Mircoeconomics Chapter 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
1
New cards
Market
Any place people come together to trade, physical or virtual
2
New cards
First side of the market
buying side, demand
3
New cards
Second side of the market
selling side, supply
4
New cards
Demand def
the willingness and ability of buyers to purchase goods at different prices during different periods
5
New cards
There is no demand when
The buyer doesn't have the ability to purchase
6
New cards
Law of Demand
As price goes up, quantity demanded goes down. As the price falls the quantity demanded goes up
7
New cards
Don't make what mistake
As price goes up quantity demanded goes down, not demand goes down
8
New cards
Quantity demanded def
the number of units that individuals are willing and able to buy at a particular price during a time period
9
New cards
What is the only thing that will cause a shift in quantity demanded
price
10
New cards
What causes a shift in demand
income, preferences, prices of related goods, number of buyers, expectations of future price
11
New cards
What causes a change in quantity demanded
a goods own price
12
New cards
Demand schedule
A numerical representation of the demand schedule
13
New cards
Individual demand curve
price-quantity combination of a particular single buyer
14
New cards
Market demand curve
price-quantity combination of a good for all buyers
15
New cards
What are related goods
Subsitute goods and complimentary goods
16
New cards
Subsitute good ex
Coke and Pepsi
17
New cards
Complimentary good ex
Tennis balls and tennis rackets
18
New cards
Normal good
A good where demand rises as income rises, price stays the same
19
New cards
Inferior good
A good where demand rises as income decreases, price stays the same
20
New cards
Neutral good
A good for which demand does not change as income rises or falls
21
New cards
Normal good ex
Starbucks coffee
22
New cards
inferior good ex
Ramen noodles
23
New cards
Neutral good ex
Gas
24
New cards
Ex of change in preferance
Twilight movies and books to zombie movies and books
25
New cards
How does the number of buyers effect demand
The more buyers = higher demand, fewer buyers = lower demand
26
New cards
Buyers may increase because of what
Immigration
27
New cards
Buyers may decrease because of what
increased death rate, war, migration
28
New cards
How does expectations of future price effect demand
If you know that the price will be raised in the future, the demand will increase because you will stockpile
29
New cards
Draw a graph of a change in quantity demanded
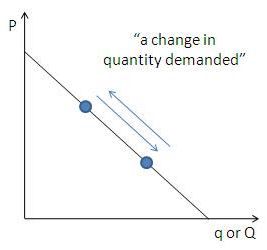
30
New cards
Draw a graph of a change in demand
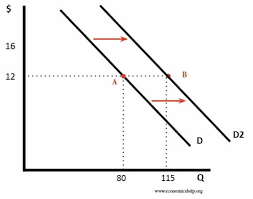
31
New cards
Supply
The willingness and ability of sellers to produce and offer to sell different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period
32
New cards
Capitalism
an economic system based on private ownership of capital
33
New cards
What does capitalism have
very little government intervention
34
New cards
Socialism
the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the community as a whole
35
New cards
Law of supply
As the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied of the good rises, as the price decreases the quantity supplied decreases
36
New cards
Fixed supply looks like what
Vertical line
37
New cards
Why supply curves are upward sloping
Higher price means higher profits, so they produce more if the price is going up
38
New cards
Supply schedule
The numerical tabulation of the quantity supplied of a good at different prices, represents law of supply
39
New cards
Reasons for shift in supply curve
prices of relevant resources, technology, prices of other goods, number of sellers, expectation of future prices, taxes and subsidies, government restrictions
40
New cards
Prices of relevant resources
If the price of wood goes down then the cost of making doors will go down
41
New cards
Consequences of prices of relevant resources
low cost of production means more profit for suppliers and more supply
42
New cards
Technology
Can lower the cost of producing a good, which means more profit for supplies, resulting in more supply
43
New cards
Prices of other goods
If a wheat farmer sees that there is more profit in planting corn, he will start planting corn thus more supply
44
New cards
Number of sellers
A decrease in the number of sellers will mean there is less supply of a certain good
45
New cards
Expectation of future prices
If firewood producers know that winter is next month and prices will be higher, they will hold off on producing firewood until they can sell it for more
46
New cards
Taxes and subsidies
Subsidies are money given to suppliers from the government, like money to corn farmers
47
New cards
Government restrictions
If California restricts the sale of guns, then the supply will decrease
48
New cards
A change in quantity supplied referes to what
a movement along a supply curve
49
New cards
Whats the only factor that can directly cause a change in the quantity supplied of a good
change in the price of a good or own price
50
New cards
What happens to the supply curve if the number of sellers decreases,
The supply curve shifts to the left
51
New cards
What happens to the supply curve if a tax is placed per unit of good
The supply curve shifts to the left
52
New cards
What happens to the supply curve if the price of a relevent resource falls
The supply curve shifts to the right
53
New cards
If the price of apples rises the supply of apples will rise
false, the quantity of apples supplied will rise
54
New cards
Equilibrium
The intersection of supply and demand
55
New cards
Simplest def of equilibirum
S = D, Qs = Qd
56
New cards
Surplus
Qs > Qd
57
New cards
Shortage
Qd > Qs
58
New cards
IPPNE
Income, preferences, price of related goods, number of buyers, expectations of future price
59
New cards
PTPNETG
Prices of relevant resources, technology, prices of other goods, number of sellers, taxes and subsidies, government restrictions
60
New cards
if you are not in equilibirum you are in
disequilibrium
61
New cards
disequilibrium price
a price other than equilibrium price
62
New cards
How does a surplus move the market to equilibirum
suppliers lower their price until equilibrium price
63
New cards
How does a shortage move the market to equilibirum
suppliers raise their price until equilibrium price
64
New cards
Real life examples of market moving to equilibirum
Stock market, if there is a shortage in stock prices will rise. Real estate, if a house isn't selling (surplus) the seller will lower their price
65
New cards
To the left of the equilibrium point there is always what
exchange
66
New cards
To the right of the equilibirum point there is always what
no exchange
67
New cards
Consumer surplus
Cs = maximum buying price - price paid
68
New cards
Consumer surplus example
You will max pay $10 at the movie theatre, but you only spend $7. Surplus is $3
69
New cards
producer surplus example
Theatre owner will sell tickets for at least $5. He sells them for $7. Surplus is $2
70
New cards
Producer surplus
Ps = price recieved - minimum selling price
71
New cards
Total surplus
Ts = Cs + Ps
72
New cards
If a market is in equilibirum, what will cause it to go into disequilibirum
Shift or change in demand or supply
73
New cards
Demand equation ex
Qd = 1500 - 32P
74
New cards
Supply equation ex
Qs = 1200 + 43P
75
New cards
How to find equilibrium pice with equations
set equations equal to eachother, solve for P
76
New cards
How to get Qd and Qs from equilibirum price answer
plug P into the equations