Chemistry 1.6 + 1.10- Chemical Equilibria, Le Chatelier’s Principle and Kc + Equilibrium Constant Kp for Homogenous Systems
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What properties define a dynamic equilibrium?
Both the forwards and reverse reactions occur at the same time
The forwards and reverse reactions occur at the same rate
The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant (but not equal to each other)
What is the general formula for the equilibrium constant Kc?
Solids are ignored
[C] means the concentration of C
![<ul><li><p>Solids are ignored</p></li><li><p><strong>[C] means the concentration of C</strong></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ab4577c2-aa9a-4bbc-a4c9-6370ed2e3f88.png)
What is a homogenous system?
A reaction where all the reactants and products are in the same phase- normally we use this to refer to equilibria where all compounds are gases
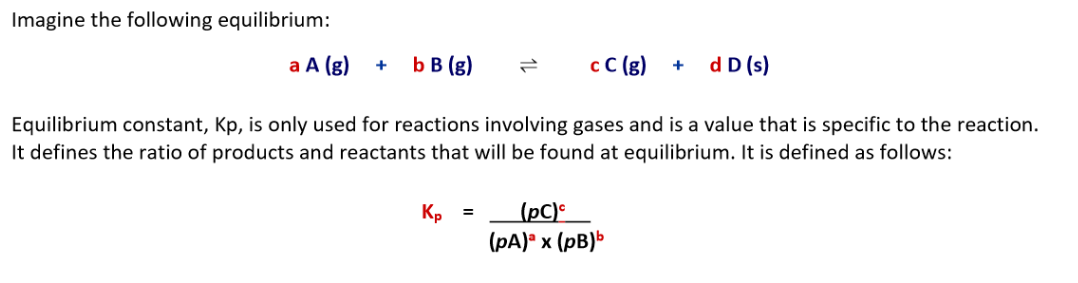
What is the general equation for the equilibrium constant Kp?
Solids and liquids are ignored
(pC) means the partial pressure of C
What is partial pressure and how do you calculate it?
The pressure a gas in a mixture of gases would exert on the container if it occupied the container on its own
The partial pressure of a gas is calculated by the total pressure x the mole fraction of the gas
The mole fraction is the number of moles of the gas over the total moles in the system
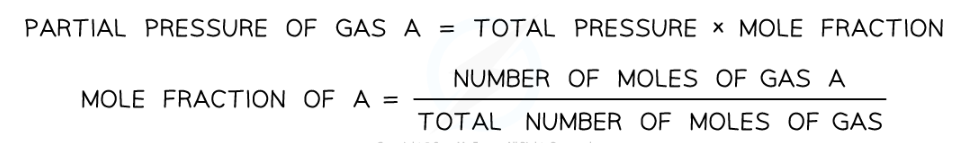
How does increasing the concentration of reactants affect the position of equilibrium and the equilibrium constant Kc?
The equilibrium position shifts to the right to bring the concentration of the reactants back down
The equilibrium constant Kc is not affected by concentration
This is because of the equilibrium position changing, so that the concentration of the products increases and the ratio of products to reactants doesn’t change overall
How does increasing the pressure affect the position of equilibrium and the equilibrium constant Kp?
The equilibrium position shifts to the side with fewer molecules of gas to bring the pressure back down
The equilibrium constant Kp is not affected by pressure
This is because of the equilibrium position changing, to restore the value of Kp
How does increasing the temperature affect the position of equilibrium and the equilibrium constants, for an endothermic forwards reaction?
The equilibrium position shifts to the right to favour the endothermic reaction that will absorb energy and bring the temperature back down
The equilibrium constants Kc and Kp increase
This is because of the equilibrium position changing, so that the ratios of concentration and pressure between the reactants and products change
How does increasing the temperature affect the position of equilibrium and the equilibrium constants, for an exothermic forwards reaction?
The equilibrium position shifts to the left to favour the endothermic reaction that will absorb energy and bring the temperature back down
The equilibrium constants Kc and Kp decrease
This is because of the equilibrium position changing, so that the ratios of concentration and pressure between the reactants and products change