CH4710 RM27
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what are the base pairs
G and C
A and T/U
how many H bonds between G and C
3
how many H bonds between A and T/U
2
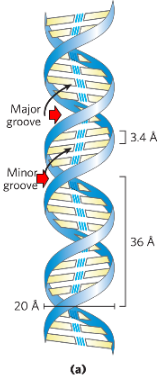
Watson and Crick model for DNA components
double helix
major and minor grooves
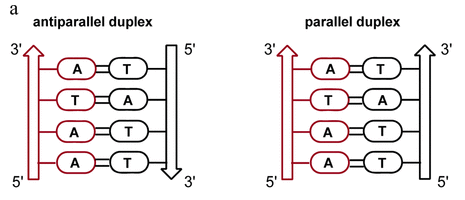
DNA parallel vs antiparallel
parallel: DNA strands both run in same direction
antiparallel: DNA strands run in opposite directions
xray analysis shows that DNA runs antiparallel
replication of DNA overall (simple)
preexisting “parent” strands become separated
each “parent” serves as a template for the biosynthesis of a complementary “daughter” strand
replication of DNA detailed
DNA polymerase binds to dNTP
DNA polymerase brings dNTP to the growing daughter strand
the first phosphate (or alpha phosphate) of dNTP makes a covalent bond with the 3rd OH of the ribose of the last nucleotide of the daughter chain
alpha phosphate (dNTP) bonds with OH of nucleotide ribose of daughter strand
beta and gamma phosphates and DNA polymerase leave
process repeats
palindrome
region of DNA that is identical when read either forward or backward
mirror repeat
looking at a DNA strand, imagine a line cut down the middle. there’s a reflection over the line (mirror image)
hairpin structures
self-complementarity within each strand
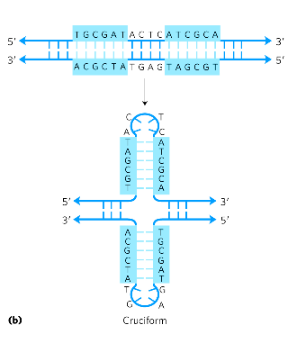
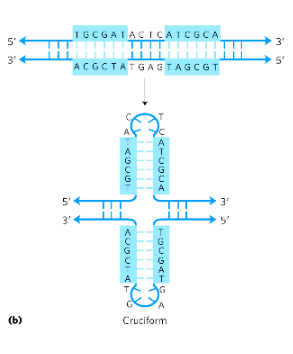
cruciform structures
self-complementarity within each strand
transcription
process by which mRNAs are formed on a DNA template
denaturation
“melting” of double helix
caused by pH extremes or high temps
separated the strands, unwinding
annealing
opposite of denaturation
rewinding of strands
spontaneous process
hypochromic effect/hyperchromic effect
hypo: decrease in absorption of UV when DNA is annealed
hyper: increase in absorption of UV when DNA is denatured
deamination
spontaneous loss of exocyclic amino groups
ex. cytosine can be recognized as foreign and is deaminated to uracil
depurination
hydrolysis of the N-beta-glycosyl bond between the base and pentose
creates “abasic site” or DNA site with no purine/pyrimidine