Immunity ll (Adaptive)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Adaptive cell characteristics
Recognition of self
Specificity
Diversity
Memory
Recognition of self in adaptive immunity is important because ___ and are accomplished by
distinguishing self and non-self
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
MHC specialize to
present peptides to T cell receptors
Main classes of MHC
Class 1 and class 2
Class 1 MHC Molecules
transmembrane, surface of all nucleated cells
made of alpha and beta chains with Ag binding sites
Ag binding sites of MHC can bind to
Self peptide (all other cells know its a healthy cell)
foreign peptide (marks the cell as an infected host cell)
Class ll MHC molecule
transmembrane, found on surface of antigen presening cells (APC) has alpha and beta chains with Ag binding sites
Ag binding sites on class II MHC bind to
displays foreign particles (signals infected host cell)
Specificity is the
recognition of one specific foreign substance
Recognition of specificity is associated with
antigen of foreign invaders
Examples of foreign invaders
Antigen - any substance that elicits an immune response
MAMPs, proteins, or polysaccharides on surfaces
Epitope
Epitope
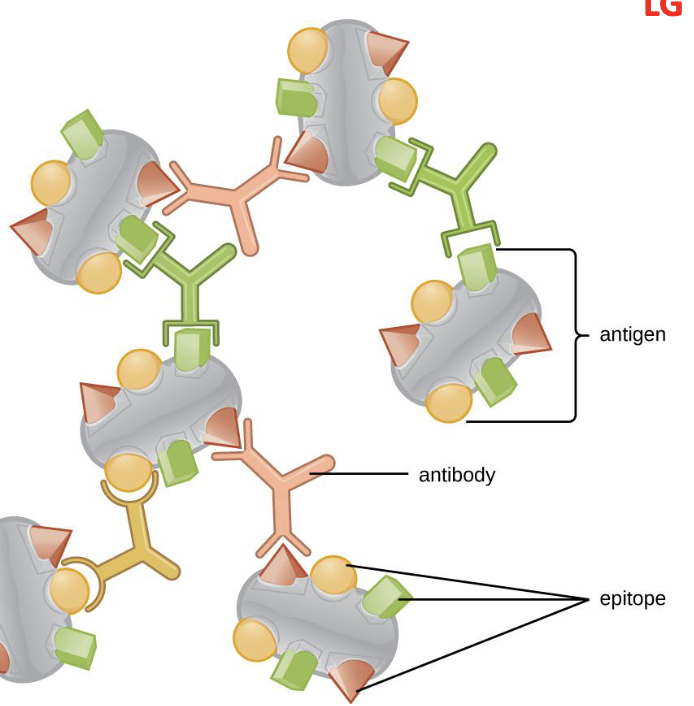
specific regions/component that binds to antibodies on the antigen
Innate defense
non-specific, 1st line of defense, active without previous exposure A
Adaptive defenses
Specific, acquired after exposure, response to antigens (Ag), involves B and T cells
Sequence the process of MHC ll
l. Lysosomes fuse with the phagosome and digest the bacterium
ll. Immunodominant epitopes are associated with MHC ll and presented on the cell surface
lll. A bacterium is engulfed by phagocytosis into a dendritic cell (APC) and is encased in a phagosome
lll > l > ll
Diversity
the recognition of trillions of unique substances
Memory results
of the actions of memory B and T cells
Memory is critical for
fighting infections faster and stronger if re-exposed to the same pathogen/substance
Sequence T cell development
l. CLP cells migrate to the thymus to become fully developed but not active/naive
ll. Common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) cells in bone marrow
lll. CLP migrate to lymph nodes and spleen to be activated when Ag is presented
ll > l > lll
Classes of T cells
Helper, regulatory, and cytotoxic T cells
CD molecules
clusters of differentiation, glycoproteins on the surface of T cells
Helper T cells CD molecule, mode of activation, function
CD4
APCs presenting Ag associated with MHC ll
Coordinate B cells and T cell responses
Regulatory T cells CD molecule, mode of activation, function
CD4
APCs presenting Ag associated with MHC ll
Downregulate strong responses
Cytotoxic T cells CD molecule, mode of activation, function
CD8
APCs/infected nucleated cells presenting Ag associated with MHC l
Destroy infected cells
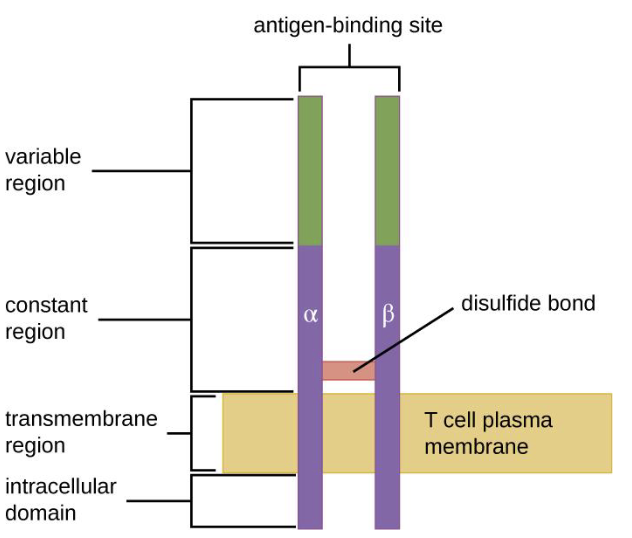
T-cell receptor (TCR)
Detects Ag fragments presented by MHC molecules
Components of TCR
Sequence activation and differentiation of helper T cells
l. APC and T cells secrete cytokines to activate T cells
ll. Interaction of CD4 with MHC ll
lll. Proliferation (mitosis) and differentiation of T cells
lV. TCR recognition of a specific epitope presented by MHC ll
lV > ll > l > lll
Sequence the activation and differentiation of cytotoxic T cells
l. Interactions of CD8 with MHC l
ll. TCR recognition of specific epitope presented by MHC l
lll. Proliferation (mitosis) and differentiation
lV. APC and T cells secrete cytokines to activate T cells
V. Release of granzymes
ll > l > lV > lll > V
Sequence B cells differentiation
l. Migration to the lymph nodes and spleen to be activated if presented with Ag
ll. CLP matures in bone marrow to be fully developed
lll. Common lymphoid progenitor (CPL) cells in bone marrow
lll > ll > l
Components of B-cell receptors
Activation of B cells
BCR interacts with specific (few) Ag
No memory cells required, thus fast processing
Sequence T cell-dependent activation
l. T cell activate and stimulates the release of cytokines that then activate B cells
ll. B cells recognize and internalize an Ag
lll. Activation of B cells triggers proliferation and differentiation into B cells and plasma cells
lV. B cell presents Ag to helper T cell through MHC ll that is specific to the same Ag
V. Helper T cell interacts with Ag presented by B cells
ll > lV > V > l > lll
Difference between T cell-dependent and independent B cells
Dependent requires the involvement of a helper T cell