N3276 - Cardiac Dysrhythmias and ECG Interpretation | Telemetry
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
horizontal axis
time (seconds); small box: 0.04 seconds, large box: 0.20 seconds
vertical axis
voltage (millivolt); small box: 0.1 millivolt; large box: 0.20 millivolt
P wave
atrial depolarization
normal P wave measurement
<0.12 seconds; round, upright, symmetrical
PR interval
time for impulse to travel from SA node through AV node; measured from the beginning of the P wave to beginning of QRS complex
normal PR intervaal
0.12 to 0.20 seconds
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
normal QRS measurement
0.04 to 0.10 seconds; nice, neat, narrow; measured to J-point
U wave
thought to represent repolarization of Purkinje fibers; may or may not be present
ST segment
early ventricular repolarization; ventricles have fully contracted; elevation or depression may indicate injury or ischemia
ST segment elevation
J point is above isoelectric line; represents injury
ST segment depression
J point is below isoelectric line; represents ischemia
T wave
ventricular repolarization; relative refractory period
QT interval
total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization; lethal if prolonged
normal QT measurement
0.35 to 0.45 seconds
six second method
count the number of QRS complexes in a 6 second strip and multiply by 10
normal sinus rhythm
rate: 60-100 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: upright, consistent
PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
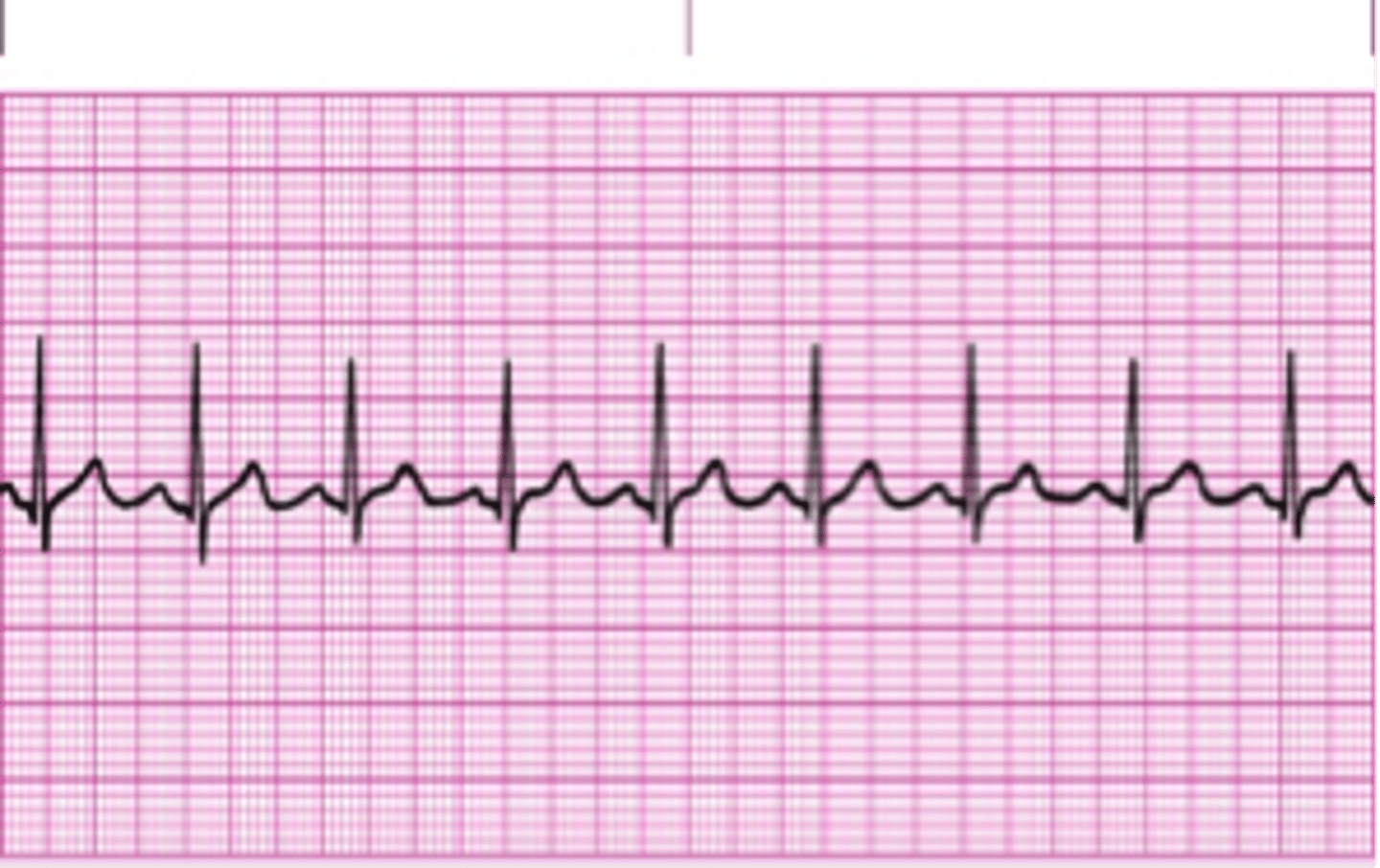
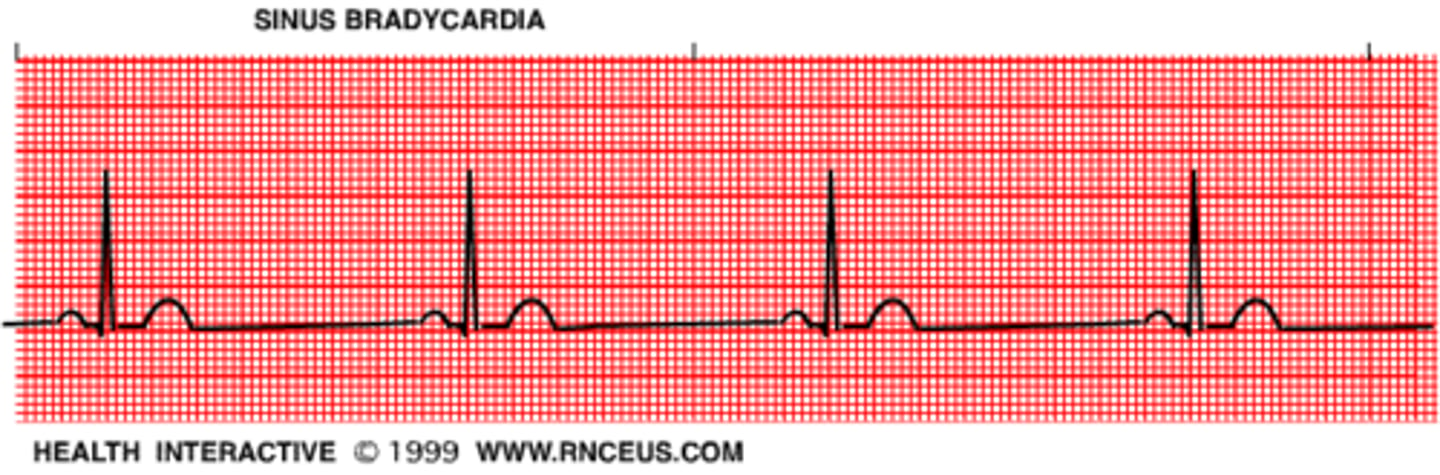
sinus bradycardia
rate: <60 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: upright, consistent
PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
management of sinus bradycardia
asymptomatic - observe
symptomatic - atropine, dopamine, epinephrine; pacing
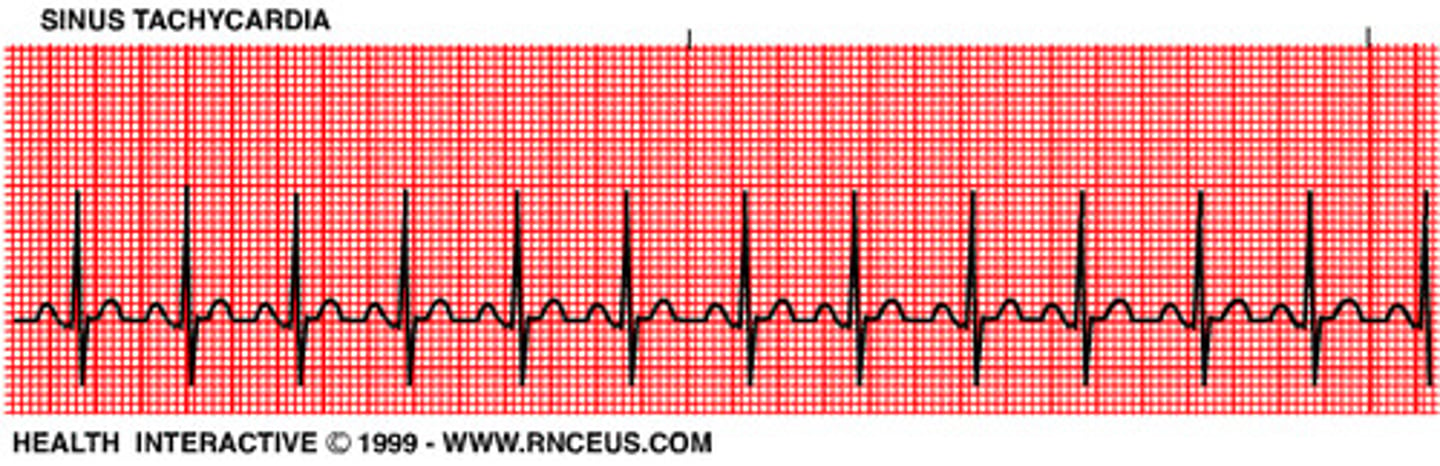
sinus tachycardia
rate: >100 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: upright, consistent
PR interval: 0.12-0.20 seconds
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
management of sinus tachycardia
check the patient, treat the underlying cause
atrial flutter
rate: atrial - 220-325 bpm ; ventricular - 75-150 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: flutter, sawtooth pattern (should outnumber the QRS complexes)
PR interval: not measureable
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
management of atrial flutter
cardioversion if unstable, anticoagulants, beta blockers
atrial fibrillation
rate: atrial - 300-400 bpm, ventricular: rapid, variable
rhythm: irregular
P waves: not identifiable
PR interval: not measurable
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
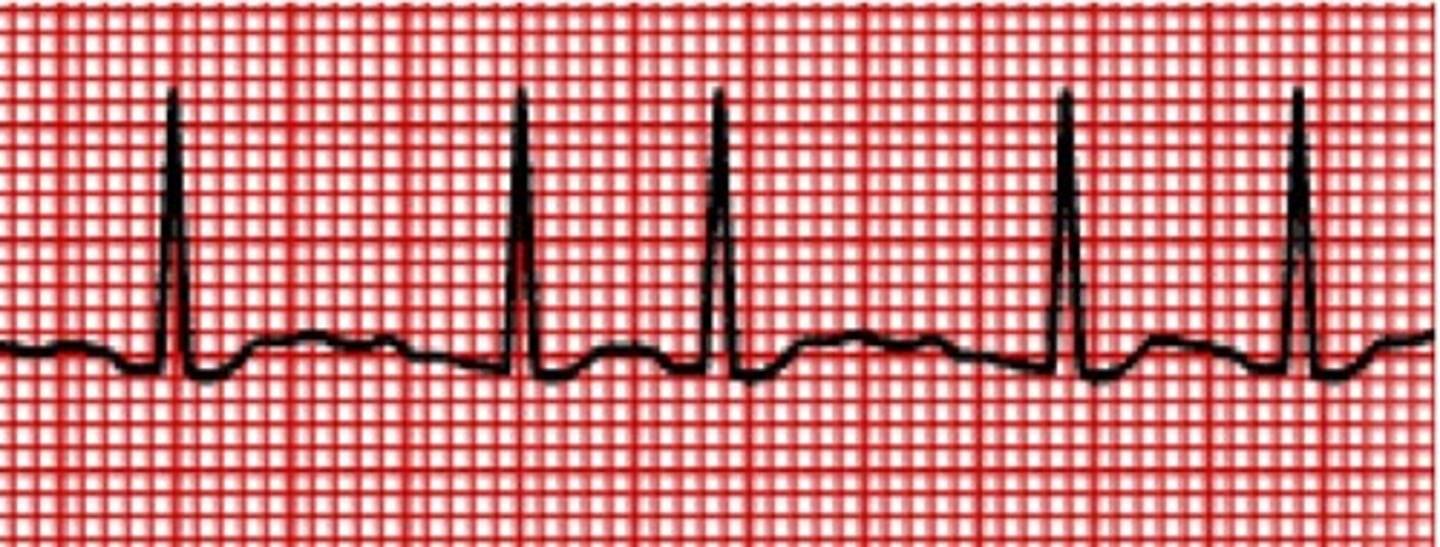
management of atrial fibrillation
check the patient, treat the underlying cause; main goal: rate and rhythm control
rate control - beta blockers, calcium-channel blockers, digoxin
rhythm control - synchronized cardioversion, pharmacologic cardioversion - amiodarone
supraventricular tachycardia
rate: >150 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: usually not visible
PR interval: not measurable
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
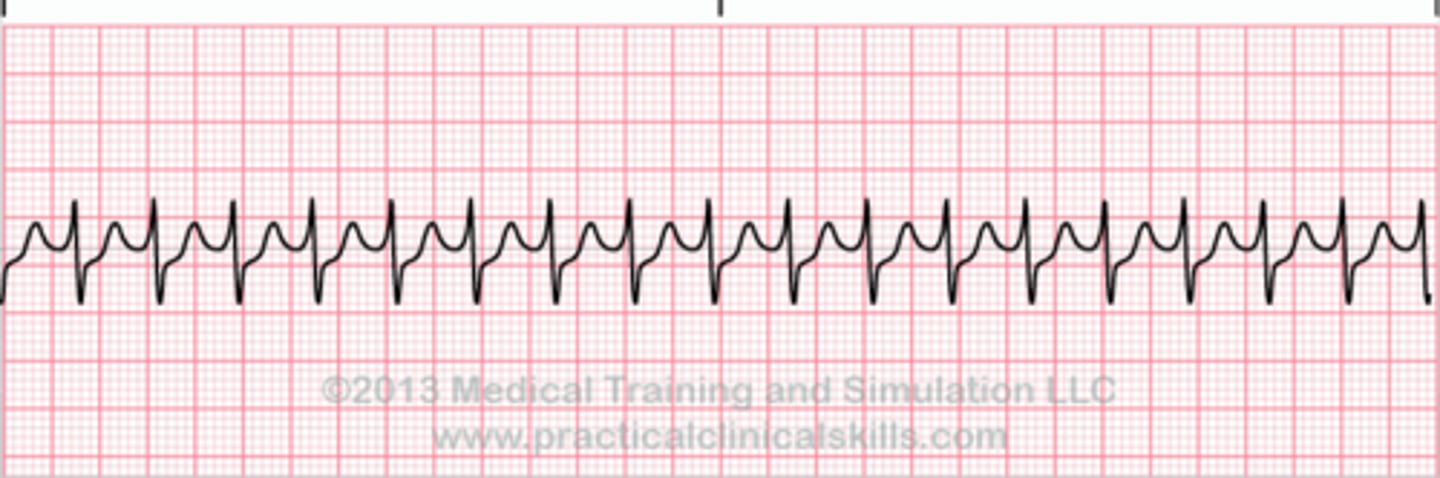
management of supraventricular tachycardia
stable - vagal maneuver, IV adenosine
unstable - synchronized cardioversion, IV beta blockers, IV diltiazem, IV verapamil
premature ventricular complex
rate: depends on underlying rhythm
rhythm: regular
P waves: may be absent
PR interval: <0.12 seconds
QRS duration: >0.12 seconds, wide, bizzare, abnormal
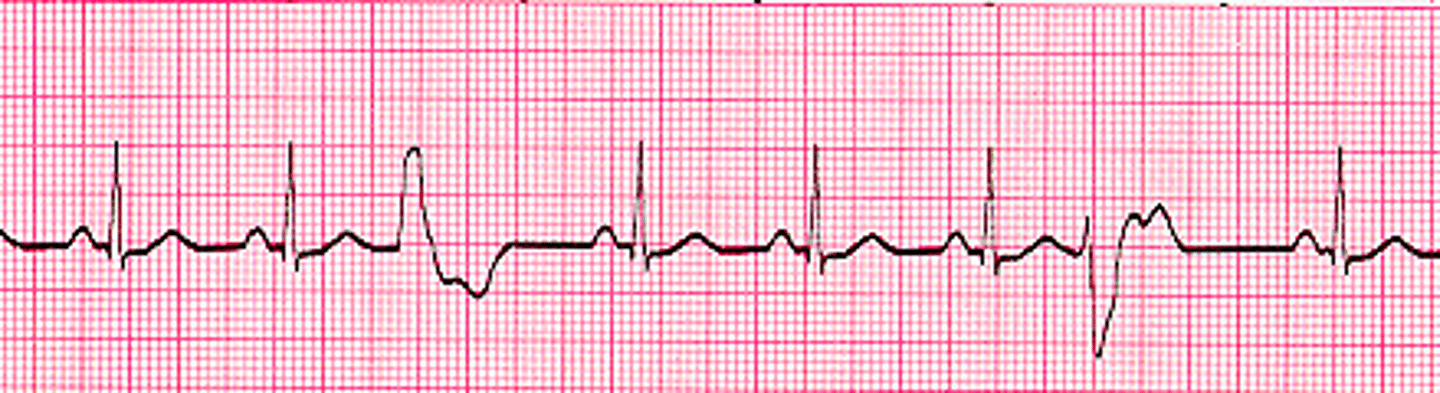
bigeminy
every other complex is premature
couplet
two sequential complexes
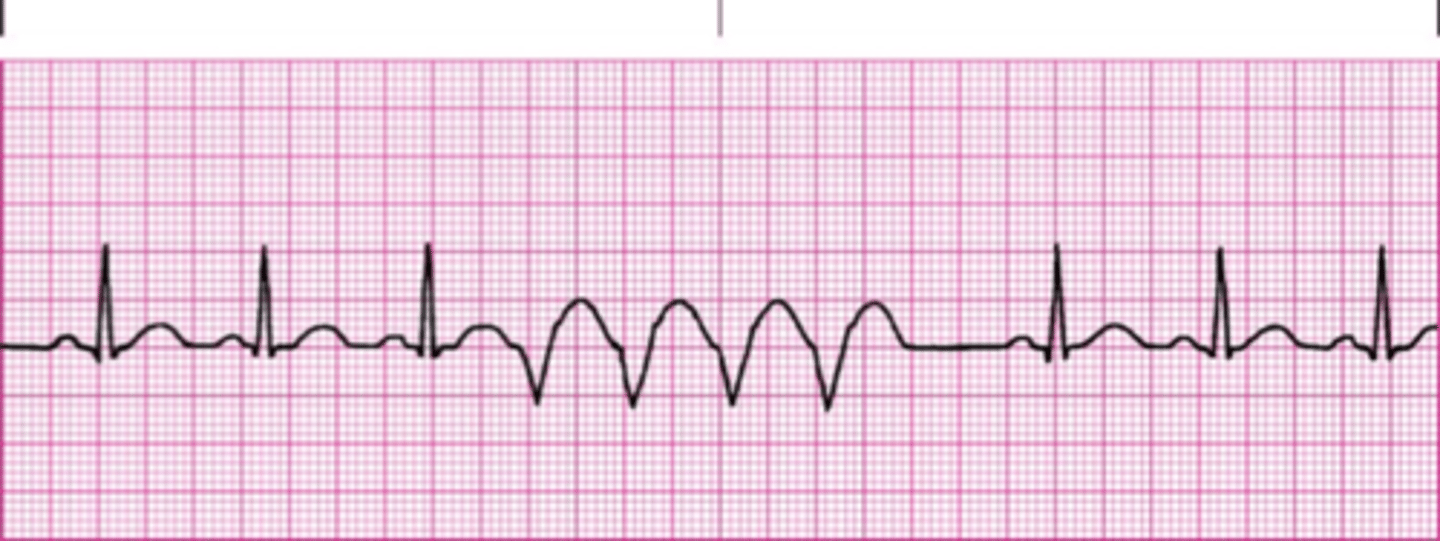
run
three or more successive PVCs (Vtach)
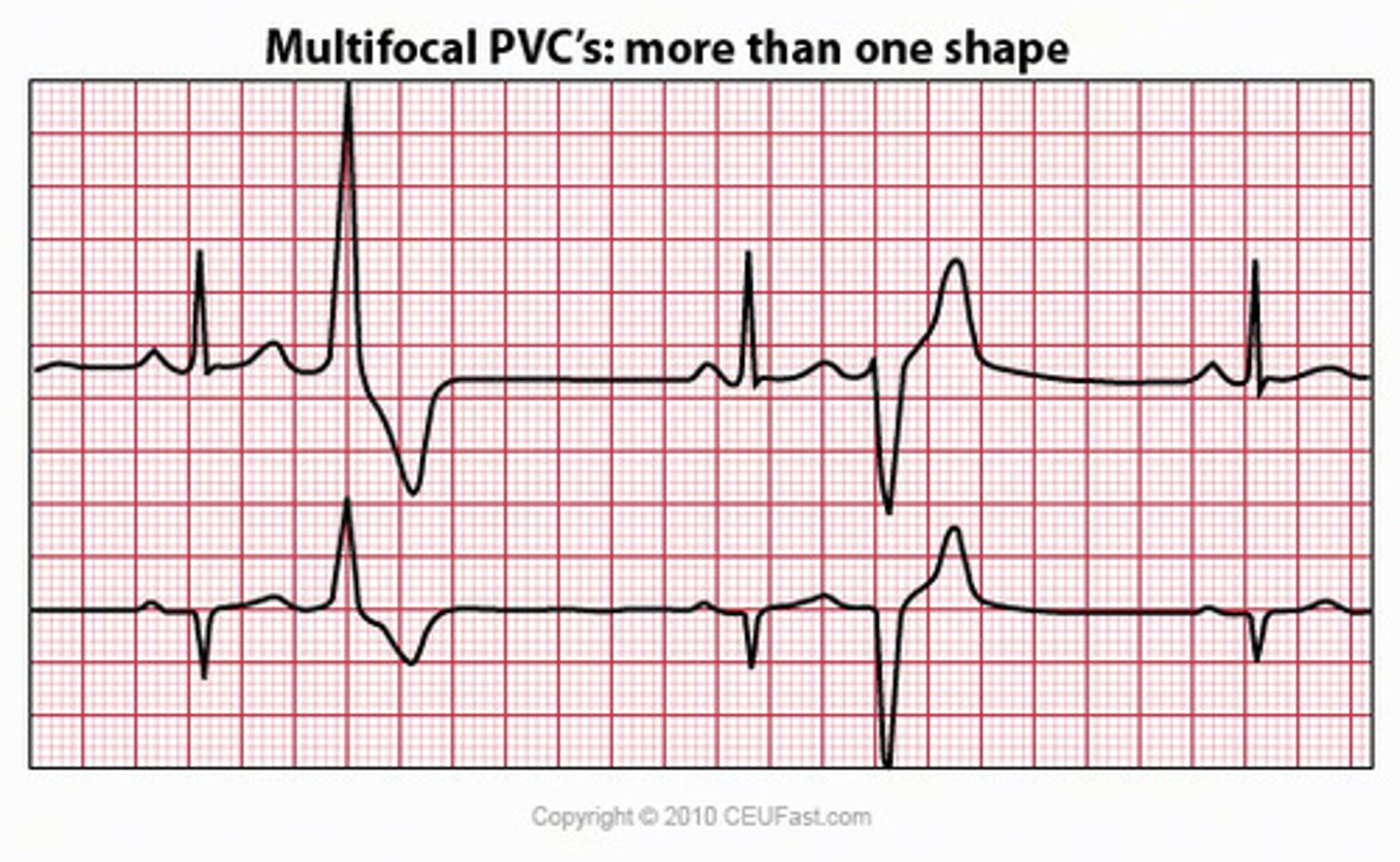
multifocal
PVCs that differ in size, shape, and direction
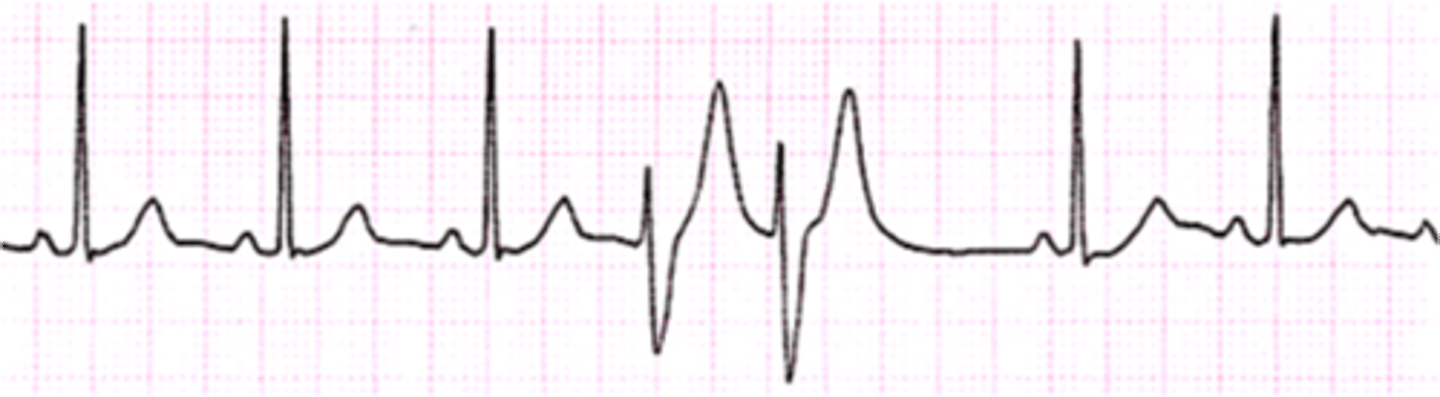
R-on-T phenomenon
PVC occurring on or near T wave
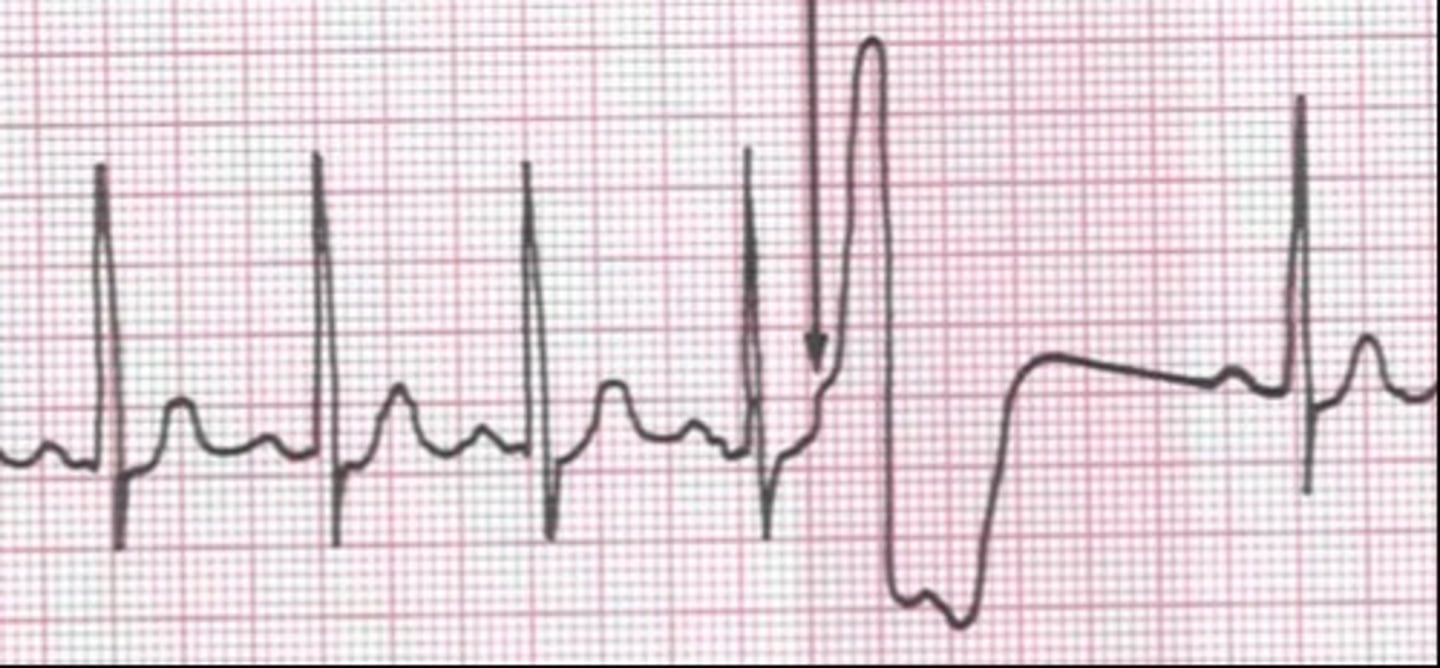
management of PVCs
treat underlying cause (stimulants, cardiac ischemia, hypoxia, etc.)
ventricular tachycardia
rate: 100-250 bpm
rhythm: regular
P waves: not visible
PR interval: none
QRS duration: >0.12 seconds, wide and bizzare
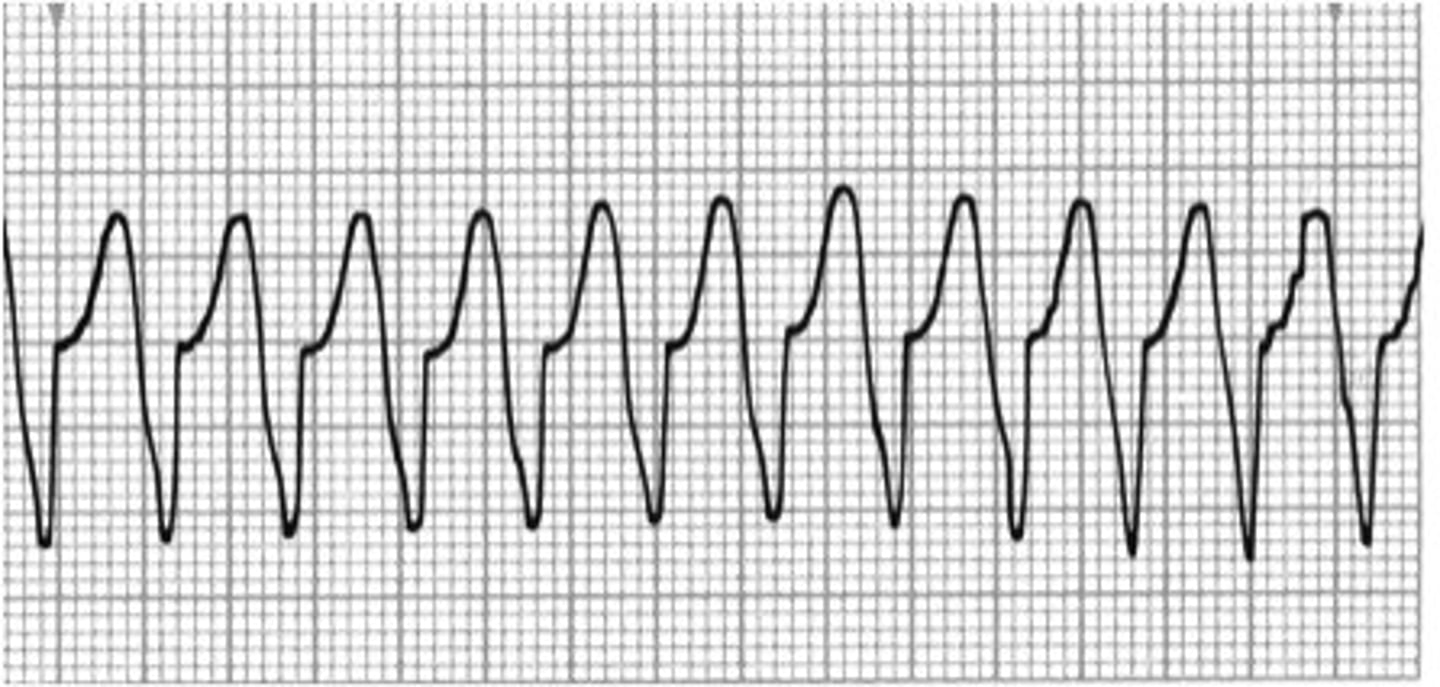
management of ventricular tachycardia
ensure patient has a pulse; correct H+T's, IV amiodarone if stable, synchronized cardioversion if symptomatic
ventricular fibrillation
rate: cannot be determined
rhythm: irregular
P waves: not visible
PR interval: not visible
QRS duration: not visible
no cardiac output, no pulse
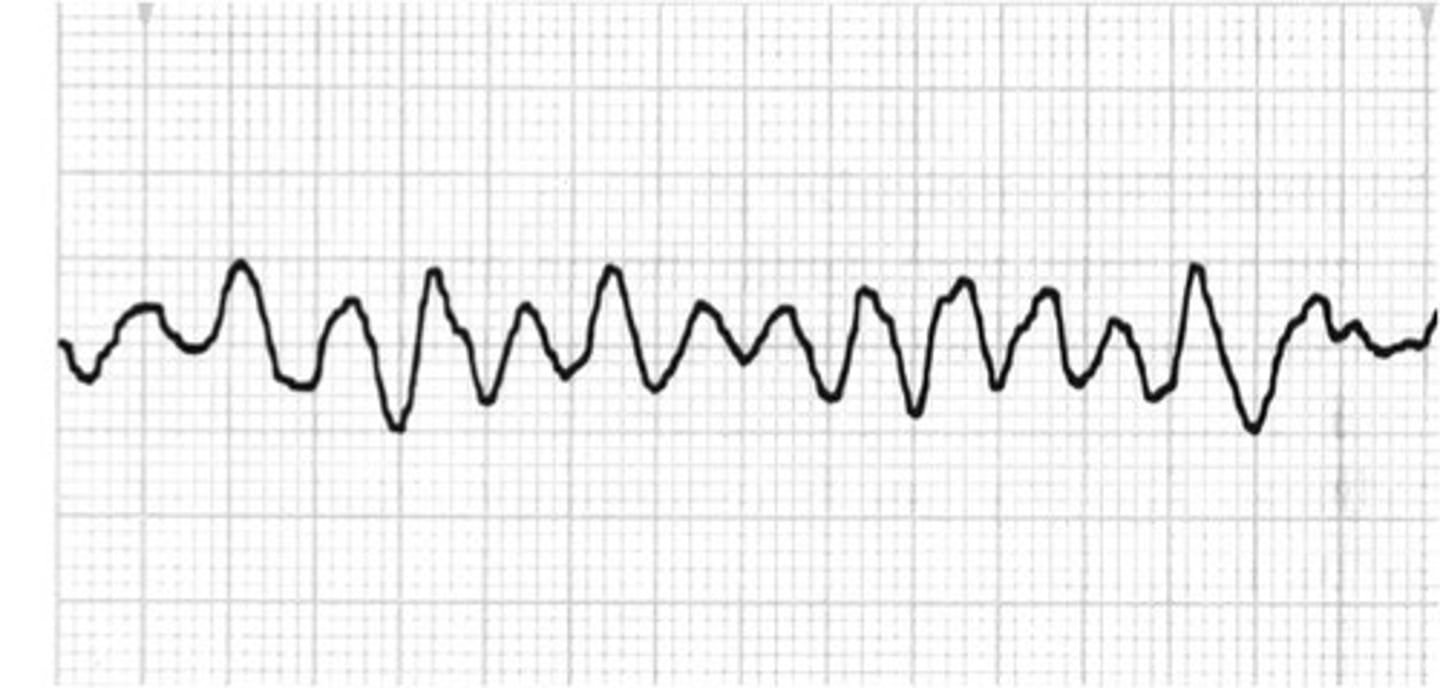
management of pulseless V-tach or V-fib
CPR, defibrillation, IV epi, establish an airway
asystole
no pulse, no waveforms, absence of cardiac electricity
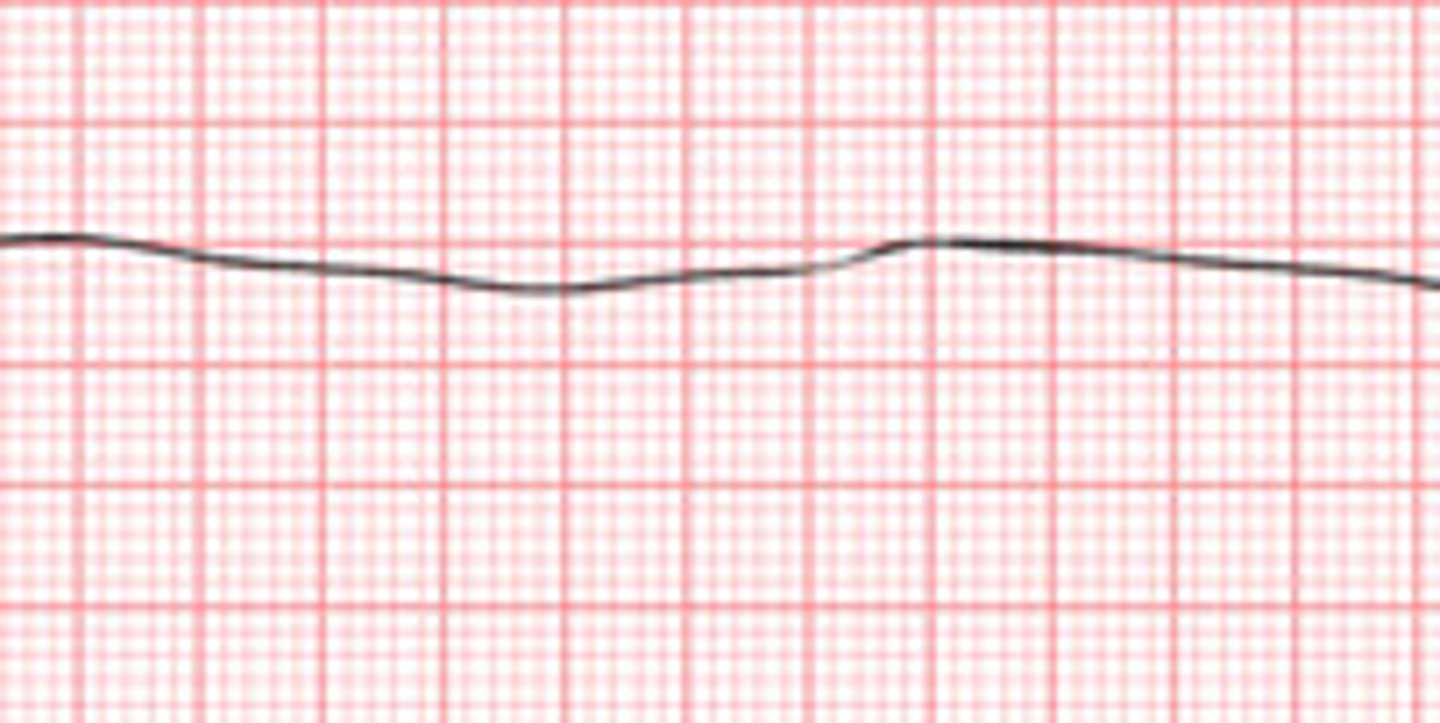
management of asystole
CPR,, identify underlying cause, correct H and T's
pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
organized electrical activity present on the cardiac monitor, but there is a mechanical failure of the heart
patient has NO PULSE, NOT BREATHING, UNCONSCIOUS
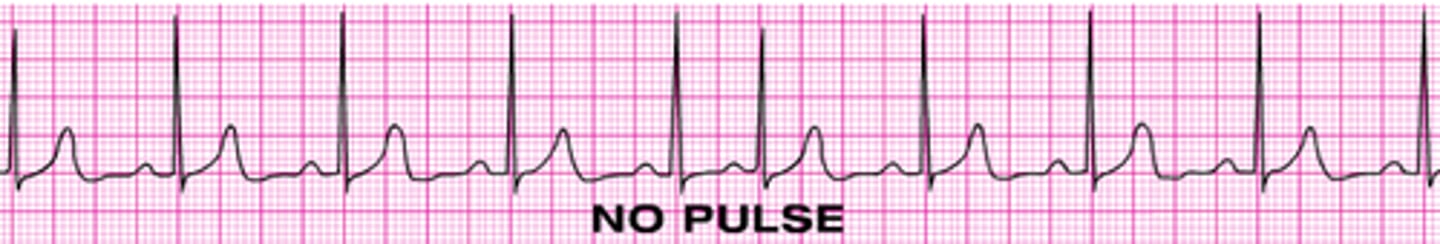
management of PEA
CPR, ABCs, identify and treat causes
first degree AV block
atrial conduction delayed through AV node, prolonged PR interval
rate: depends on underlying rhythm
rhythm: regular
P waves: present before each QRS, consistent in size and shape
PR interval: >0.20 seconds
QRS duration: <0.10 seconds
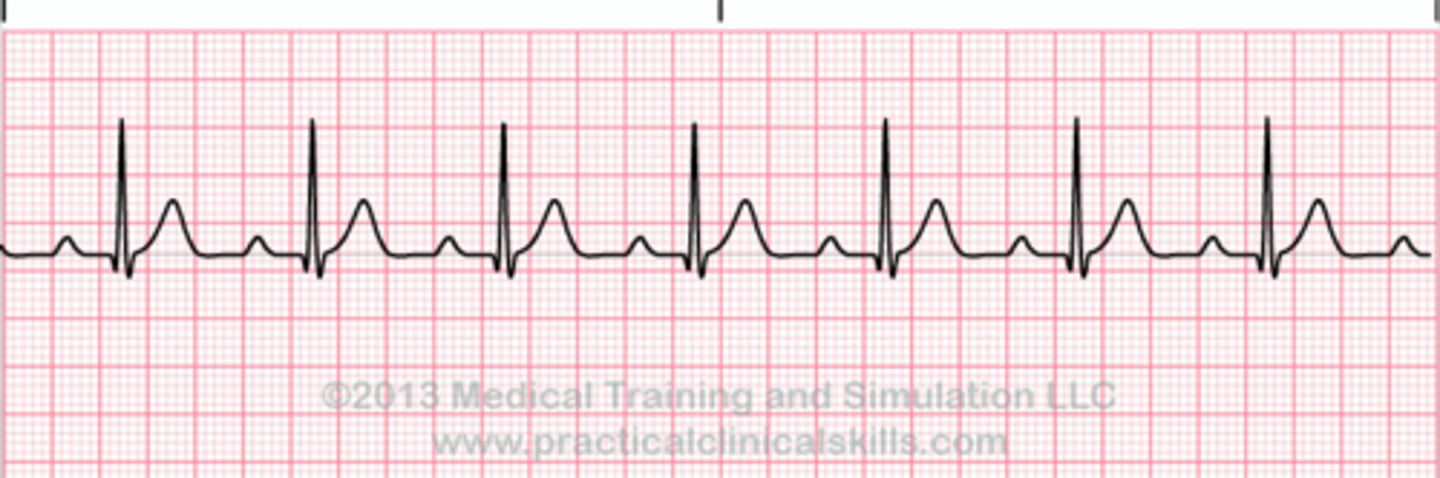
first degree AV block poem
If the R is far from P, then you have a FIRST DEGREE
second degree type 1 AV block (Wenckebach)
repeating pattern where all but one of a series of atrial impulses are conducted through AV node;
each impulse takes a longer time for conduction than the one before, until one is blocked
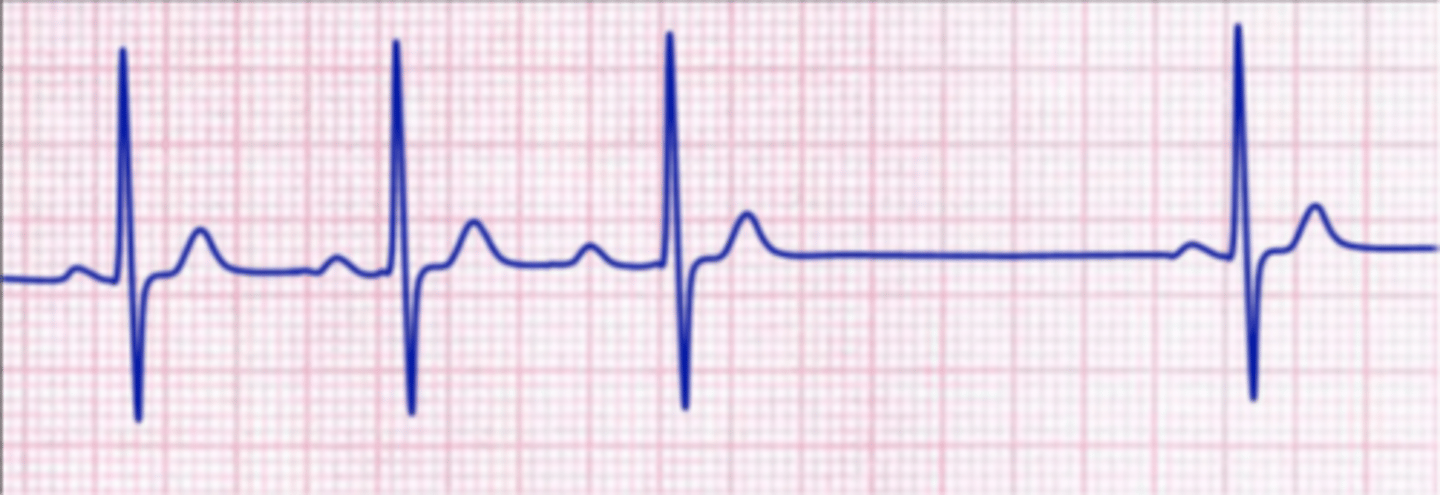
second degree type 1 AV block poem
Longer-longer-longer-dropped! Now you have a Wenckebach!
second degree type 2 AV block (Mobitz II)
only some of the atrial impulses are conducted through AV node into the ventricles
PR interval: consistent until a QRS is dropped
P waves not followed by a QRS
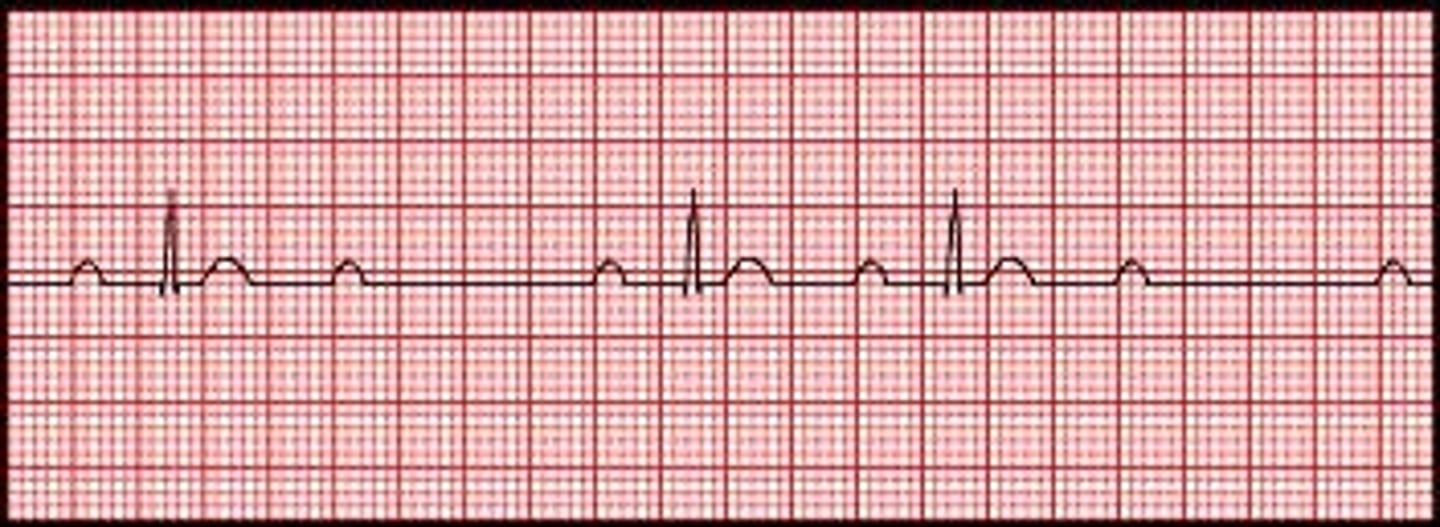
third degree AV block
no atrial impulse is conducted through the AV node into the ventricles
two separate impulses are happening at the same time
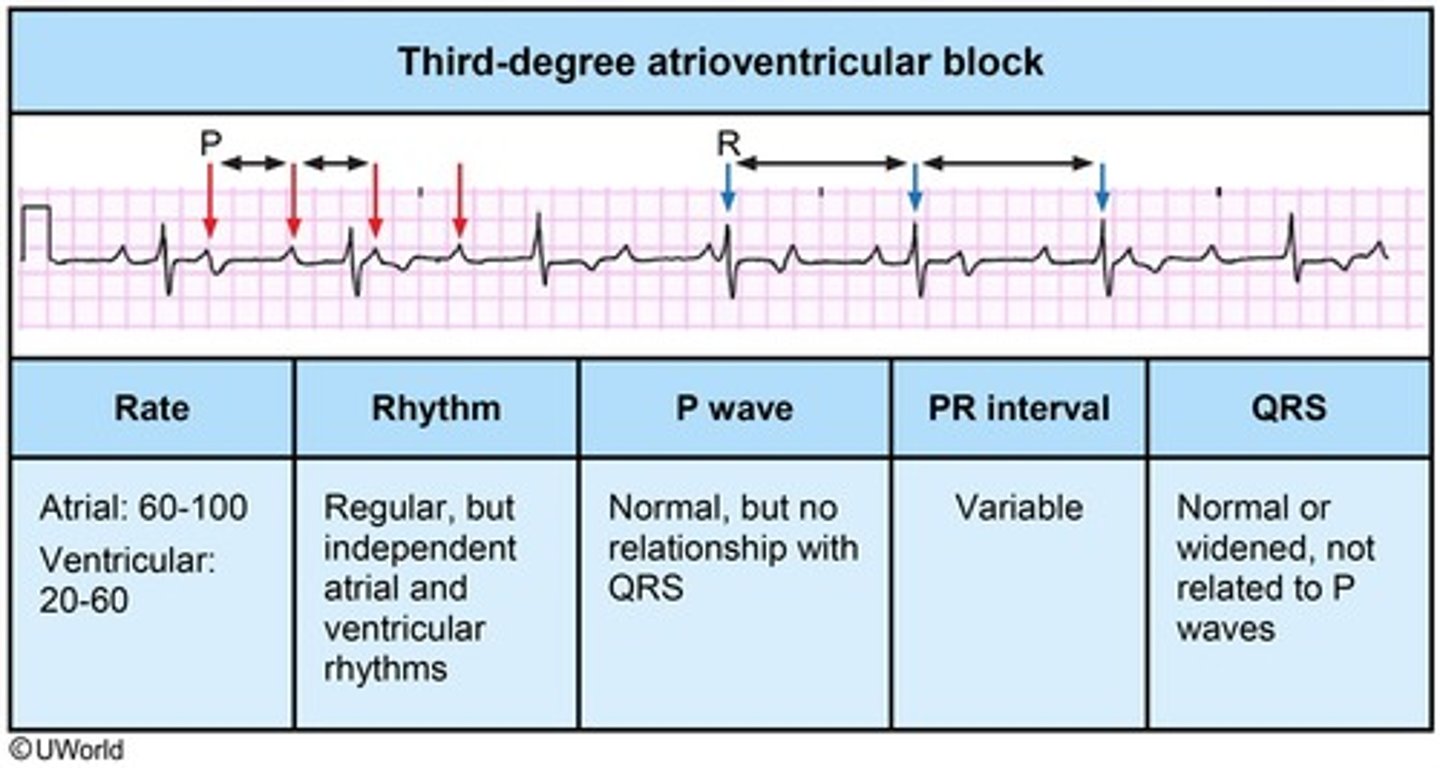
third degree AV block poem
If P's and Q's don't agree, then you have a THIRD DEGREE
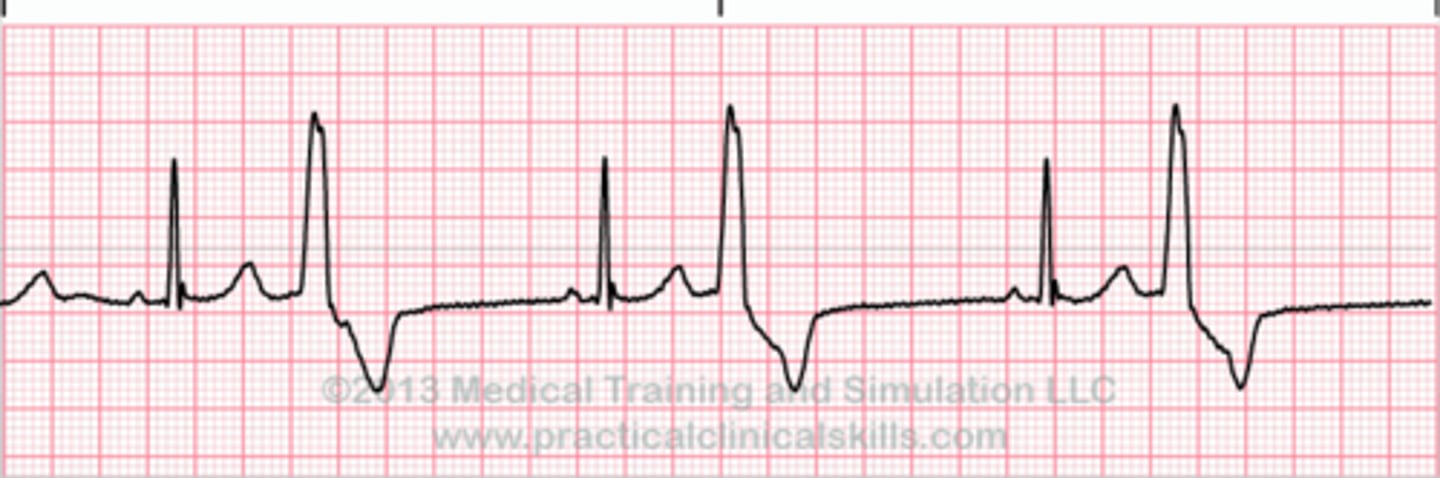
atrial pacing
pacer spike happens immediately before p wave
ventricular pacing
pacer spike happen immediately before QRS
failure to sense
pacer fails to sense patient's own intrinsic beat and fires causing competition problems
failure to capture
pacer spike occurs but no depolarization of muscle detected with QRS complex