Unit 4 AP US Government Vocabulary
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
American Values
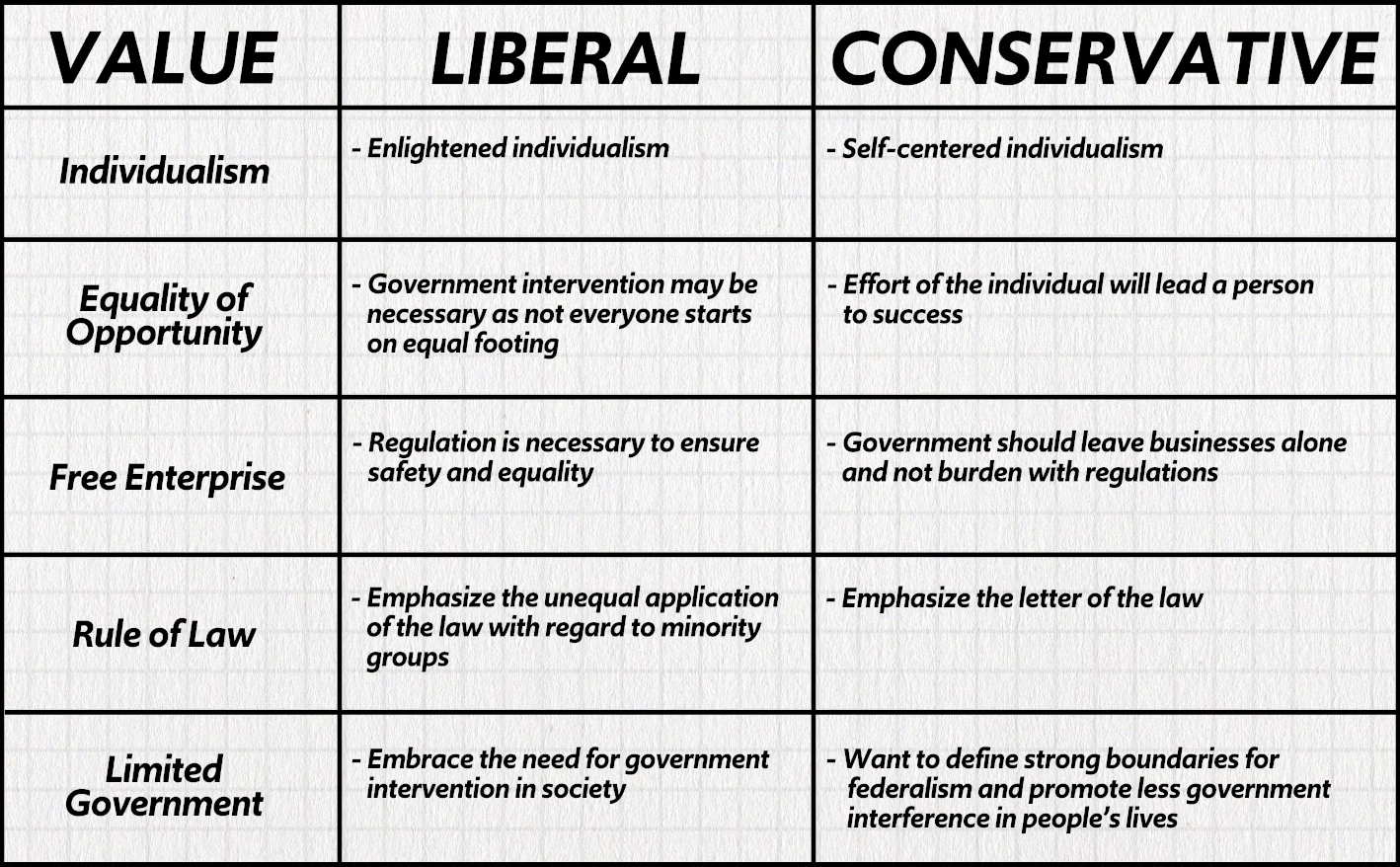
Individualism
Equality of Opportunity
Free Enterprise
Rule of Law
Limited Government
Individualism
Places value on a person’s independence and self-reliance
Equality of Opportunity
Every American, no matter their or class, should have equal rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
Free Enterprise
Government should adopt a laissez faire attitude toward business, and allow forces like supply and demand to govern the marketplace
Rule of Law
Every citizen is equal under the law—no one has any special privileges
Limited Government
Government whose limits are well-defined and is restrained through the separation of powers and a system of checks and balances
Liberal
Push for new reforms in order to make society more and just and equitable
Prefer a larger government that provides an abundance of services to its citizens
Believe that more government involvement is necessary in achieving individualism and free enterprise
Conservative
Cherish established institutions and seek to preserve them for the good of society
Want a smaller government that provides less services
Liberal vs. Conservative
Political Socialization
Family
School
Peers
Media
Social Environments
Globalization
American Generations
Silent Generation
Baby Boomers
Generation X
Millennials
Silent Generation
Refers to the cohort of Americans born between 1928 and 1945, characterized by their experiences during the post-World War II era, economic expansion, and significant social changes. (Conservative, VOTE)
Millennials
More Liberal than previous generations
Value cooperation and diplomacy
More ethnically diverse
More highly educated
Not opposed to government regulation of business for the purpose of consumer protection and a clean environment
Major Events (Factor of Political Socialization)
Have a disproportionate impact on a person’s political socialization.
Political Ideology
An interlocking set of ideals that form the basis for political decision making
Conservatives have been becoming more conservative, while liberals have been becoming more liberal.
Democratic Platform
Protecting a woman’s rights to abortion
Equal rights for women and the LGBTQ+ community
Healthcare for the poor
Republican Platform
Cutting taxes
America-first trade policy
Anti-regulation of business
Dream Act
Legislation aimed at providing a pathway to legal status for undocumented immigrants who were brought to the U.S. as children.
Keynesian Economics
Associated with Liberal
Addresses fiscal policy
When demand is too low, the government should step in and put more money into the economy by reducing taxes or increasing government spending, or both
Supply-Side Economics
Associated with Conservative
Addresses fiscal policy
Emphasizes reliance on the forces of supply and demand, and that the government should keep their hands out of these forces
Libertarianism
Has social convictions of liberals
Has political convictions of conservatives
Wants least intrusive government possible
Monetary Policy
How much currency is in circulation
Buying and selling government bonds, setting reserve requirements, and setting interest rates
Federal Reserve
responsible for managing monetary policy
Polls
surveys used to measure public opinion and preferences on various issues, with questions free from bias as much as possible.
Opinion Polls
Conducted to get a feel for the public’s opinion or feeling on certain candidates or policies
Benchmark Polls
Taken at the beginning of a candidate’s run, gives the campaign a benchmark against which they can compare future polls to see how the candidate is faring
Tracking Polls
Conducted over time, usually with the same group of people, that give information on how the group feels about a given issue
Entrance Polls
Conducted before people enter their polling location, ask how they will vote
Exit Polls
Conducted after voters leave their polling location, ask how they voted
Reliable Sample
Representative Sample
Random Sample
Good Margin of Error
Plus or Minus 4%
Mass Survey
Sample is as big as possible, best for quantitative data
Focus Groups
10-40 People, emphasizes qualitative data
Bandwagon Effect
When a certain candidate is doing good in the polls, there’s an impulse to get behind the winning candidate.
Social Desirability Bias
The tendency for respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others, often leading to inaccurate or misleading data.
Non-Response Bias
The bias that occurs when certain individuals do not respond to surveys or polls, which can skew the results and lead to unrepresentative data.