physics topic 4
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what type of wave is visible light
transverse wave
angle of incidence =
angle of reflection
angle of reflection=
angle of incidence
what is the normal line
a line perpendicular/at a right angle to the surface at the point of incidence
what happens to light when it is in more dense material
it slows down
when in more dense medium how does light act towards normal line
bends towards normal line
when in less dense medium how does light act towards normal line
bends away from normal line
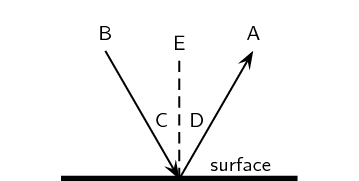
label from a-d
a reflected ray
b incident ray
c angle of incidence
d angle of reflection
e normal line
Refraction practical
• draw around the block
• draw a normal line 90* from the top of the box
• aim the light towards normal line
• plot the angles/light rays
• turn of ray box + remove block
• connect the angles
• create another normal line for exiting angle
• measure and compare angles
What is the law of reflection
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
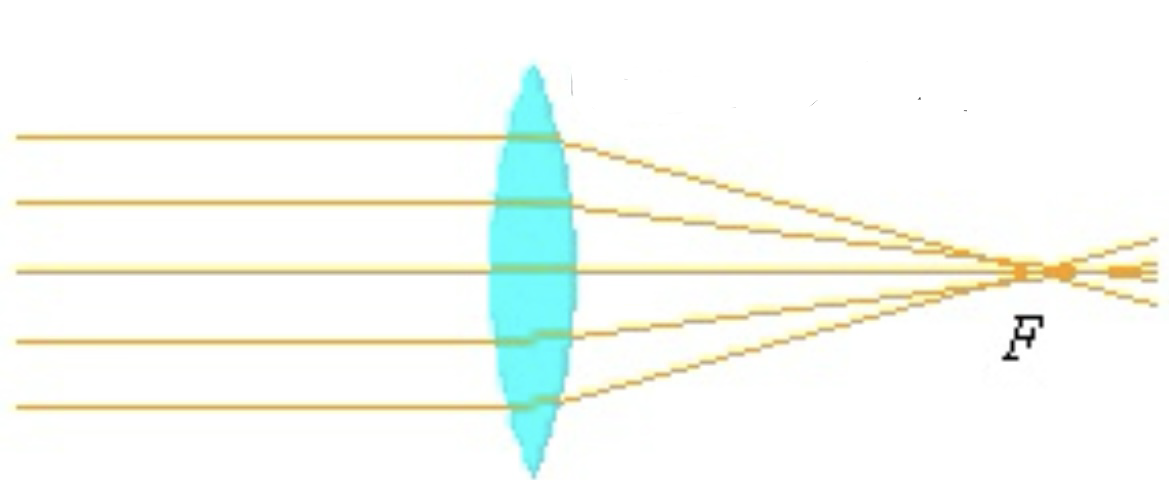
What is a converging lense
A lens that brings parallel rays of light together at a focus.
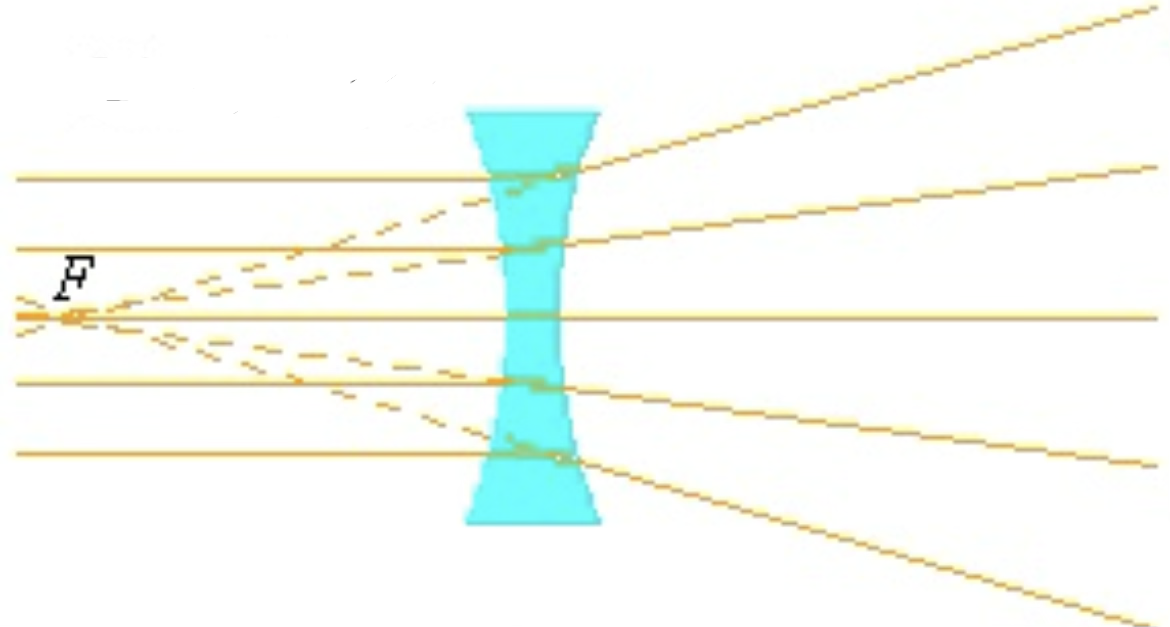
What is a diverging lense
A lens that spreads parallel rays of light apart as if they come from a focus.
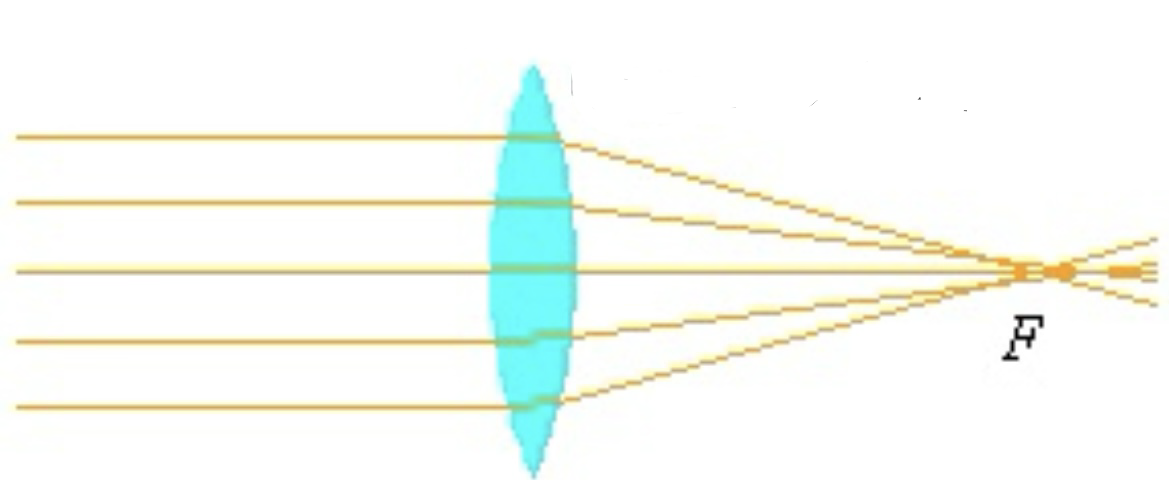
What type of lens is this
Converging lens
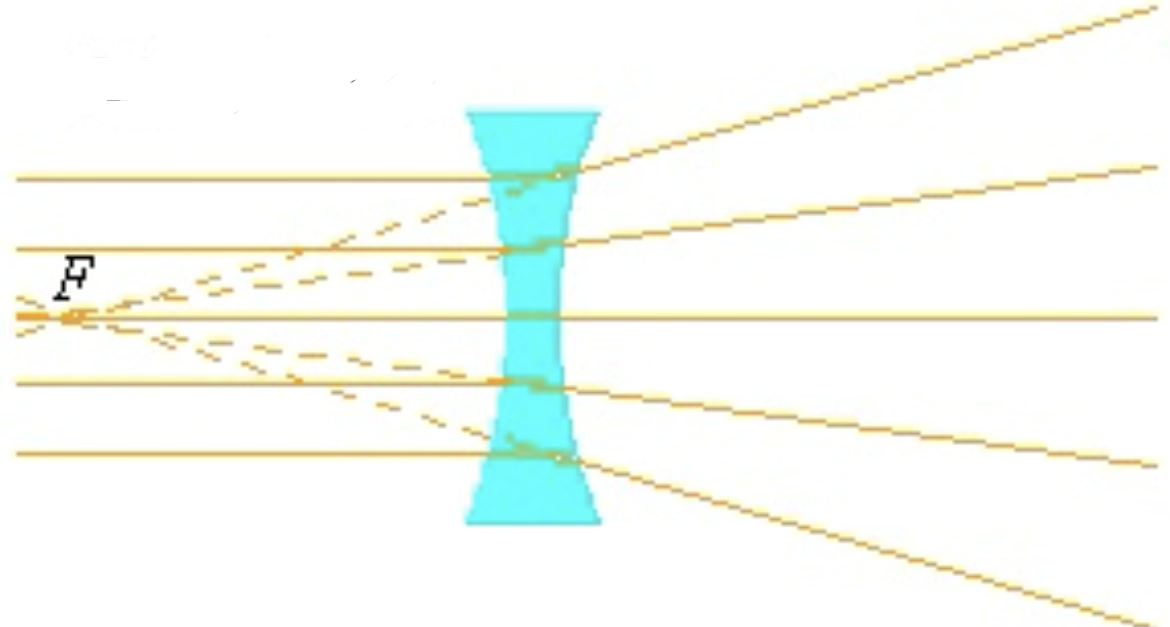
what type of lens is this
Diverging lens
focal point on the right
Real
Focal point on the left
Virtual
3 lens facts
• lens is used to refract light in different ways
• transparent material that refracts light to improve the resolution of image
Higher the power of the lens the more it bends light
What type of wave is light
transverse wave
How fast does light travel
3×108 m/s
Properties of electromagnetic spectrum
• transverse waves
• can travel through a vacuum
• travel at the same speed in a vacuum
• transfer energy from one place to another
Order of electromagnetic spectrum
Radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-ray, gamma ray
The lower on the electromagnetic spectrum means
Long wave length, low frequency
The higher on the electromagnetic spectrum
short wavelength, high frequency
Conduction
The transfer of heat through a solid by particles (vibrating and passing energy to neighbouring particles.)
Convection
The transfer of heat in liquids or gases (when warmer, less dense fluid rises and cooler, denser fluid sinks.)
Radiation
The transfer of heat by infrared waves, (which can travel through a vacuum (no particles needed).)
Absorbtion
taking in energy
Emmiting
letting energy out to the surroundings
Reflecting
energy makes contact with surface and changes direction
In transverse waves, oscillationss are
right angles to the direction of the wave
In longitudinal waves, oscillations are
parrallel to the direction of the wave
Frequency is
The number of waves passing a point every second
Period is
The length of time it takes for one wave to pass through a point
Calculation for wave speed
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
Units for wave speed
M/s
Units for frequency
Hz
Units for wavelength
M
frequencies with less that 20hz are
Infrasound
secondary waves are
longitudinal
Transverse
Slow
Can only pass through solids
Primary waves are
longitudinal
Faster
Can travel through solids and liquids
Wave period equation
1/frequency
Ultra sound is
Above 20,000 hz
Infrasound is
Below 20,000 Hz
Equation for ocean thing
speed = distance/time
Transverse waves movements are
side to side
Longitudinal waves movements ate
back wards and forwards as it compresses and releases
Seismic waves are
Waves of energy that travel through the Earth after an earthquake or explosion.
Specular reflections are
When light is reflected evenly from a smooth surface, producing a clear image.
diffuse reflection
When light is scattered in many directions from a rough surface, so no clear image is formed.
Cm to metres is
/ by 100