cell growth, cell cycle, mitosis and cytokinesis
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
in unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the …
entire organism
multicellular eukaryotes depend on cell division for…
development from a fertilized egg
growth
repair
cell division is an integral part of the …
cell cycle (the life of a cell from formation to its own division)
most cell division results in …
two daughter cells with identical genetic information, DNA
what is the exception to the fact that most cell division results in two daughter cells with identical genetic information
meiosis, special type of division that can produce sperm and egg cells
all the DNA in a cell constitutes the cell’s …
genome
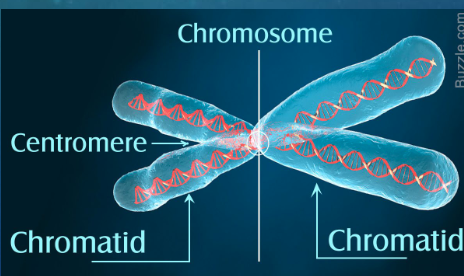
DNA molecules in a cell are package into …
chromosomes
eukaryotic chromosomes consist of …
chromatin
what is chromatin
complex of DNA and protein that condenses during cell division
… cells have two sets of chromosomes
somatic (non-reproductive cells)
… have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells
reproductive cells (sperm and eggs)
in preparation for cell division…
DNA is replicated and the chromosomes condense
each duplicated chromosomes has two…
sister chromatids (joined copies of the original chromosome)
what is the centromere
the narrow “waist” of the duplicated chromosome, where the two chromatids are most closely attached
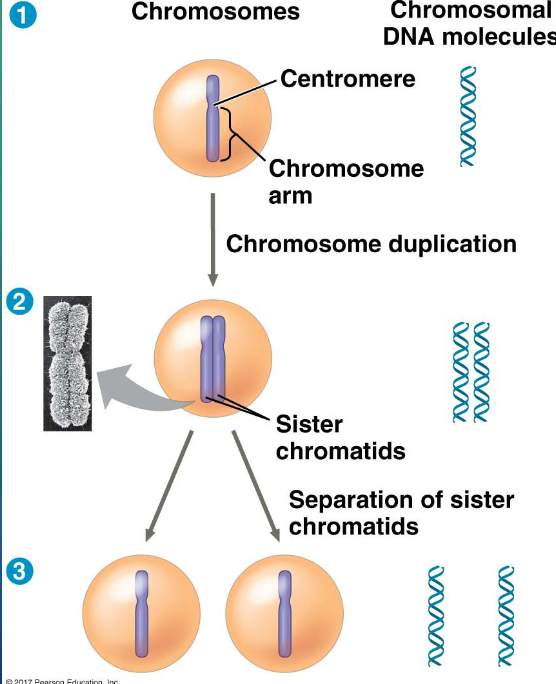
during cell division, the two sister chromatids of each duplicated chromosome…
separate and move into two nuclei
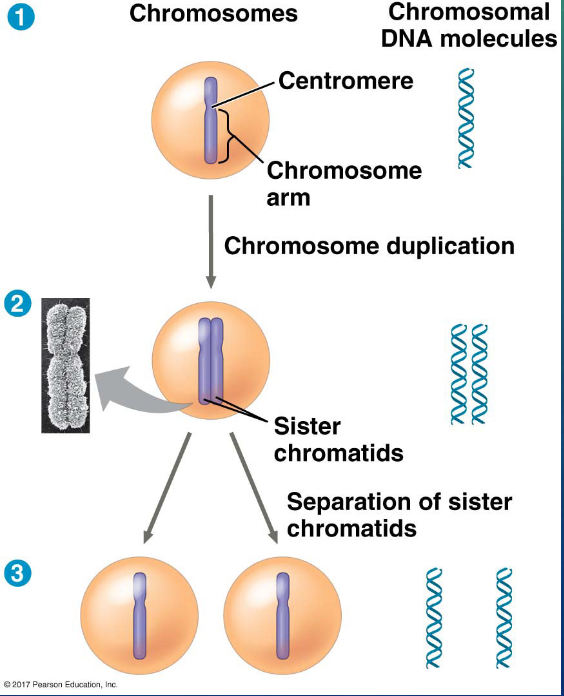
once separated, the chromatids are called…
chromosomes
eukaryotic cell division consists of…. (2 types of division)
karyokinesis (division of genetic material)
cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm)
the cell cycle consists two main phases…
mitotic (M) phase= mitosis and cytokinesis
interphase= cell growth and copying of chromosomes in preparation for cell division
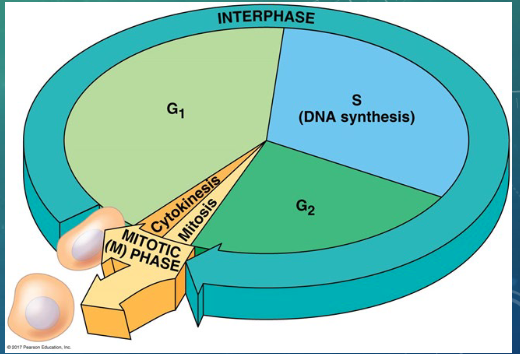
interphase makes up around… of the cell cycle
90%
what are the three phases of interphase
G1 phase= first gap
S phase= synthesis (CHROMOSOMES DUPLICATED)
G2 phase= second gap
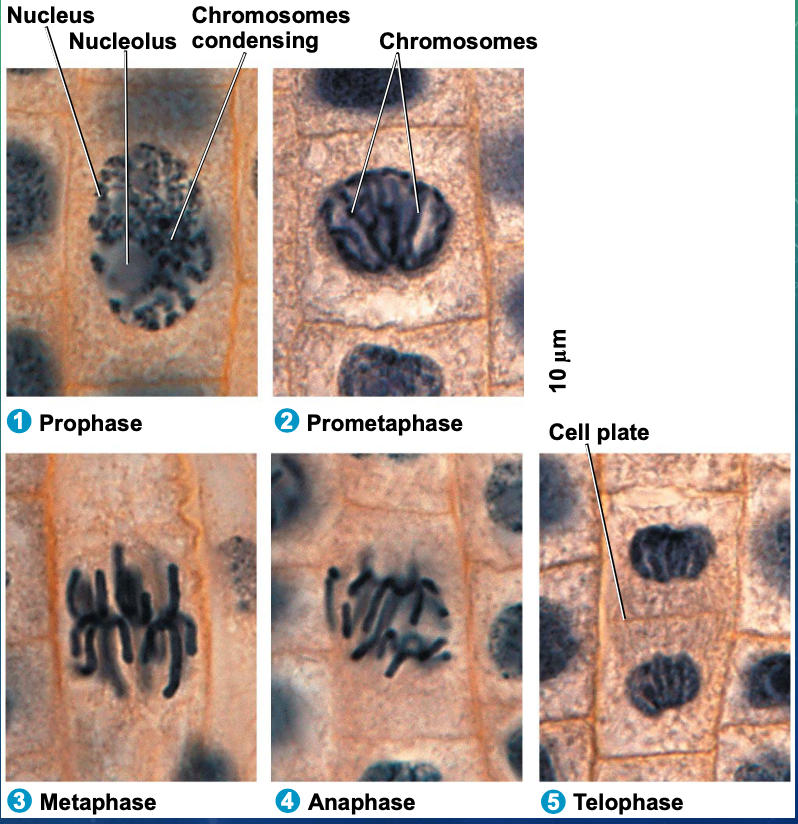
mitosis is broken down into four stages
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
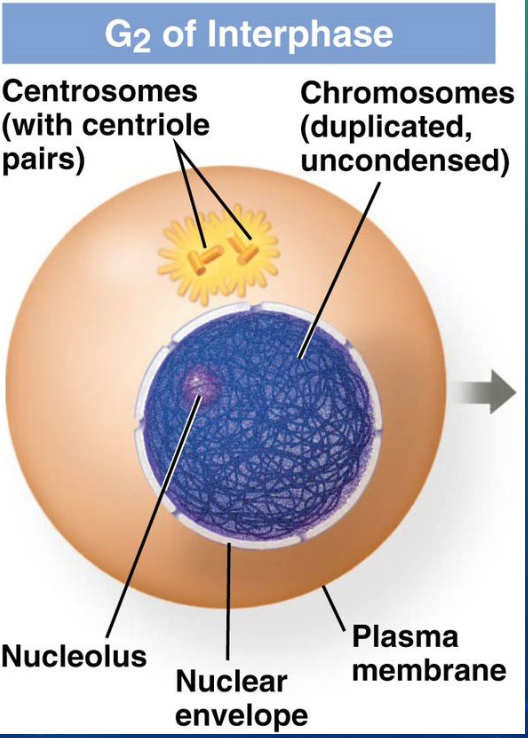
before mitosis happen… what happens in G2 phase of interphase?
centrioles duplicate and begin moving to opposite poles of the cell
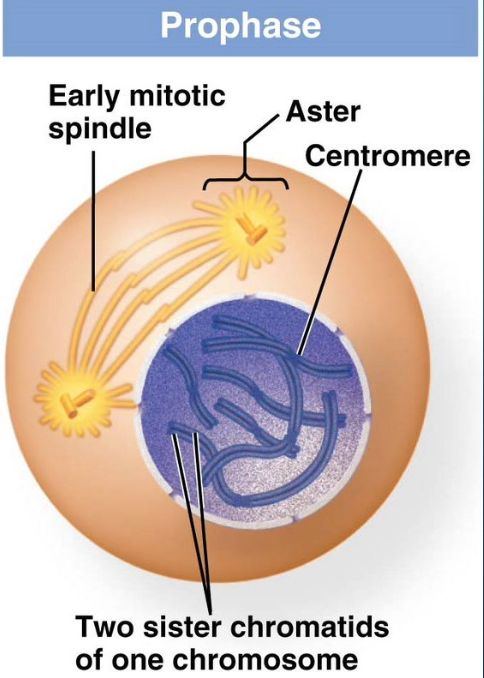
outline what happens during prophase
chromosomes condense
nuclear envelope begins to dissolve
early mitotic spindle begins to form
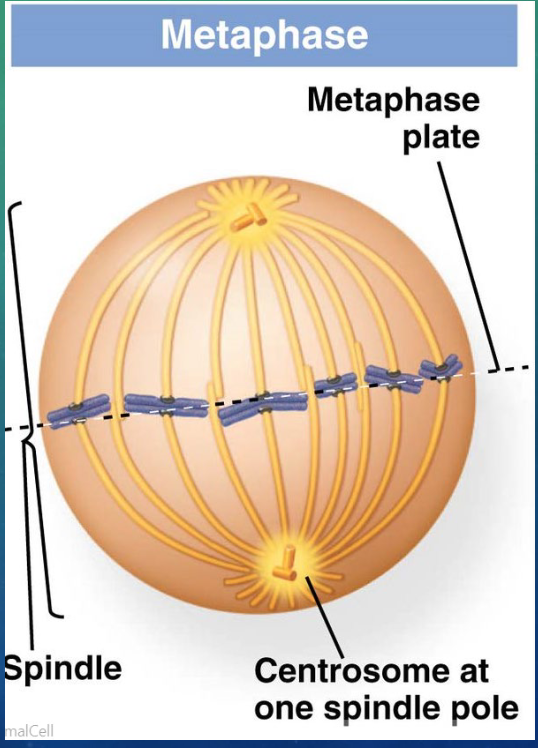
outline what happens during metaphase
chromosomes line up along metaphase plate in the center of the cell
mitotic spindle is fully formed
microtubules connect to kinetochore, the constricted middle of the chromosome
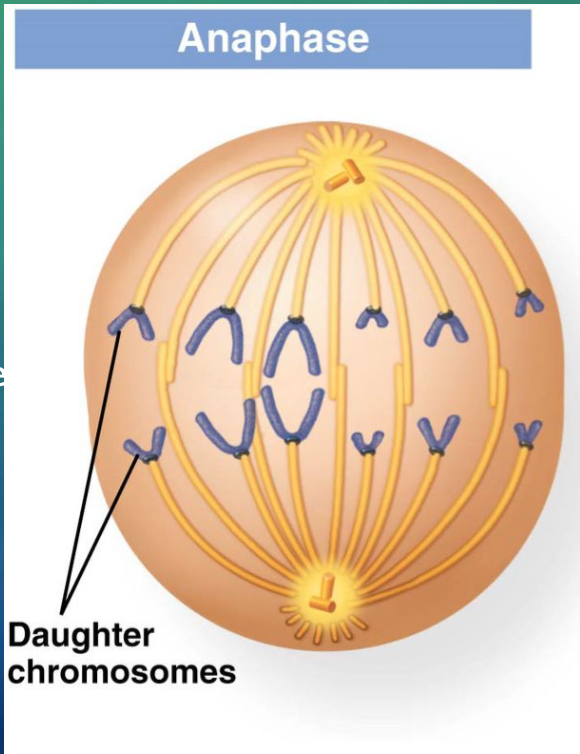
outline what happens in anaphase
spindle microtubules pull apart the duplicated chromosomes
chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
the sister chromatids are now properly called daughter chromosomes
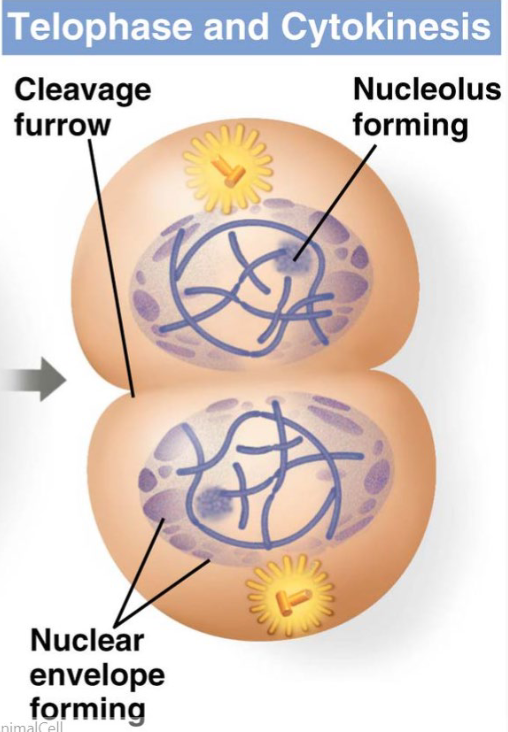
outline what happens during telophase
chromosomes uncondense
nuclear envelope reforms
spindle microtubules are disassembled
cytokenesis occurs (division of the cytoplasm via a cleavage furrow
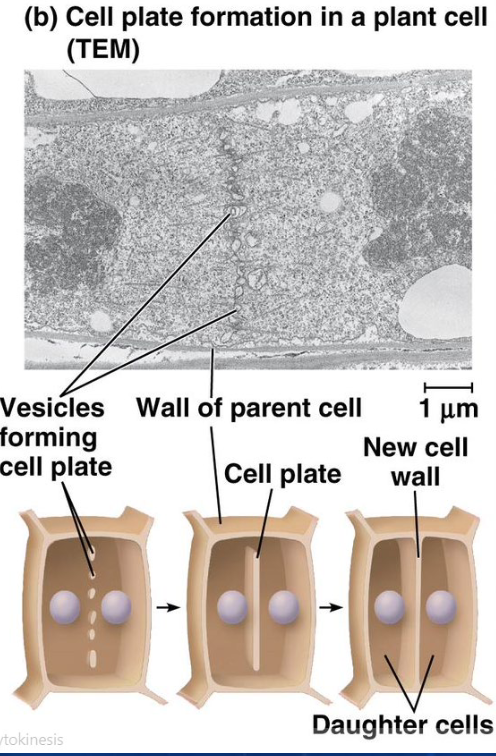
what means that plate cells cannot “pinch” in two in plant cells
cell wall
what forms in the middle of the two plant cells and grows outward
cell plate
the frequency of cell division varies with the type of cell, these differences result from …
regulation at the molecular level
… cells manage to escape the usual controls of the cell cycle
cancer
the sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct…
cell cycle control system (comparable to a clock)
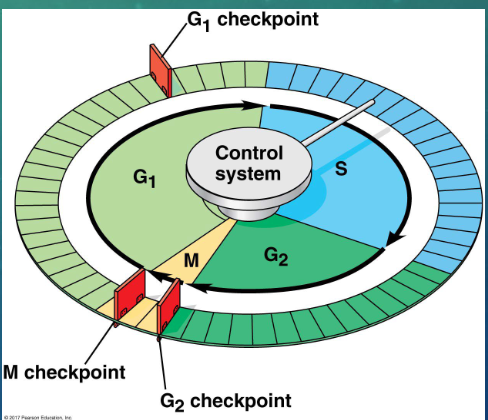
the cell cycle control system is regulated by both… and … controls
internal and external
the cell cycle control system has specific … where the cell cycle stops until a go-ahead signal is received
checkpoints
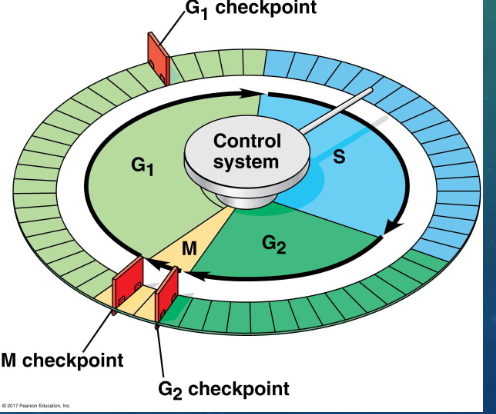
where are the three important checkpoints
G1, G2 and M phase
what checkpoint seems to be the most important
G1 checkpoint
why is the G1 checkpoint most important
if the cell receives the go ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it will usually complete the S, G2, and M phases and divide
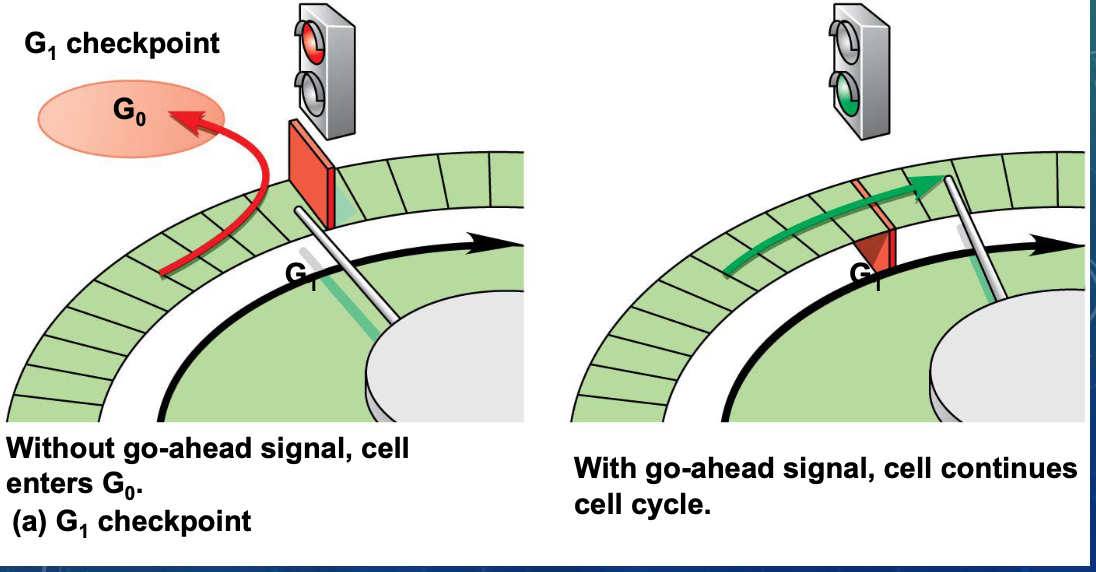
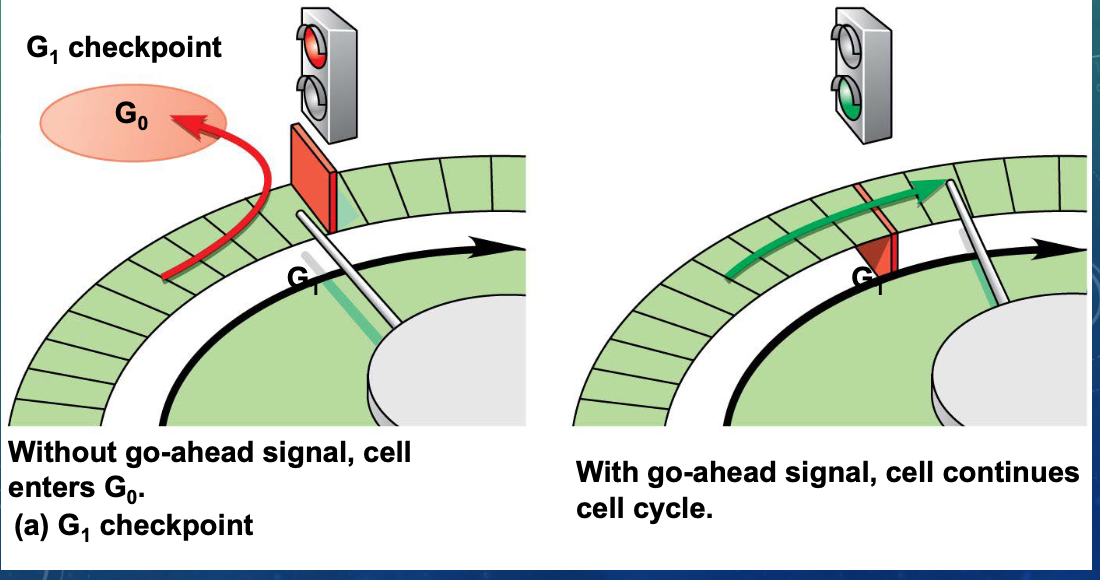
what happens if the cell does not receive the go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint
it will exit the cycle, switching into a nondividing state called the G0 phase
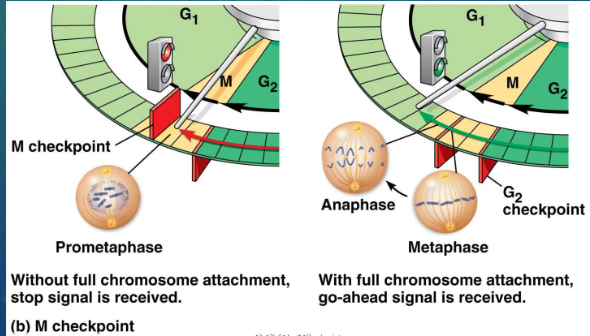
explain the function of the M checkpoint
cells will not begin anaphase until all the chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle at the metaphase plate
this mechanism ensures that daughter cells have the correct number of chromosomes
external factors that influence cell division include specific …
growth factors
growth factors are …
released by certain cells and stimulate other cells to divide
… is made by blood cell fragments called platelets
platelet-derived growth factor
in density-dependent inhibition…
crowded cells will stop dividing
cancer cells do not need growth factors to grow and divide…
they make their own growth factor
they may convey a growth factor’s signal without the presence of the growth factor
they may have an abnormal cell cycle control system
cell that acquire the ability to divide indefinitely are undergoing…
transformation
if abnormal cells remain only at the original site, the lump is called a .. tumor
benign
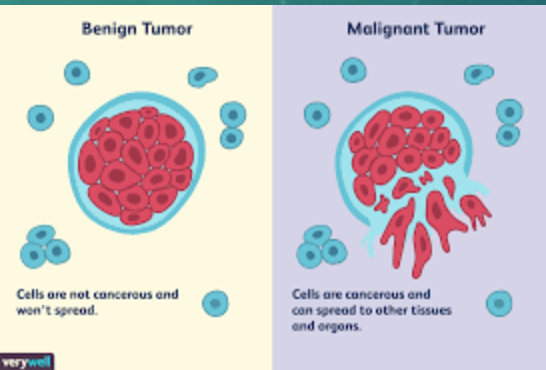
… tumors invade surrounding tissues and undergo metastasis
malignant
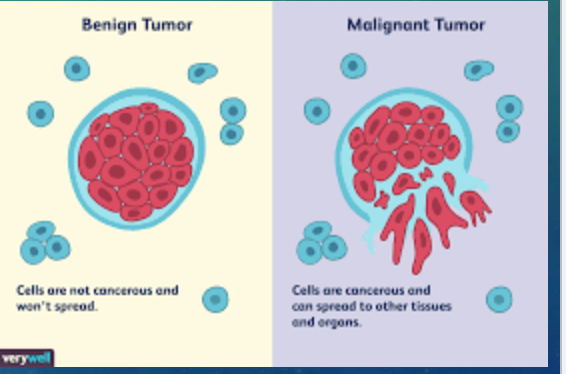
define metastasis
the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body, where they may form additional tumors