AP Psychology Unit 1: History and Research Methods
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Psychology
The science and study of behavior and mental processes.

Goals of Psychology
To describe, explain, and classify behavior; predict conditions triggering behaviors; apply knowledge to promote goals and prevent unwanted behavior.

Careers in Psychology
Specialty areas include Clinical/Counseling, Forensic, Educational, Industrial-organizational, and Psychiatry.

Psychiatry
A field requiring a medical degree, allowing professionals to prescribe medication.

Nature vs Nurture
The debate on the influence of genetics and environment on behavior, with the conclusion that both play a role.
Natural Selection
The principle that inherited traits aiding survival and reproduction are likely passed down.
Evolutionary Psychology
Focuses on applying natural selection to the mind and behavior.
Behavior Genetics
Studies the impact of genetic and environmental factors on behavior.

Trephination
A surgical procedure involving drilling a hole in the skull to relieve pressure or treat various conditions.

Socrates & Plato
Believed in dualism, where the mind and body are separate, and in innate knowledge.

Aristotle
Argued for monism, where the mind and body are one, and that knowledge is gained through experience.

Rene Descartes
Advocated for dualism, proposing the mind and body as distinct entities with free will.

Sir Francis Bacon
Developed the scientific method and emphasized perceiving patterns and remembering events.

John Locke
Proposed the concept of the mind as a 'tabula rasa' shaped by experience.

Wilhelm Wundt
Established the first psychology research lab and coined the term 'psychologist', known for introspection.

Sigmund Freud
Founder of psychoanalysis, identifying the id, ego, and super ego in the mind.
William James
Introduced functionalism, seeking causal relationships between internal and external behaviors.

Structuralism
Focuses on the basic components of the mind, while functionalism emphasizes the purpose of behavior.

Edward Titchener
Further developed structuralism to analyze conscious experiences.

Modern Psychological Perspectives
Include the behavioral perspective, focusing on observable actions and learned behavior.
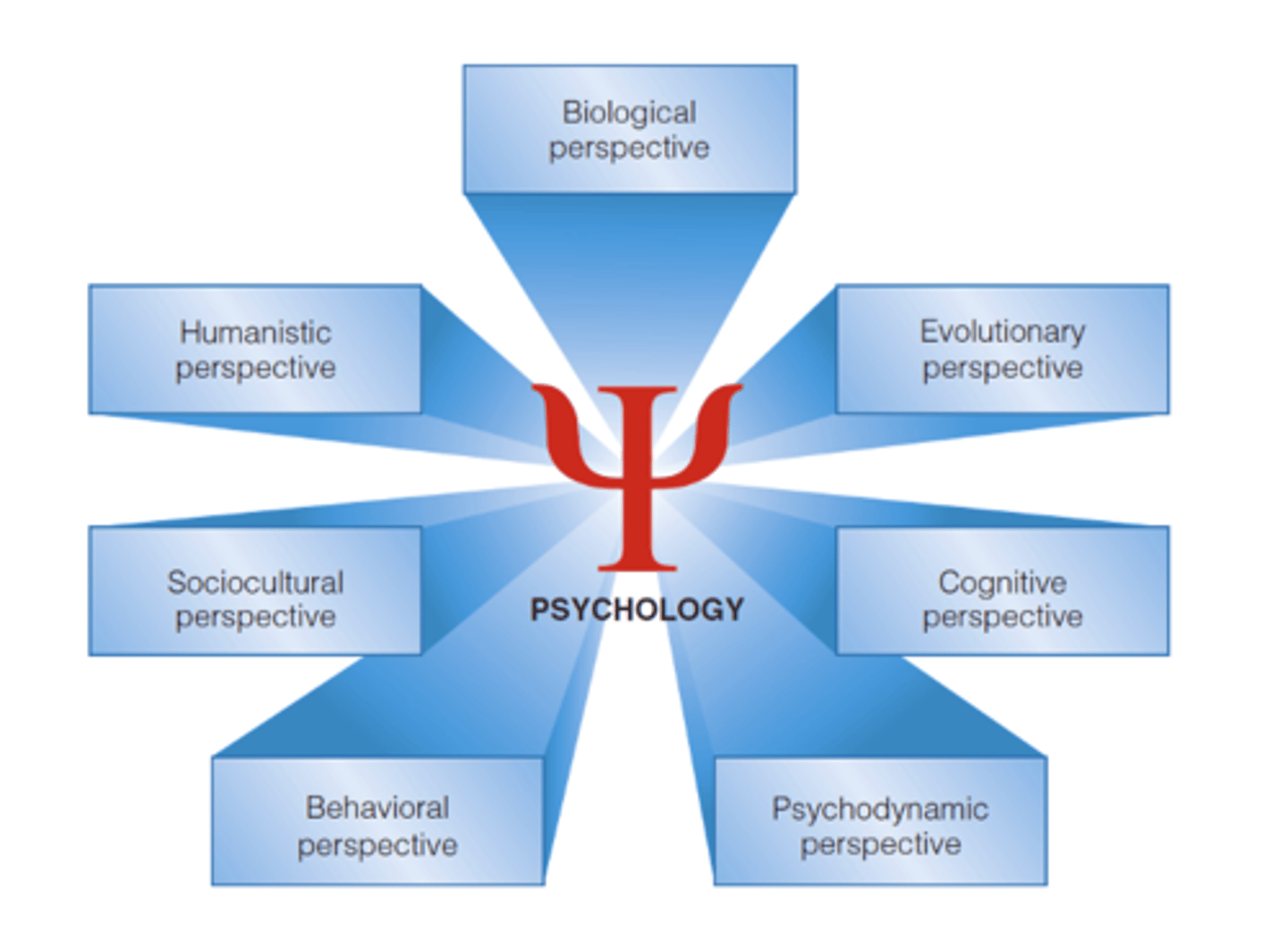
Humanistic
Humans have the desire to reach their full potential; emphasize free will and motivation (Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers)

Psychodynamic
Emphasizes the unconscious mind; repressed memories, free association, & dream interpretation (Sigmund Freud)

Biological
Physical basis for behavior, emphasis on nervous and endocrine system
Cognitive
Focuses on how humans gather, store, and process sensory information, with an emphasis on memory, thought, and problem-solving

Socio-cultural
Explores how culture and society affect behavior, thoughts, and feelings

Evolutionary
Focuses on how the principles of evolution explain psychological processes and phenomena, with a focus on natural selection (Charles Darwin & Robert Sapolsky)
Critical Thinking
Thinking style that examines assumptions, appraises sources, discerns hidden biases, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions

The Scientific Method
A process involving observation, theory development, hypothesis testing, experimentation, evaluation, theory modification, and replication

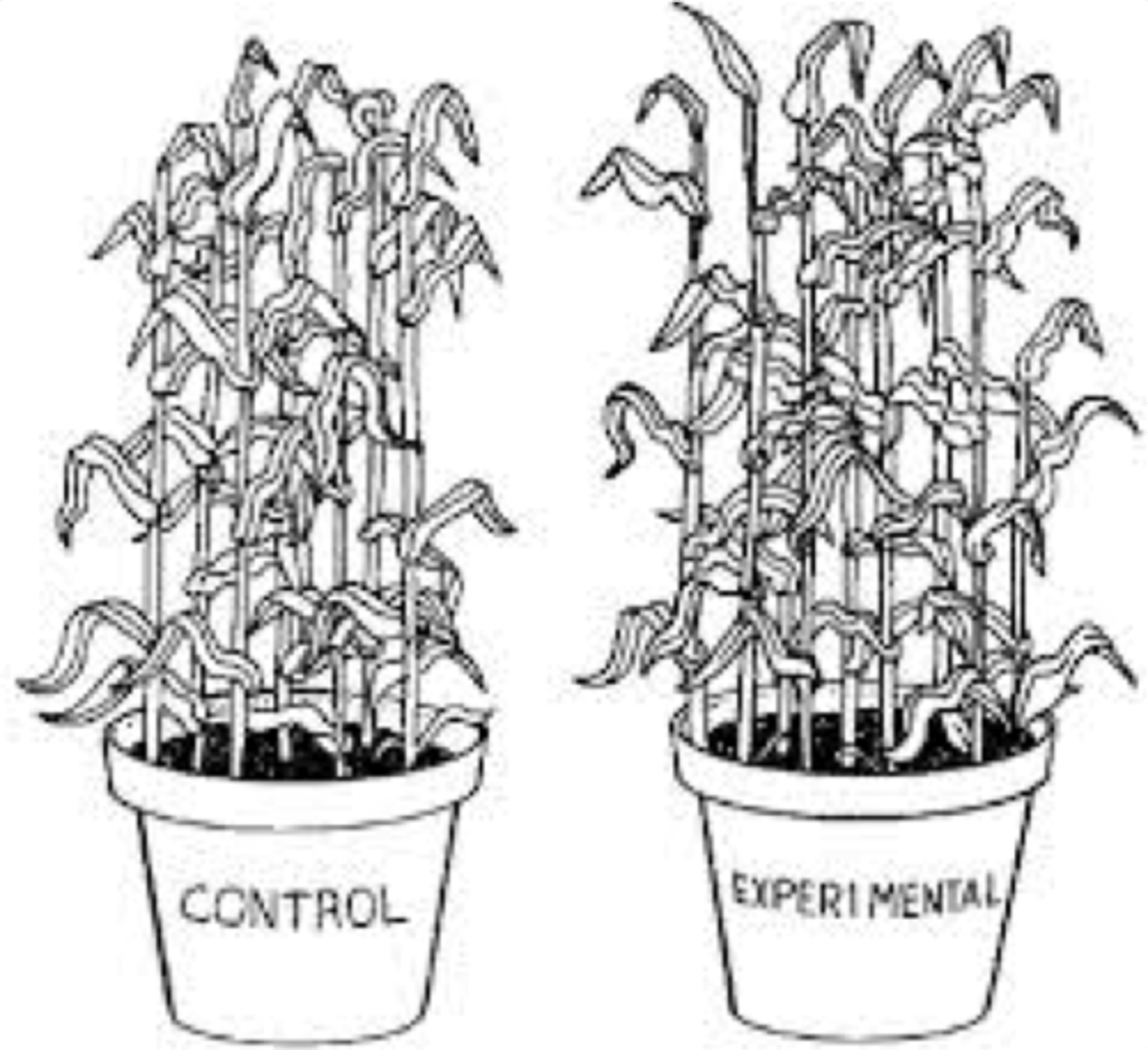
Experimental Research
A method where the investigator manipulates variables under controlled conditions to observe changes in another variable

Descriptive/Correlational Research
A method where variables cannot be manipulated, focusing on behavior patterns or links between variables

Experiment
A controlled investigation method used to establish cause-and-effect relationships
Hypothesis
A testable, tentative statement describing the relationship between variables

Independent Variable
The factor manipulated by the experimenter
Dependent Variable
The factor measured by the experimenter

Operational Definition
A precise description of how a variable in a study will be manipulated and measured
Control Group
Subjects who do not receive special treatment given to the experimental group
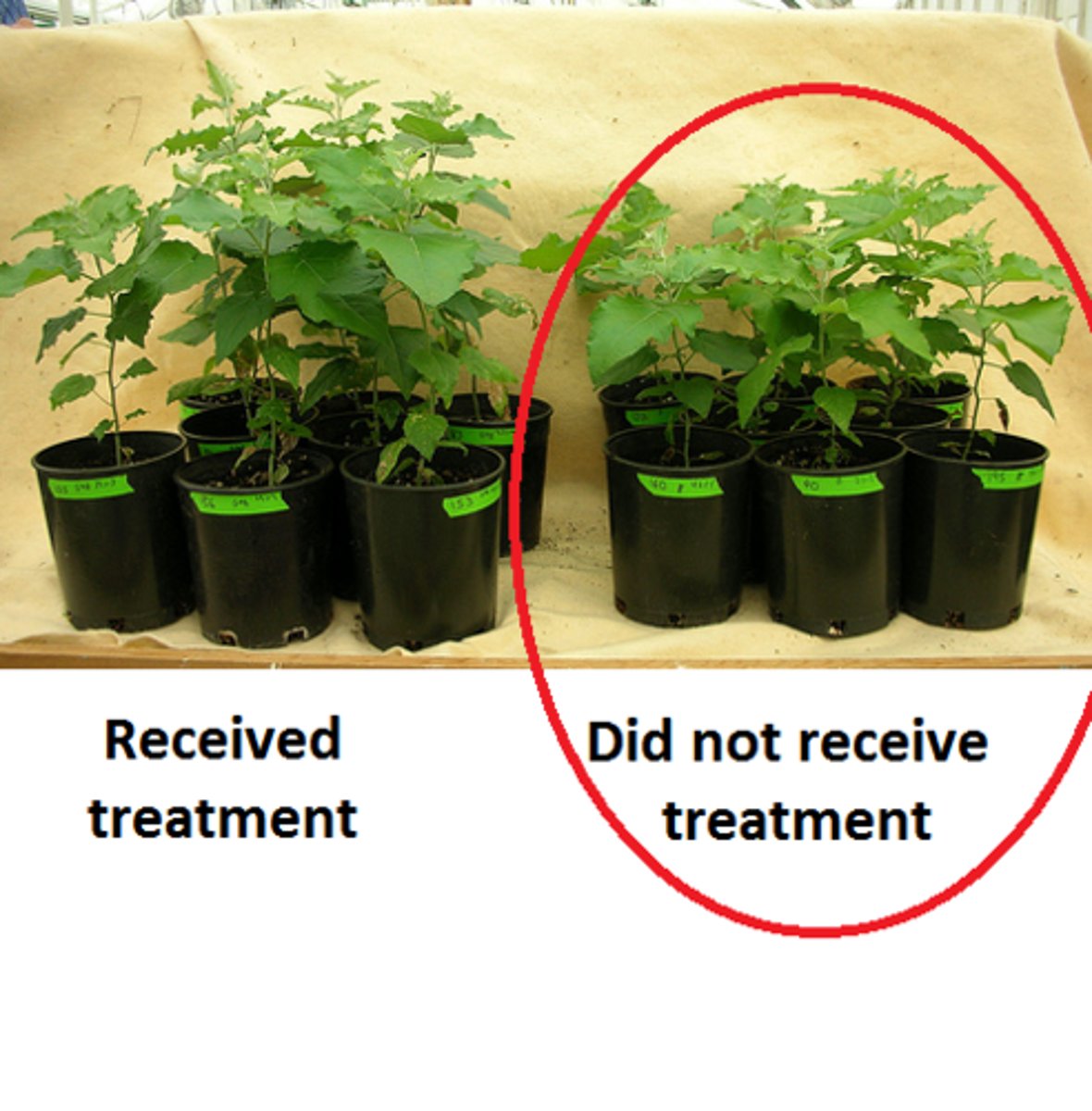

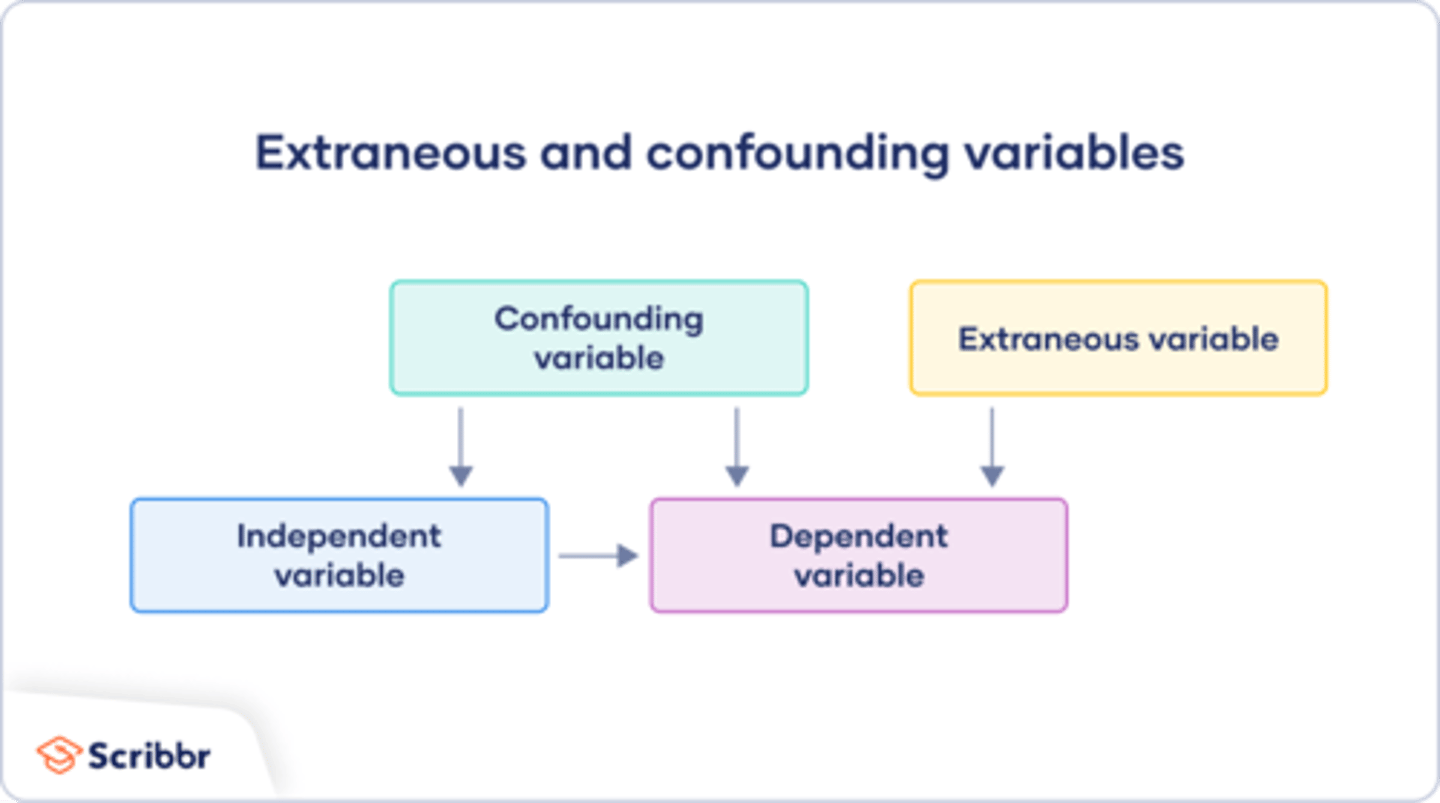
Confounding Variables
External factors that can affect experiment results, making it hard to determine the true cause
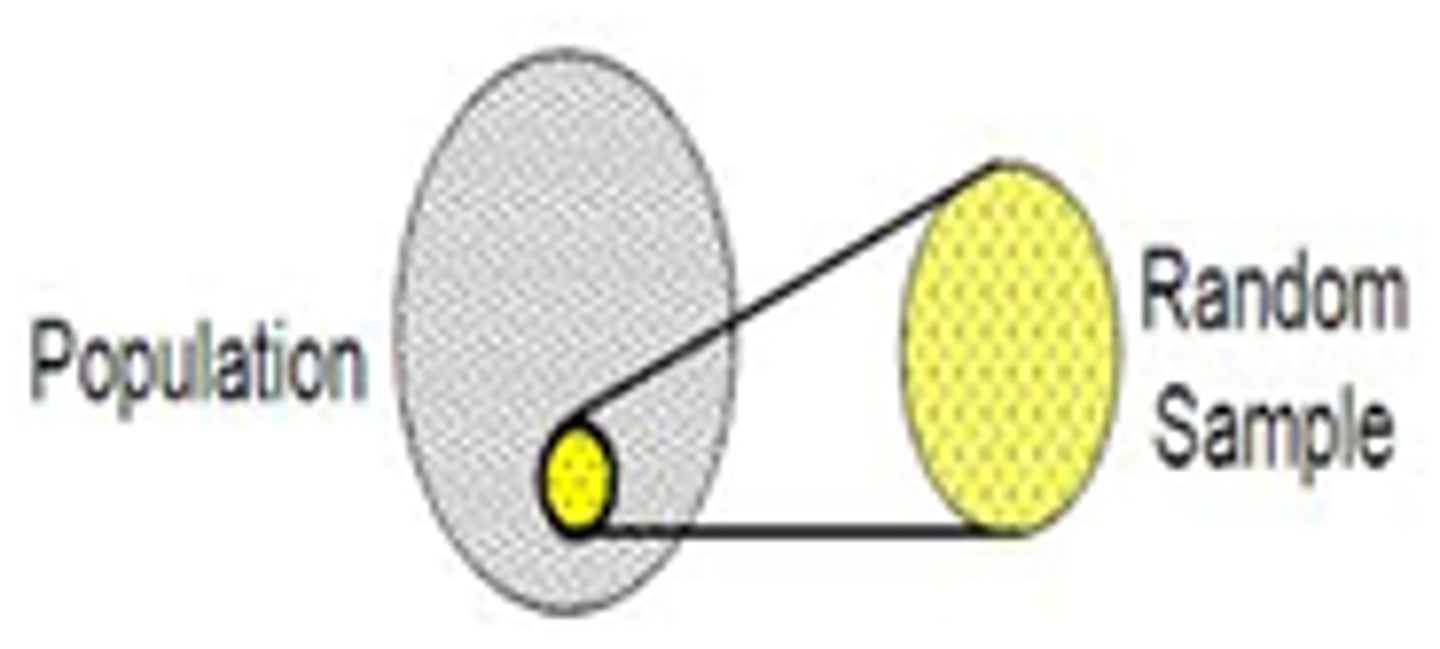
Random Selection
Gathering participants so all members of a population have an equal chance of being chosen
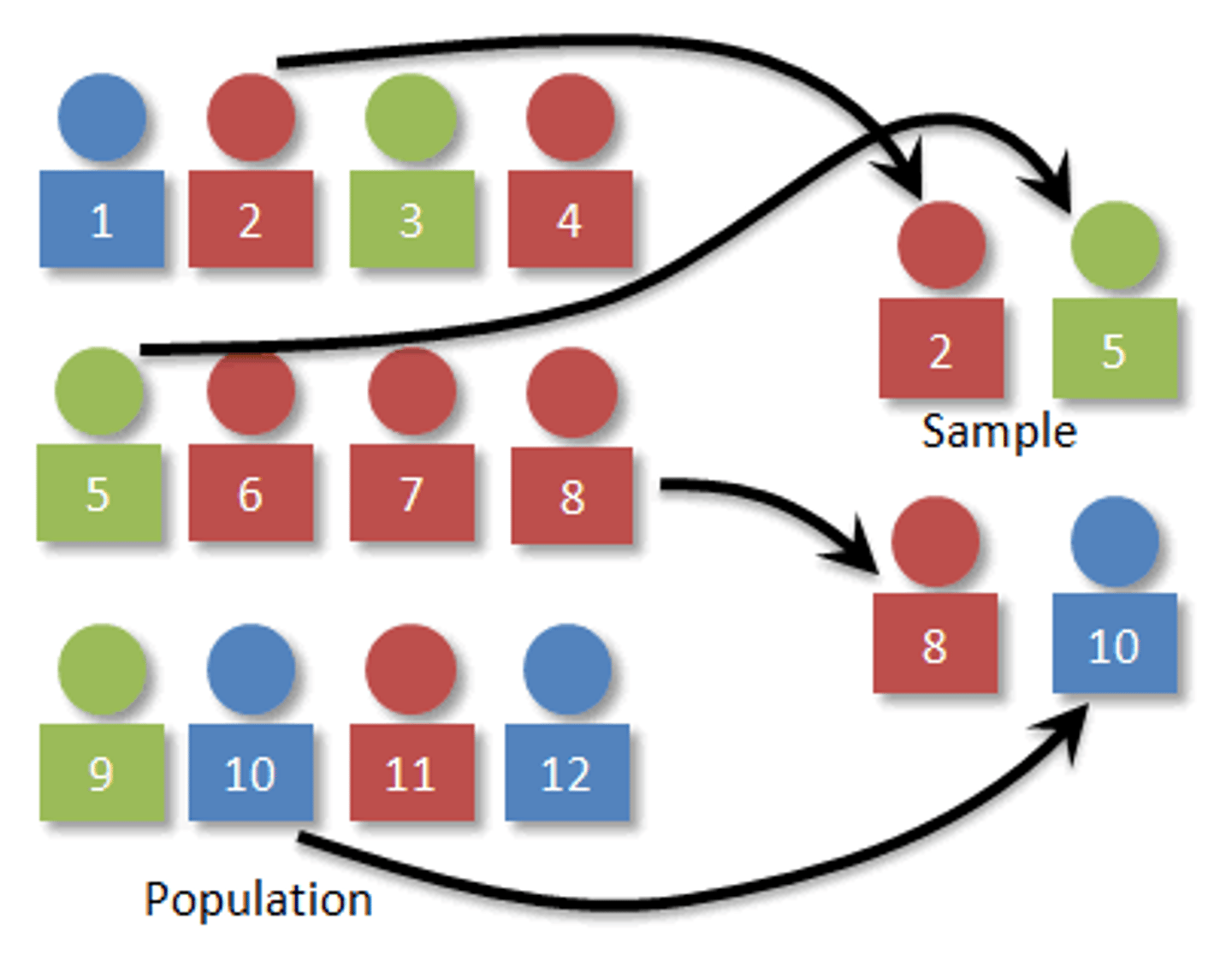
Random Assignment
Ensures participants have an equal chance to be assigned to any group or condition in a study

Double-blind Procedure
A research strategy where neither participants nor experimenters know group assignments to prevent bias

Replication
Repeating an experiment to ensure similar results can be obtained
Sampling Bias
Occurs when a sample is not representative of the population from which it was drawn

Experimenter Bias
When a researcher's expectations influence the obtained data

Placebo Effect
Subjects feeling change despite receiving an empty, fake, or ineffectual treatment

Hawthorne Effect
Modification of behavior by study participants due to being observed or singled out for special treatment

Barnum Effect
Occurs when individuals believe personality descriptions apply specifically to them, even when they are general

Naturalistic Observation
Observing subjects in a natural setting to capture honest behavior

Survey
Descriptive technique to collect self-reported attitudes and behaviors

Representative Random Sample
Participants chosen fairly without bias to represent a population
Descriptive Statistics
Used to organize and summarize data

Inferential Statistics
Interprets data to draw conclusions

Mean
Average of a score's distribution
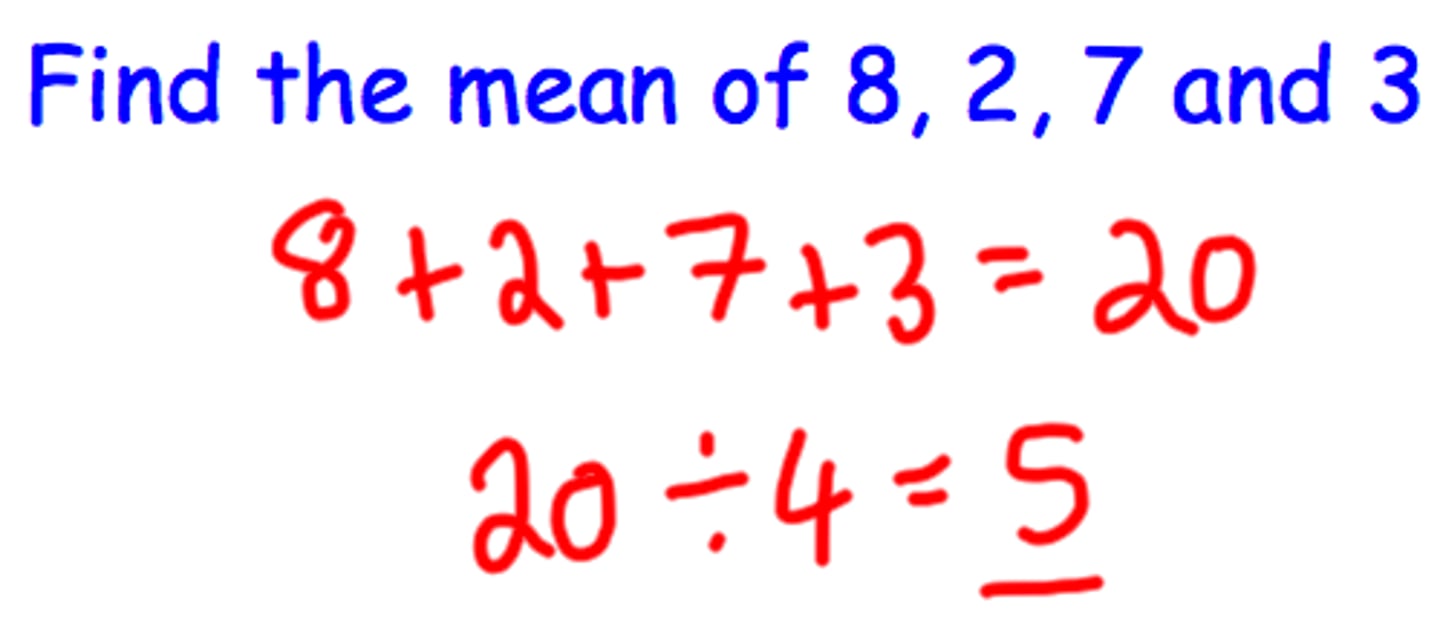
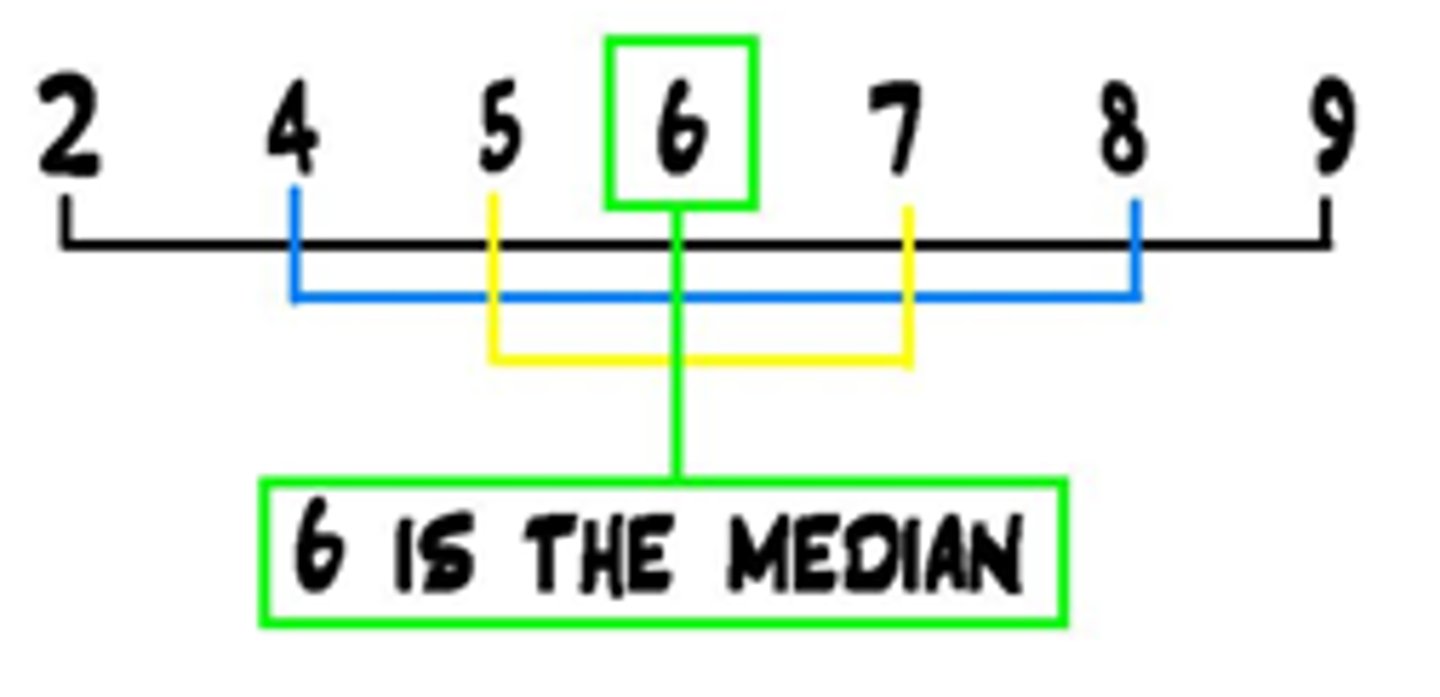
Median
Score in the center of the distribution of scores
Mode
Most common score in a distribution

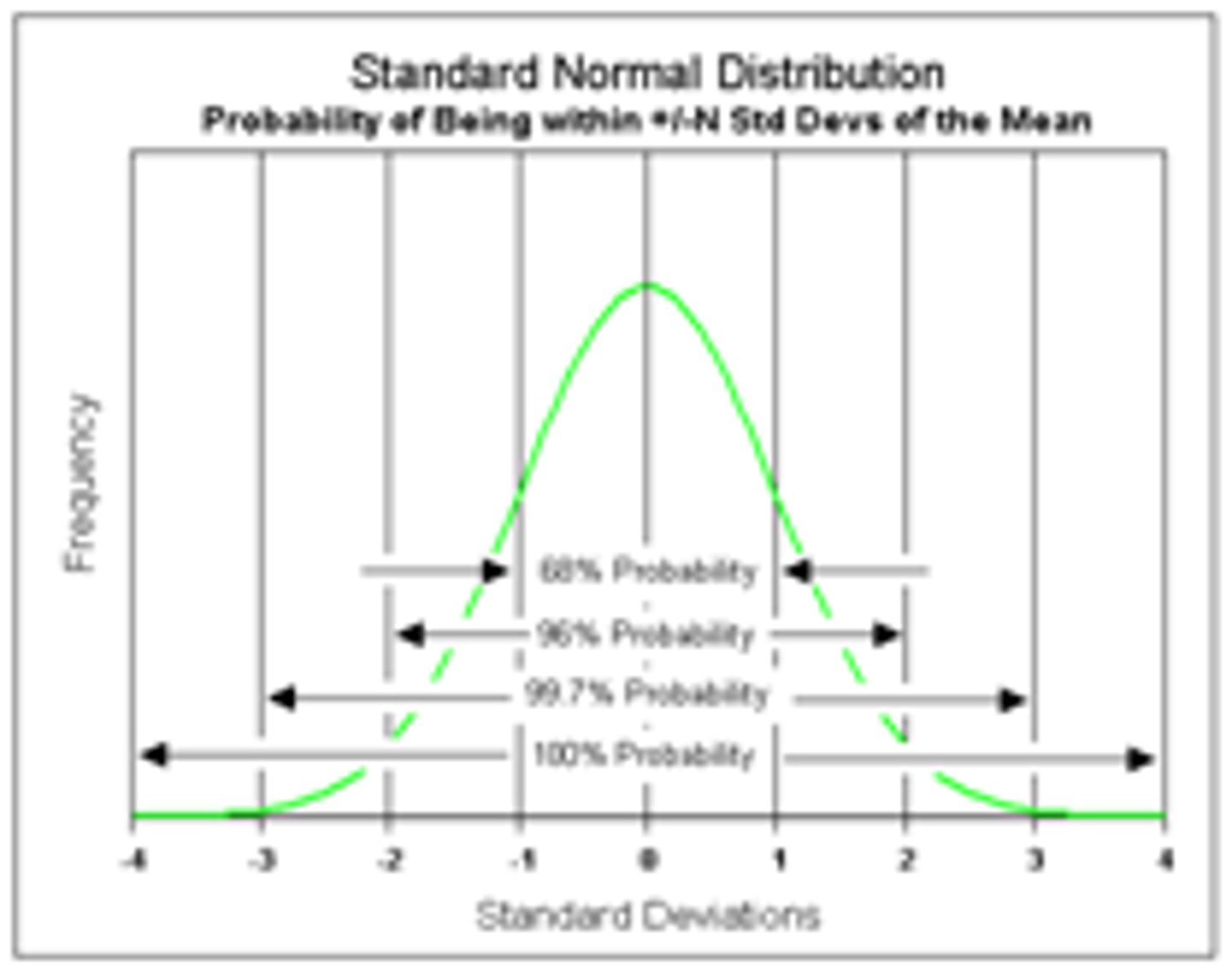
Standard Deviation
Index of variability in a set of data
Correlation
A relationship between two variables

Correlational Coefficient
Numerical index of the relationship strength between variables

Positive Correlation
Variables trend in the same direction
Ex: The more you study, the higher your grade.
Negative Correlation
Variables trend in opposite directions
Ex: The more absences you have, the lower
your grade.

Illusory Correlation
Believing in a relationship between variables that doesn't exist

Regression Toward the Mean
Tendency for extreme scores/events to return to average

APA Ethical Guidelines
Rules for ethical research practices on humans and animals

What is the Stanford Prison Experiment?
A controversial study on social roles and external pressures.
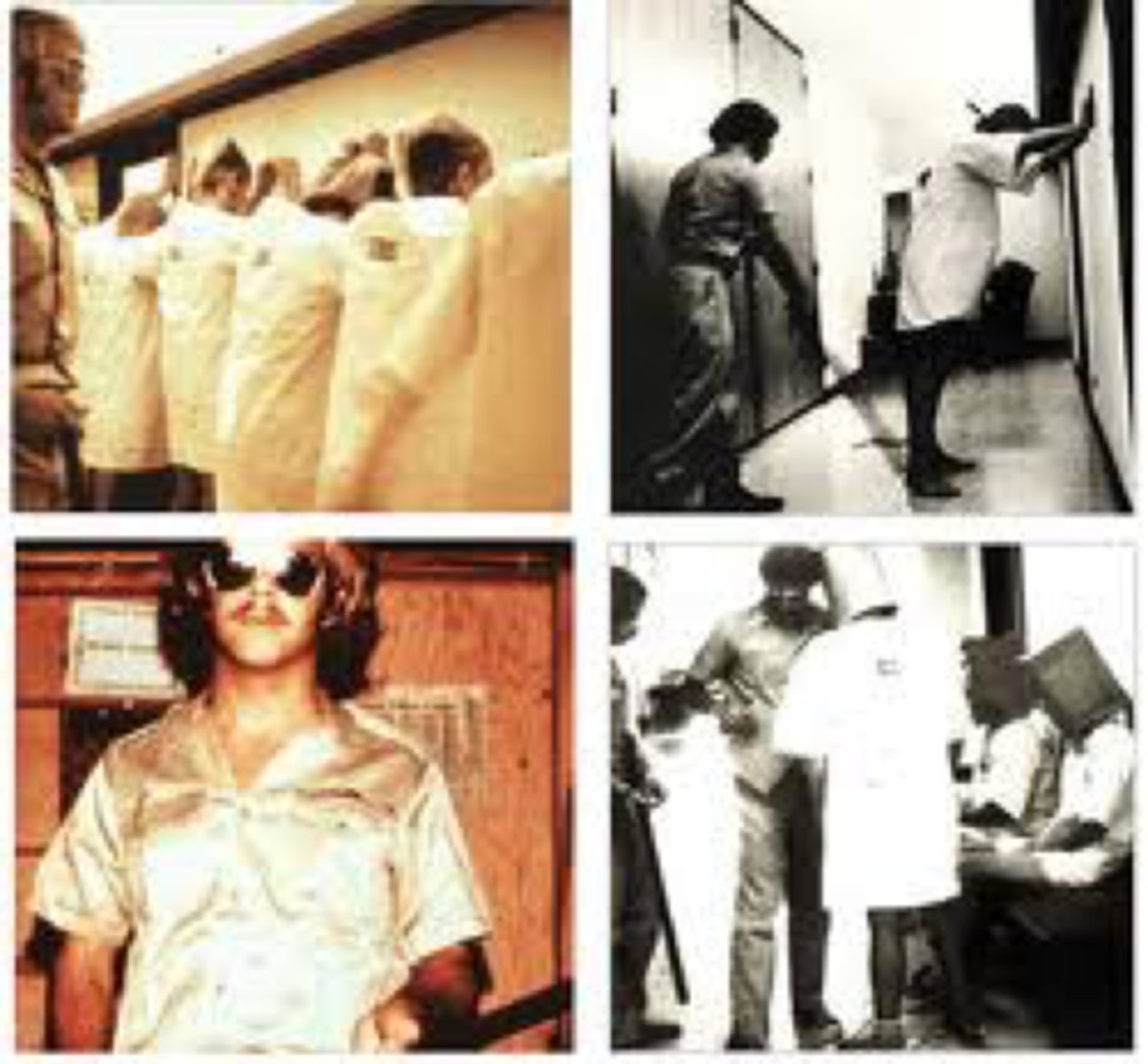

What was the aim of the Stanford Prison Experiment?
To show how circumstances can bring out the worst personality traits in people and how social roles and external pressures can influence our actions.

What are some criticisms of the Stanford Prison Experiment?
Criticism includes lack of realism, unrepresentative sample, lack of informed consent, and manipulation.

Ecological Validity
Degree to which a setup matches real-world situations

Informed Consent
Participants' agreement after understanding the study's purpose
Empiricism
Knowledge gained through observation and experience

Functionalism
Focuses on the purpose of consciousness and behavior

Behaviorism
Studying observable behavior without considering mental processes
Cognitive Neuroscience
Study of brain mechanisms underlying cognition

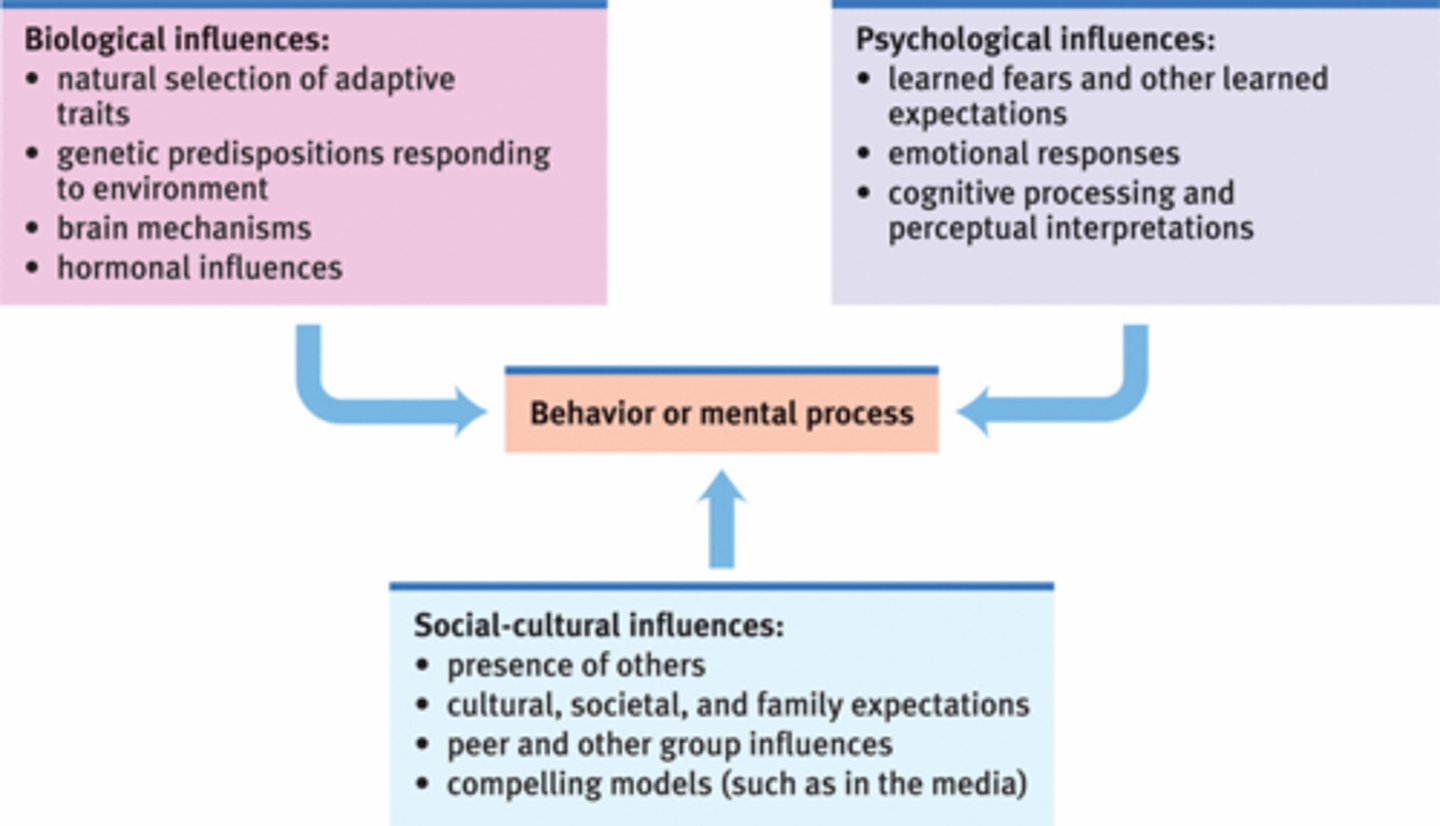
Biopsychosocial Approach
Understanding behavior through biological, psychological, and social factors
Psychometrics
Study of psychological measurement