Ch 55_Motor Functions of the Spinal Cord; the Cord Reflexes
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about motor functions of the spinal cord and cord reflexes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Breakdown the importance of each in regards to the nervous system
Spinal Cord
Brain stem
Cerebrum
Relatively simple reflexes.
more complicated reflexes
most complicated reflexes
What is the Gray Matter?
The area where cord reflexes are integrated.
sensory signals enter the cord through the posterior root (afferent) and will terminate in the gray matter cord OR be transmitted to higher levels of nervous system
Which two neurons are found within the grey matter?
anterior motor neurons and interneurons
Describe Anterior Motor Neurons
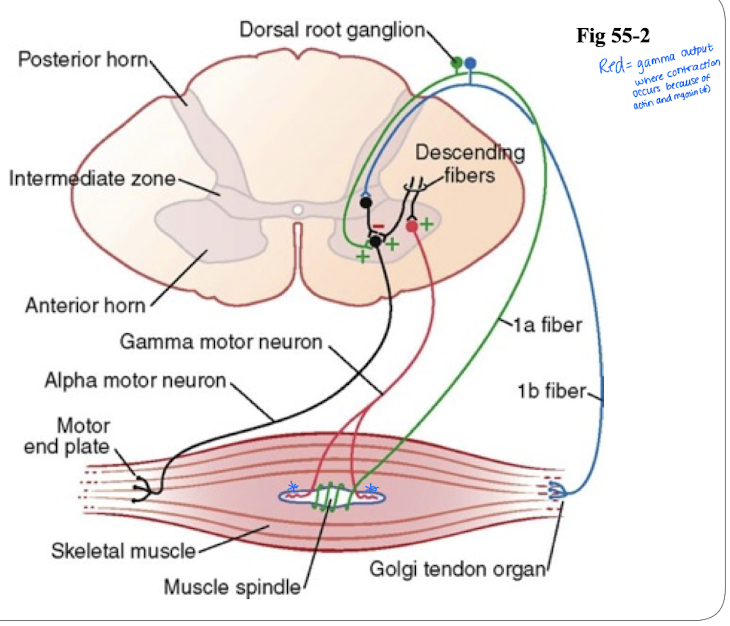
Located within the anterior (ventral) horns of the cord gray matter & innervate skeletal muscles.
consist of alpha motor neurons (large type) and gamma motor neurons (innervate the intrafusal fibers (muscle spindle and fibers)
α-motor neurons
Large type Aα (motor units).
γ- motor neurons
½ as many as α-motor neurons; Smaller type γ fibers innervate the intrafusal fibers.
Describe interneurons
located in the dorsal and ventral horns of the gray matter
small and highly exciteable
consist of renshaw cells
Which neuron of the grey matter is responsible for most of the integrative functions of the spinal cord?
Interneurons
What are Renshaw cells
Inhibitory neurons located in the anterior horns of the spinal cord close to motor neurons
inhibits adjacent motor neurons (lateral inhibition - for fine precision and controlled movements) to focus or sharpen its signal.
What are Sensory Receptors?
What are the purpose of them?
Name the two types
Provide continuous feedback of sensory information indicating functional status of each muscle.
intrinsic muscle control
Muscle spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs (GTO)
How is information sent to the brain from the spinal cord using sensory receptors?
Spinal cord, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex
What are Muscle Spindles?
Sensory receptor providing information regarding muscle length or rate of change of length.
Which sensory receptor has no actin and myosin but the ends are activated by gamma motor nerves called gamma efferents
muscle spindles
receptor is stimulated by stretch
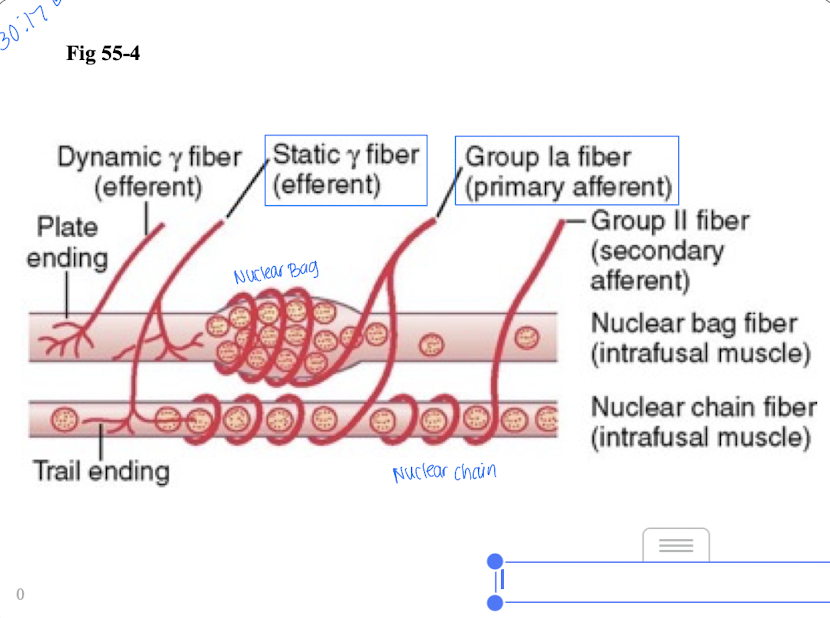
Muscle spindle (sensory receptor) have sensory fibers that encircle the midportion of the receptor. What are the two types?
BOTH ARE SENSORY
Primary ending - large type Ia fiber (fast)
Secondary ending - smaller type II innervates on the side of the primary ending
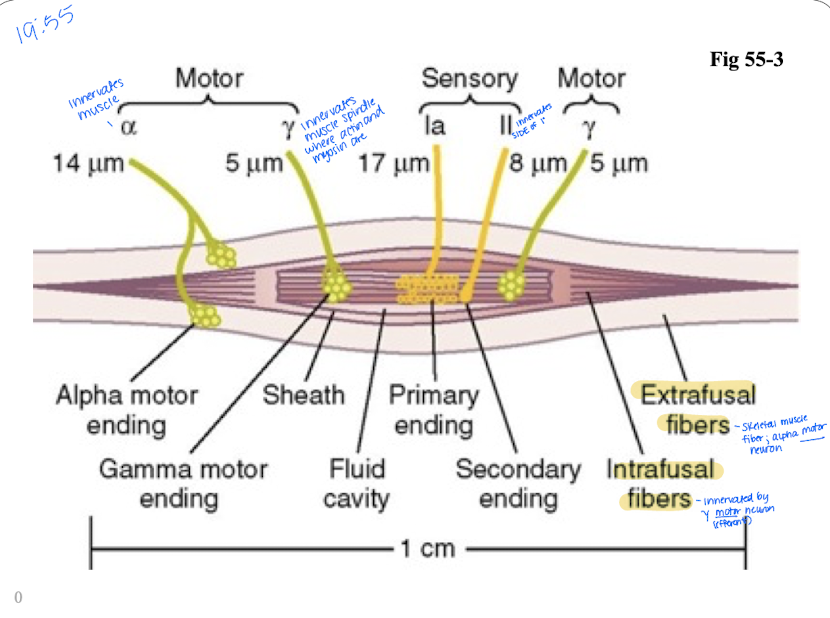
Within the muscle fiber are two types of intrafusal muscle fibers. Define both
nuclear bag fibers - innervated by primary ending
Nuclear chain fibers - innervated by primary ending and secondary ending
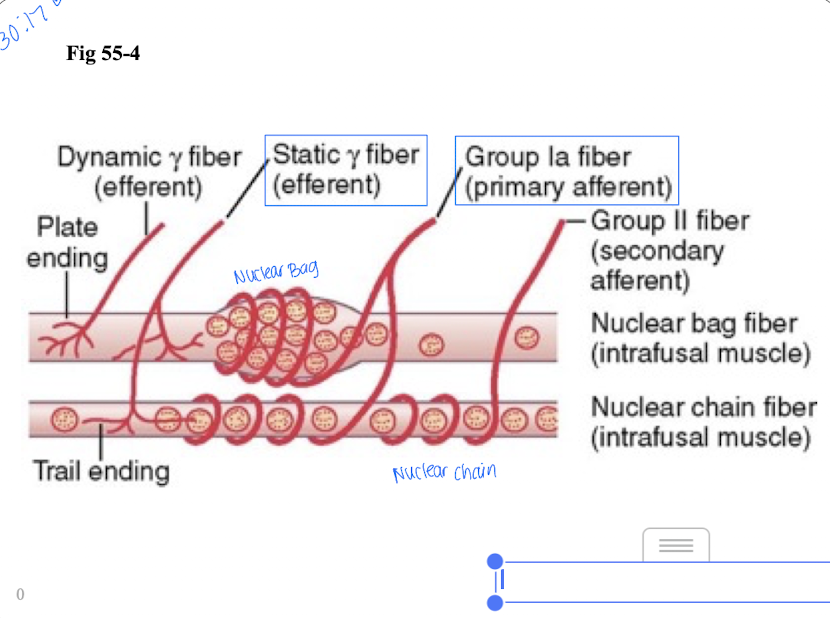
What responses are intrafusal fibers responsible for?
Response is based on the type of stretch
static response - when spindle is stretched slowly (both primary and secondary endings respond)
we are always at static response because info is always being relayed and incoming because of muscle tone
dynamic response - when length increases suddenly (primary ending only responds)
once stretch is over, static response will occur
Muscle Stretch reflex
Stretch of the muscle causes excitation of the spindle causing reflex contraction of skeletal muscle. What two pathways can the stretch reflex occur in?
What are the two reflex components
Monosynaptic and Polysynaptic (more synapse = relay takes longer)
The reflex has two separate components
Dynamic stretch reflex and static stretch reflex
Which stretch reflex is continued for prolonged periods of length change and responsible for maintaining contraction and tone?
Static stretch reflex
What are Golgi Tendon Organs (GTO)?
Sensory receptors that detect changes in muscle tension located at the end of muscles
use dynamic and static response
Once change in muscle tension is detected, impulses will be sent to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord AND cerebellum a cerebral cortex with large type Ib fibers (afferent)
GTOs are inhibitory - when activated they inhibit the anterior motor neurons from firing
What does it mean that GTO are inhibitory?
when activated they inhibit the anterior motor neurons from firing
They participate in a negative feedback loop
in an event of extreme tension is placed on a muscle, the lengthening reaction (instantaneous relaxation of muscle) may occur as a protective mechanism (when you left heavy and can no longer hold the weight, signal is sent to the brain to let it go”
What are the primary and secondary functions of GTO
Negative feedback loop for lengthening reaction
Equalize contractile forces of separate muscle fibers = fibers with excessive tension are relaxed and fibers with too little tension become more excited
Nuclear bag fibers
Nuclei are congregated; contains primary ending.
Nuclear chain fibers
Nuclei arranged in chain fashion; contains primary and secondary endings.
Static response
When spindle is stretched slowly, both endings respond.
Dynamic response
When length increases suddenly, primary ending only responds.
Muscle Stretch Reflex
Simplest manifestation of muscle spindle function.
What is Damping?
Important function of stretch reflex - Smoothing of jerky body movements.
muscle spindles act to dampen the signals for smooth contraction
What is Coactivation?
What is the purpose?
Allows for contraction of intrafusal (alpha motor neurons) and extrafusal fibers (gamma motor neurons) of the muscle spindle simultaneously.
Keeps length of receptor portion from changing during contraction AND maintains proper dampening function
Gamma motor system
Where are impulses from?
Why are they necessary?
bulboreticular facility of brain stem
Necessary for stabilization of body position during motor actions (gross and intricate) where muslces on both sides of the joint are activated
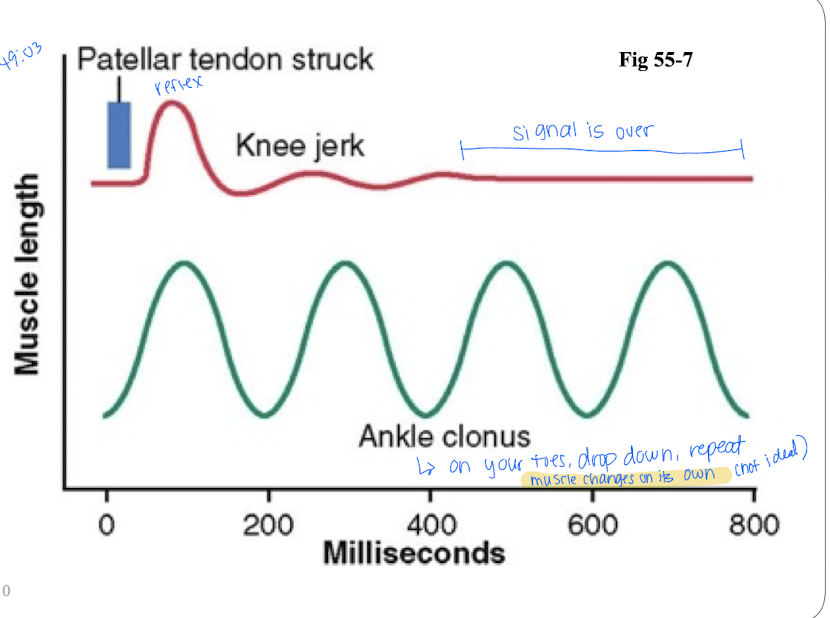
what is the Patellar tendon reflex
Stretches quad muscle and excites a dynamic stretch reflex; used to asses the degree of facilitation of spinal cord centers.
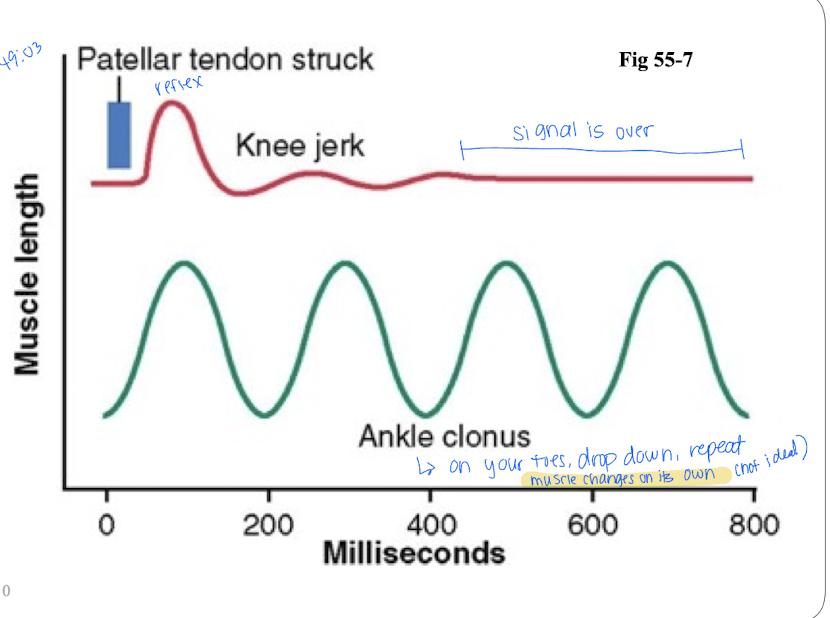
What is Clonus?
Oscillation of a muscle.
toe raises are used to assess the presence of upper motor neuron lesions, where the muscle involuntarily contracts and relaxes repeatedly.
What is the Flexor reflex?
Cutaneous sensory stimulus from a limb causes (flexor) muscle contraction, withdrawing the limb from the object.
aka nociceptive reflex or pain reflex
What are the 3 types of circuits in neuronal mechanism of flexor reflex?
Diverging-Spread reflex to necessary muscles for withdrawal.
Reciprocal inhibition - Inhibit antagonists.
Afterdischarge - After stimulus is over; repetitive firing of excited interneurons (immediate); recurrent pathways that initiate oscillation in reverberating interneurons (prolonged).
T/F: both flexor reflex and crossed extensor reflex use polysynaptic pathways
true
Crossed Extensor Reflex
Extension occurs in the limb opposite of the flexor reflex very quickly after flexor reflex.
has a longer afterdischarge than flexor reflex
What is reciprocal inhibition?
when a stretch reflex excites one muscle or group of muscles while simultaneously inhibiting the antagonist muscle or group