Female Reproductive System I
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Hypothalamic components
GnRH
Pituitary gland components
Gonadotropins
Ovary components
Oogenesis
Steroidogenesis
Oviduct components
Gamete transport
Site of fertilization
Site of segmentation
Uterus components
Thick, muscular organ
Maintenance of lining (endometrium), regulated by estrogen and progesterone
The ______ is the functional unit of the overy, providing a niche with the purpose of _______________
follicle, producing a healthy mature oocyte
Preantral follicle growth is __________
gonadotropin-independent
Antral follicle growth is _________
gonadotropin dependent
Corpus luteum formed in ________
luteogenesis
Primordial follicle has granulosa cells arranged in ______
one layer
Qualities of primary and secondary
Cuboidal granulosa
Zona pellucida surrounds oocyte
Amtral follicle
Cumulus granulocytes
Central cavity forms
Graaf follicle
Preovulatory/tertiary follicle
About to be activated
Large central cavity
Increased granulosa cells
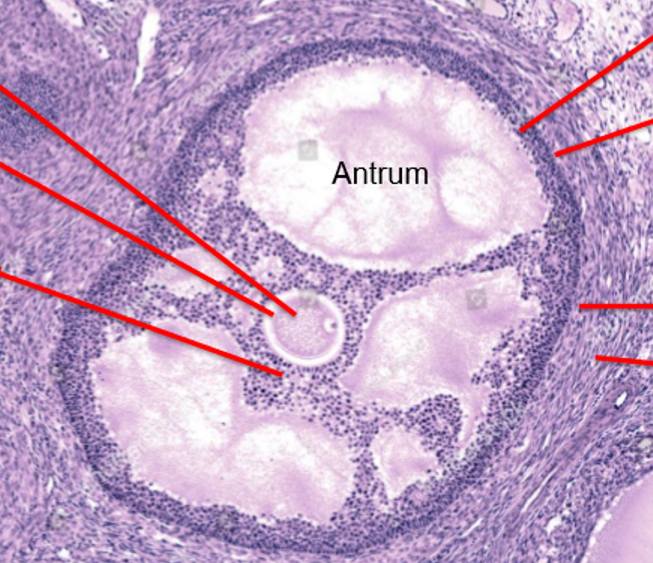
Ovarian follicle structure
Oocyte
Zona pelucida
Cumulus granulosa
Mural granulosa
Basement membrane
Theca interna (granulosa)
Theca externa
________ orchestrate the uterine cycle
hormones
Follicular phase
Dominant follicle selection
Menses
Proliferative phase
Luteal phase
Corpus luteum
Secretory phase
Concentration of estrogen throughout ovarian cycle
Highest right before ovulation, then drops, rises and falls at mid-secretory stage
Concentration of progesterone through ovarian cycle
Low until mid-secretory phase
LH during ovarian cycle
Low, surges right below ovulation
FSH during ovarian cycle
Low throughout, small spike with LH surge
The mid-secretory stage of the luteal phase also corresponds to the ______
receptive state
Primordial follicles
Contain prikmary oocyte (9-25um)
Single layer of squamous granulosa cells
First noted at 16 weeks of intrauterine life in humans
Surviva LH/FSH independent
Constitute resting pool
Primordial follicles remain ________, undergo _______, and enter a _______ ()
quiescent, apoptosis, growth phase (recruitment/initiation)
Primordial follicle quiescence is maintained by inhibiting ____ activation
AKT
Non-growing oocyte
TSC1/2 inhibits mTORC1 in granulosa
FOXO3A and LHX8 keep oocyte in meiosis I
Inhibits PDk1 and thus AKT activation
Growing oocyte
Unknown activation of mTORC1
Increased protein synthesis
KIT ligand binds KIT
PI3K and AKT activated
Stops arresting in meiosis I
Cumulus granulosa infiltrate the zona pelucida via ______, which is important for ____ of the oocyte
Transzonal projections, nutrition
Transzonal projections enable _____ to communicate with the oocyte and provide ______ to support oocyte growth
cumulus granulosa cells, essential molecules
Transzonal projections are narrow _____ extend through the ZP and contact the _______
cytoplasmic bridges, oolemma
Gap junctions in cumulus granulosa provide portals for molecules up to _______
1 kDa
Cumulus cells provide ____ (), _____, and ______
amino acids (alanine, glycine, proline), pyruvate, cholesterol
FGF8
Fibroblast growth factor 8
Granulosa cell proliferation
Oocyte to cumulus cells
GDF9
Growth differentiation factor 9
Granulosa cell proliferation
Increased cholesterol biosynthesis
BMP15
Bone morphogenic protein 15
Increased cholesterol biosynthesis
From cumulus cells
KITL; continued oocyte protein synthesis
Preantral growth occurs through life, uninterrupted until _____
menopause
Granulosa cells proliferate to _____, oocyte diameter to _____
~600, 80um
Granulosa cells express _____, _____, and ____ receptors
FSH-R, estrogen, androgen
Granulosa cells in preantral growth phase are sensitive to ____ and _____ but won’t die without
LH, FSH
In preantral growth, _____ are recruited from the stroma by ____ secreted from granulosa, and become ____, acquire ______, and express ______
Theca cells, GDF9, epithelioid, increased organelles, LH-Rs
Follicles develop _______ in preantral growth phase
Vascular wreath
Tonic growth phase (preantral)
600-fold increase in granulosa cells
Increase in follicle diameter
Gonadotropin support is required but able to thrive in low levels
Observed in ovaries from juvenile females and pregnant women
Growth occurs over several menstrual cycles
Fluid-filled antrum will develop
Order of follicular development
Primordial → primary → secondary → antral → selection and dominance → graafian dominant follicle
Selection and dominance requires high levels of ______
gonadotropins
If no FSH and LSH, follicles will undergo _____ at the ___ stage
atresia, antral
Dominant follicles have ______ since they have more granulocytes
FSH receptors
Selection and dominance takes _____, the same length as the ____ phase. Therefore, primoridal follicles are recruited ~ ____ before
in 14 days, follicular, 6 months
Follicles can be classified according to their ____, and are constantly undergoing ____
size, atresia
Gonadotropin dependent stage occurs between days ____ and ____, characterized by ______
70-90 days, exponential growth
Theca cells responsive to ___ and granulosa responsive to___
LH, FSH
Lh helps convert ____ into _____ and ___ helps convert ____ into ____
cholesterol, progestins, androgens, estrogens
Steroidogenesis in theca cells
Cholesterol → Pregnenolone → 17-OH-pregnenalone → DHEA → androstenedione
LH/FSH mediated steroidogenesis leads to increased ___ and _____
cAMP, PKA
Steroidogenesis in granulosa cells
Androstenedione (theca) → estrone → estradiol-17B
Androstenedione converted to estrone via _____
Aromatase
_____ has positive feedback on FSH when at a high enough amount, and has negative feed back at extremely____- and ____ amounts
Estradiol, high, low
Estradiol increases at ovulation dramatically because the ______ has increased ____ and therefore express more FSH receptors
dominant follicle, granulocytes
Estrogen _______ GnRH and LH/FSH but ______ at high levels
inhibits, activates
______ inactivates FSH/LH
inhibin
Progesterone inhibits _______ but also activates ____ at high levels
GnRH, LH/FSH
Estrogens and progestrones stimulate
Somatic tissue growth
Development and maintenancy of mammary gland
Cyclic changes in reproductive organs
Hormonal contraceptives modify ______
feedback
Why does estrogen and inhibin exert negative feedback?
Energy resources
Only want the best oocyte
Corpus luteum regression leads to a drop in ___, ____, and ____ removing _________ on pituitary, allowing ____ to rise
progesterone, estrogen, inhibin, negative feedback, FSH
Transient ______ initiates ________ tonic growth the next cycle, as rising ____ from developing follicles gradually suppresses _____ again
FSH increase, pre-antral follicle, estradiol, FSH
In the early follicular phase, increased ____ stimulates ____- to increase ___ production/secretion
FSH, aromatase, estrogen
In the mid-follicular phase, the follicle producing the most ____ has an advantage
estrogen
Traits of dominant follicle in mid follicular phase
Enhanced follicular fluid generation
Increased LH/FSH receptor content
Increased number of granulosa cells
Increased inhibin production
2X vascularity than subordinate follicles by day 9
From day 1 to day 14, ______ amount decreases as ______ amount increases
activin, inhibin
a-subunit + Ba subunit comprise inhibin ___
A
a-subunit + Bb subunit comprise inhibin __
B
_____ secreted by the ovary inhibit pituitary _____
Inhibin A and B, FSH secretion
Ba subunit + Bb subunit = _______ , which when secreted by the pituitary, can stimulate pituitary _____ (via _____)
activin A, FSH secretion, activin B
Inhibin A or B prevents ____ from binding its receptor
activin
Activin-mediated FSH production
Activin binds activin type I/type II receptor
Smad phosphorylated
Promotes FSHB production
In primordial follicles activin __ regulates _____ and ______
A, germ cell proliferation, primordial follicle formation
In primary and secondary follicles, activin stimulates _____________, ____, and ___ growth
Granulosa cell proliferation, follicle, oocyte growth
In the antral follicle, activin accelerates ______ and stimulates ______
oocyte maturation, aromatase
In the pre-ovulatory follicle, the ____ has activin receptors
oocyte
In corpus luteum, activin delays ______ inhibiting ______
luteinization, progesterone production
In corpus albicans, activin _____ promotes regression of the ______ during luteal regression
A, corpus luteum
In early follicular phase ____>____
activin, inhibin
The early follicular phase favours a less ____ environment due to high ____
androgenic environment, activin
Inhibin and activin are released from ______
granulosa cells
IN late follicular phase, _____ >_____
inhibin, activin
By mid-follicular phase, one follicle is producing more ____ than the others
estrogen
In late follicular phase, granulosa also stimulates ___ and _____/__ to act on theca cells
insulin, IGF-I, II
Role of estrogens
Proliferation of granulosa cells
Survival of the follicle
Increase ERa, LH-R, FSH-R, aromatase
Increased gap junction formation
Era-KO mice are infertile, no antrum formed
BERKO mice subfertile; ovaries small and folliculogenesis minorly impaired
Aromatase KO mice infertile, antral follicles but do not ovulate; cystic follicles
Role of FSH
Receptors only on granulosa cells
Granulosa cell proliferation and differentiation
Increases aromatase
Synergizes with E to increase FSH-R
Gap junctions in granulosa cells
Role of LH
Acts upon thecal cells to stimulate androgen production
Induces 17a-hydroxylase to convert pregnenolone into DHEA
Ovulation and luteinization
(In follicular phase) Granulosa cells express enzymes necessary to make _______ and to make ______ from androgens but lack ____ to make androgens
progesterone, estrogen, 17a-hydroxylase
Why is progesterone not made during the follicular phase?
Enzyme dependent
Activity of HSD3B2 which converts pregnenolone to progesterone is more prominent in luteal phase
Granulosa cells are regulated by signals from the _____ and _____ during folluculogenesis
theca, oocyte
BMP-4 secreted from the ______ and enhances _____ action
Theca, FSH
BMP-7 is released from the _____ and inhibits ______ via ______
theca, progesterone synthesis, HSD3B2
_____ and _____ are released from the ______ to inhibit progesterone synthesis via HSD3B2 and are no longer present after ______
BMP-15, BMP-6, oocyte, ovulation
Menopause is defined as a _______ of menses that results from the depletion of the ________
Permanent cessation of menses, ovarian reserve
Average age of menopause transition is ___
51 yo
Menopause is preceded by a period of _______ caused by____ and _____
subfertility, less follicles, environmental toxins