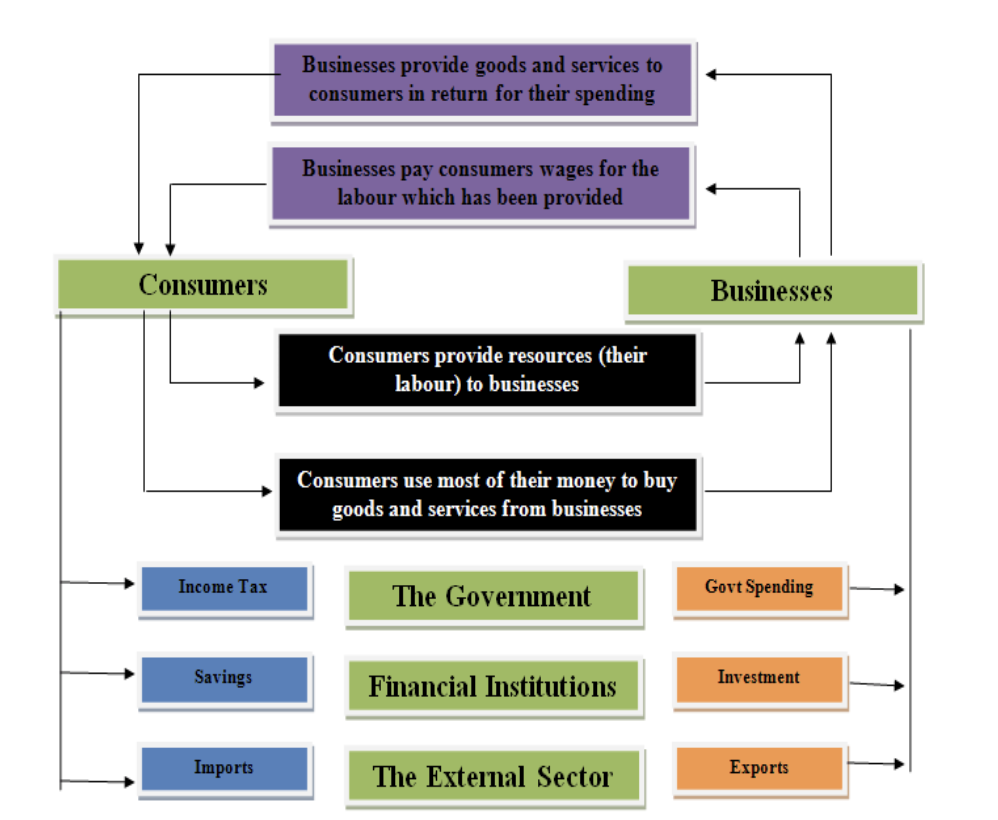
5 sector flow model
Macroeconomics goals
full employment, strong and sustainable economic growth, low and stable inflation
Inflation
The rate of increase in prices over a period of time (impacts: reduces demand, diminishes savings), goal inflation → 2%-3% per annum
Consumer price index
measure of average change over time in prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services
Unemployment definition
Those of the working age who are not employed, carrying out activities to seek employment during a specific period.
Full employment
people who are both willing and able to find work are able to do so, aiming for unemployment between 4% and 5%.
Economic growth
more goods and services are produced/consumed in the country in this year than last year, hoping for a higher standard of living. The government aims to achieve a sustainable level of economic growth, having acceptable living standards but enough resources for the future. Goal economic growth → 3%-3.5% per annum
GDP
Gross domestic product is what measures economic growth, representing total volume/quantity of goods and services produced in Australia over a period of time.
Business cycle/economic cycle
Types of unemployment
Frictional unemployment (including seasonal), Cyclical unemployment, Structural unemployment
Frictional unemployment
The unemployment due to people being in the process of moving from one job to another
Cyclical unemployment
The overall demand for goods and services in an economy cannot support full employment
Structural unemployment
A mismatch between the jobs available and the skill levels of the unemployed (often for the demand of specific types of labour/skills, e.g. laying off workers because they don’t have the necessary IT skills)
Globalisation
A process by which national and regional economies, societies, and cultures have become integrated through the global network of trade, communication, immigration and transportation.
Material living standards
The quality of peoples lives measured by their ability to purchase goods and services. If the economy is contracting, this means less people have a job (increase in unemployment), so those people will have less money to buy goods and services, meaning their material living standards will decrease.
Non material living standards
The quality of people’s lives as measured by a variety of, often intangible, indicators, such as happiness, health and level of education.
Imports
goods or services brought into a country (for e.g. Australia) from another country (for e.g the US)
Exports
good or service produced in one country (for e.g. Australia) and sold to a buyer abroad (for example, to China).
Benefits of trade
availability of goods and services, increased competition, productive efficiency, allocative efficiency, learning, access to markets, economies of scale, production costs, source of foreign exchange,
Drawbacks of trade
domestic job losses due to increased competition, potential for exploitation of resources and labor, and the risk of currency fluctuations impacting businesses
Types of trade protection
tariffs, quota, subsidies, administrative barriers
Tariffs
Tariffs are taxes put on imported goodsas they enter the domestic economy and haveto be paid by the individual or organisationimporting the goods.
Quotas
A quota is a method of trade protectionwhere a domestic government sets either avalue or a quantity limit on imported goods intothe domestic economy.
Subsidies
By subsidising domestic producers, governments are giving their producers a cost advantage over foreign producers, which acts as a trade barrier.
Administrative barriers
Administrative trade barriers occur when the government imposes excessive rules, regulations, and bureaucracy on imported goods.
Exchange rate definition
An exchange rate is the price of one country's currency compared to another country’s currency.
Currency appreciation
Currency gets stronger, imports are cheaper, exports are more expensive, tourists get more foreign currency
Currency depreciation
Currency gets weaker, imports are more expensive, exports are cheaper (better for exporters), tourists get less foreign currency
Economic integration
The economies of different countries move closer together in terms of their trading relationships and economic policy making.
Free trade
Where goods and services are exchanged across borders without tariffs or government regulations
Cause of inflation
Rising Production Costs: higher raw material costs, wage increases, or supply chain disruptions can cause businesses to raise prices to maintain profitability, driving up the overall price level.
Imbalance Between Supply and Demand:
When demand for goods and services outpaces supply, prices tend to rise as consumers compete for limited resources. This can be caused by increased consumer spending, government spending, or a rise in exports.
Effect of inflation
Higher Interest Rates:
Central banks often raise interest rates to curb inflation by making it more expensive to borrow money, which can slow down economic activity.
Economic Instability:
Inflation can create uncertainty in the economy, leading to reduced investment, saving, and consumer confidence.
Impact on Exports and Imports:
Higher inflation can make a country's exports more expensive in the global market, potentially harming trade competitiveness, and increase the cost of imported goods.
Goal inflation rate
2%-3% per annum
Goal unemployment rate
4-5%
Economic growth goal percentage
3-3.5%