AP Human Geography : Unit 1 Terminology
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Reference Map
Maps that show the absolute location of places including boundaries and place names; examples: political maps, physical maps, road maps
Thematic Map
A broad category of maps that tell stories, typically showing the degree of some attribute (a theme) or the movement of a geographic phenomenon.
Isoline Map
A map that contains lines which show spatial bands in which some measured attribute is equal across the entire band; e.g. isotherm map or topographical map
Topographic Map
A type of isoline map which reveals in two dimensions the contours of a landscape through the use of lines of equal elevation; used by hikers; scale = 1:24,000
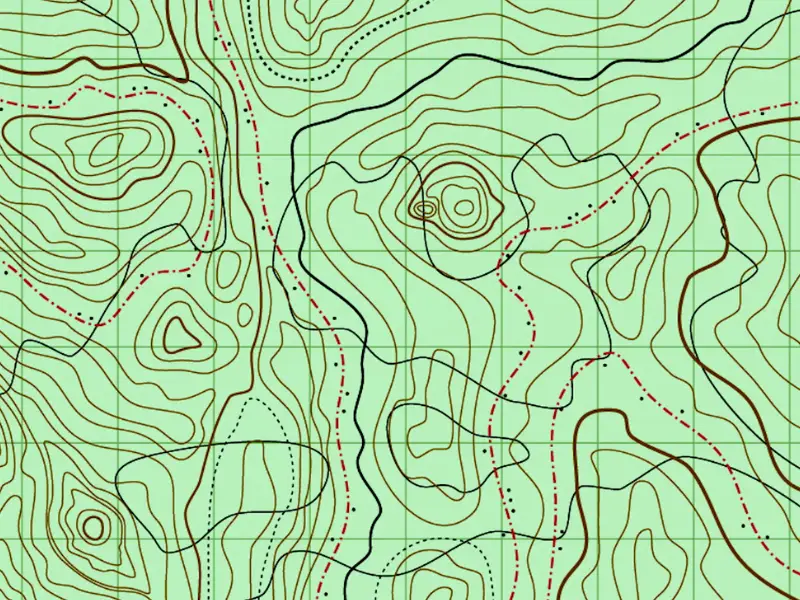
Elevation
Vertical distance above sea level

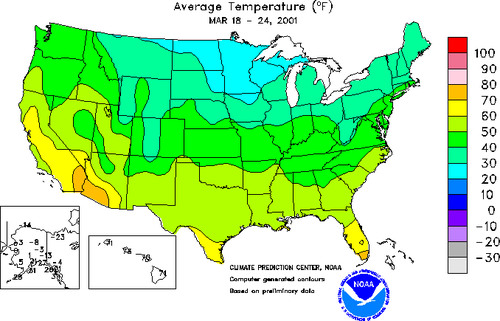
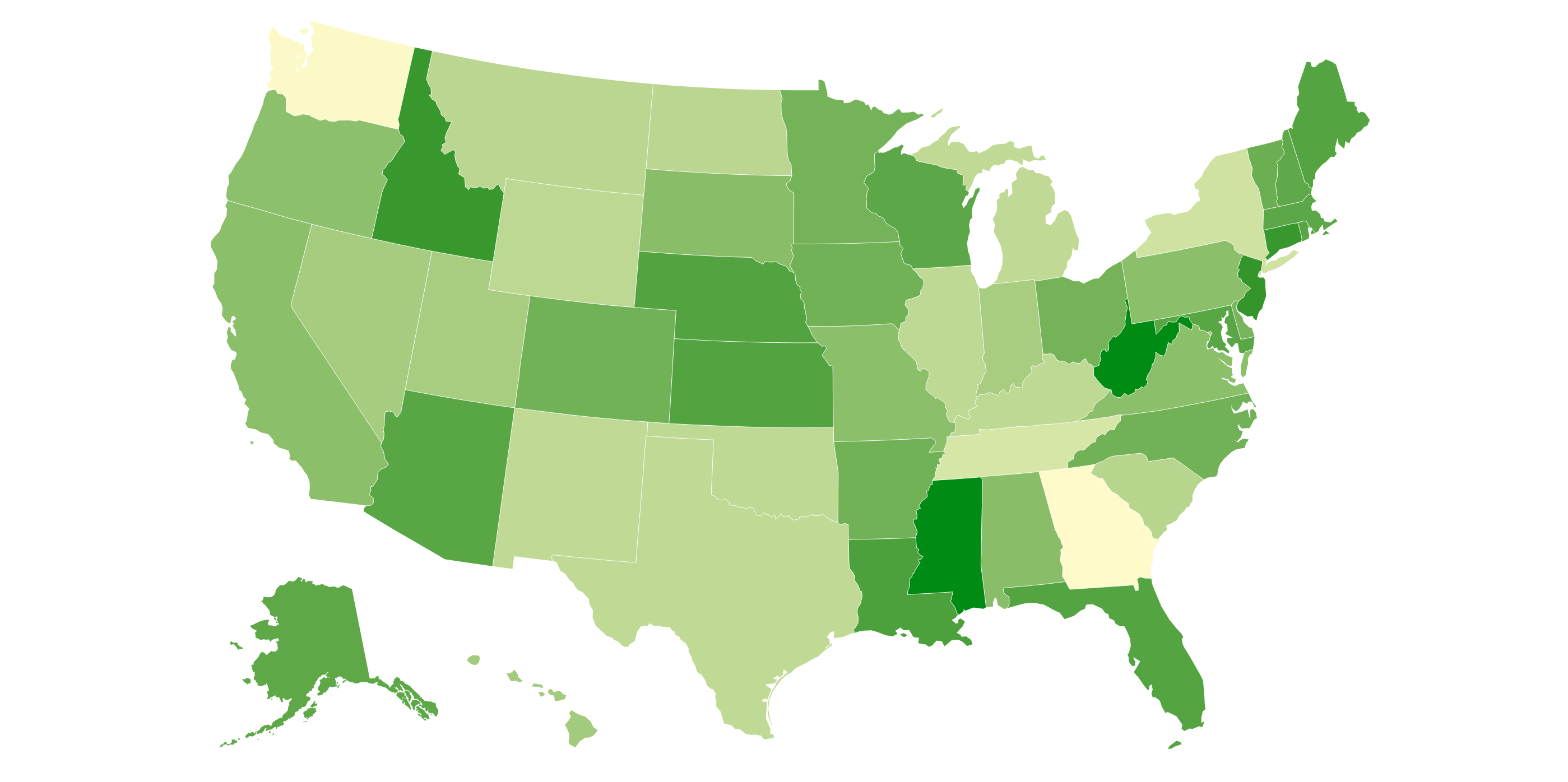
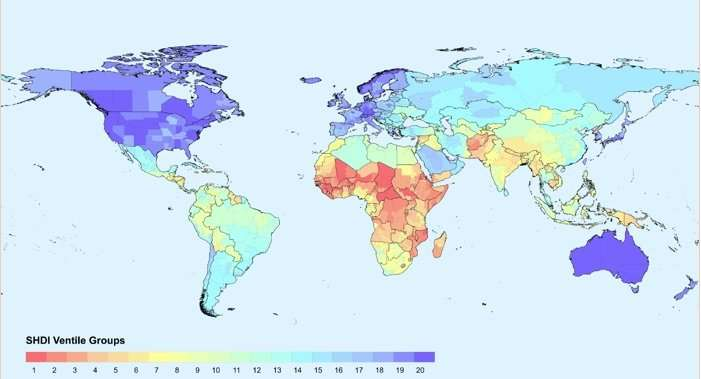
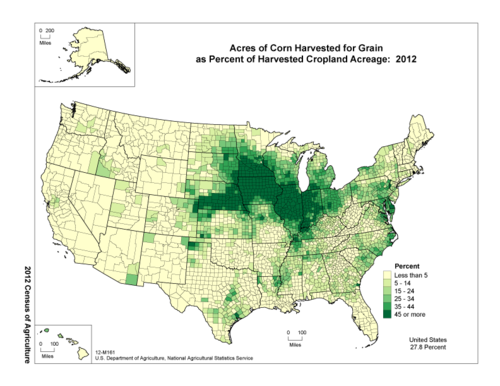
Choropleth Map
A map in which geographical areas or regions are colored, shaded or patterned in relation to a data variable. This provides a way to visualize values over a geographical area, which can show variation or patterns across the displayed location.
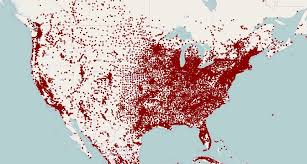
Dot Density/Distribution Map
A type of thematic map that uses dots on a map to show the presence of some variable; a high concentration of dots would be considered a clustered spatial pattern while distance between dots would be considered a dispersed spatial pattern.
Clustered Spatial Pattern
A high concentration/presence of a variable in one location
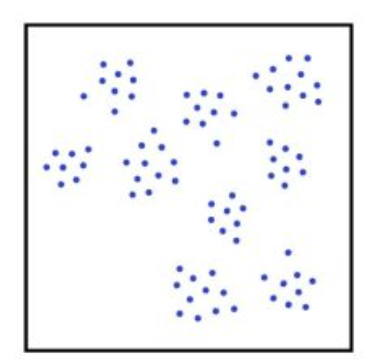
Dispersed Spatial Pattern
A low concentration of a variable in one location; spread out
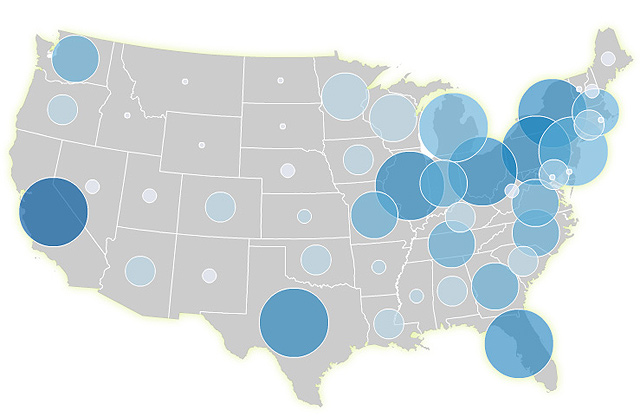
Graduated Symbol Map
A map which scales the size of symbols - usually circles -proportionally to the quantity or value of some variable at that location
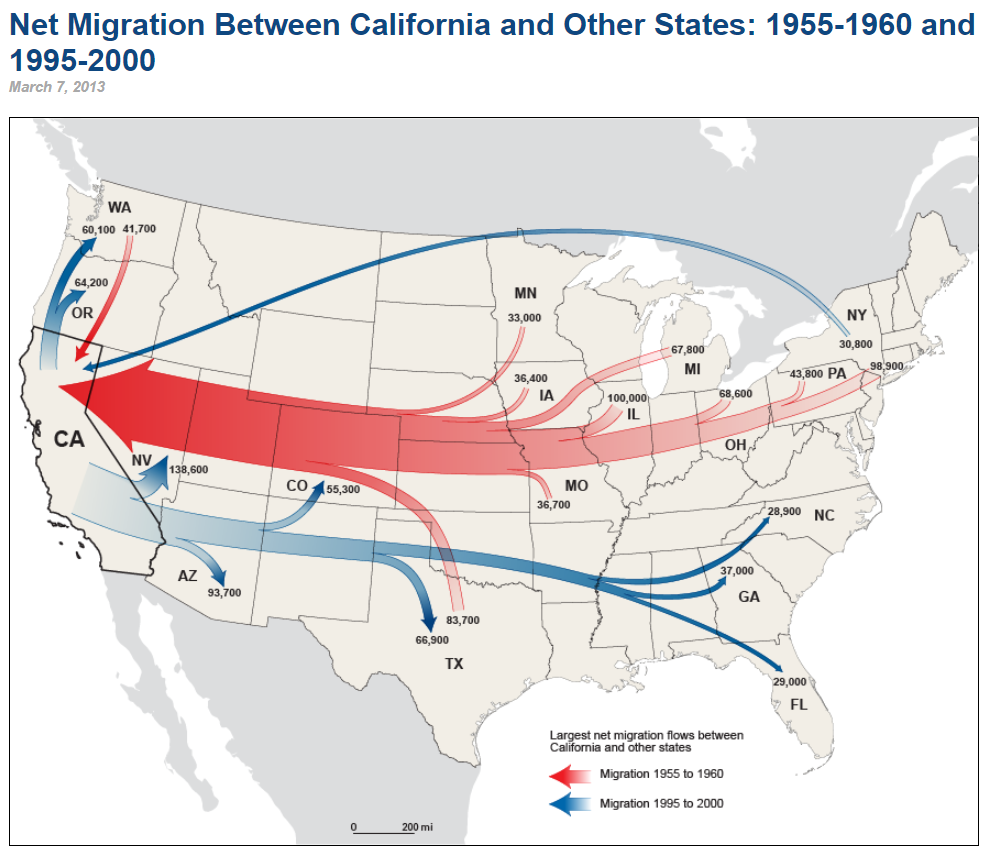
Flow Map
A type of thematic map used to show the movement (flow) of an entity between different areas, often utilizing varying widths of a band or an arrow to show varying volumes of flow.
Cartogram Map
A map in which some thematic mapping variable is substituted for land area, using size distortion to convey the comparative value of different states
Mental Map
A mental picture of the way space is organized as determined by an individual's perception, impression, and knowledge of that space.
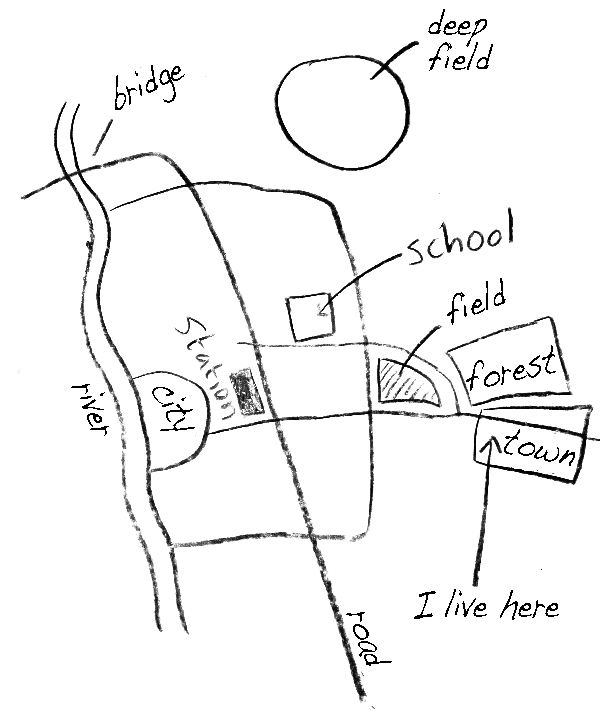
Absolute Location
Where something is precisely located, typically expressed by latitude and longitude coordinates
Relative Location
A place in relation to other locations
Global Positioning System (G.P.S.)
A global navigation satellite system owned and operated by the US government which provides precise geolocation anywhere on earth to anyone with a GPS receiver; system utilizes around 32 satellites with 4 required for access by a receiver; other examples are GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China)
Remote Sensing
A method of collecting data through the use of instruments (e.g. satellites, aircraft, drones) that are physically distant from the area or object of study; can be either active (e.g. radar, lidar) or passive (e.g. the world at night images)

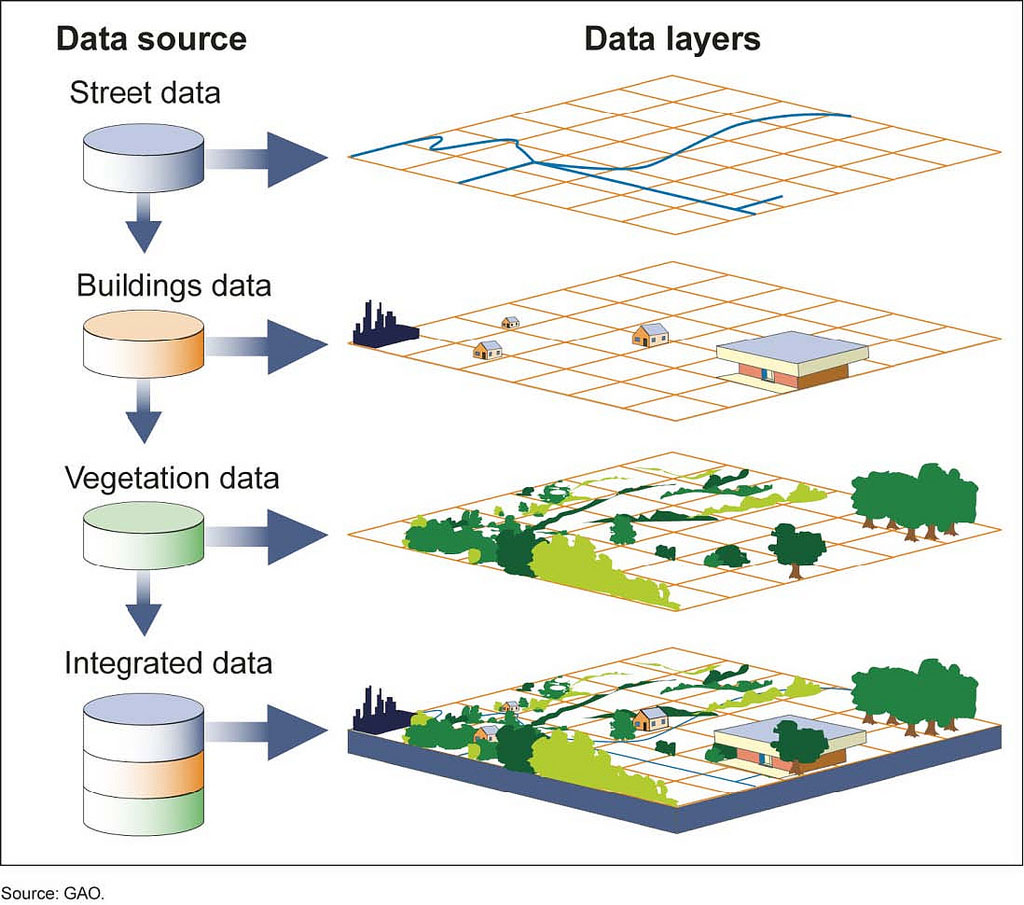
Geographic Information Systems (G.I.S)
Layers of information applied to a map as a way of managing and analyzing data in a spatial format; e.g. a municipal crime map; ArcGIS is most commonly used program
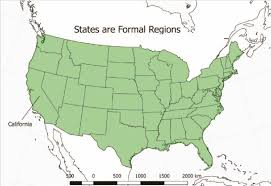
Formal Region (a.k.a. Uniform or Homogenous Region)
An area in which there is uniformity of some attribute; this describes most areas demarcated on a map; a country map is good example
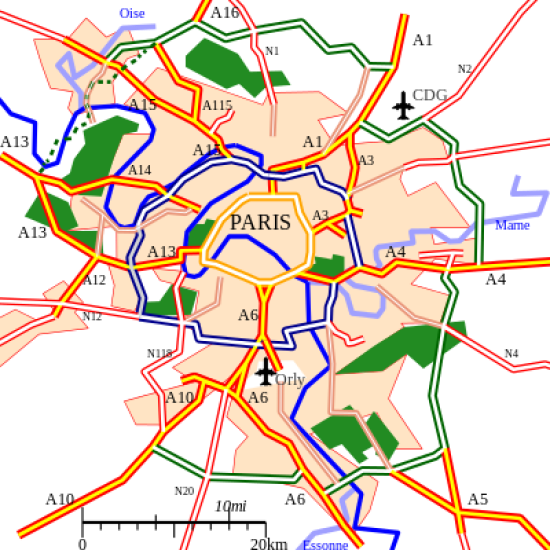
Functional Region (a.k.a. Nodal Region)
An area centered around a node, focal point, or central hub related to trade, communications, or transportation
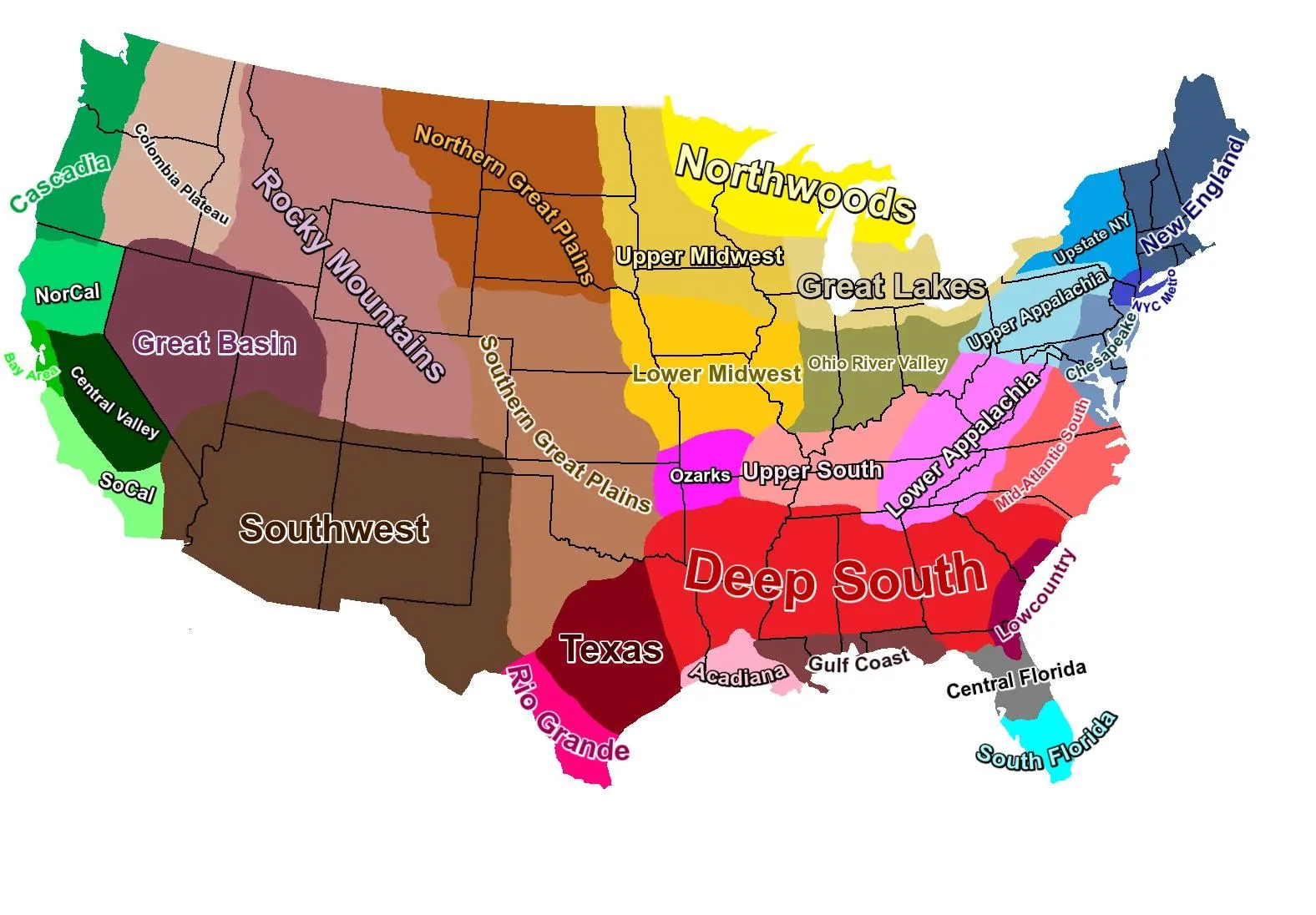
Perceptual (a.k.a.Vernacular Region)
An area whose existence or demarcation is based on perception and is often the subject of debate; a region whose demarcation is not officially recognized; e.g. the Middle East
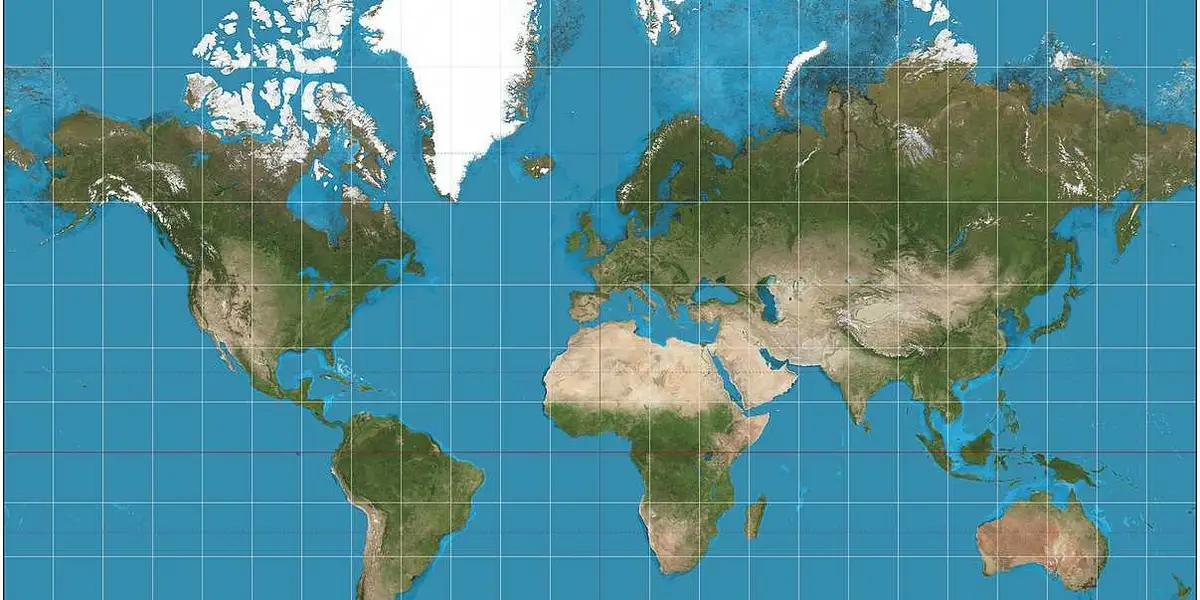
Mercator Projection
A cylindrical map projection (originally created by Gerardus Mercator in 1569) which has been used for navigation as it generally preserves direction and shape; it exaggerates land masses towards the poles
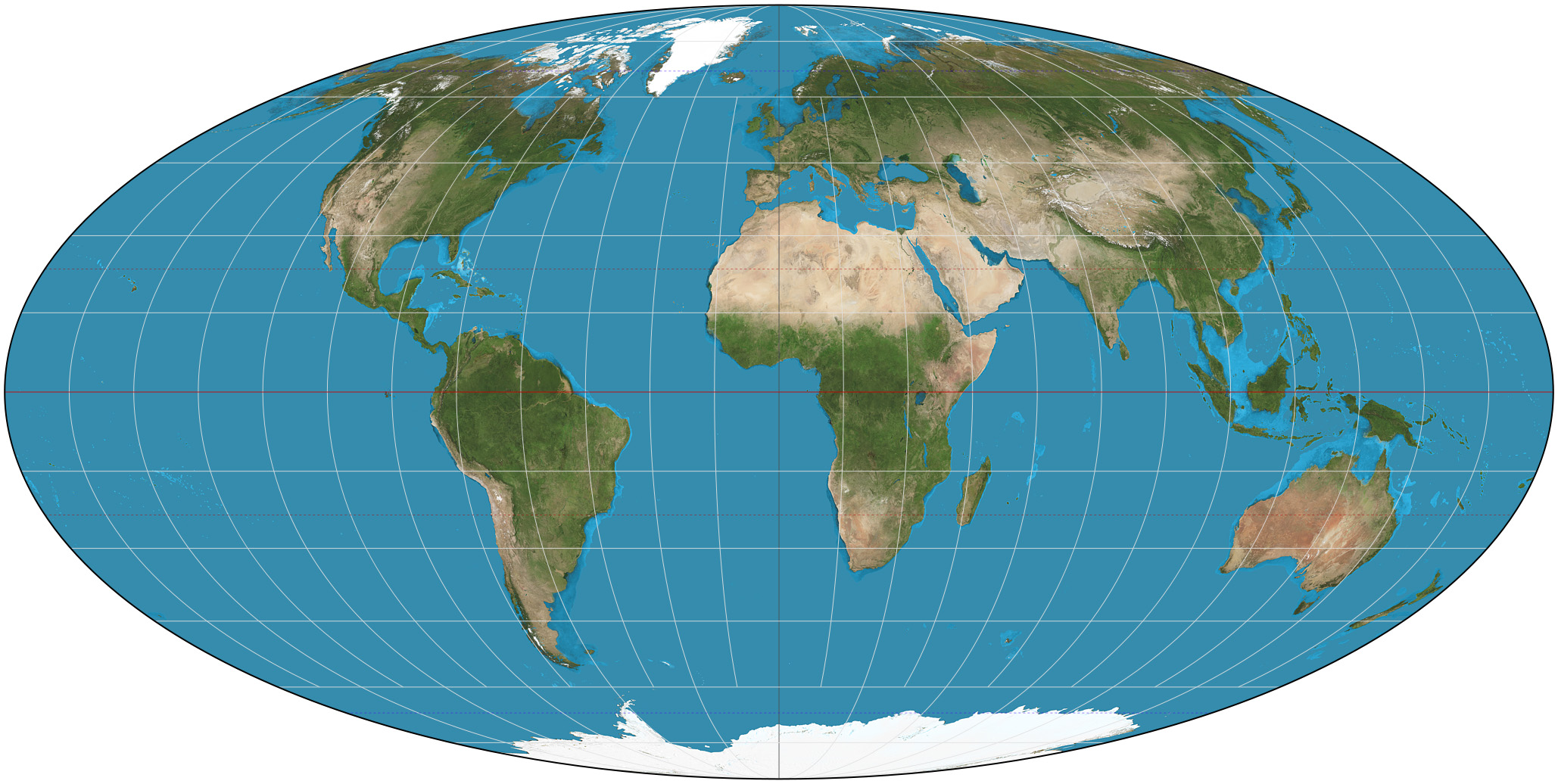
Equal Area Projection
A map projection which preserves relative area while distorting shape in the process; three examples are Robinson, Gall-Peters, and Mollweide (knowing these three examples is not important)
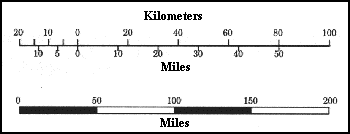
Scale 1st Definition
- The relationship of a distance on a map to the corresponding distance on the ground; e.g. 1 inch = 1 mile or 1:63,360 or ------1------2-----3 Miles
Scale 2nd Definition
The largest political entity on a map; e.g. local scale, sub-national scale, national scale, regional scale, global scale
Scale of Analysis
The level at which comparisons can be made on a map; e.g. a map of the United States with each state showing different degrees of college graduation rates - the scale of analysis would be at the state level, not the national level
Census Tract
A geographical region representing the smallest territorial entity for which there is census data, usually equaling around 4,000 inhabitants, and in cities, is typically the size of a neighborhood
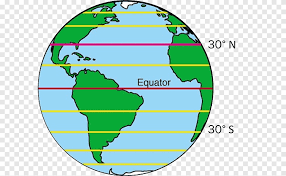
Latitude/Parallel
A coordinate that specifies the point on the surface of the earth ranging from -90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator; think of horizontal lines which are parallel to each other
Longitude/Meridian
A geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the surface of the Earth measured from the prime meridian at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England; think vertical lines which run from north pole to south pole; longitude lines run from 0° at Greenwich, westward across the Western Hemisphere with negative degrees and eastward across the Eastern Hemisphere with positive degrees from 1 to 180 until the International Date Line which is opposite the prime meridian.
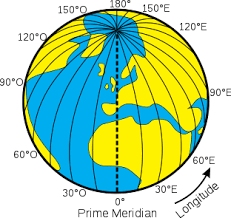
Prime Meridian
An arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°, running roughly through Greenwich, England.

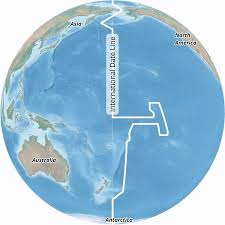
International Date Line (IDL)
An internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South Pole and North Pole and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day (24 hours), while crossing the date line westbound increases the date
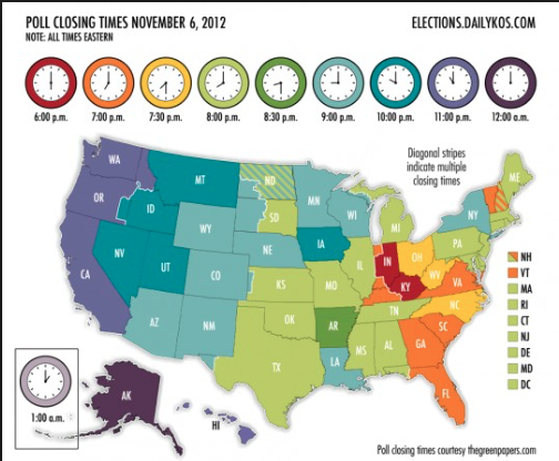
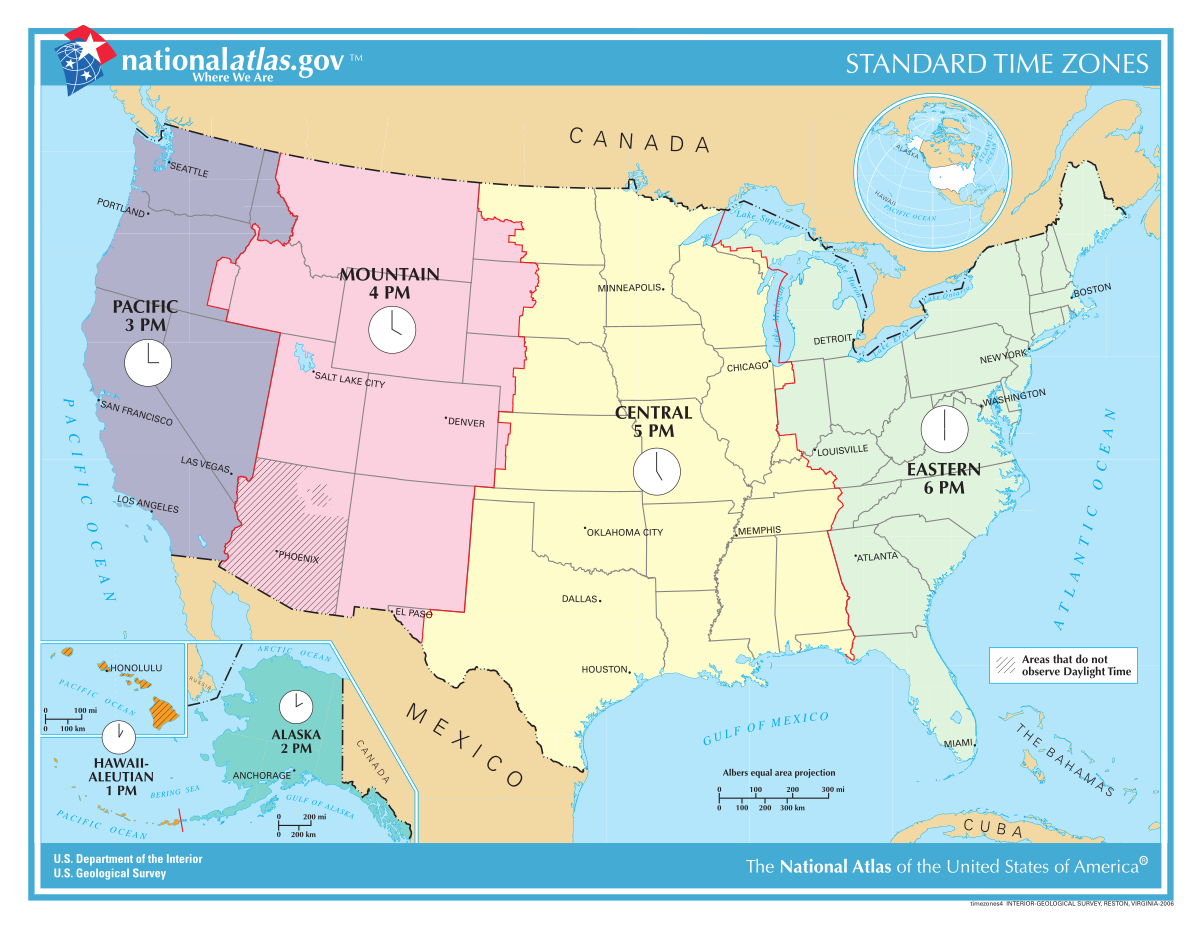
Time Zone
An area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes; it is as an offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the successor to Greenwich Mean Time
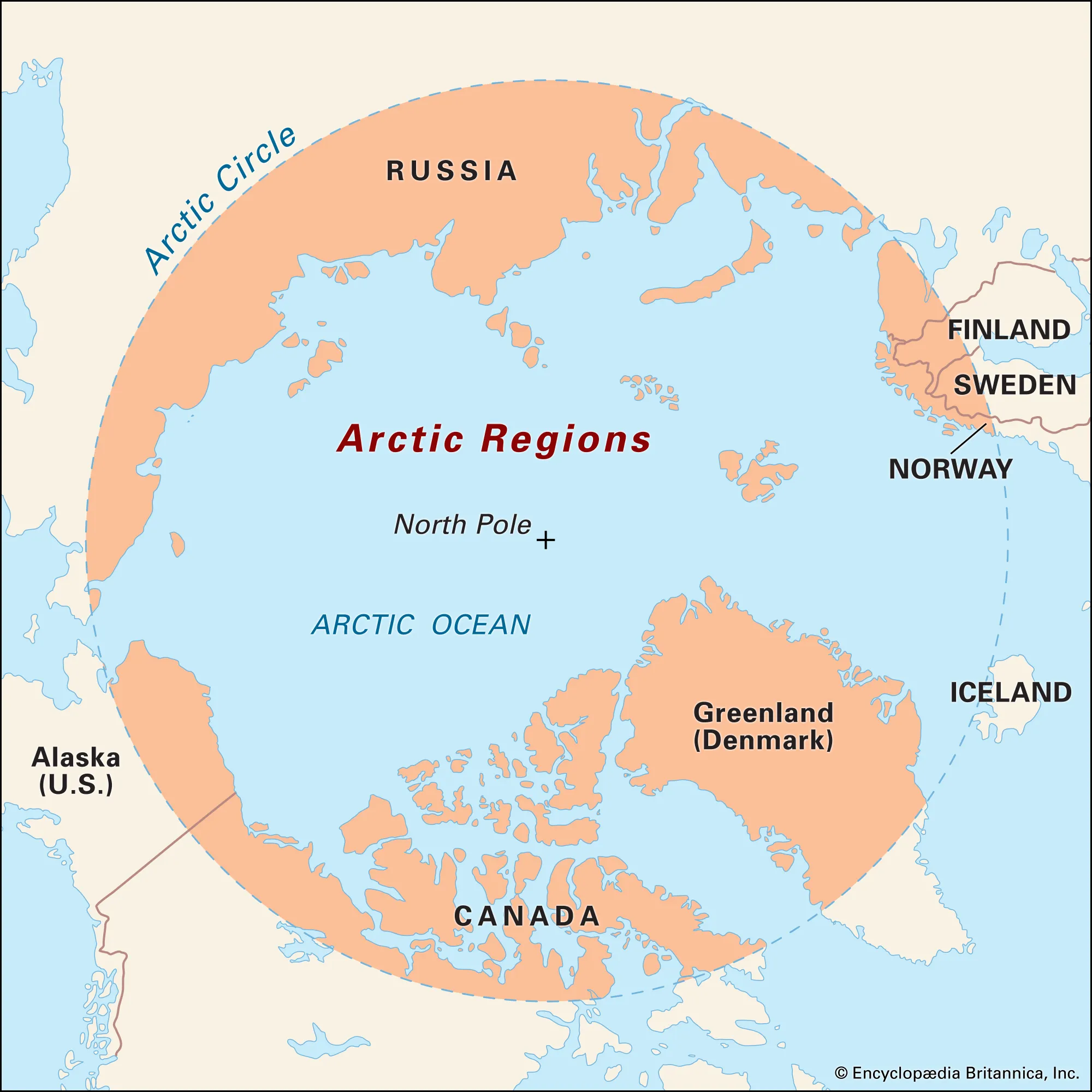
Arctic Circle
The northerly of the two polar circles marking the southernmost latitude at which, on the December solstice, the shortest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not rise all day (polar night), and on the June solstice, the longest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not set (midnight sun); generally at 66°33′.
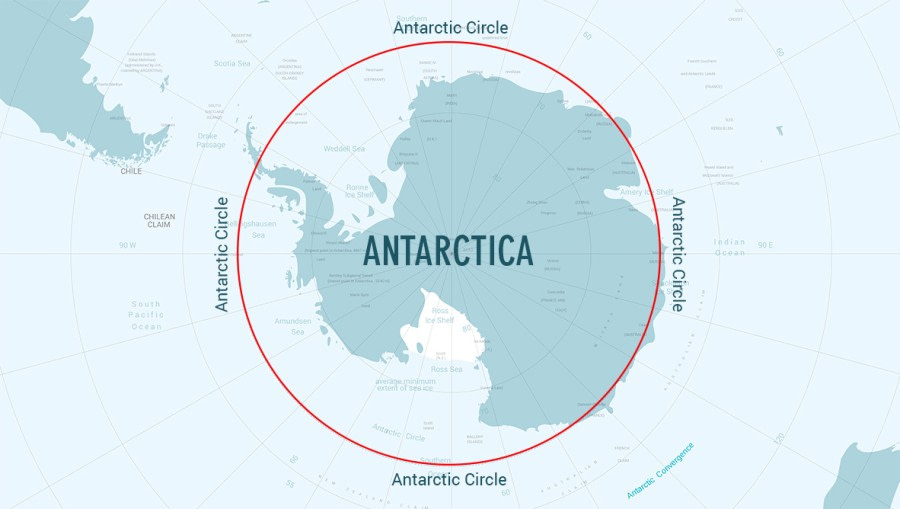
Antarctic Circle
The southerly of the two polar circles, marking northernmost latitude at which the sun is above the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year (and therefore visible at midnight) and the sun is below the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year; generally at 66°33′.
Equator
A circle of latitude (about 24,901 mi in circumference) that divides earth into the northern and southern hemispheres located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles; constant temperatures year-round
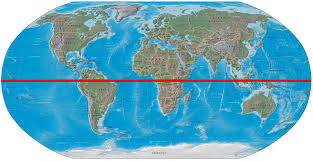
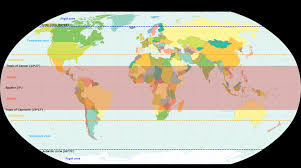
Tropics
The regions of Earth surrounding the Equator between the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at 23.43634° N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at 23.43634° S; the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons.