equine anatomy
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
basic components of life
organic compounds
carbon (C), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H) are basic building blocks
carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
tissue
group of similar cells
organ
group of similar tissues functioning together
system
group of organs with similar function
digestive system
breaks down and absorbs nutrients from food
skin and coat
protection
synthesis of vitamin D
temperature regulation (sweating)
anhydrosis - inability to sweat
sensation (touch)
urinary system
removes waste from the blood
expels wastes as urine
regulates pH
respiratory system
exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
external respiration: breathing
internal respiration: oxygen used by cells
upper airway anatomy
pharynx
nasal cavity
nostrils
sinuses
nasal septum
larynx
trachea
why can’t horses breathe through their mouths?
they have a long soft palette
roaring
recurrent laryngeal neuropathy/hemiplasia
caused by laryngeal hemiplegia
dorsal displacement of the soft palate
soft palate displaces and sits on top of the epiglottis - obstructs airway
usually intermittent
treatment - nosebands, surgery
breathing
controlled by the respiratory center (medulla oblongata)
also - voluntary control
phonation, parturition, defecation
locomotion - respiratory coupling during gallop
horse only inhales in suspension phase
EIPH
exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage
seen in performance animals
intense exercise
increased pressure in pulmonary capillaries
capillary walls rupture
blood leaks into alveolar sac
exits via nostrils (epistaxis)
heaves (COPD)
chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
caused by respiratory irritants
treatment
remove irritant
increase turnout
bronchodilators
circulatory system
supply body with nutrients and remove waste
heart
arteries
veins
capillaries
average thoroughbred heart weight
3.5 kg
how does blood get back to the heart?
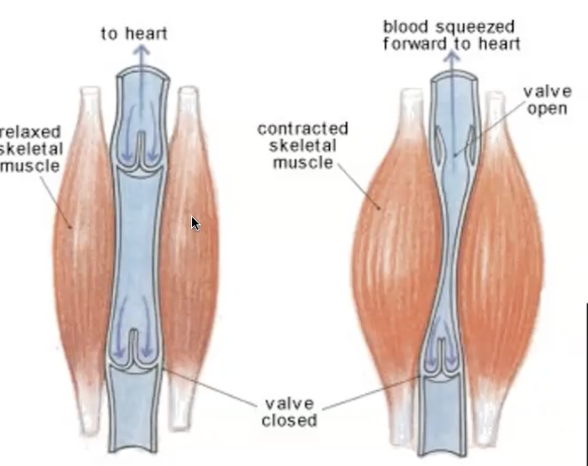
blood percentages
9% of body weight (45L)
20% pulmonary (lung), 80% systemic
60% veins, 40% arteries
blood components
RBCs
WBCs
platelets
plasma
blood sampling
jugular vein
collected into tubes
anticoagulant = plasma
no anticoagulant = serum
hematocrit (PCV)
percentage of RBCs in blood
30-45% is normal
decrease if anemic, increase during stress and dehydration
spleen
stores and releases RBCs during exercise for increased oxygen delivery
control systems
nervous system
endocrine system
maintain homeostasis - respond to external stimuli and change
equine sight
wide range of vision
mostly monocular
some binocular
blind spot immediately front and behind
equine eye
eye is flattened
retina closer to lens at bottom
visual streak
dichromatic vision
see blue and yellow-green, not red
tapetum lucidum (reflective)
night vision
hearing
better than humans
ears can rotate 180 degrees via 16 muscles
deteriorates with age
sound wave → eardrum vibrates → electrical impulses
taste
highly linked to smell
taste buds in papillae on tongue
horses prefer sweet tastes
smell
selection of food
predator detection
communication
social, reproduction
smell droppings
what other horses have been here?
vomeronasal organ (organ of Jacobson)
specialized olfactory (“scent”) cells
can detect chemicals called pheromones
enhanced with the flehmen response
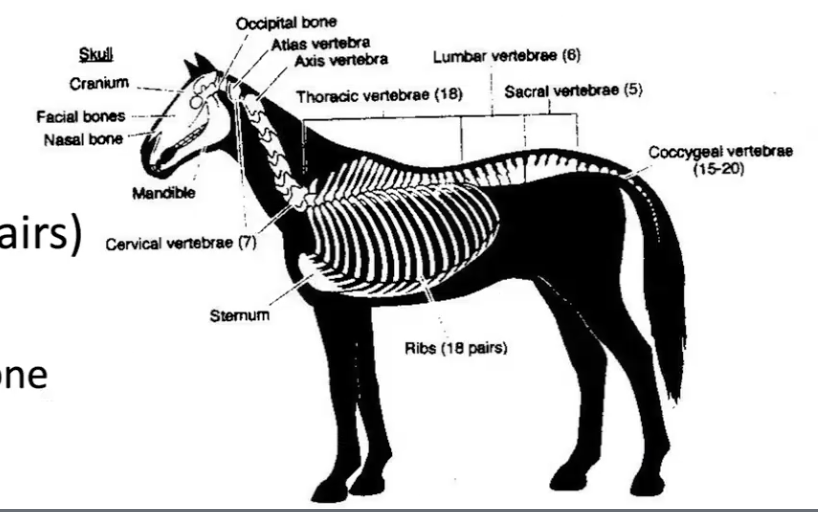
axial skeleton
bones that run along the central axis of the body
skull
vertebrae
ribs (18 pairs)
sternum
breastbone
touch
nerve endings in the skin → transmit signals to the brain
particularly sensitive over ribs
communication
vertebrae

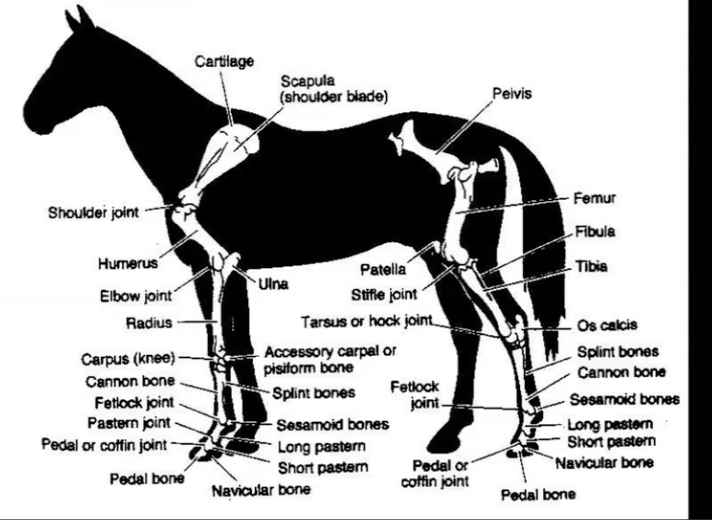
appendicular skeleton
attached to axial skeleton at:
pectoral girdle
no collarbone, muscular attachment only
pelvic girdle
forelimb
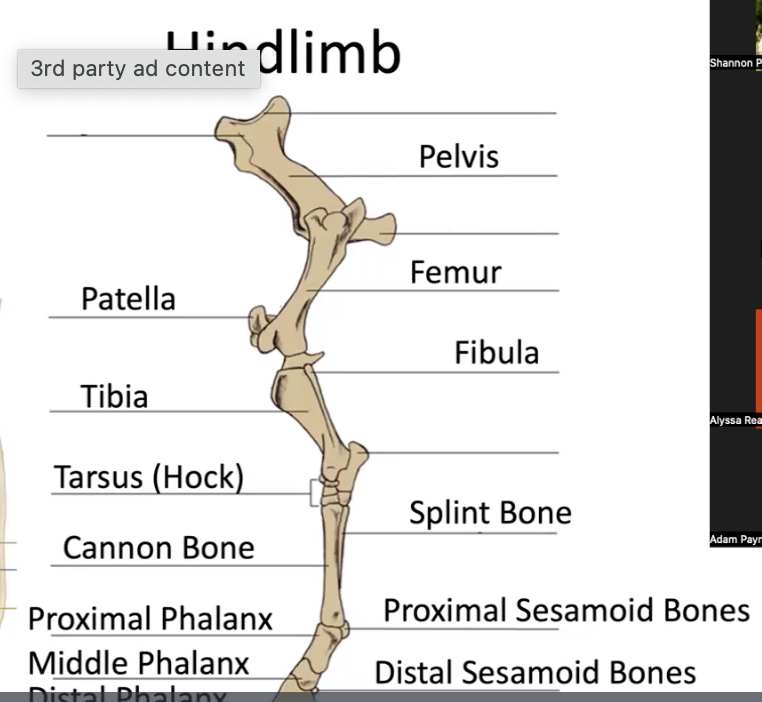
hindlimb
joints
union of bones
joint capsule
synovial fluid
articular cartilage
fibrous joints
or fixed, such as skull structures
cartilaginous joints
such as between the intervertebral discs
synovial joints
or free moving, the most common in horses
joint movements
flexion
extension
lateral bending
rotation
shoulder joint
ball and socket, flexion and extension only
stifle joint
a hinge joint similar to the human knee. femur and tibia, femur and patella
elbow
a hinge joint
knee
a gliding. joint similar to the human wrist, actually multiple joints
hock
a gliding joint similar to the human ankle, 4 joints. mostly absorb shock in lower 3
arthritis
inflammation of the joint
arthritis management
oral joint supplements
IM injections
IA injections
rest
pain meds
types of muscle
cardiac, smooth, skeletal
muscles of the head
splenius
rhomboideus
masseter
brachiocephalicus
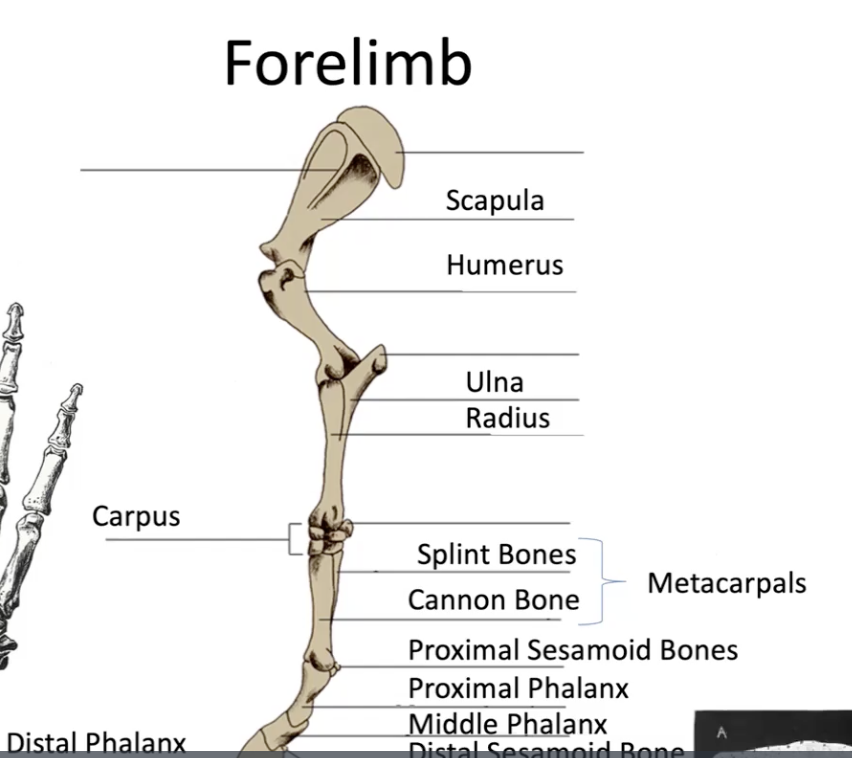
muscles of the forelimb
no muscles below the carpus (knee), all tendons and ligaments
deltoid
triceps
pectoral
muscles of the trunk
trapezius
latissimus dorsi
intercostal
abdominals
muscles of the hindlimb
no muscles below the carpus (knee), all tendons and ligaments
gluteals
quadriceps
gastrocnemius
exertion rhabdomyolysis
muscle pain, tying up, azoturia, elevated CK
recurrent - TBs, Standardbreds, arabians
calcium issue inside muscle cell
polysaccharide storage myopathy
muscle pain, stiffness, exercise intolerance
quarter horse/related breeds
hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
impressive bloodline (QH)
weakness, muscle tremors, paralysis
hoof functions
protection
support weight, reduce concussion
prevent slipping
circulation
the lower limb
support the weight of the horse
60% of the horse’s weight is in the front end
1000 lb horse → 600 lb front end → 300 lb per foot
coffin bone supports almost all of this
with help:
suspensory ligament
navicular bone
laminae/hoof capsule
tendons
attach muscle to bone
muscle contracts → pulls tendons → moves bone
flexor tendons
attach bone to muscles which contract to bend or flex a joint
extensor tendons
attach bone to muscles which contract to straighten or extend a joint
ligaments
attach bone to bone
hold tendons and joints in place
check ligaments
help support flexor tendons
superior and inferior
suspensory ligament
between cannon bone and DDFT
supports full weight of the horse
stay apparatus
stay apparatus
allow horse to rest while standing
minimal muscle energy
stay apparatus - forelimb
opposing angle of joints and tendons/ligaments work together
stay apparatus - hindlimb
opposing angle of joints and tendons/ligaments work together
locking patella
rotated over femur
reciprocal mechanism - locks stifle and hock