integumentary system
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
• Describe the general structure of the integument • Identify the varied functions of the integument • Describe the structure and composition of the epidermal layers • Describe the organisation and function of the layers of the dermis. • Identify nerve and blood supply to the dermis.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
integument
hair skin nails, sweat glands and sebaceous glands
largest organ (7-8% body weight)
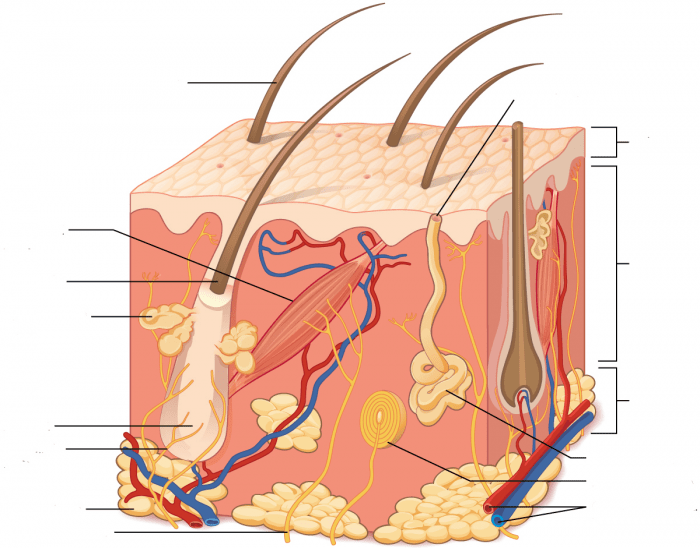
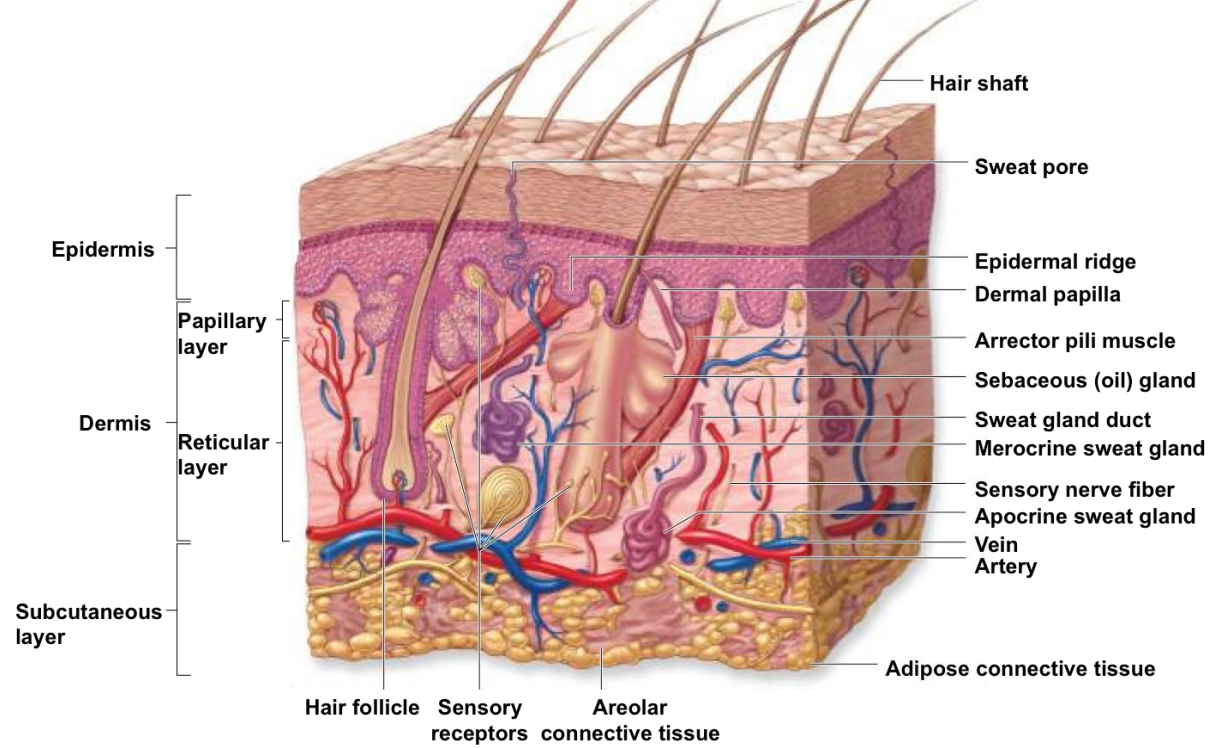
cutaneous membrane layers
epidermis → stratified squamous epithelium, avascular
dermis → areolar and dense connective tissue
hypodermis → subcutaneous layer ( not part of the skin ) mainly adipose
identify the varied functions of the integument
protection
prevention of water loss
temperature regulation
metabolic regulation
immune defense
sensory reception
excretion/secretionn
epidermis characteristics
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
4-5 layers ( strata) depending on skin type
avascular ( no surrounding blood vessels)
epidermal strata
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum ( thick skin)
stratum corneum
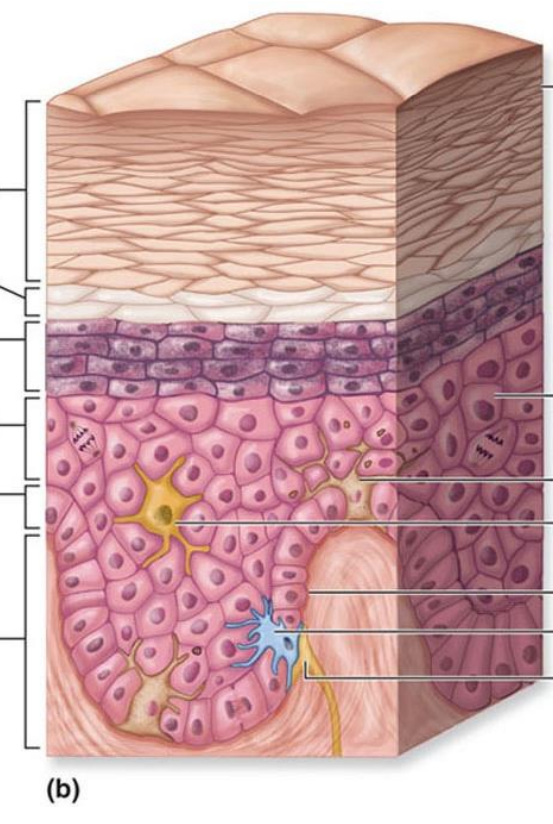
epidermal strata
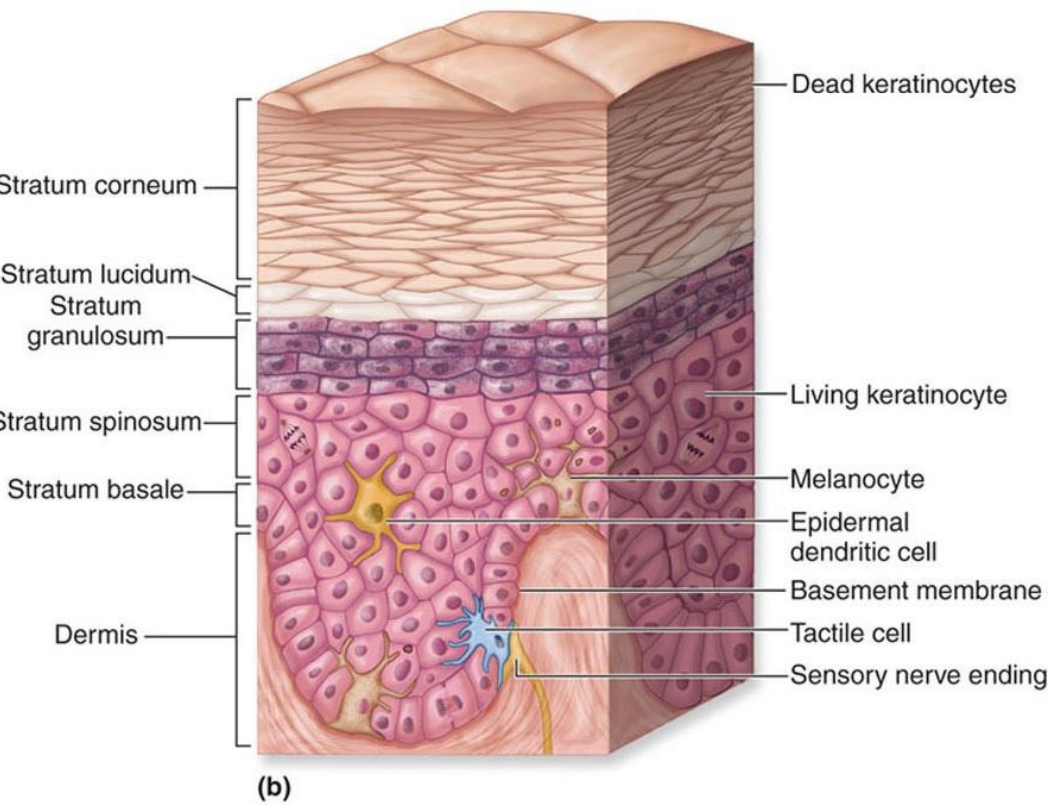
stratum basale
undergoes mitosis, one layer of cells
cells:
keratinocytes → produces keratin
melanocytes → produces melanin, protect DNA from UV danage
tactile cells → sense touch
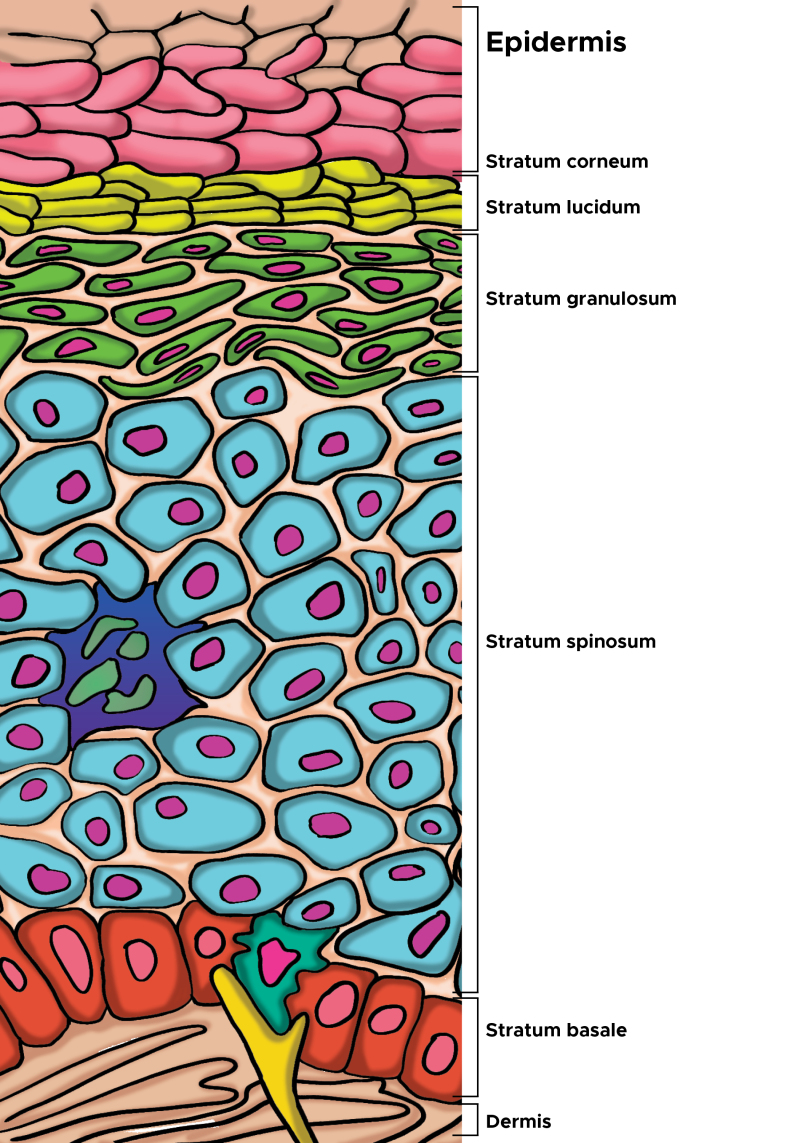
stratum spinosum
connected by desmosomes; helps in mechanical strength
stratum granulosum
contains keratohyalin granules 4 keratin production
stratum lucidum
only found in thick skin
transparent, protective layers
stratum corneum
dead keratinized cells providing an outer layer
dermis
lies between the epidermis, vascular
2 layers
papillary layer
reticular layer
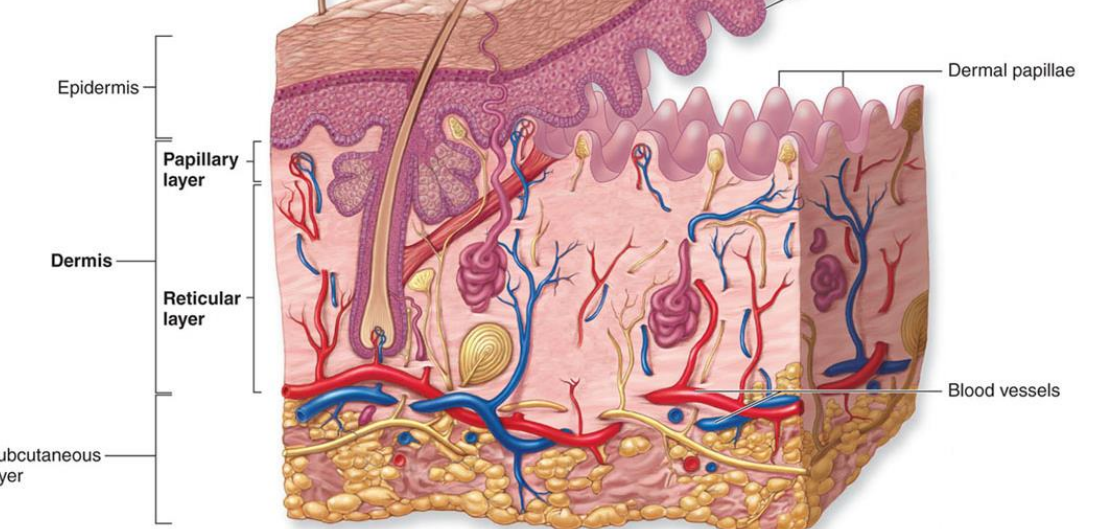
papillary layer
superficial, areolar ct
dermal papillae containing capillaries for epidermal nutrition
dermal papillae and epidermal ridges interlock, increasing the surface area between epidermis and dermis
directly under stratum basale
reticular layer
dense irregular connective tissue
forms most of the dermis
contains collagen bundles, blood vessels, glands and nerve endings
functions of dermis
provides strength and elasticity ( via collagen)
supplies nutrients and houses sensory structures
innervation
nerve fibers r present in the dermis
functions
tactile receptors
control blood flow
control glandular secretion
blood supply
epidermis: avascular, dermis: vascular
important in controlling blood pressure
vasodilation → releases heat by widening vessels, vasoconstriction → conserves heart by narrowing vessels
collagen bundles
blood vessels
nerve endings
hypodermis
subcatenous layer, deep/ not really part of integument
composed of areolar ct and adipose ct
functions
protects underlying structures
stores energy
provides thermal insulation
epidermal derivatives
hair
exocrine glands
nails