Introduction to the Nervous System
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
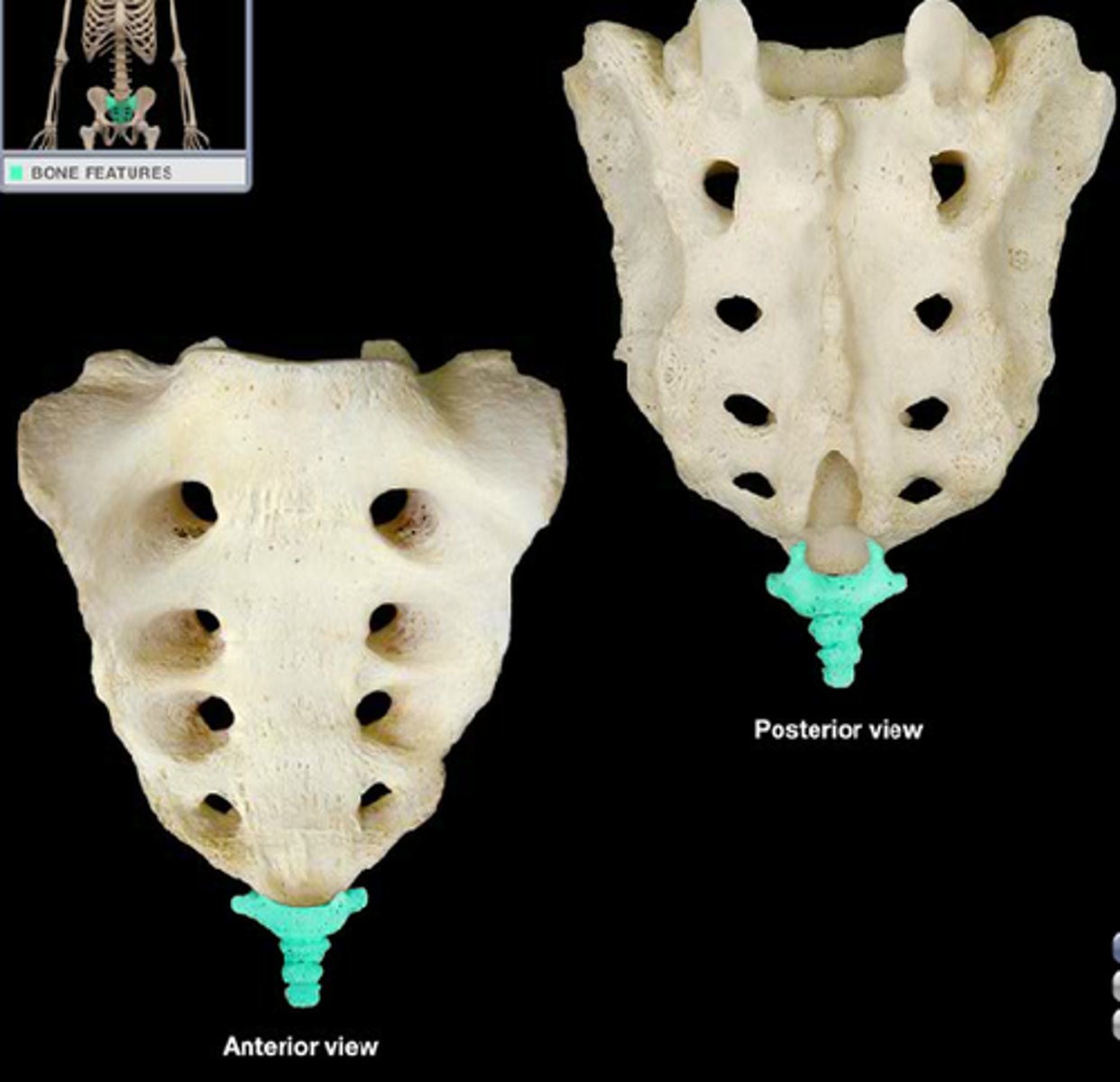
coccygeal vertebrae
1
caudal
toward the tail
rostral
toward the nose
central nervous system
-brain, spinal cord; covered in meninges
-stay and connect in brain/spine
-upper motor neurons
meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
-cranial nerves, spinal nerves
-Starts in CNS and ends in ____
-Lower motor neurons
somatic nervous system
innervates structures of the body (muscles, skin, mucous membranes)
autonomic nervous system
-visceral
-controls smooth muscles and glands of internal organs and returns sensory info to the brain
parasympathetic nervous system
-rest and digest
-located at brainstem/sacral
sympathetic nervous system
-fight or flight
-located middle of spine
brain
cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem
cerebrum
-largest part of the brain
-telencephalon
-diencephalon
telencephalon
Cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system
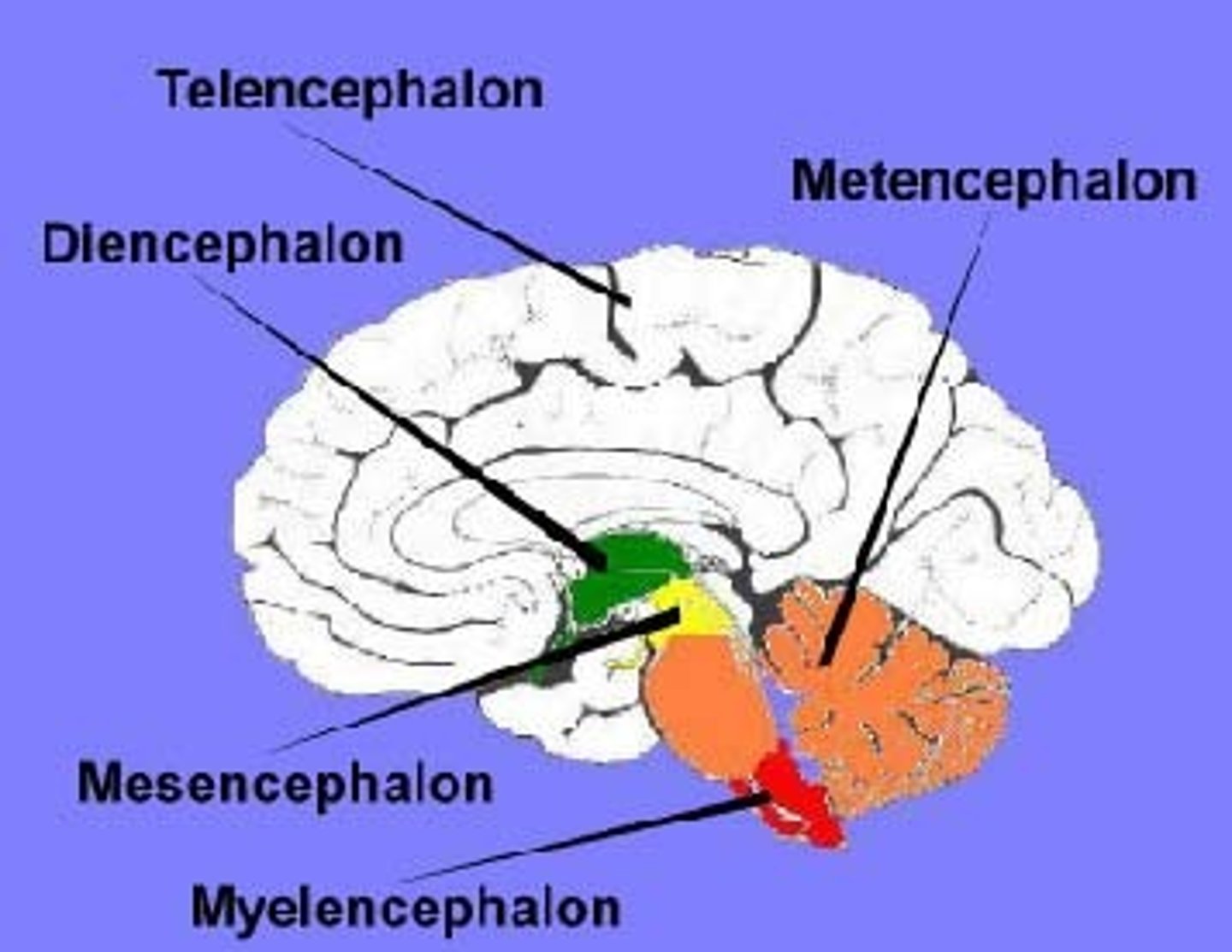
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
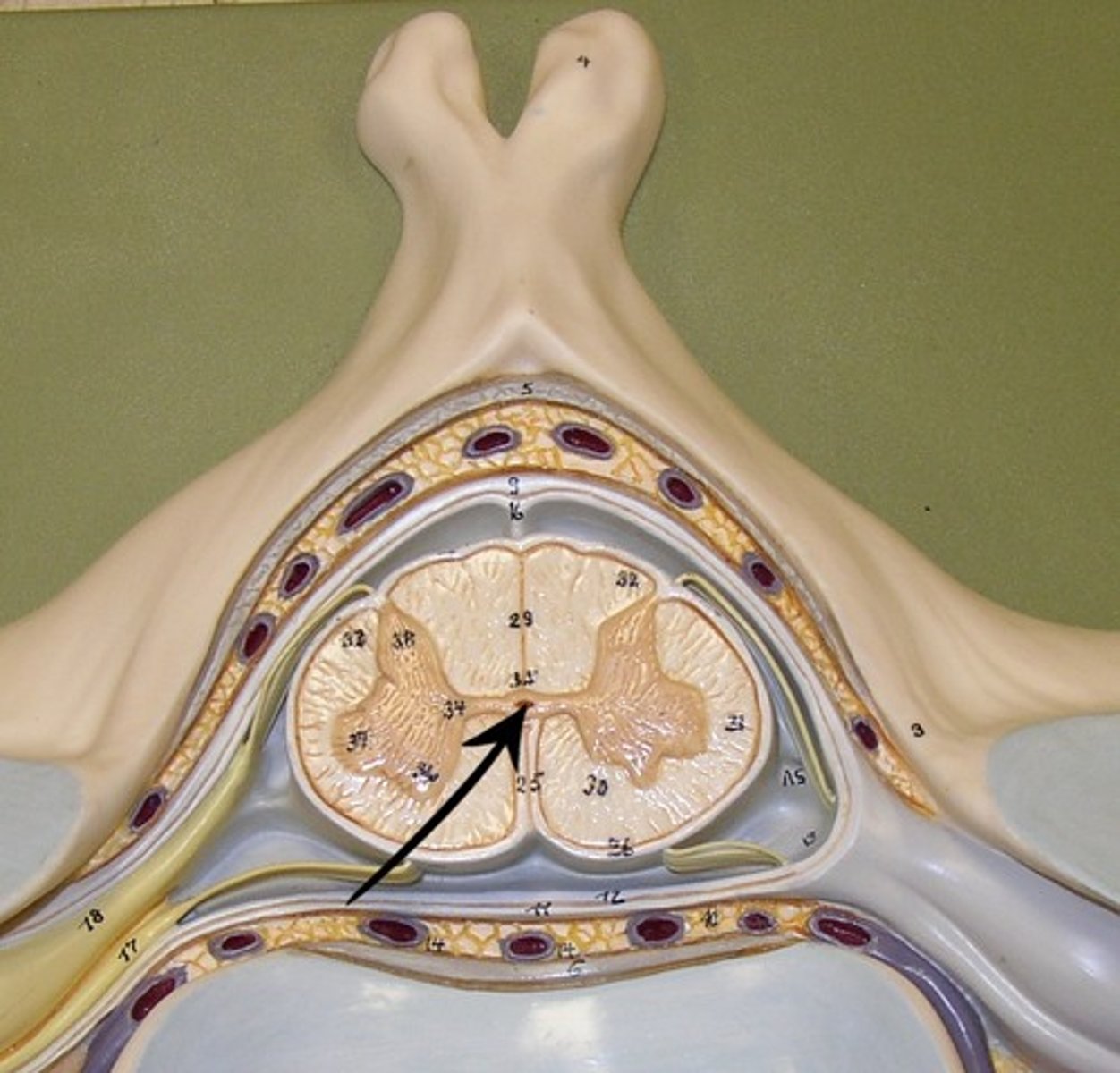
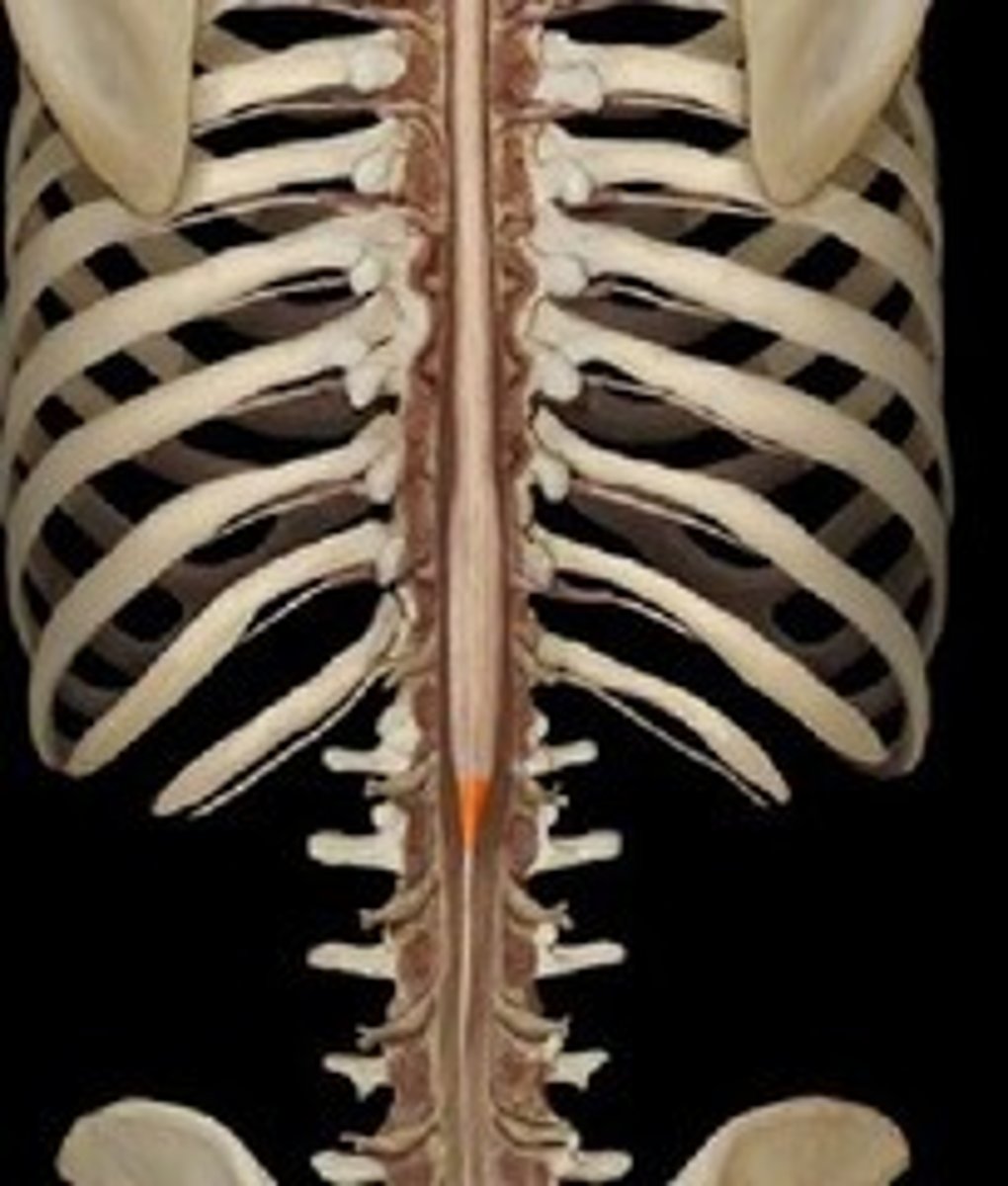
spinal cord
-Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
-cord, conus medullaris
-cauda equina
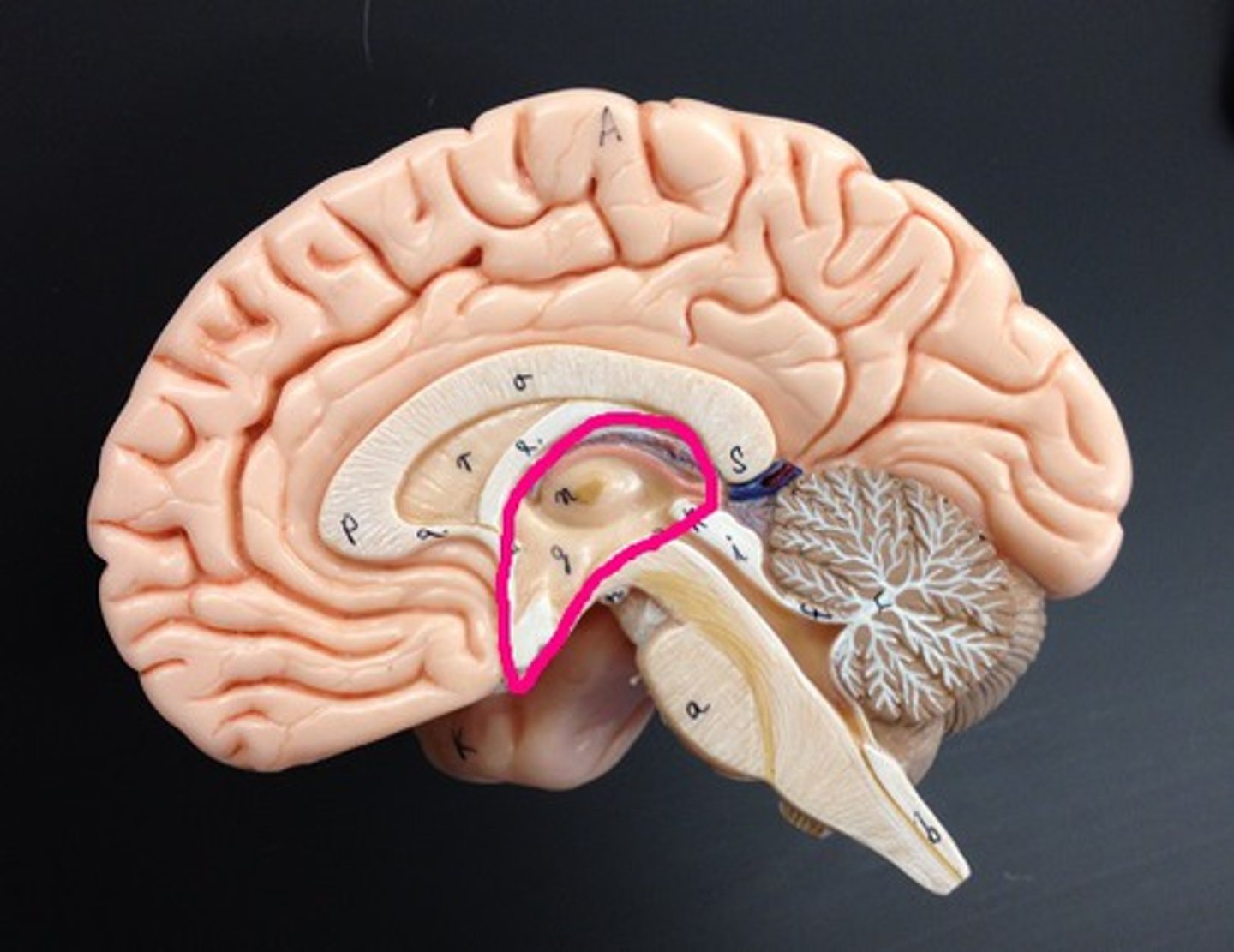
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord
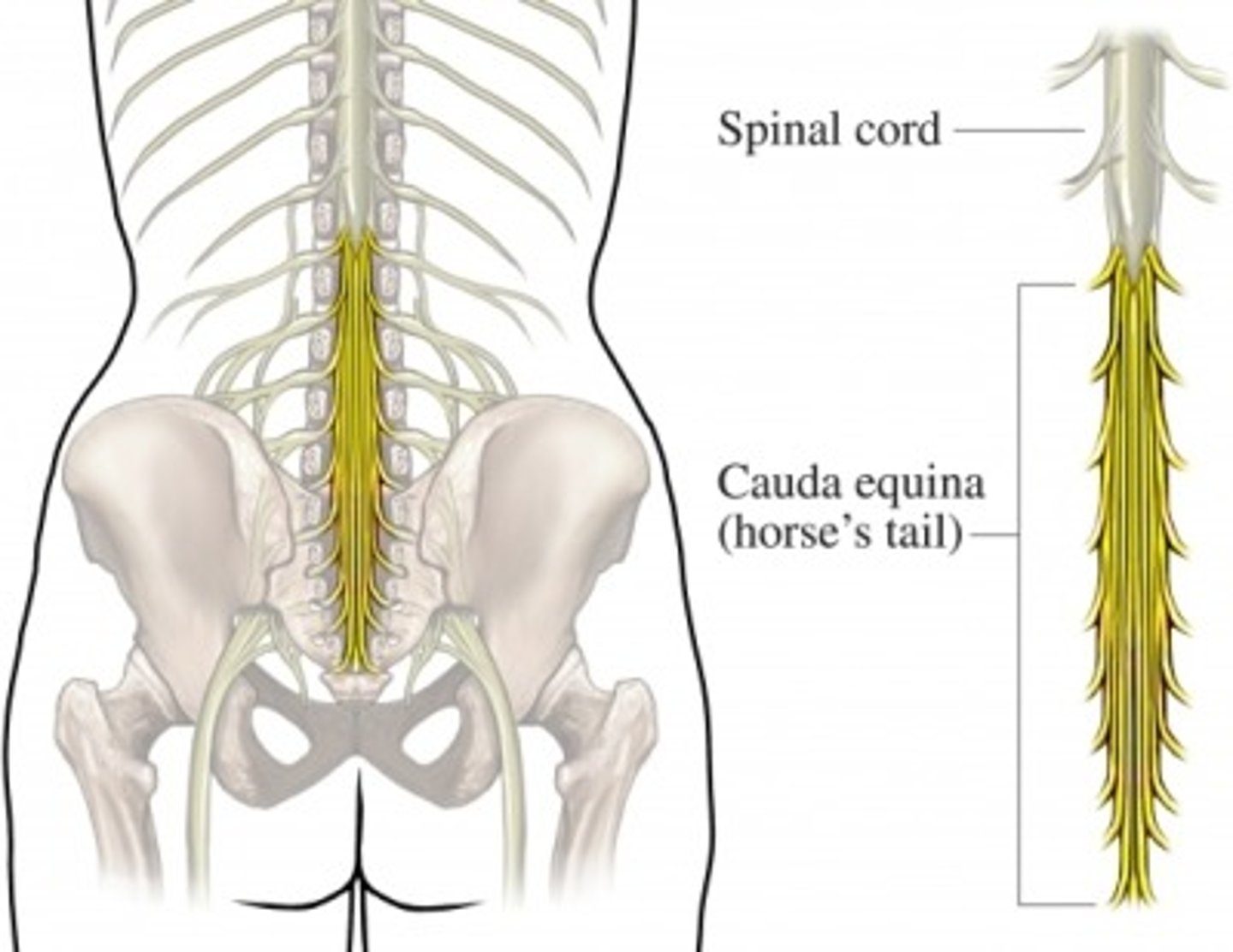
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
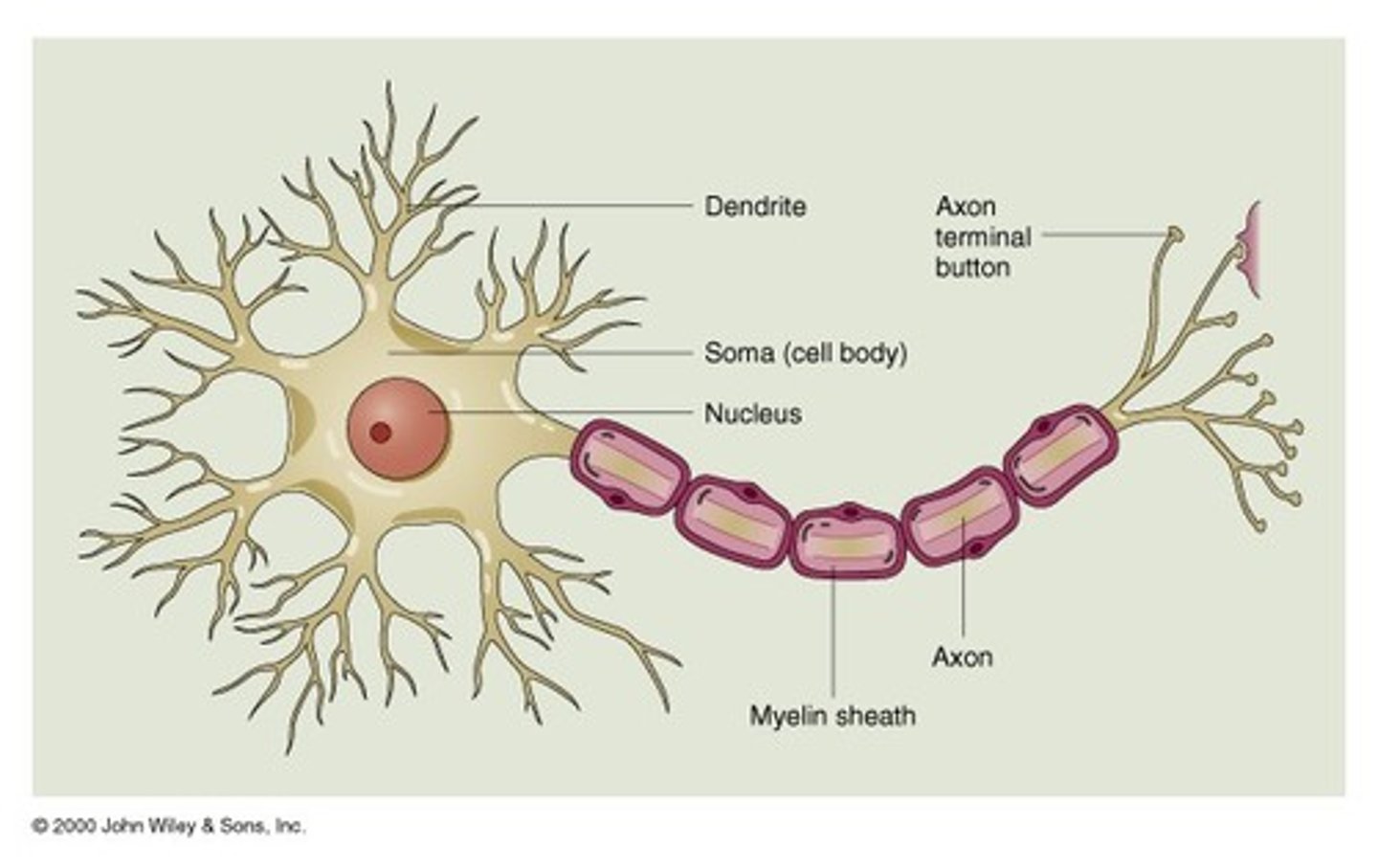
neurons
nerve cells, send signals via retro or anterograde transportation
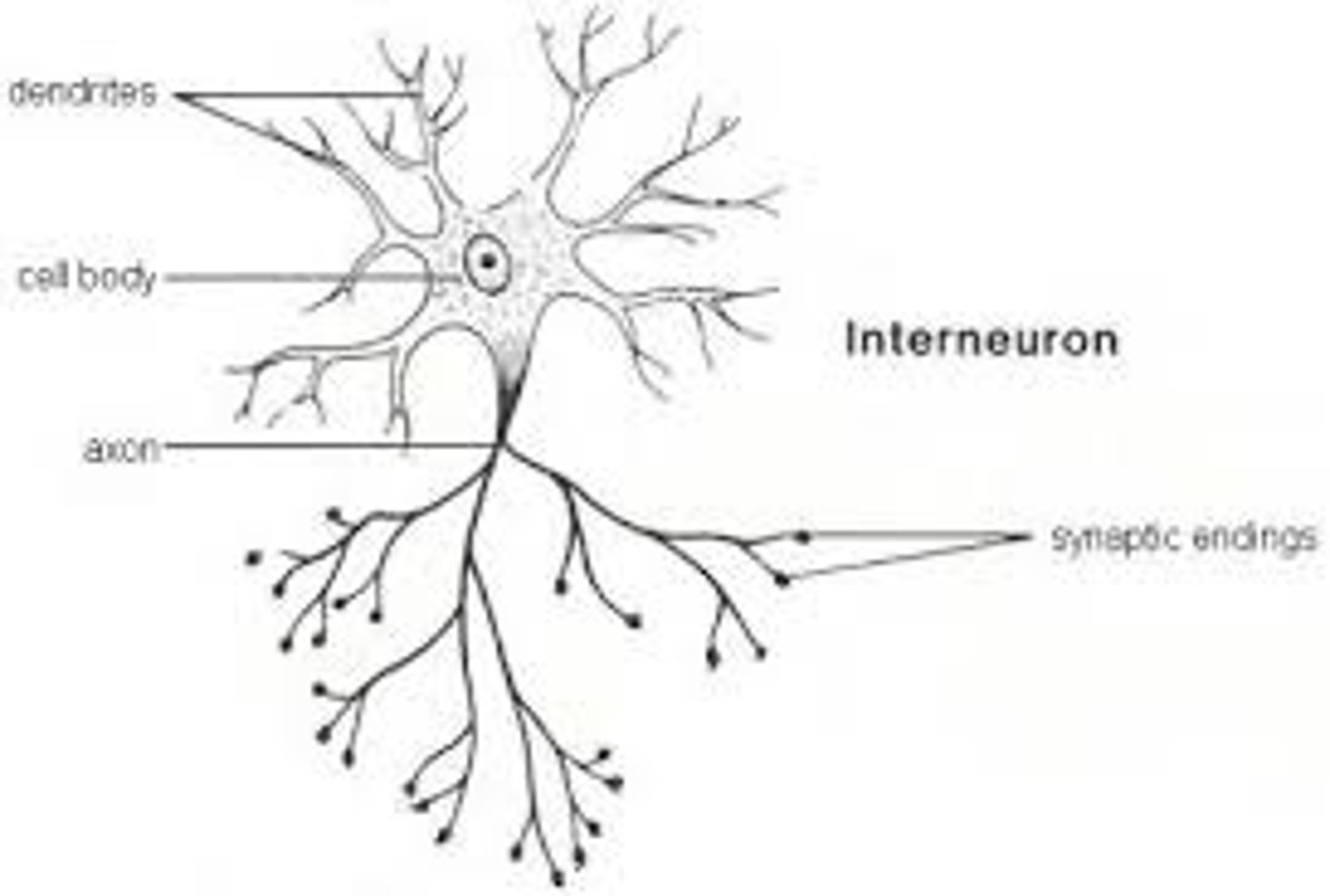
interneurons
nerve cells with short axons, send information locally; stop gap between longer neurons
nuclei
nerve cells with common function, grouped in cluster, inside CNS
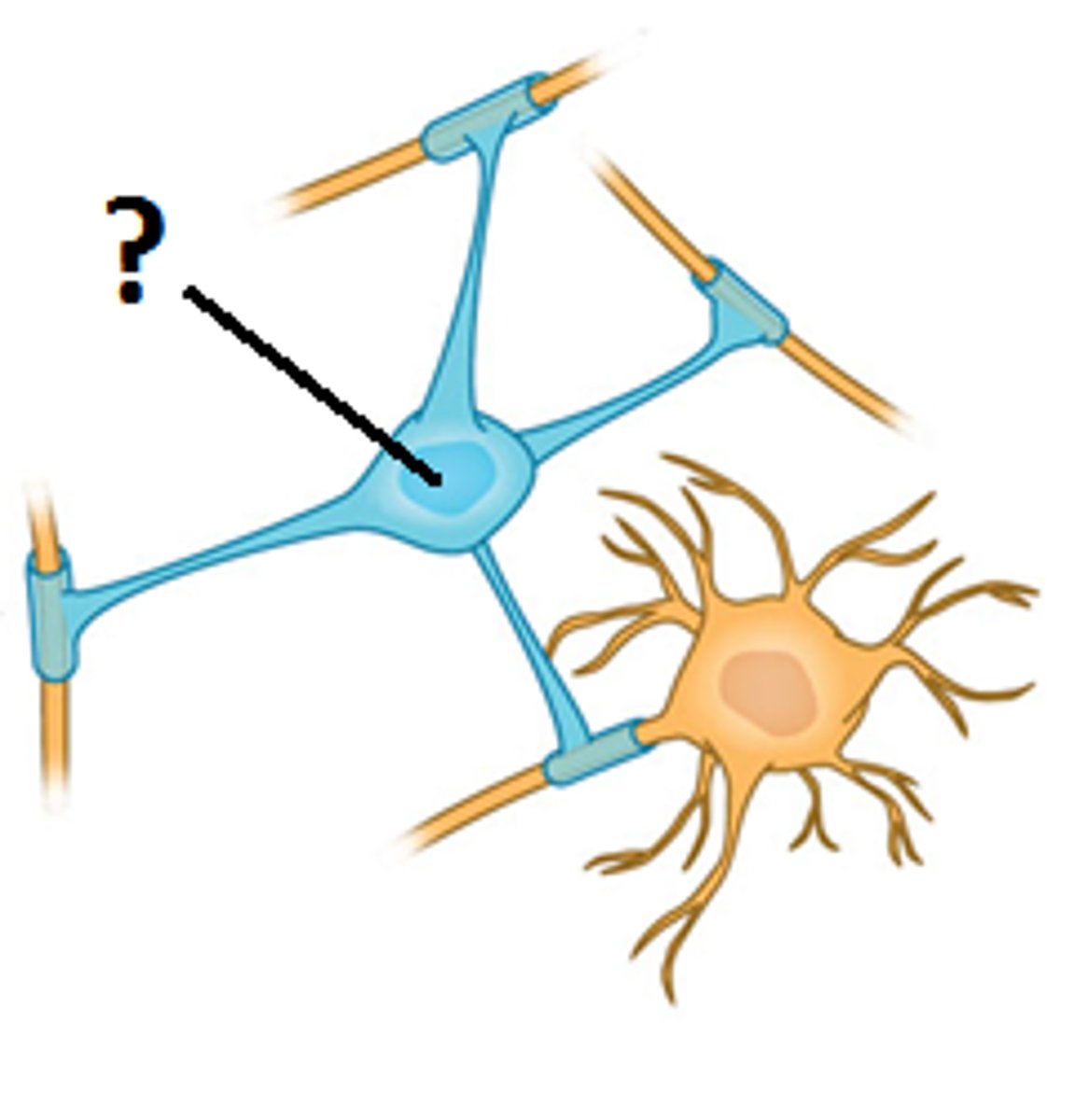
glial cells
support (physical/chemical) activity of neurons; 10:1 glial cells to neurons; many different types
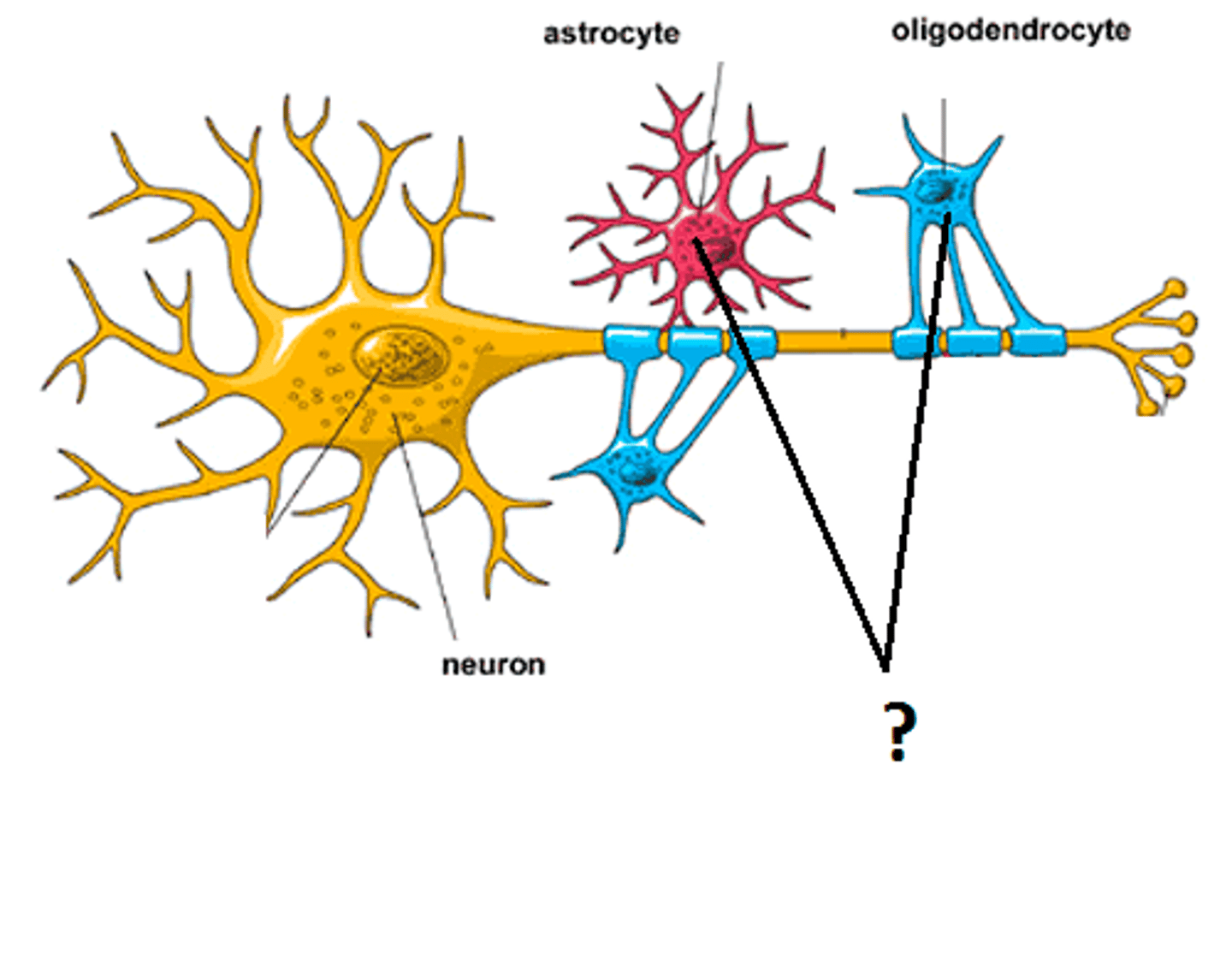
oligodendrocytes
creates myelin sheath in CNS
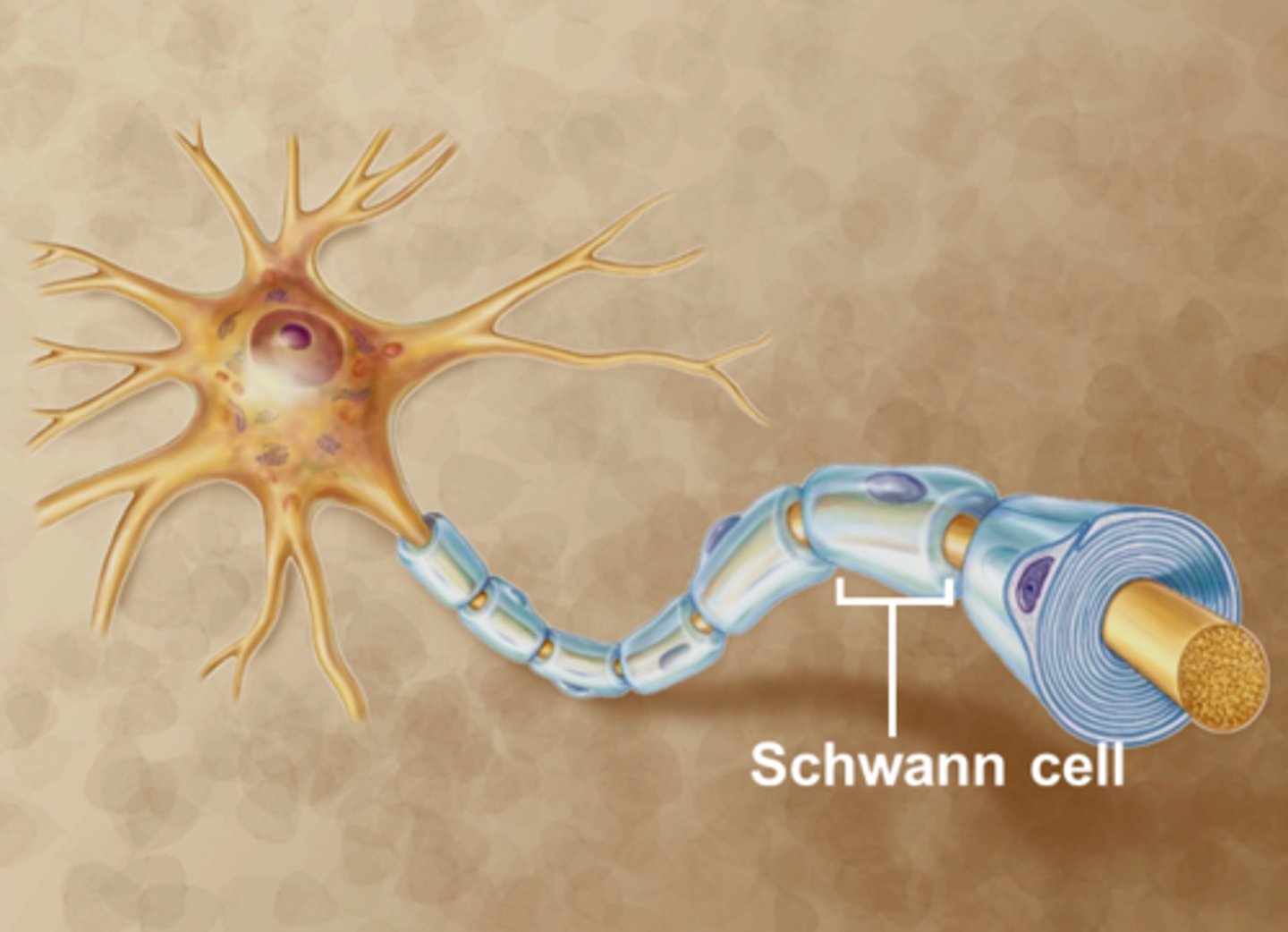
schwann cells
creates myelin in PNS
ganglia
nerve cells with common function grouped outside CNS
synapse
junction between axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron, chemical transmitters that may cause excitation or inhibition
monosynaptic
1 synapse, reflex
polysynaptic
-multiple synapses
-complex behavior
efferent neuron
motor neuron away from CNS
afferent
sensory; ascend
tracts
-bundles of axons in the CNS
-fasciculi
fasciculi
Tracts of myelinated fibers in the spinal cord with the same function; in PNS
columns (funiculi)
bundles of axons traveling up and down spinal cord, provide avenues of communication between different levels of CNS
decussate
to cross over to the other side of the brain
commissures
Connections of nerve fibers which allow the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate with one another; lateral in CNS
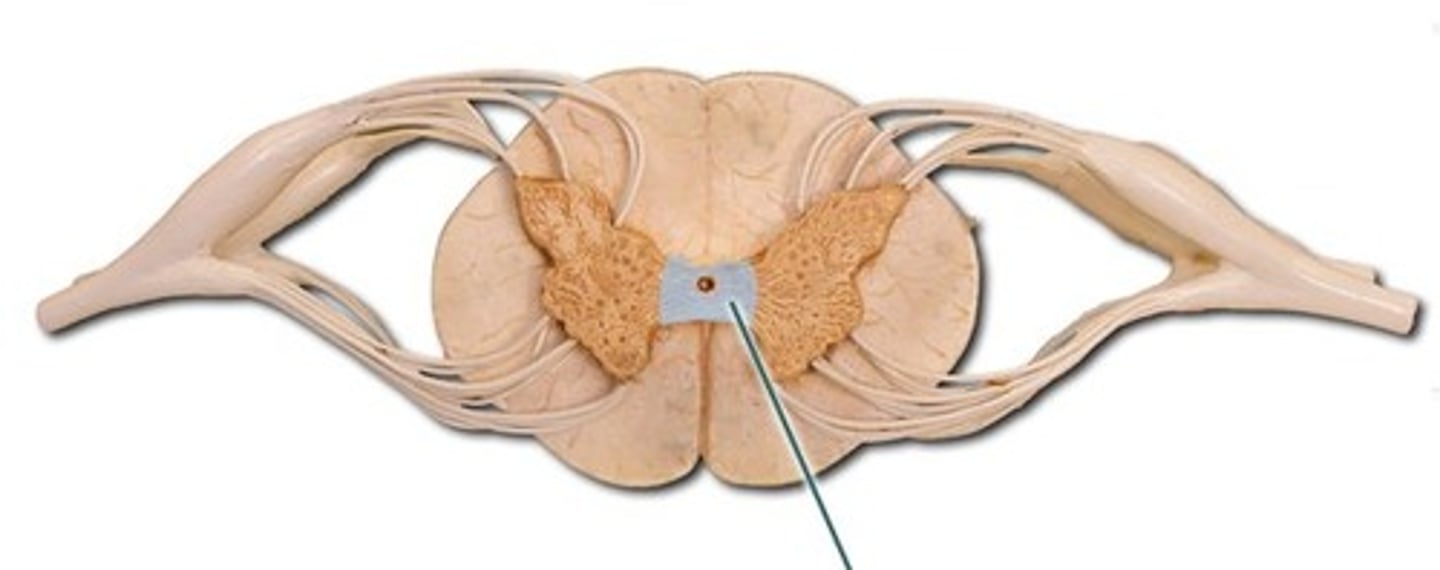
crossed representation
The left cerebral cortex receives sensory information from and controls motor functions to the right side of the body, while the right cerebral cortex receives sensory information from the left side of the body.
right hemisphere
controls left side of body; creativity, intuitive, spacial
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; analytical, language, math
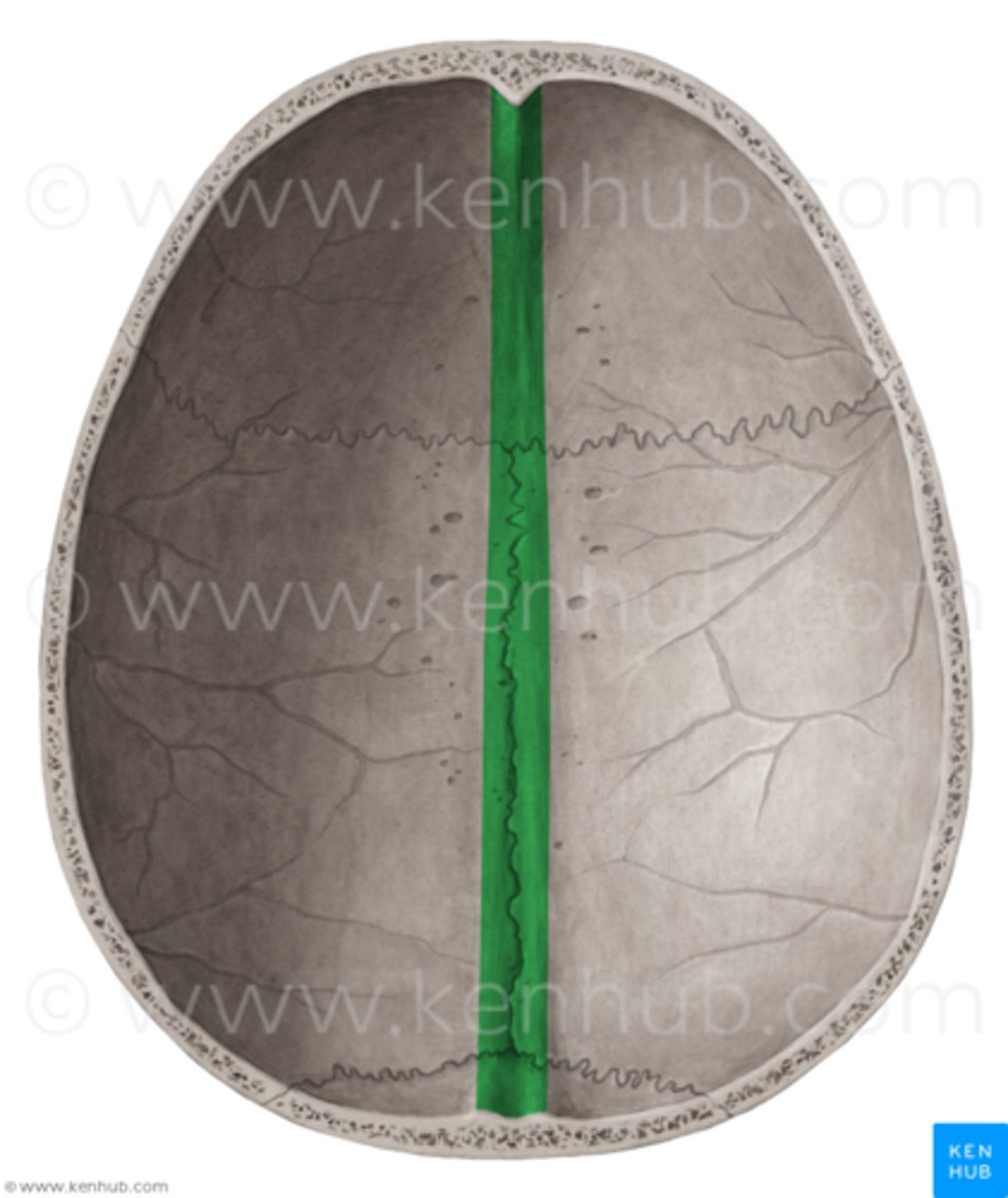
sagittal sulcus
vertical groove that runs down the midline of the endocranial surface
cerebral cortex
-The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
-gray matter
-cell-rich
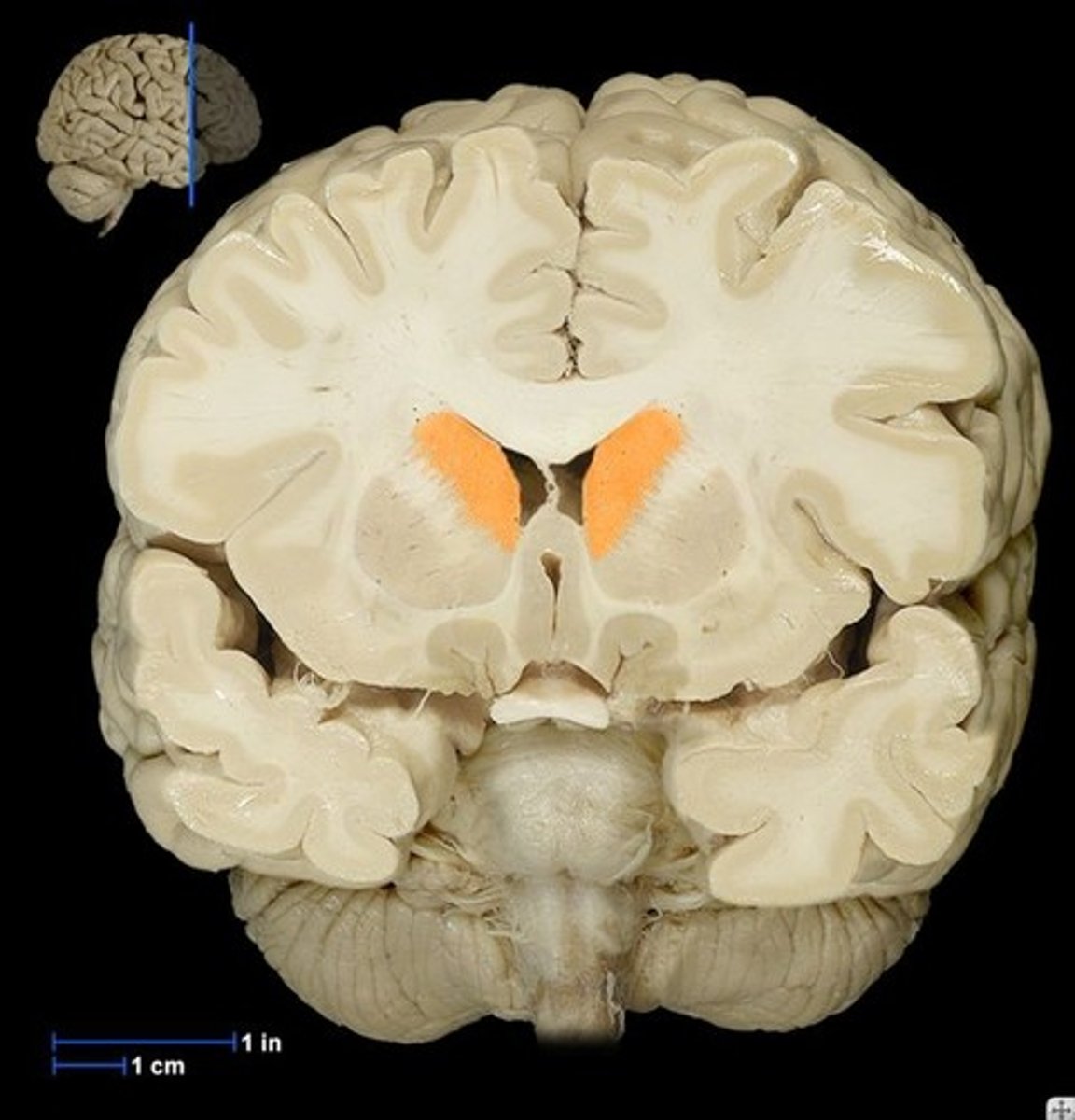
nuclei
cluster of cells
white matter
-myelinated axons
-connects brain regions
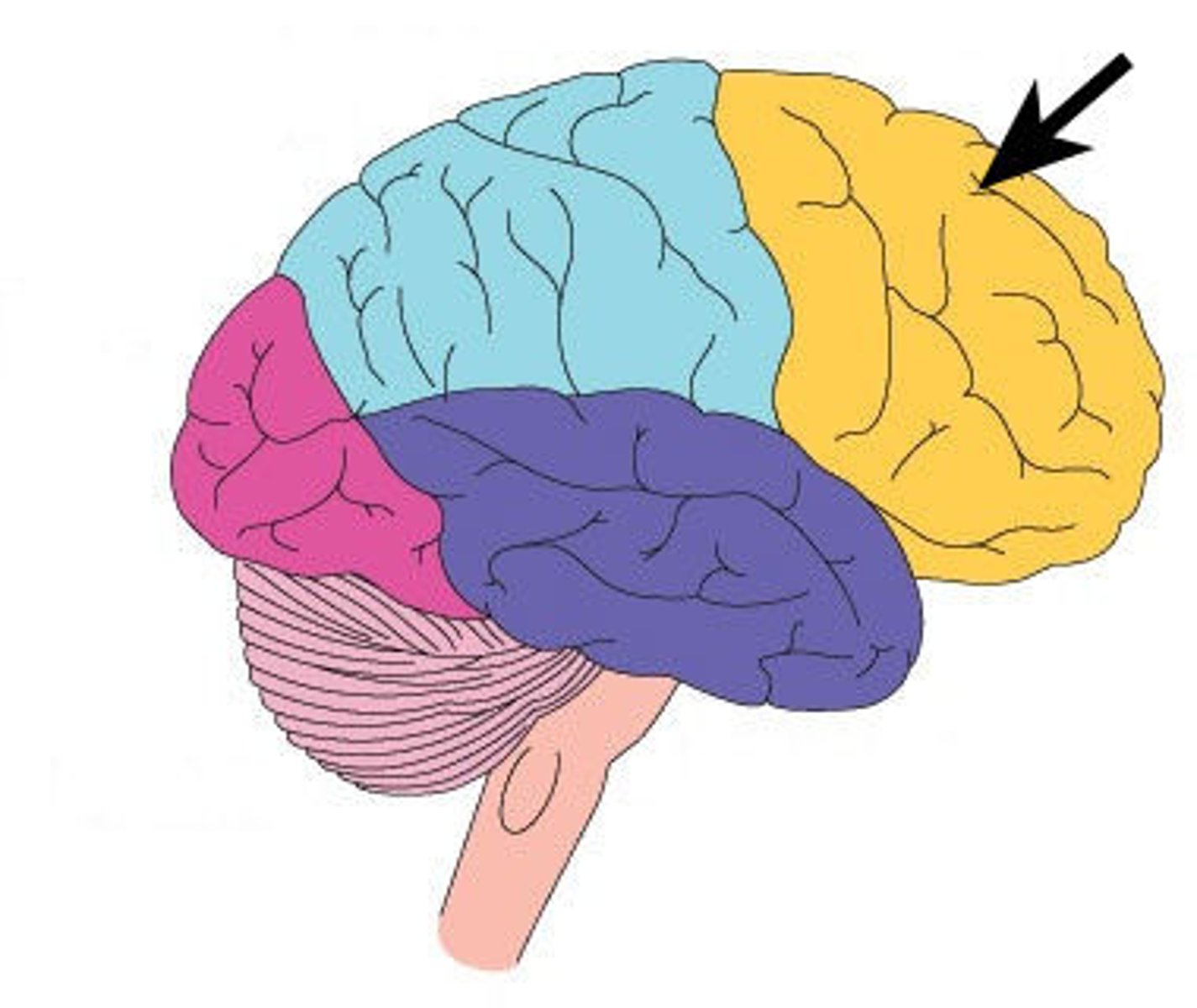
frontal lobe
thoughts, planning, actions, decisions
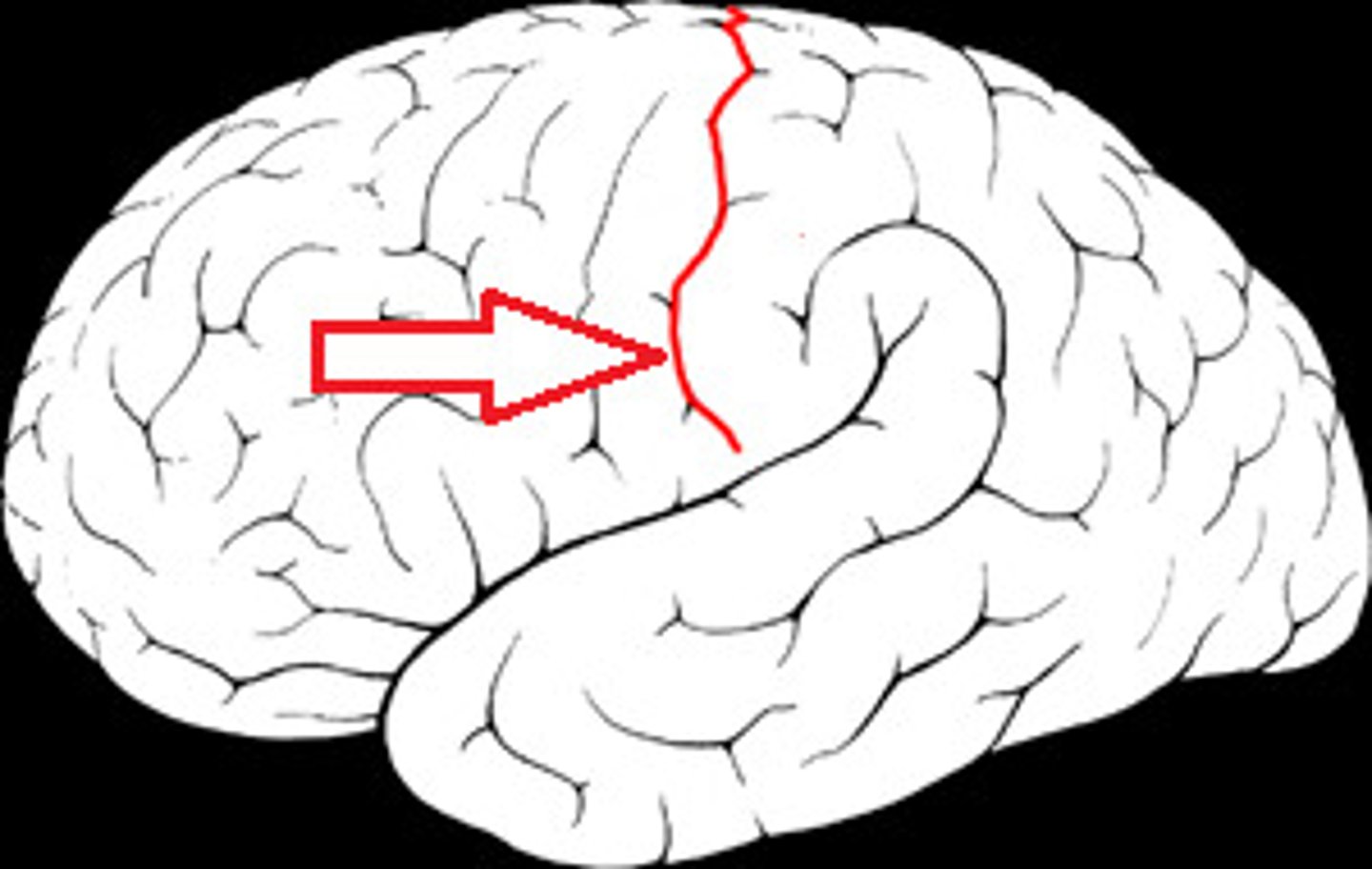
central sulcus
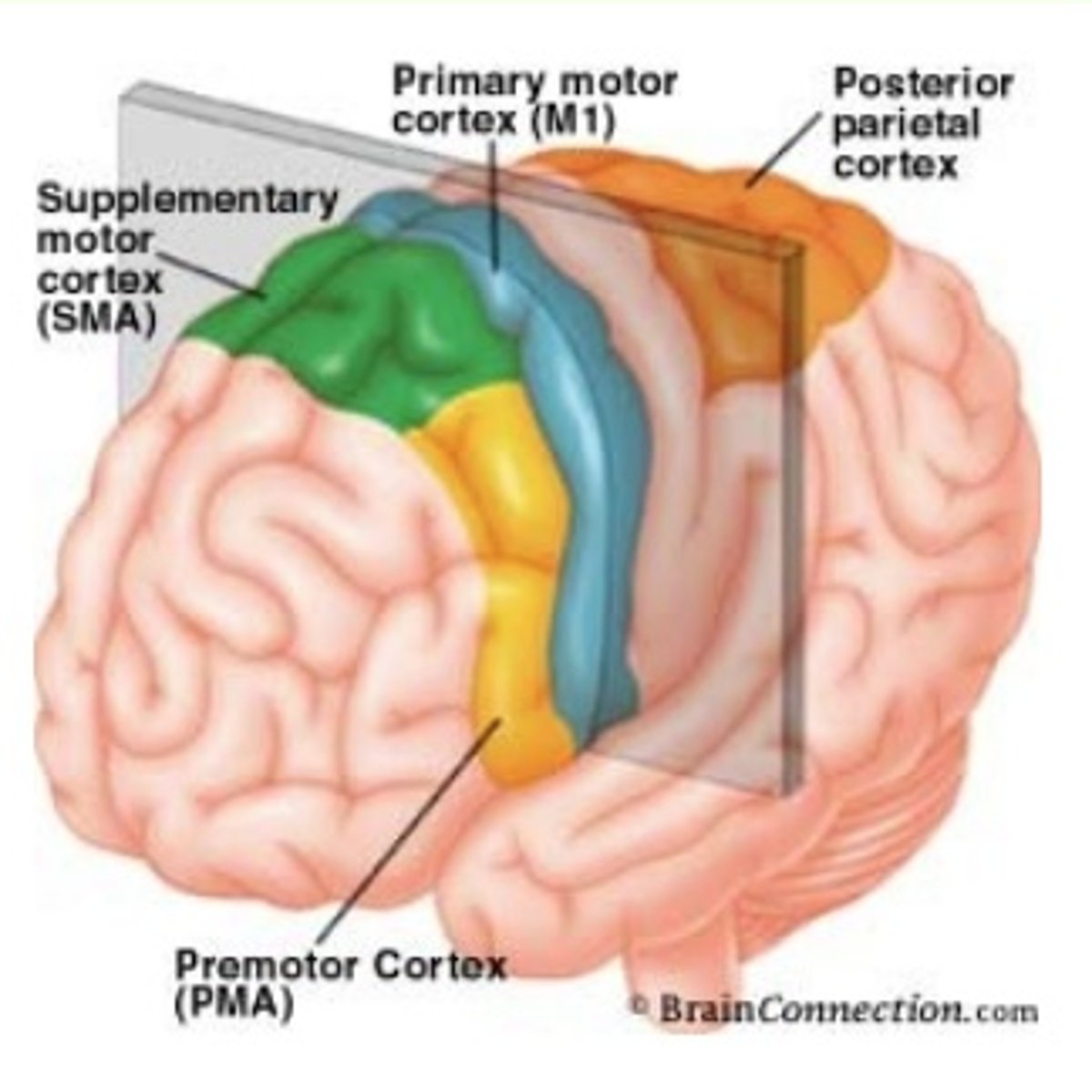
cortical motor system
-controls voluntary movement
-initiated by upper motor neurons in the primary motor cortex
impulsive and can't think about actions
What happens if there is damage to the frontal lobe?
parietal lobe
sensation, perception

sensorimotor system
The parts of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves that produce movement and provide feedback about movement
rostral boundary
anterior commissure along lamina terminalis to optic chiasm; central sulcus
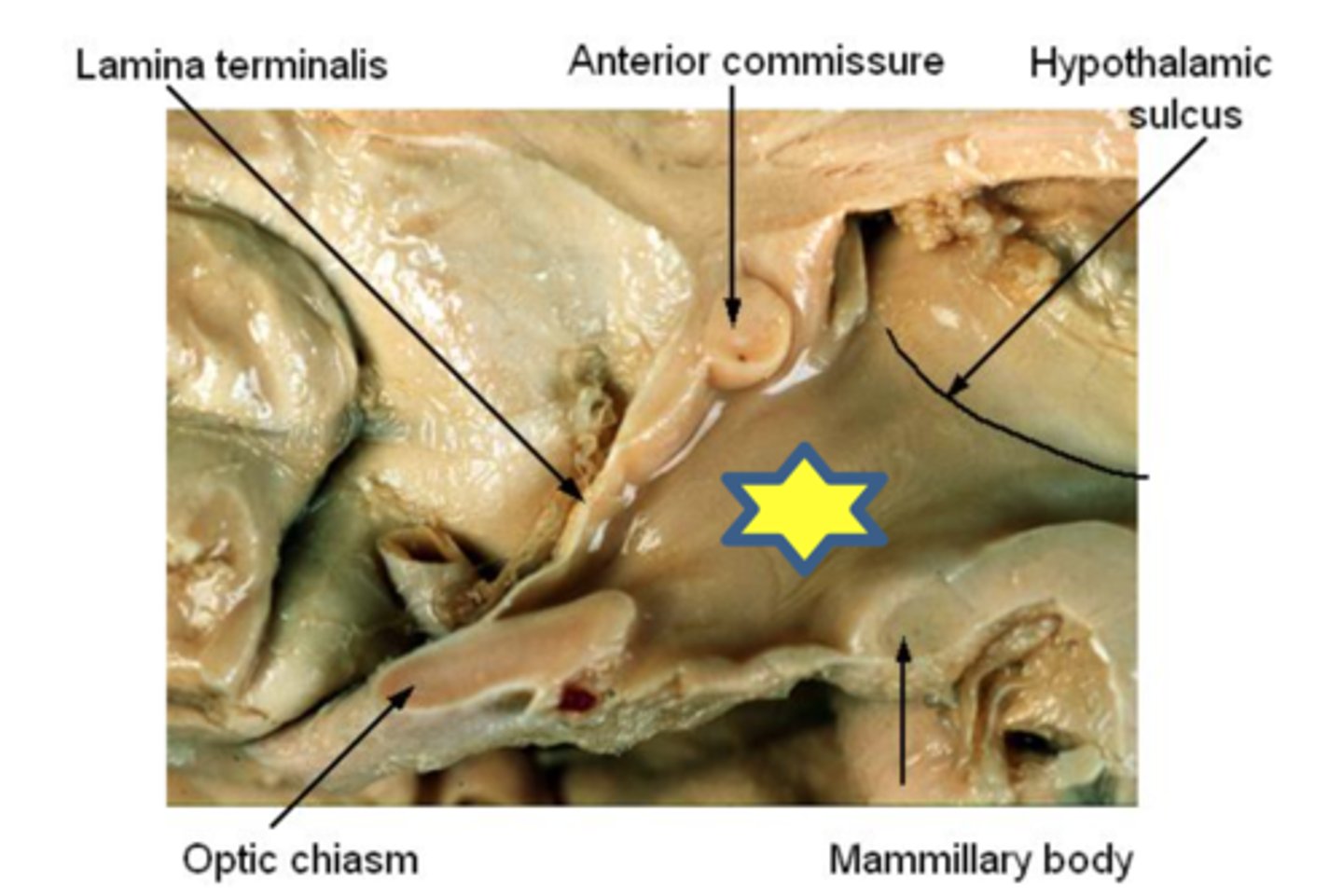
caudal boundary
formed by the thoracic outlet (space between the last pair of ribs by the costal arch, the body of the 12th thoracic vertebrae and the xiphoid process or the last sternebra); parietal occipital sulcus
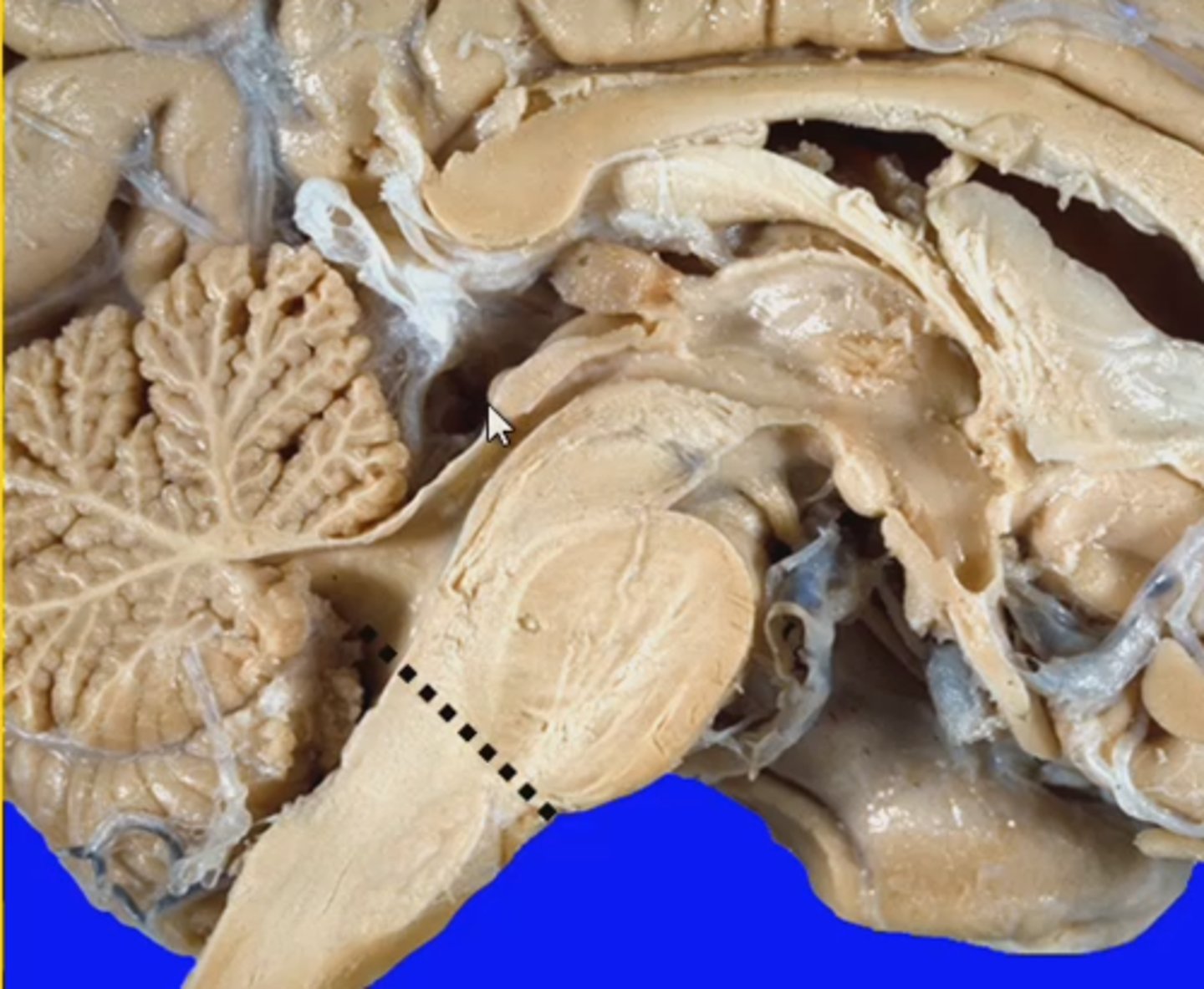
parietal-occipital sulcus
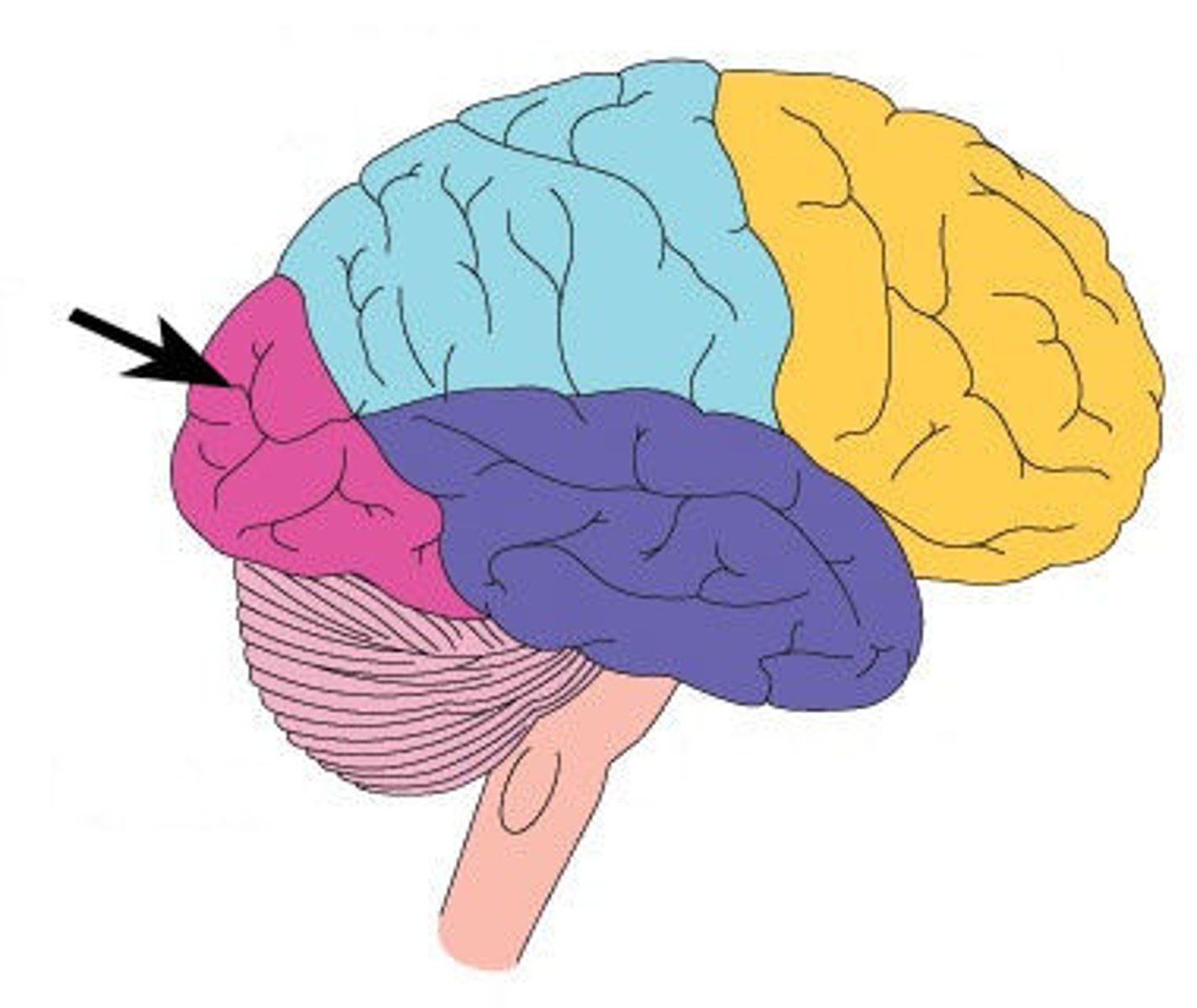
occipital lobe
dedicated to vision
dorsal stream
where pathway; to parietal lobe
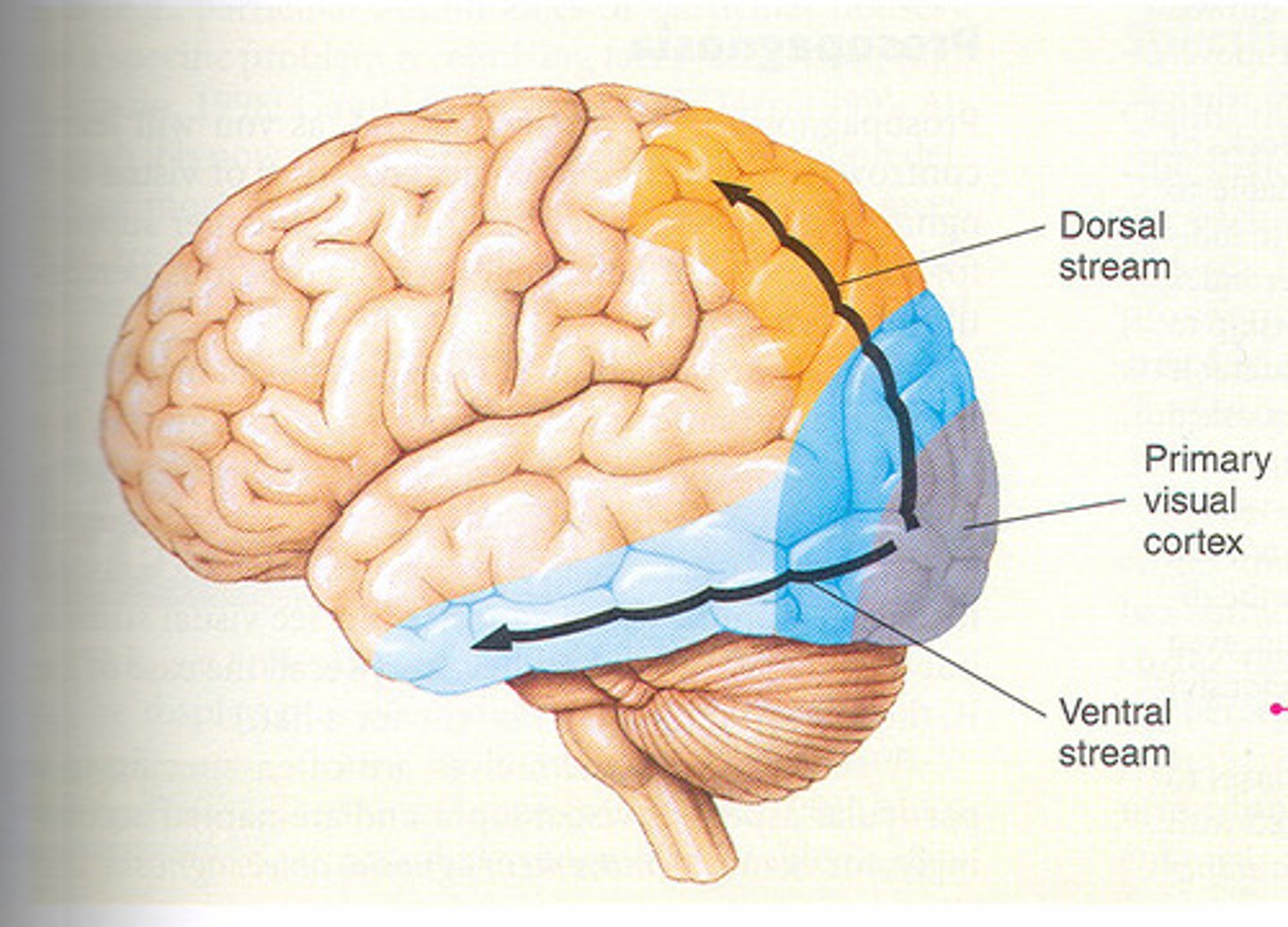
ventral stream
what pathway; to temporal lobe
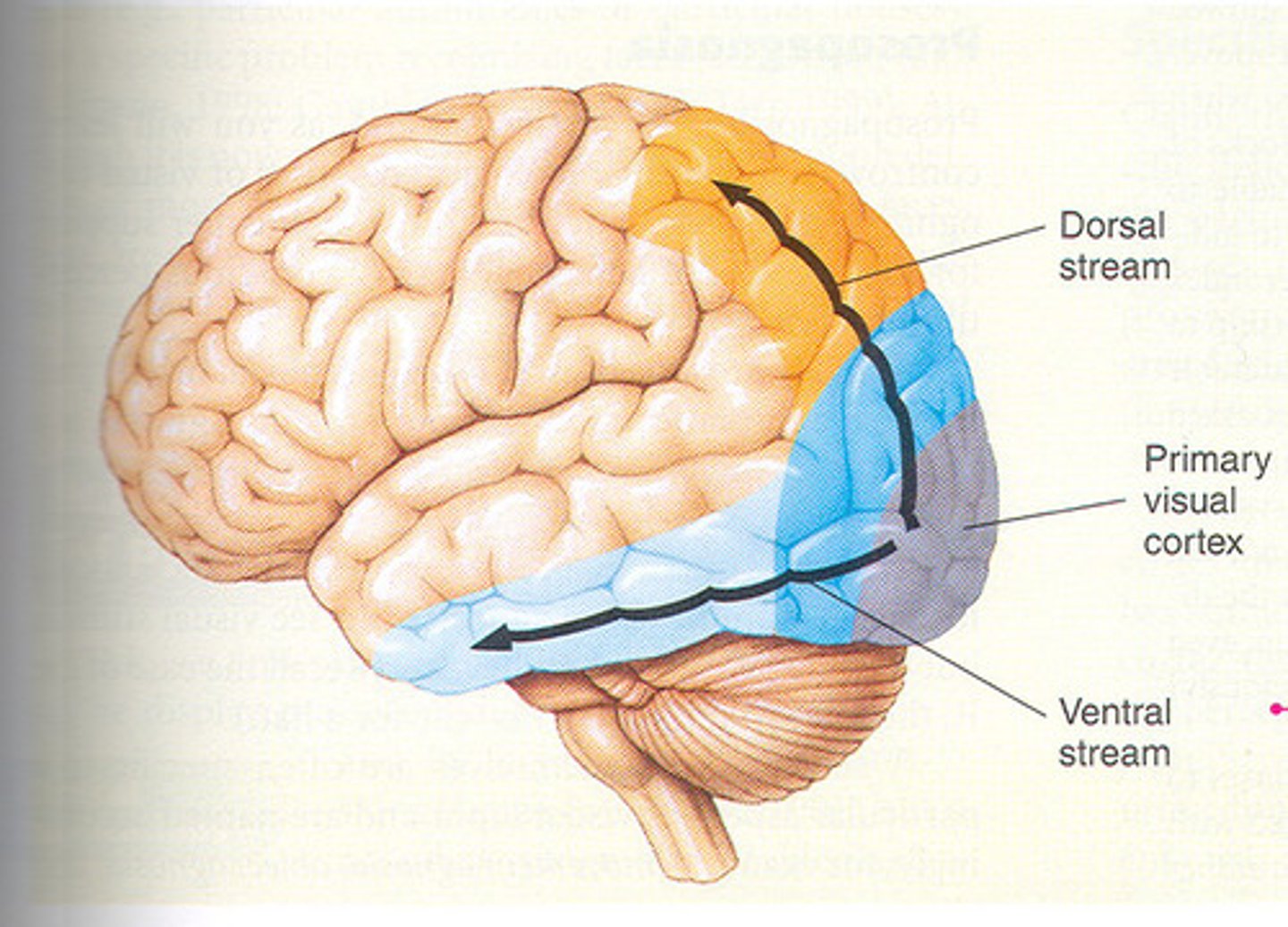
temporal lobe laterally and parietal lobe medially
What are the boundaries of the occipital lobe?
temporal lobe
-auditory processing, language, memory, object identification ("what pathway")
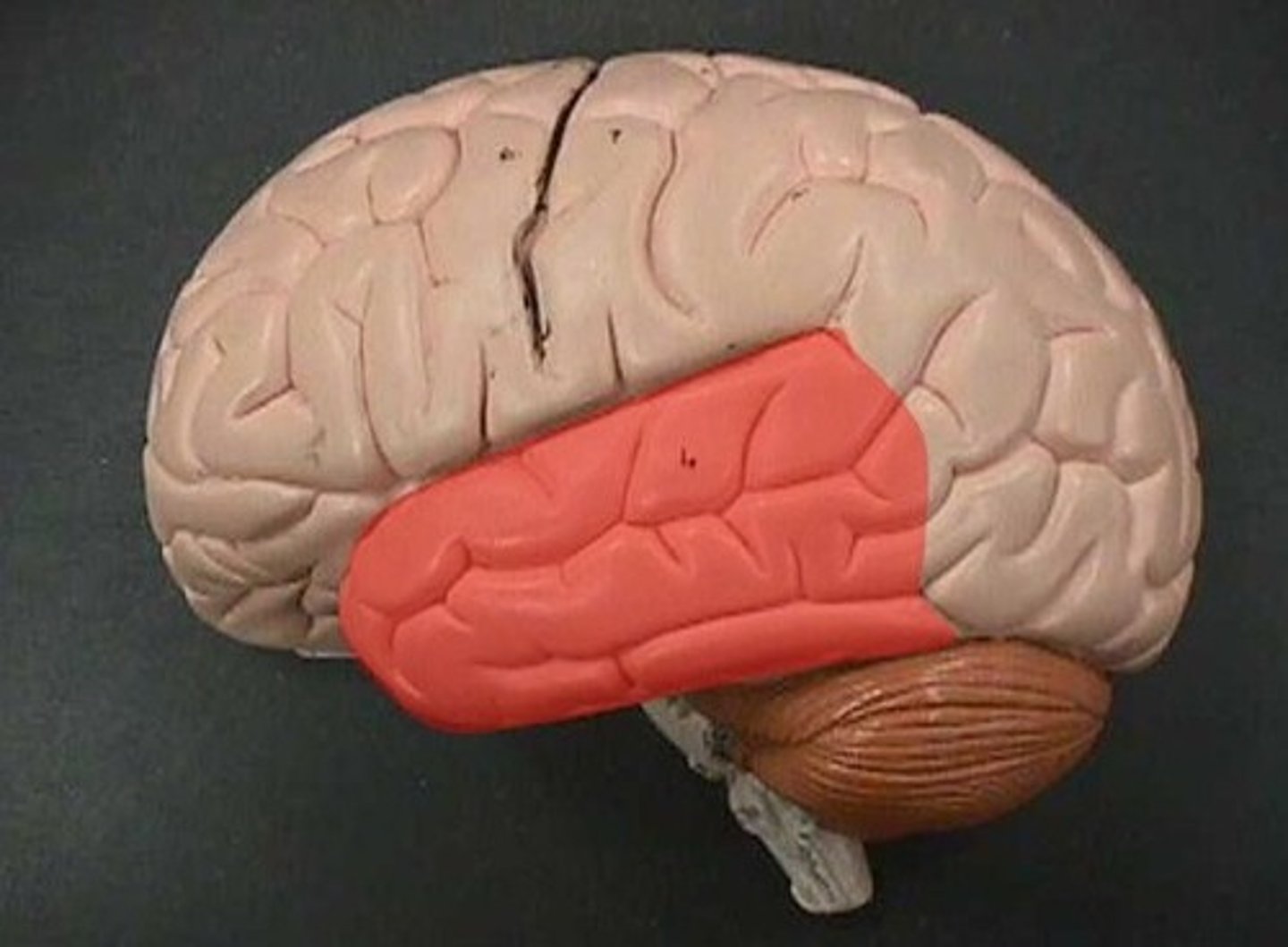
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
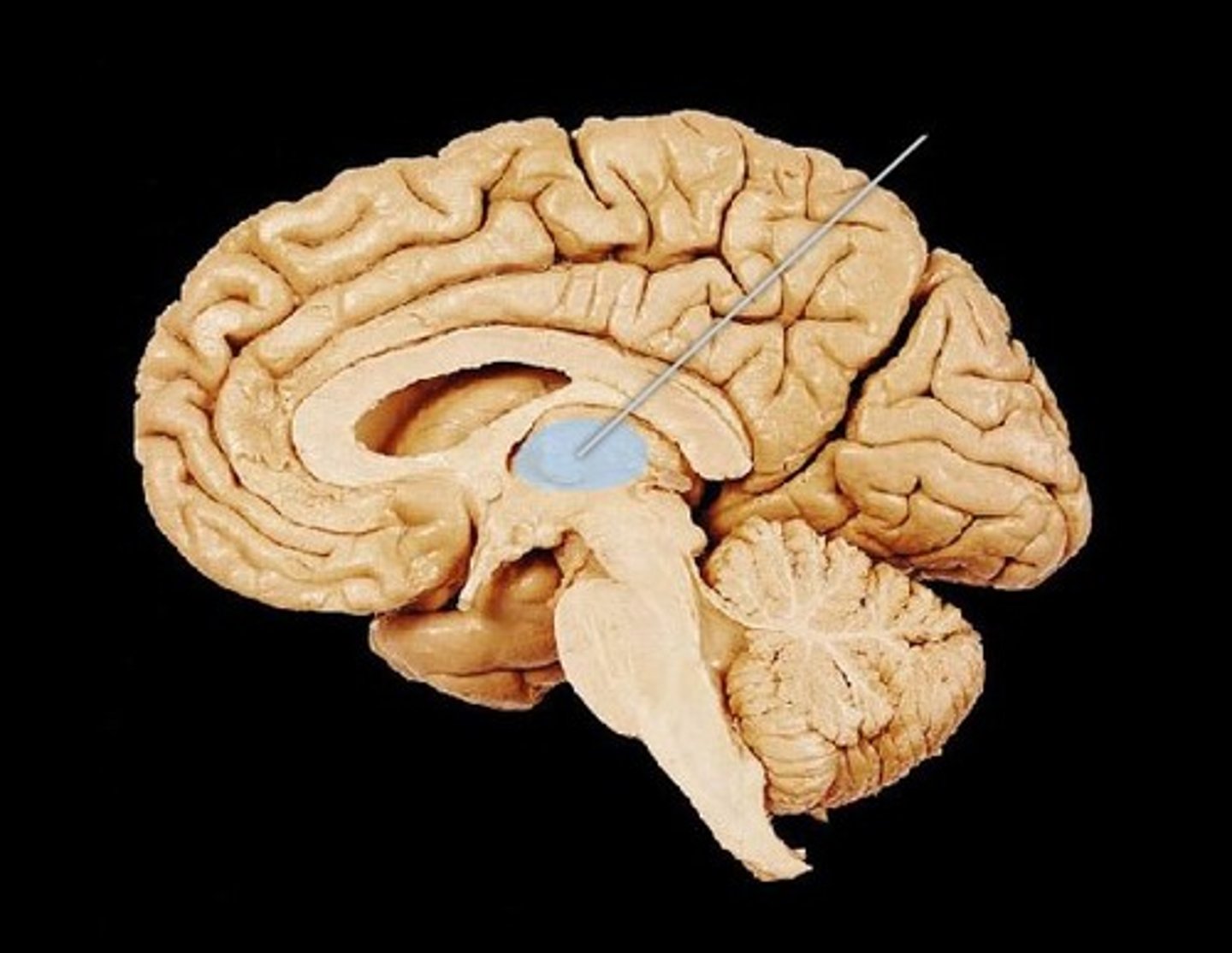
thalamus
-the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
-sensory relay station
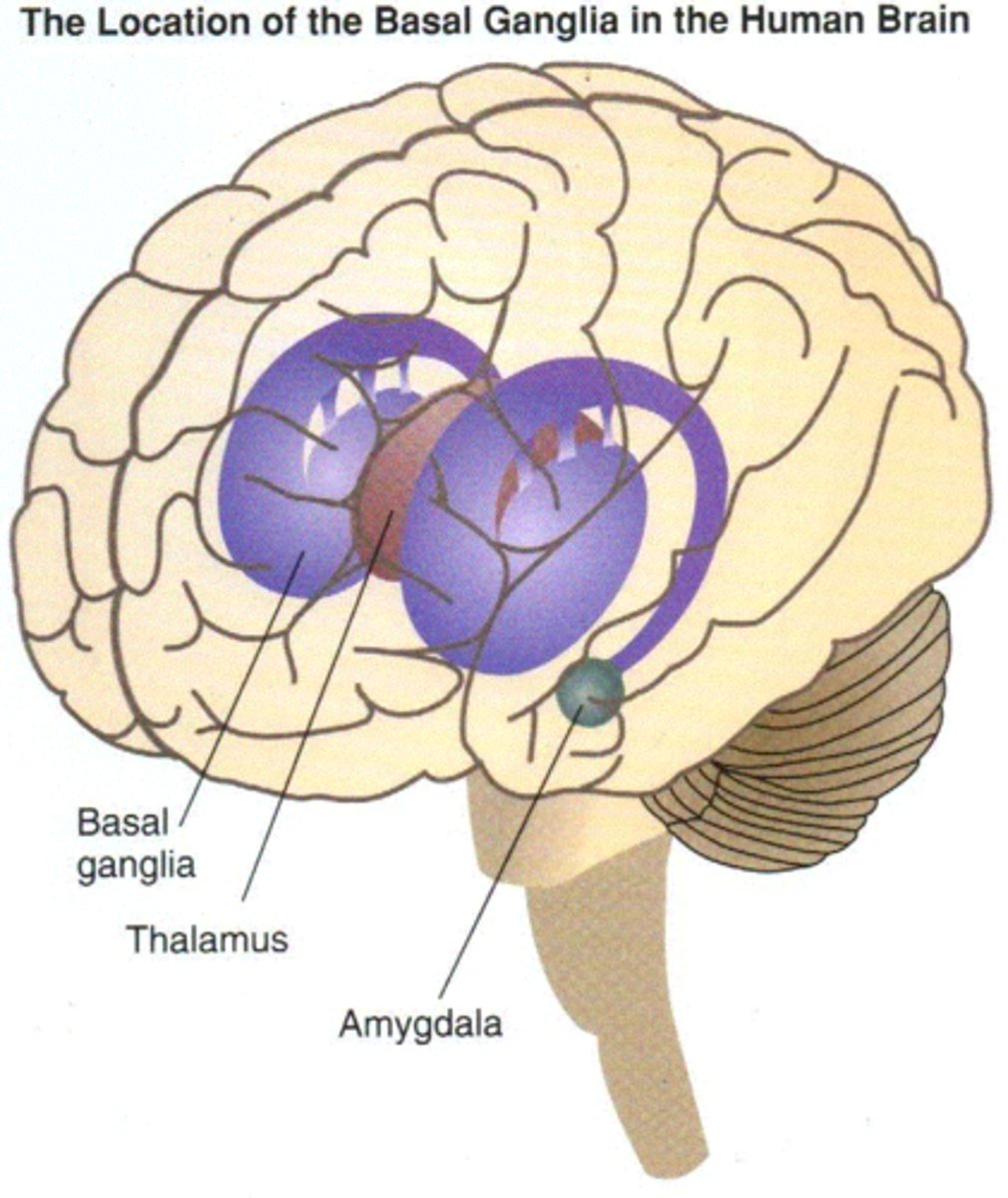
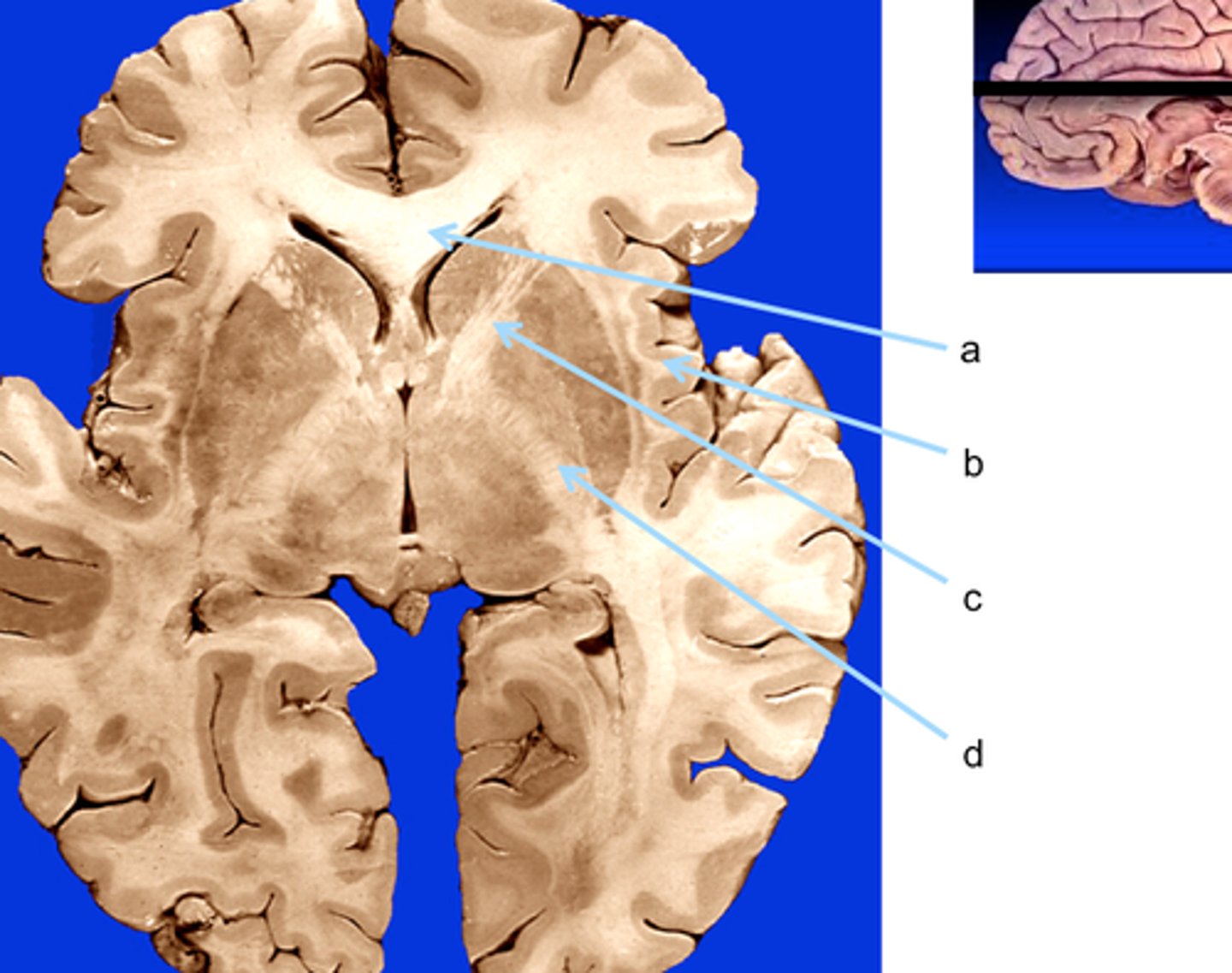
basal ganglia
set of subcortical structures that directs intentional movements
hypothalamus
-A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
-autonomic
function of hippocampal formation
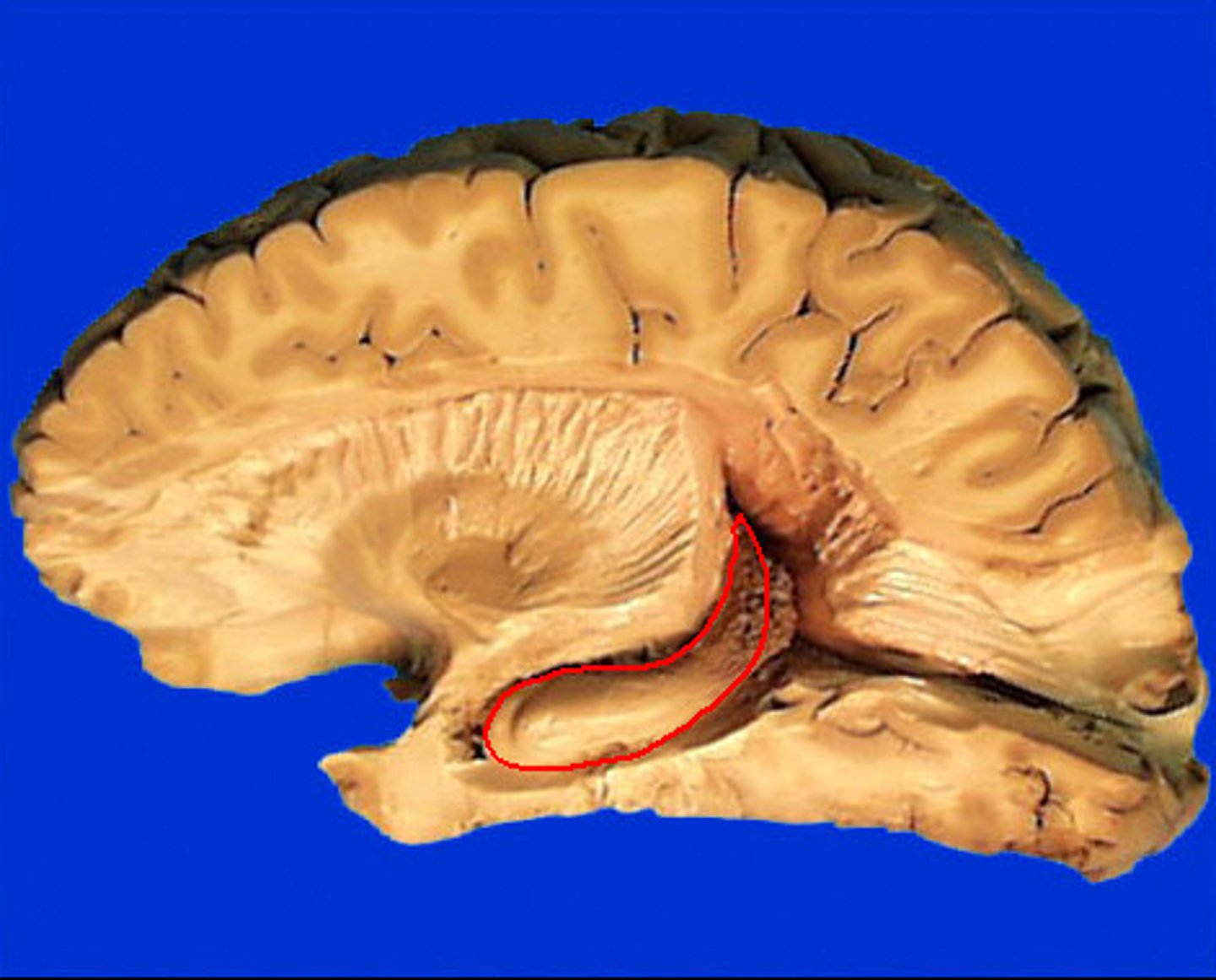
memory and learning
amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
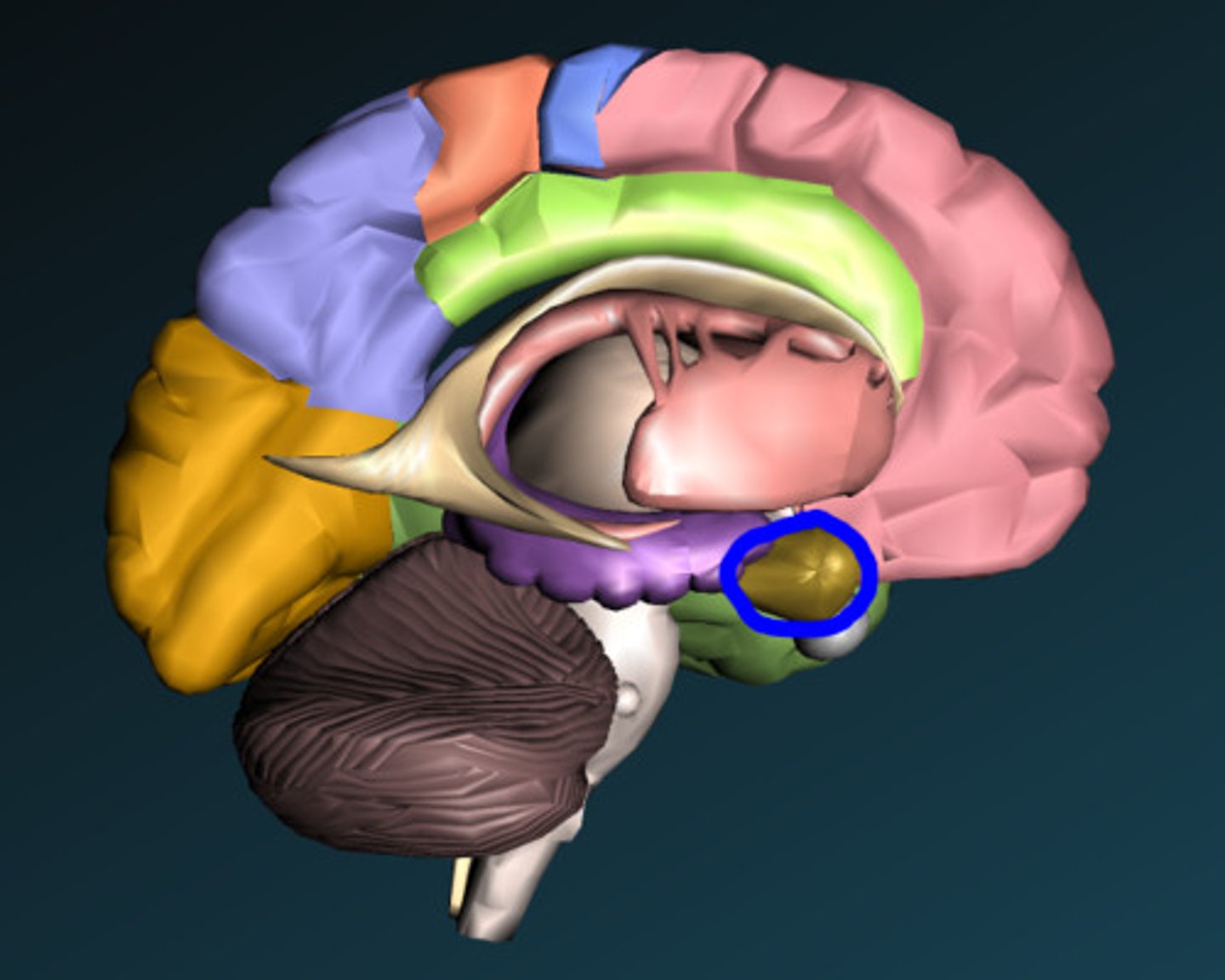
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them; cut this when there are seizures
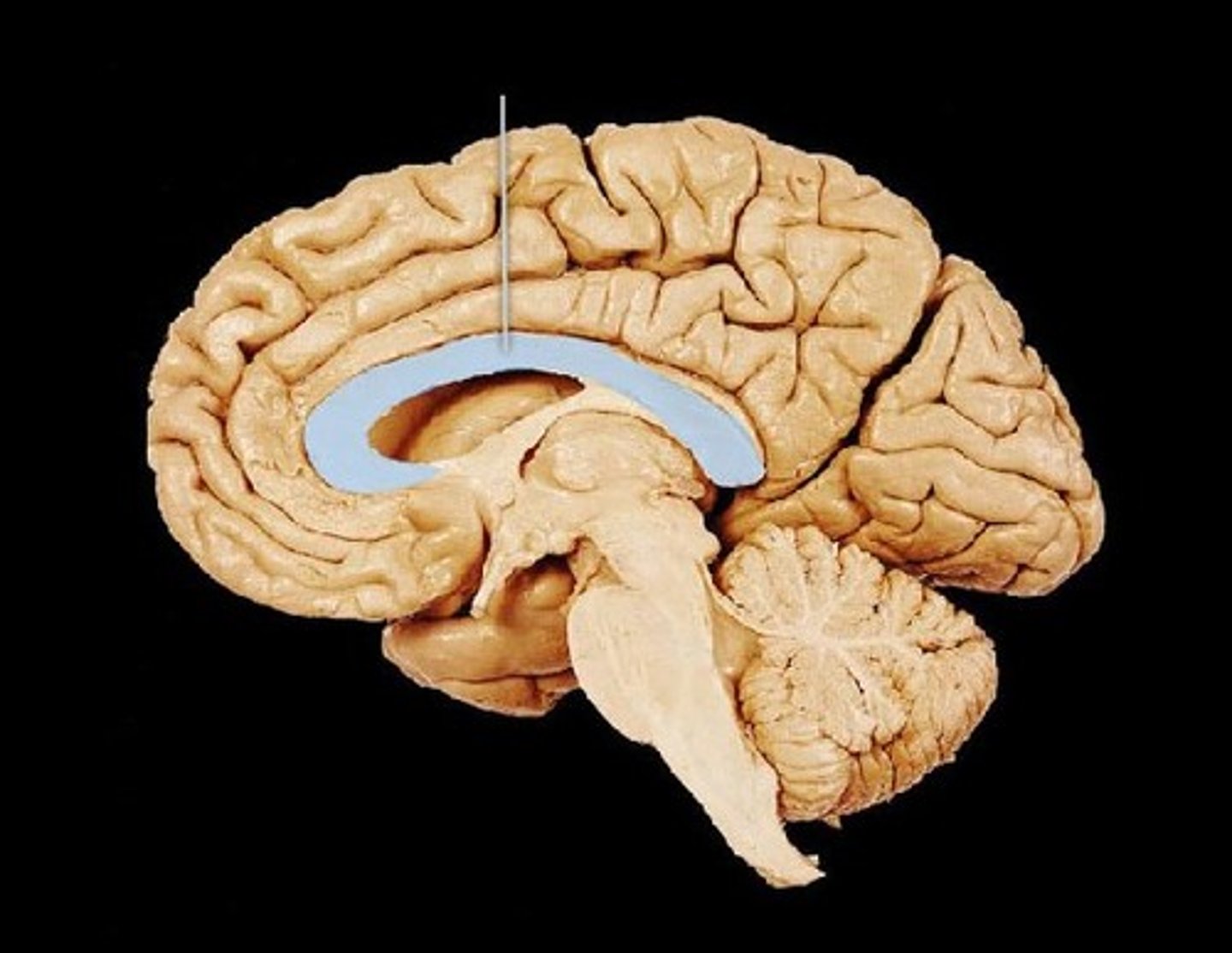
anterior commissure
bundle of axons that connects 2 hemispheres of cortex

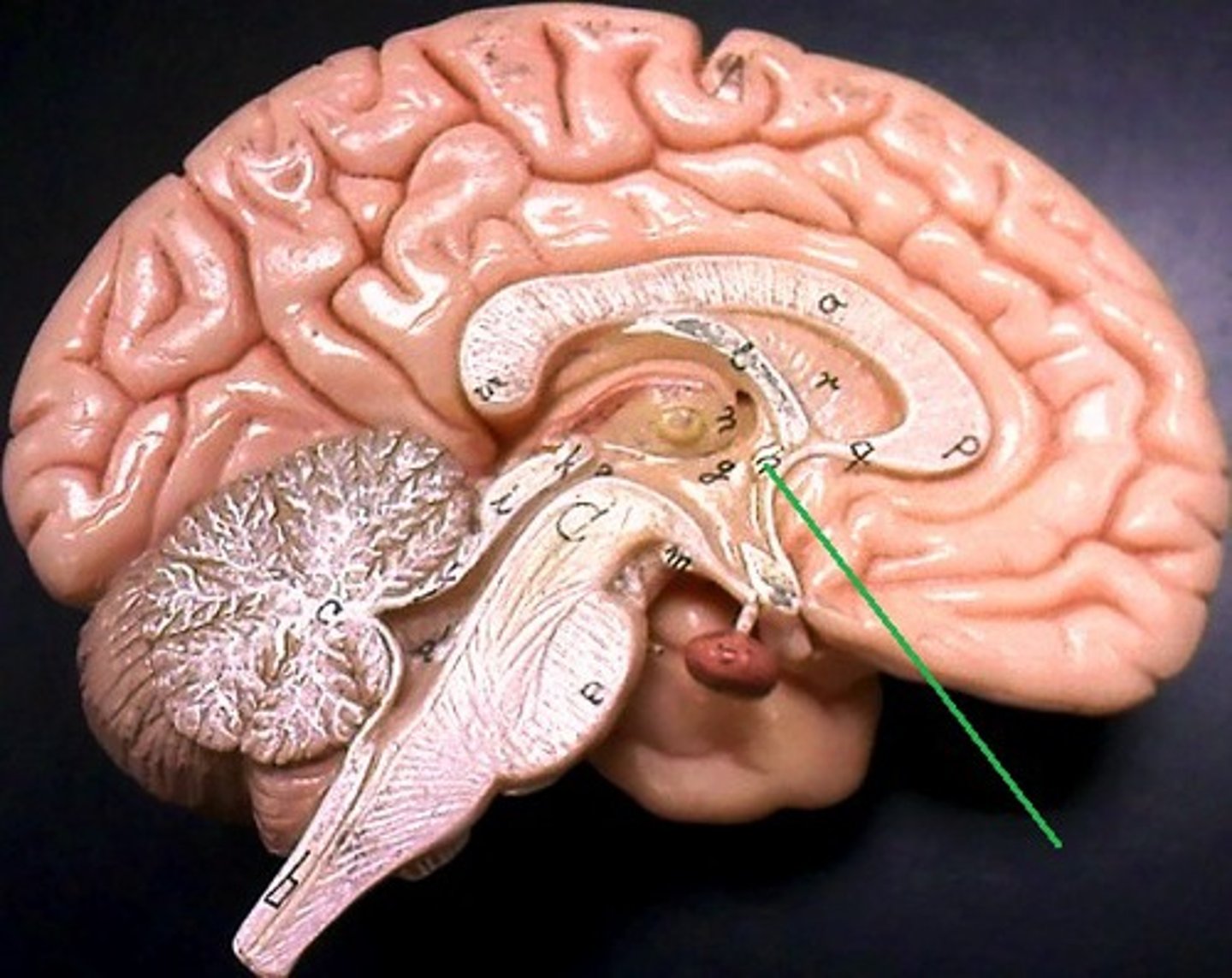
internal capsule
large collection of axons that connects telencephalon with diencephalon
corona radiata
information that connects cerebral hemispheres to the brainstem
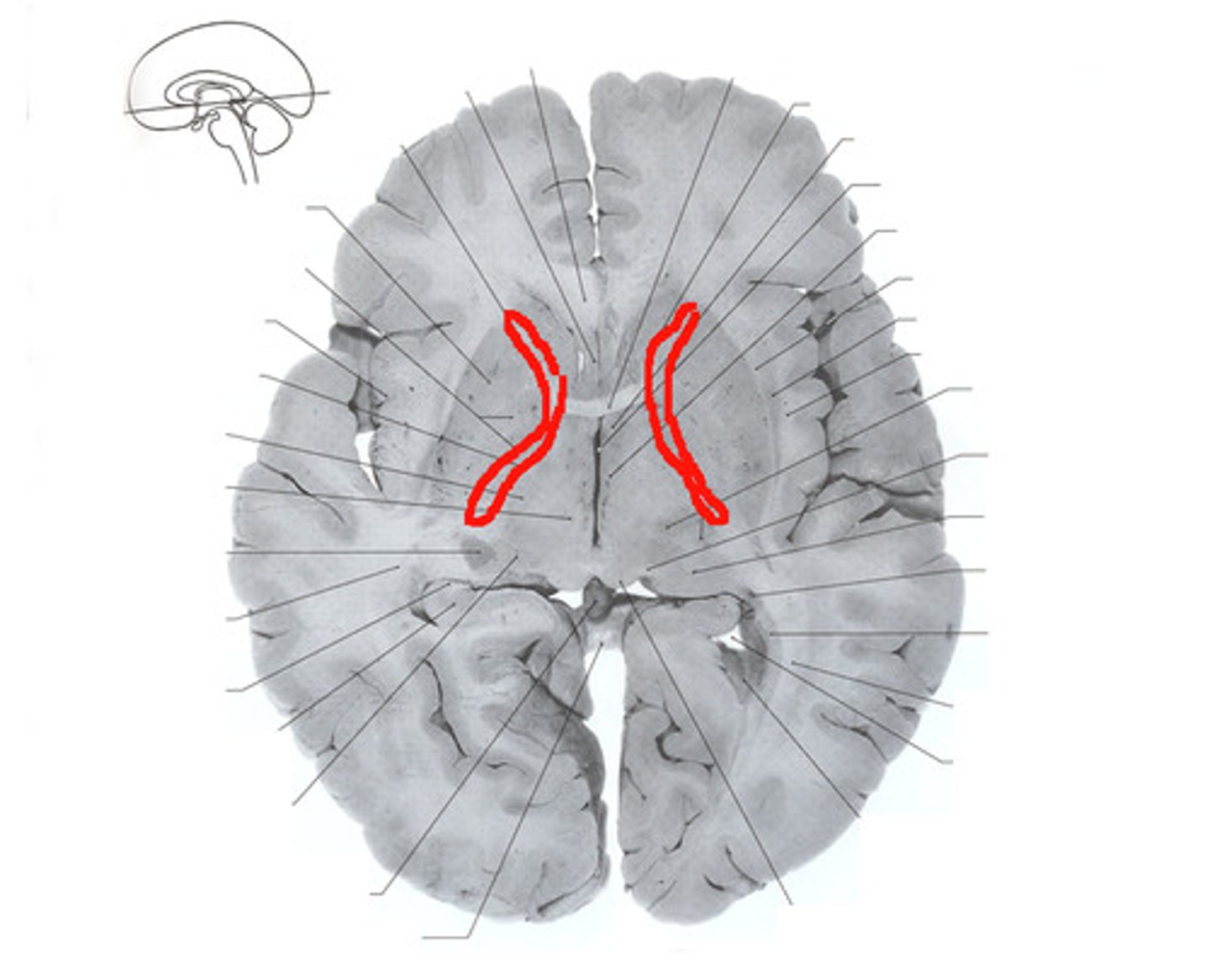
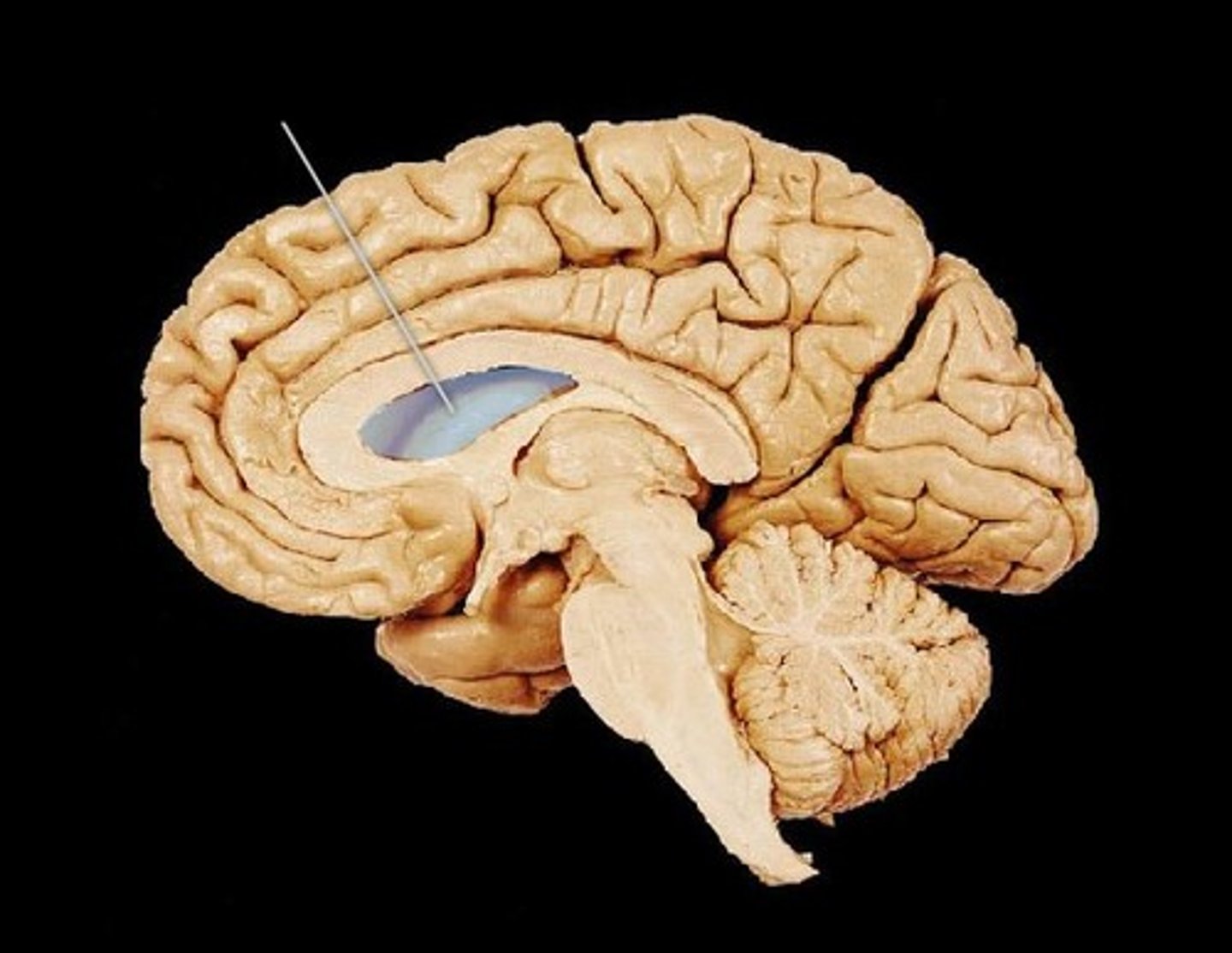
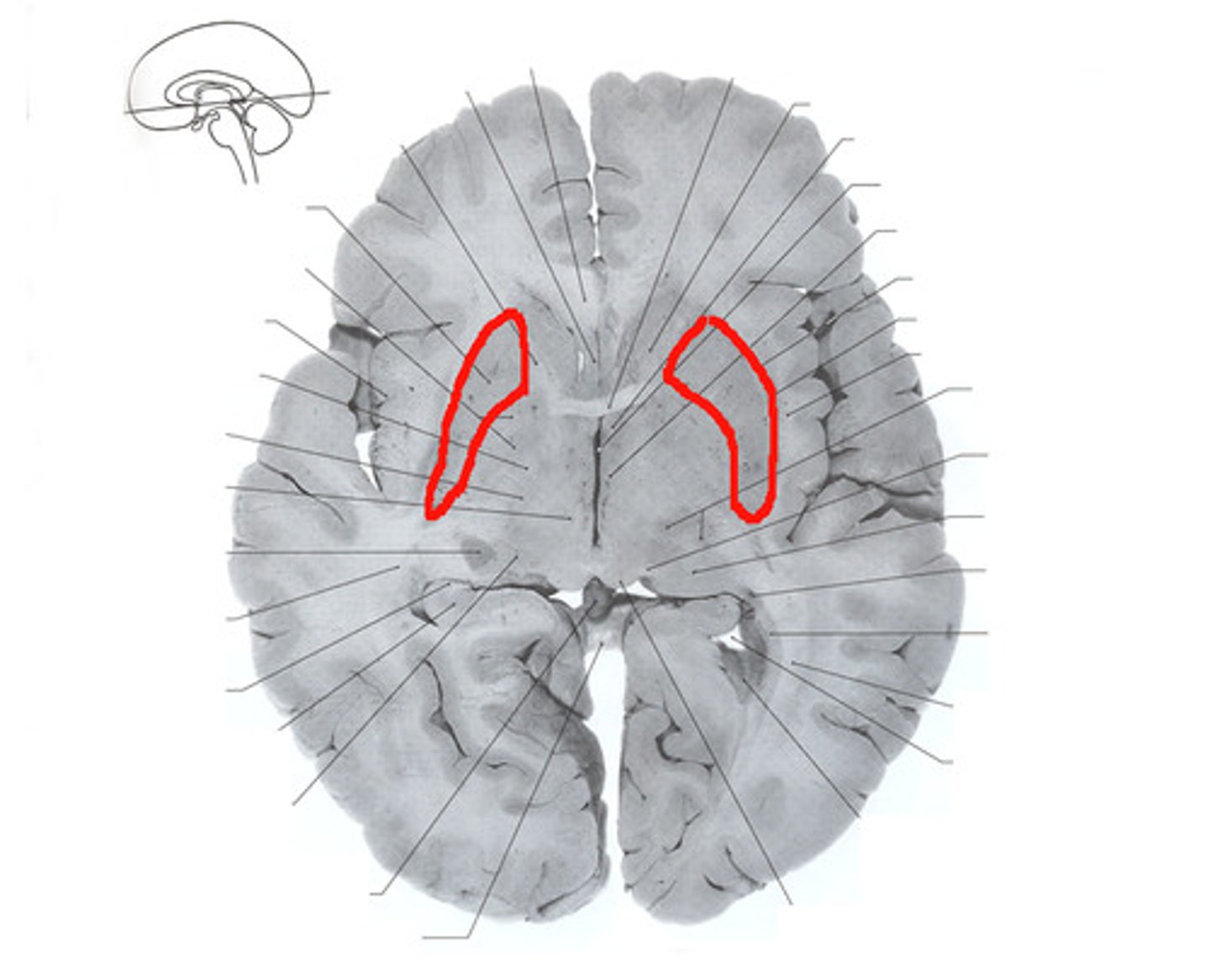
lateral ventricle
one of the two ventricles located in the center of the telencephalon
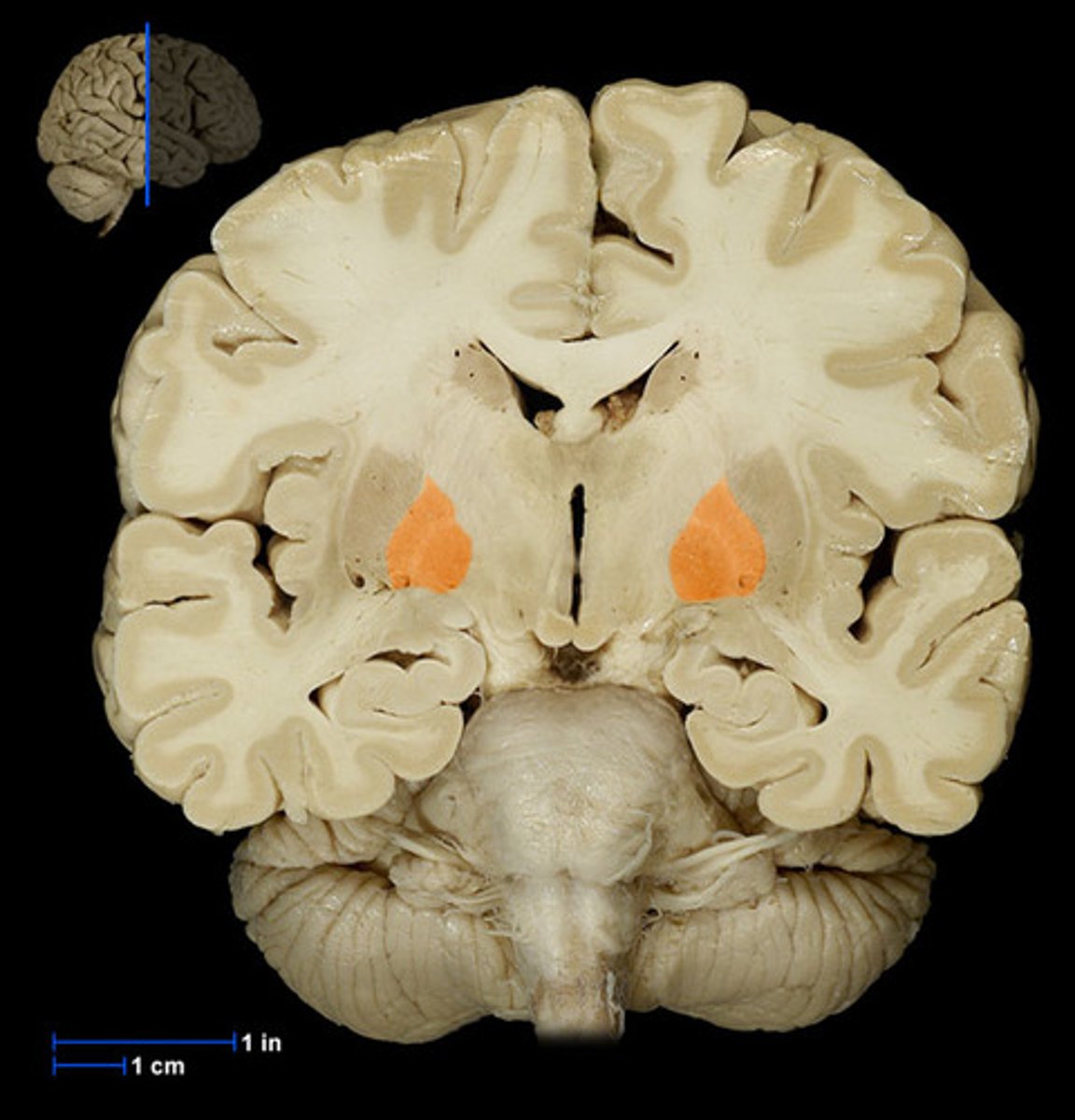
anterior limb of internal capsule
Bounded by the lentiform nucleus and head of the caudate nucleus
-Anterior thalamic radiation; corticopontine
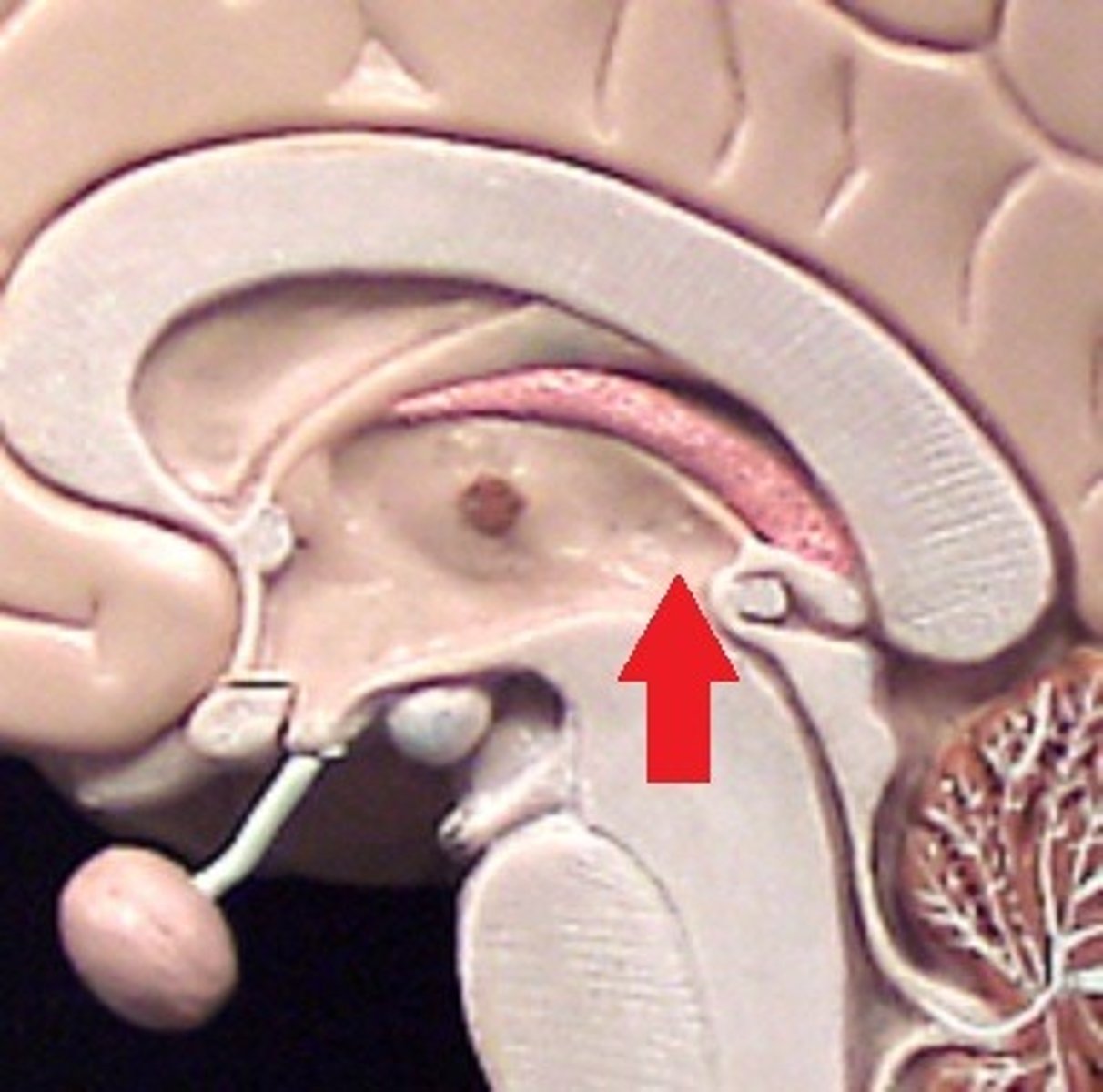
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
globus pallidus
component of the basal ganglia that connects to the thalamus which relays information to the motor areas and the prefrontal cortex
putamen
large subcortical structure, part of the basal ganglia
midbrain
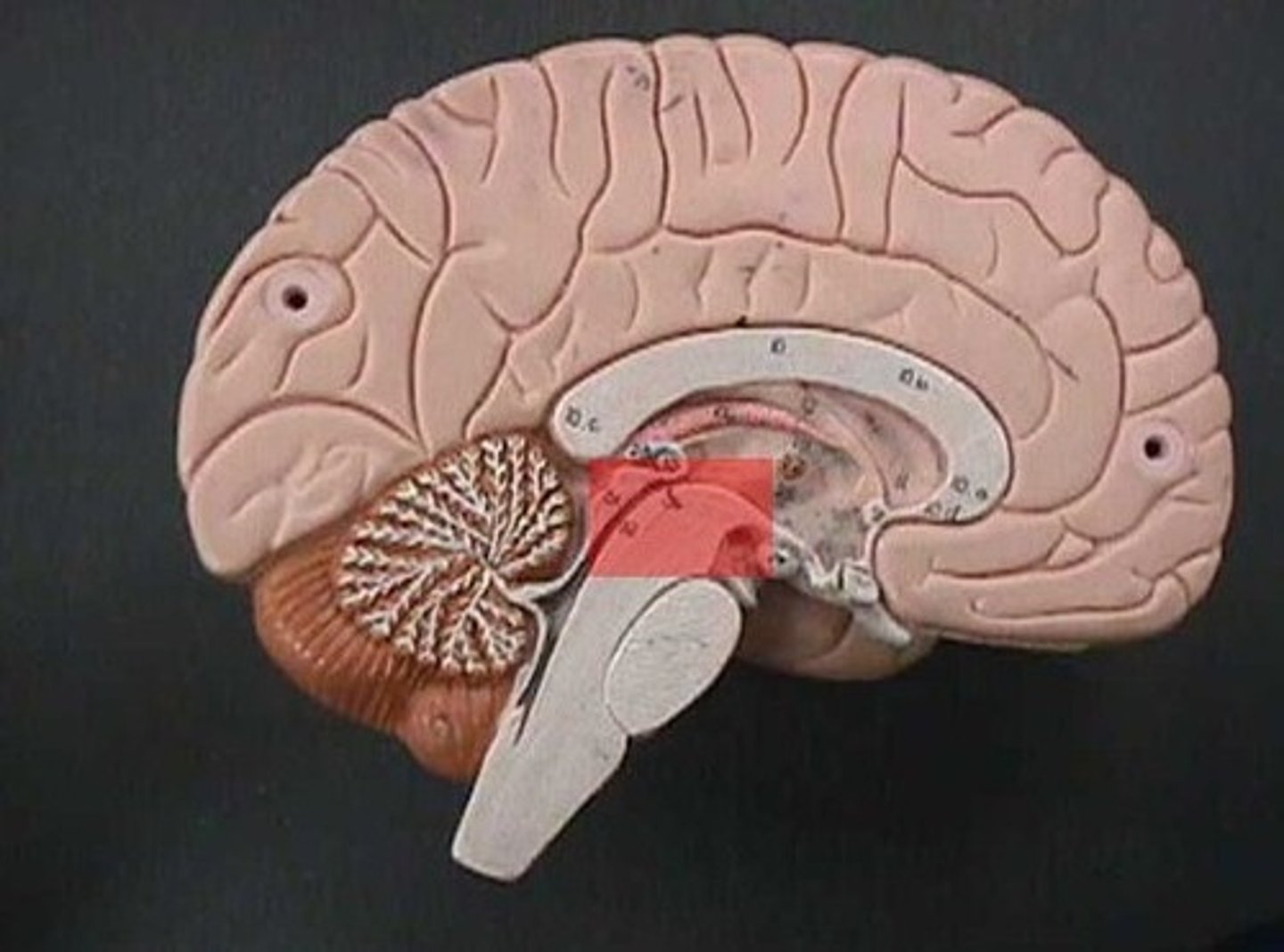
part of brain that integrates sensory info and relays it upward

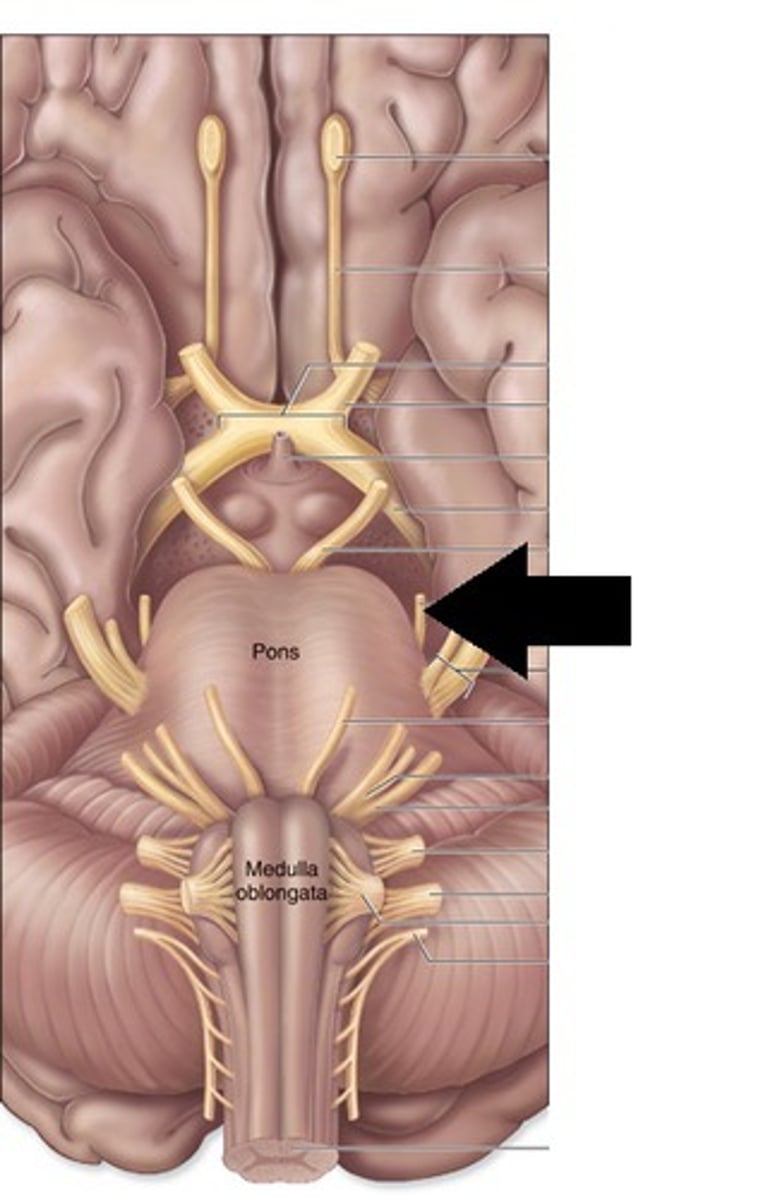
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
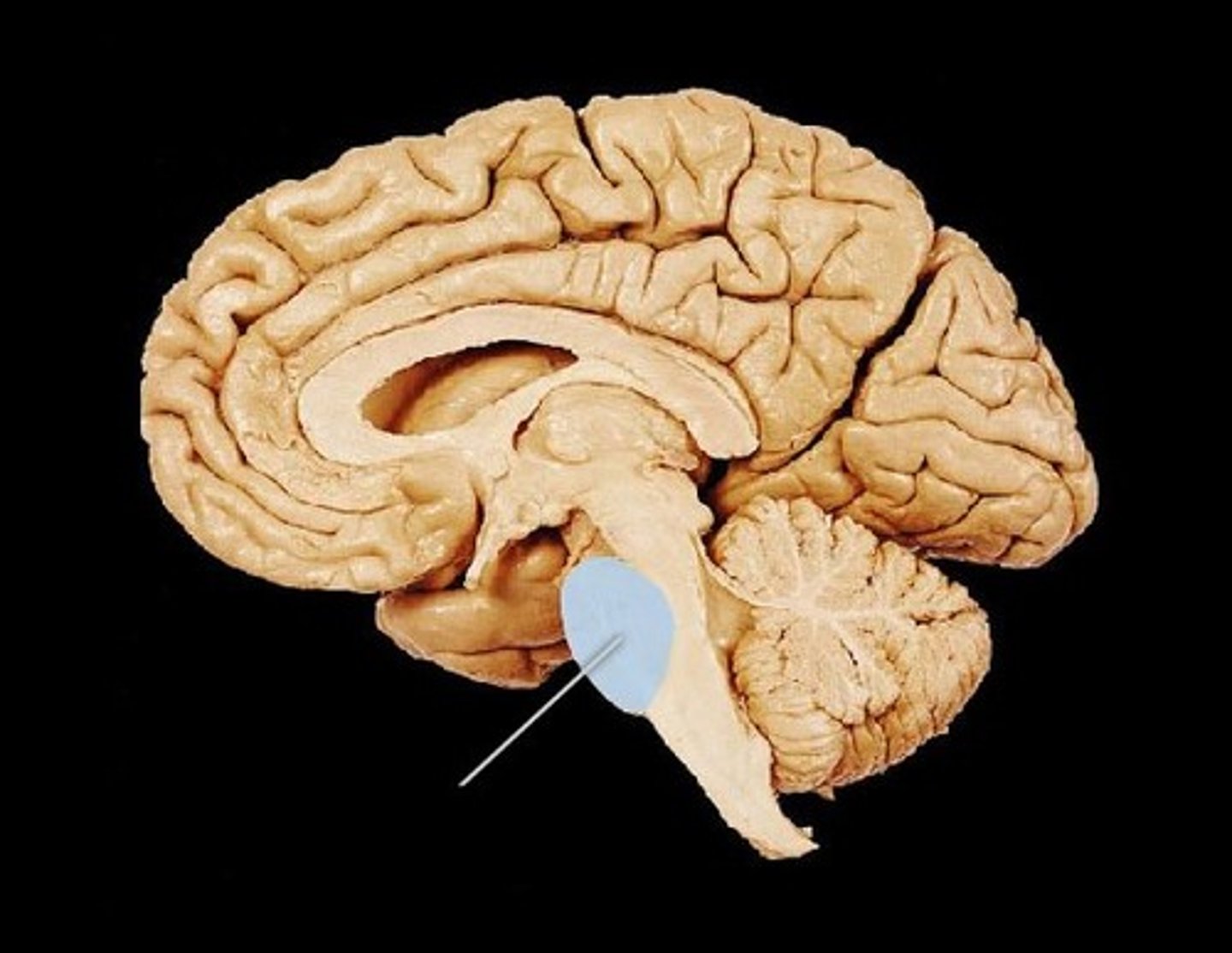
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
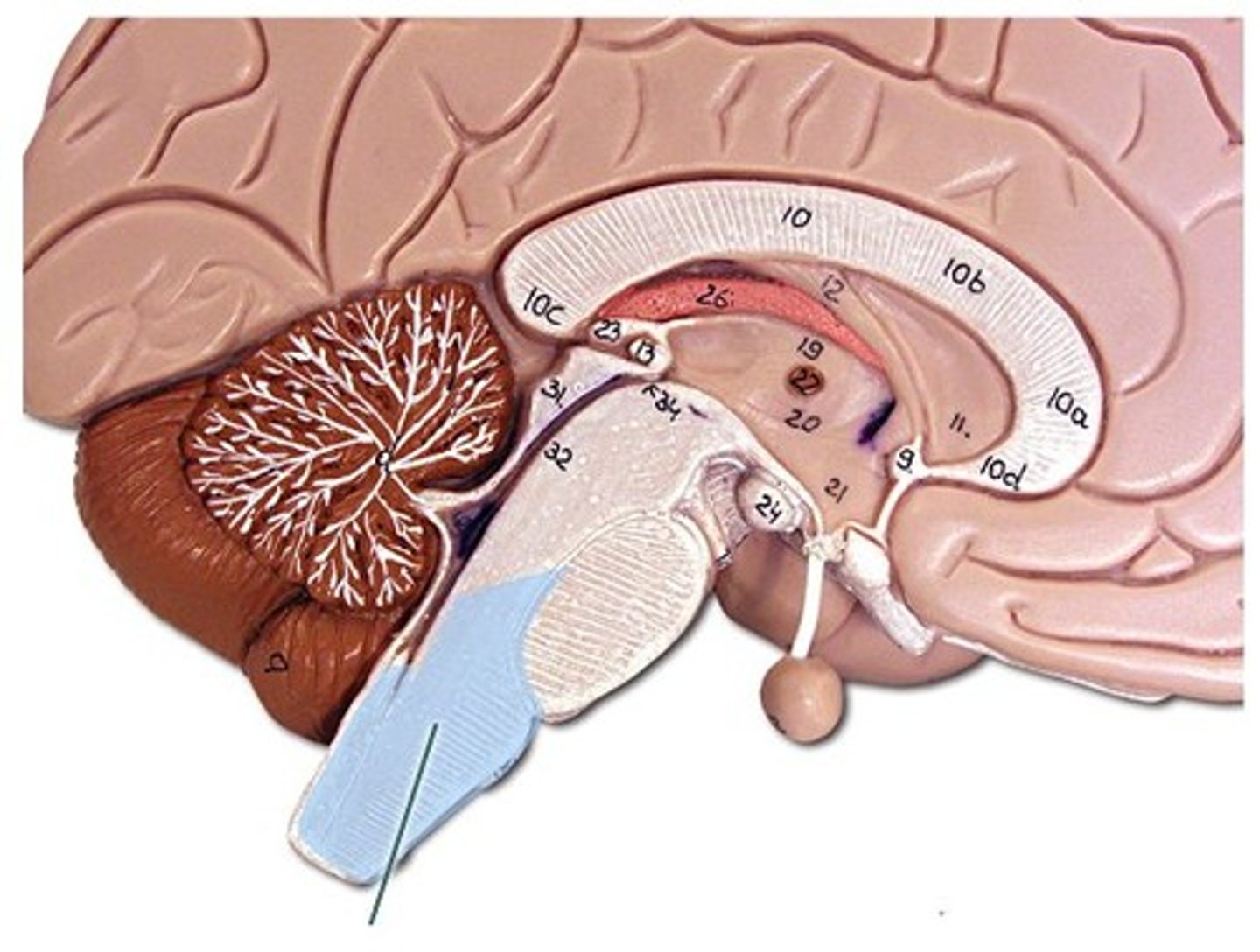
complex nuclei
hearing, respiration, arousal, posture, locomotion
CN I
Olfactory (smell); nose; sensory
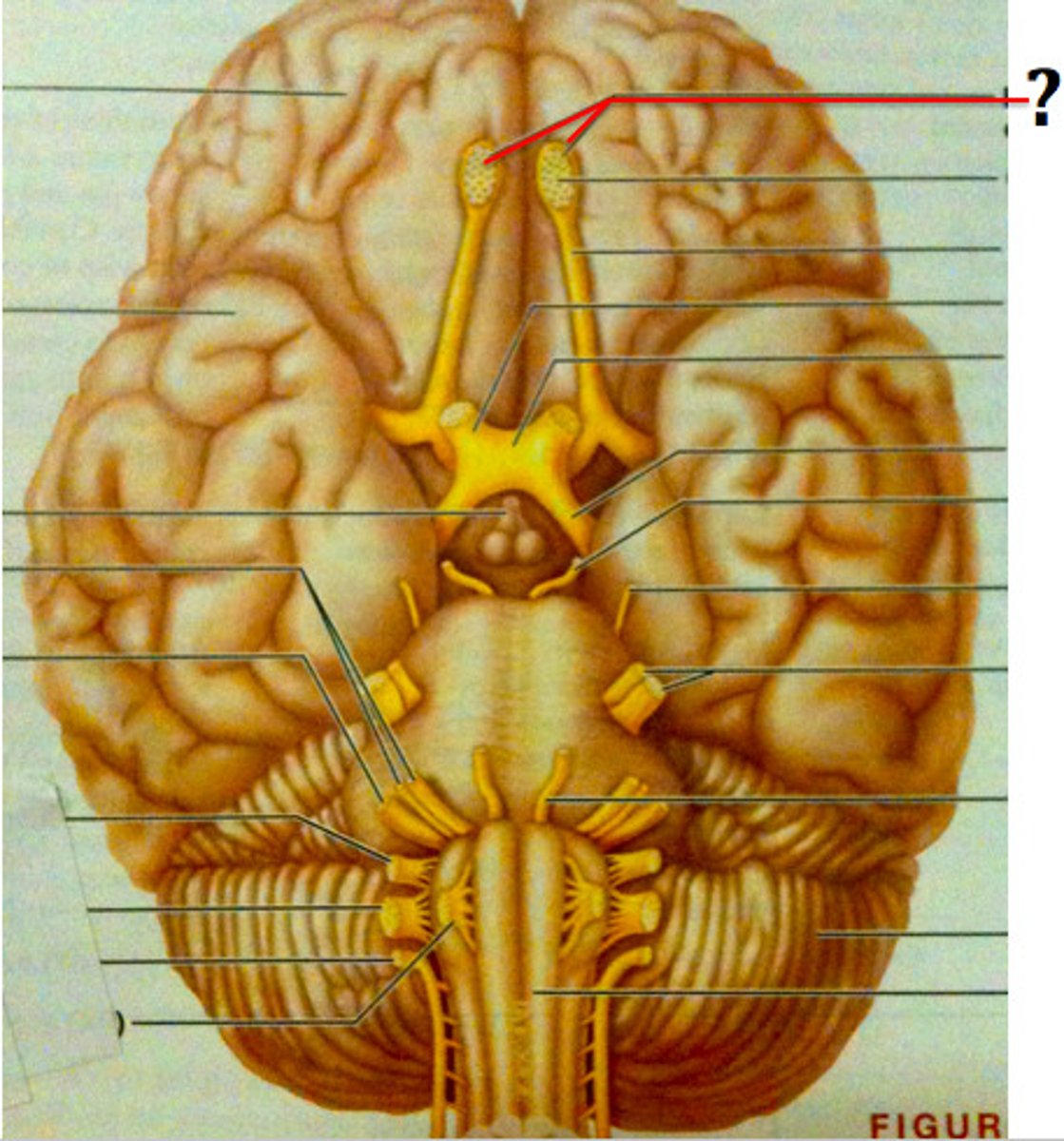
CN II
Optic; eye; sensory
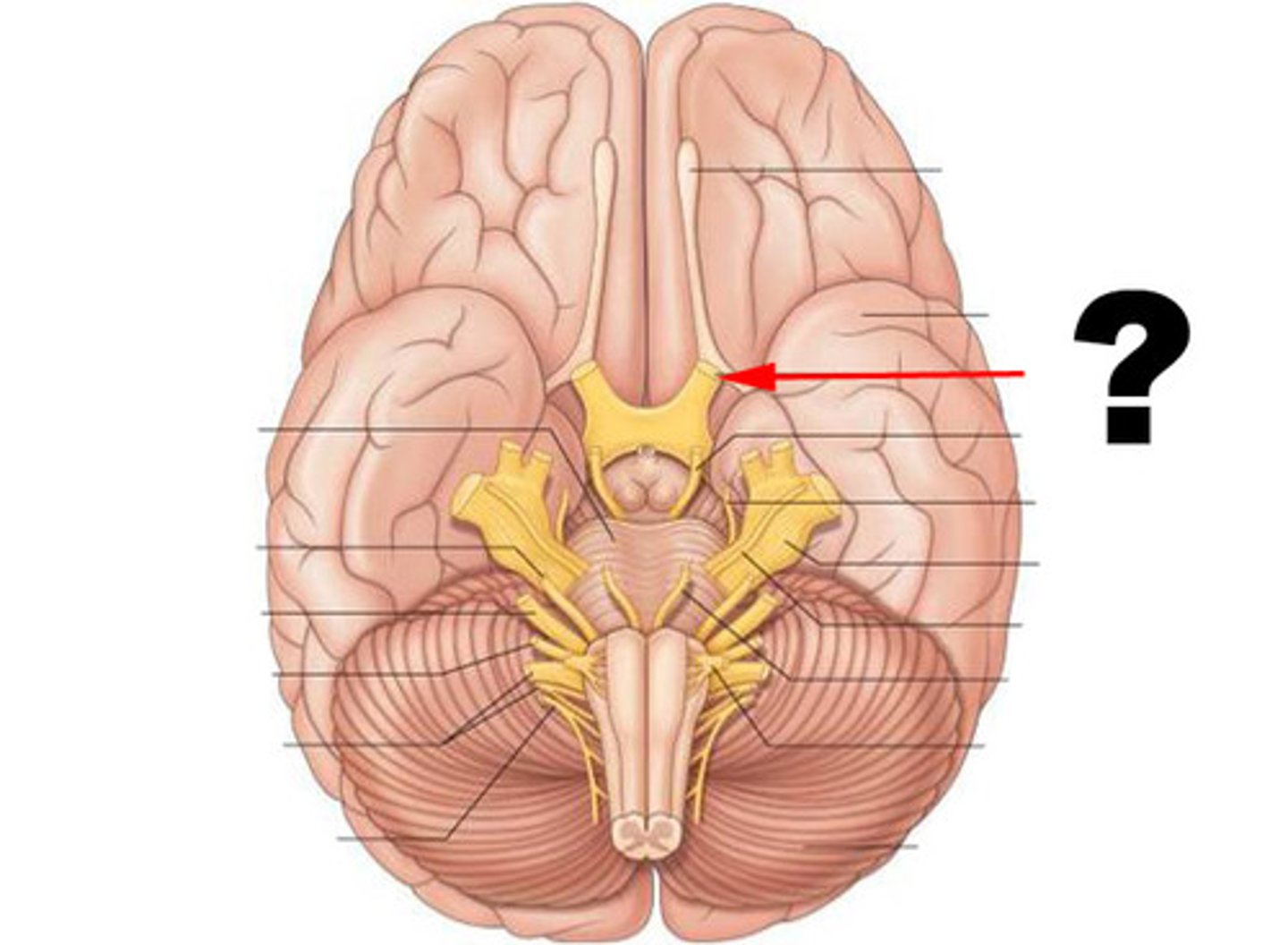
CN III
oculomotor, all eye muscles except those supplied by IV and VI, motor
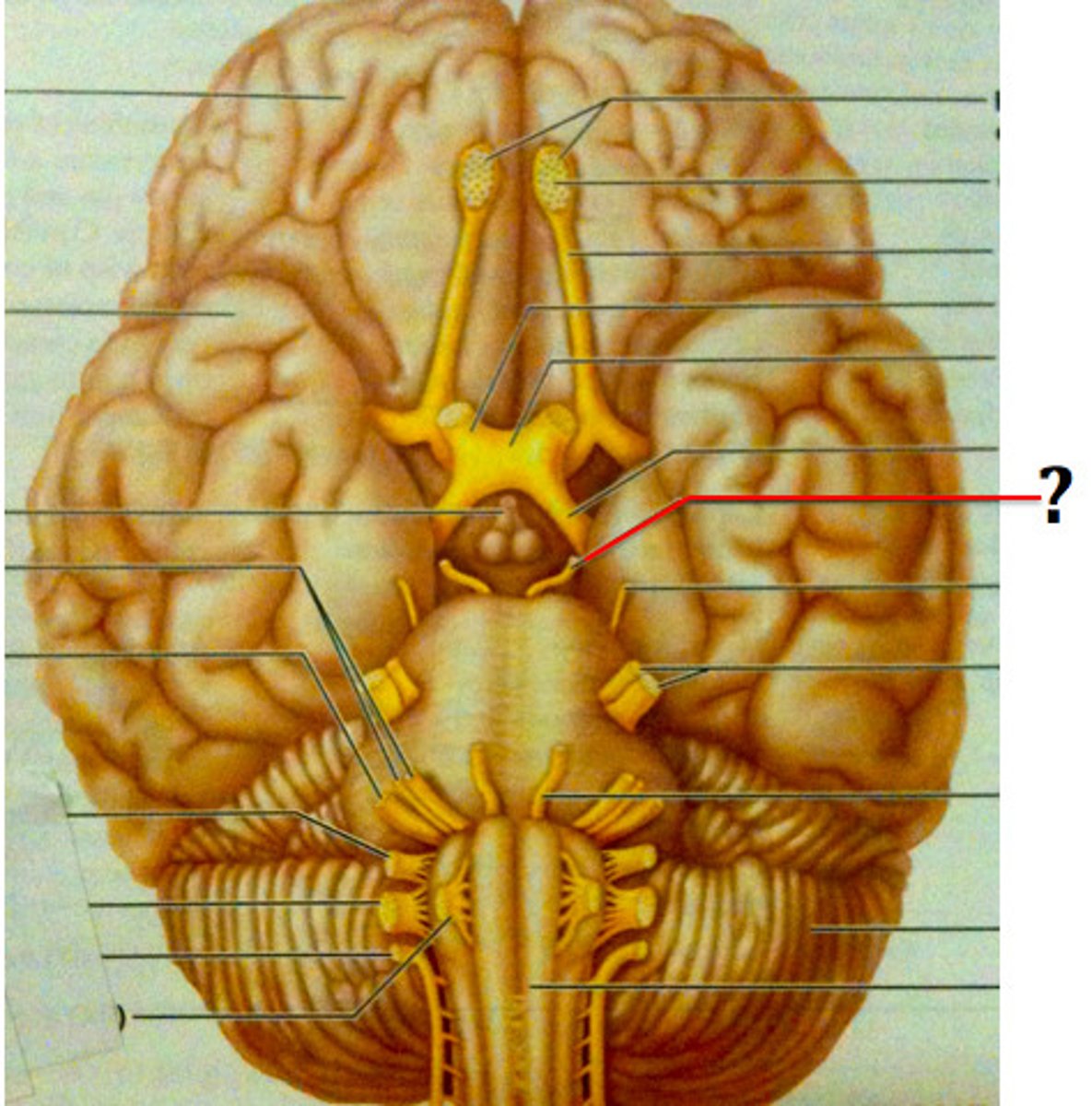
CN IV
Trochlear (motor); superior oblique muscle; motor
CN V
trigeminal
Sensory: faces, sinuses, teeth, etc.
Motor: muscles of mastication
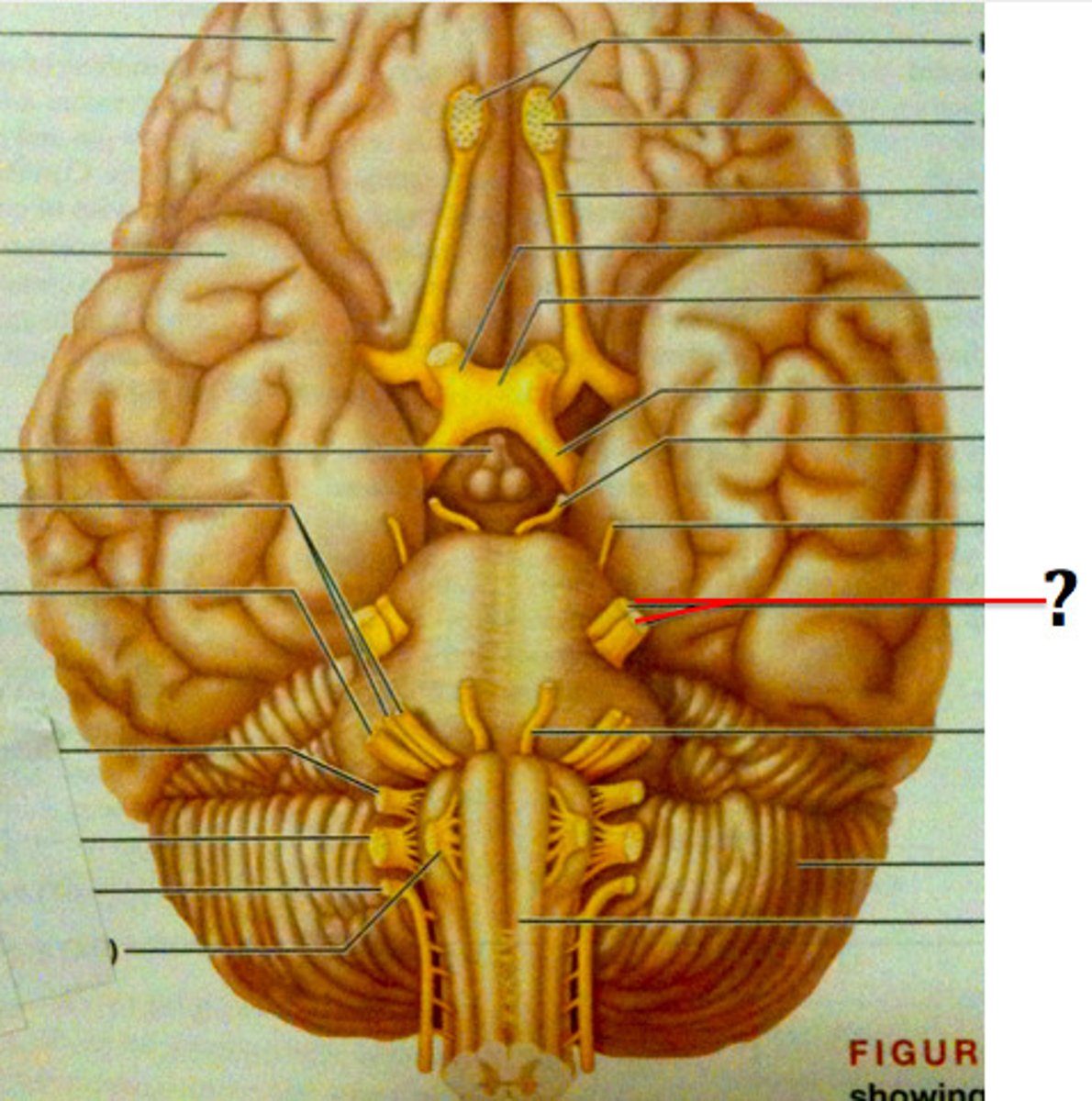
CN VI
Abducens
Motor: external rectus muscle
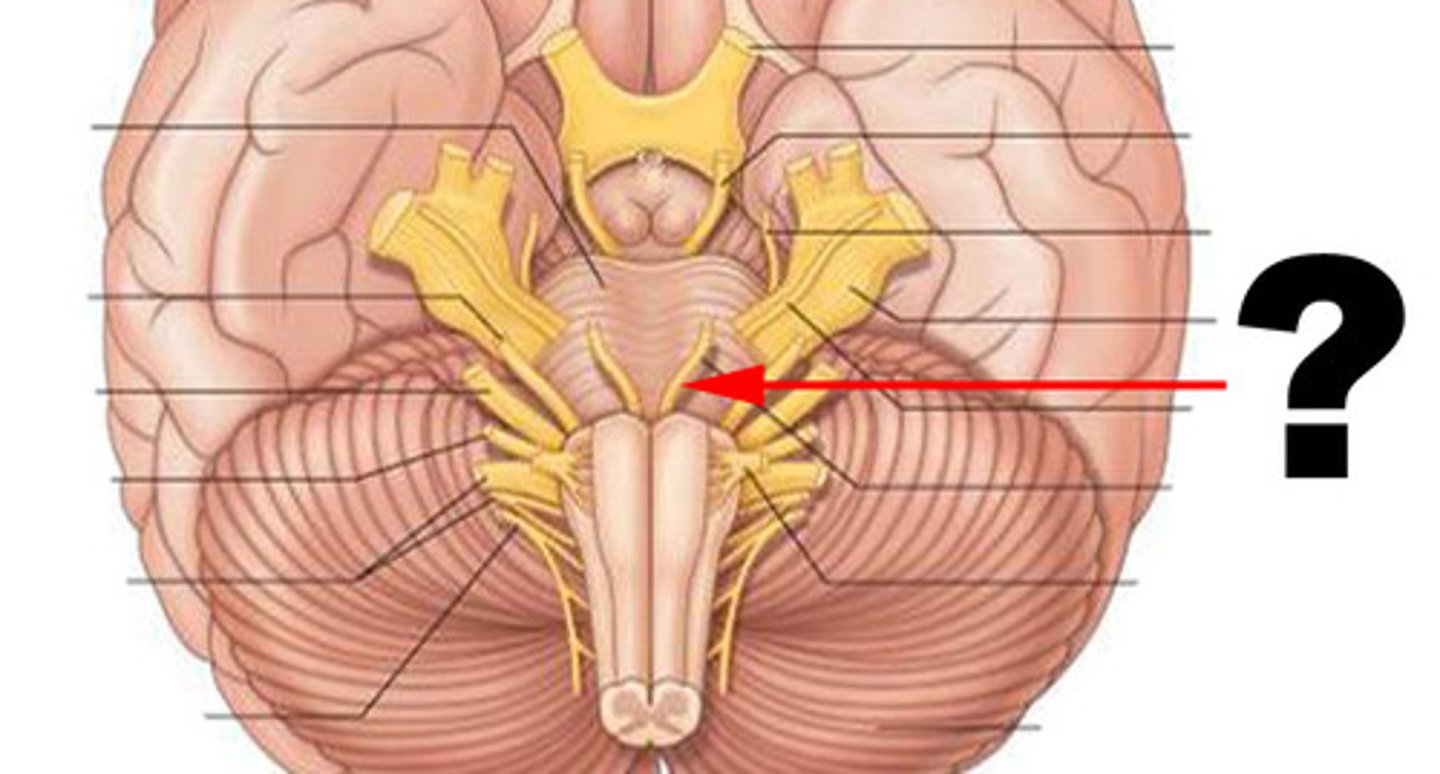
CN VII
facial nerve; motor: muscles of the face
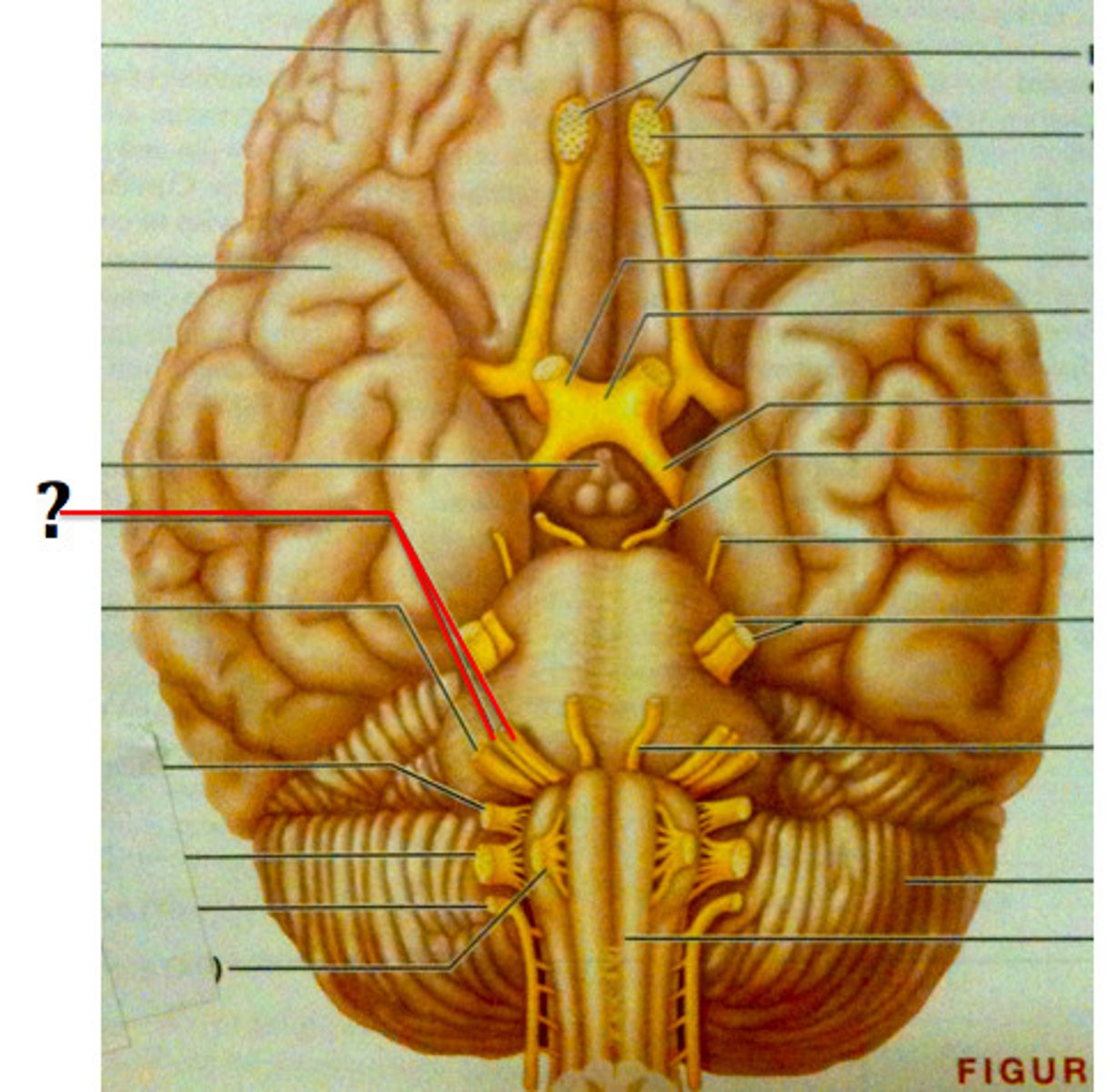
CN VIII
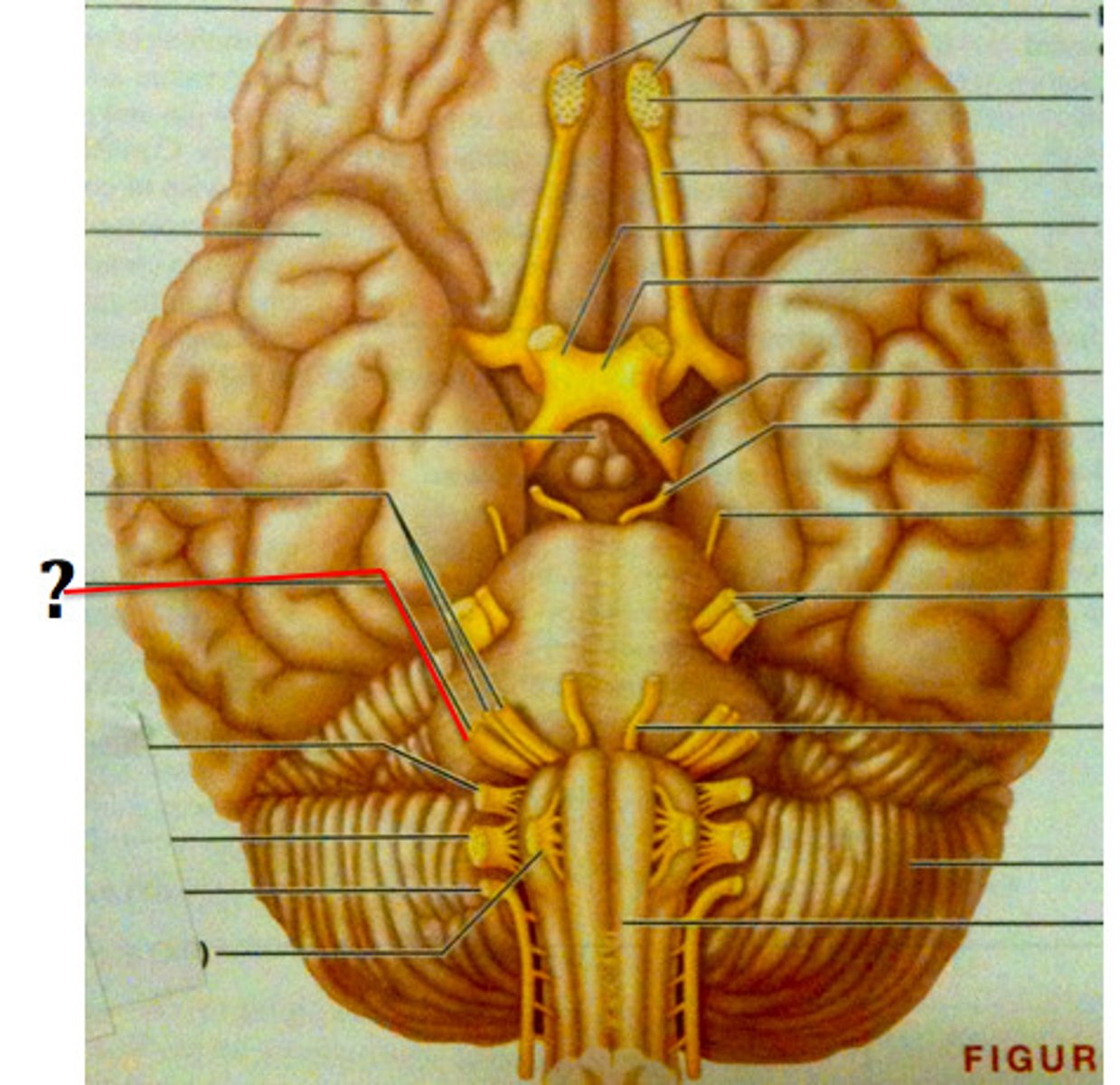
vestibulocochlear (hearing and balance), sensory: inner ear

CN IX
-glossopharyngeal
-assess mouth for taste
-assess mouth for movement of soft palate and the gag reflex
-assess swallowing and speech
-motor: pharyngeal musculature
-sensory: posterior part of tongue, tonsil, pharynx
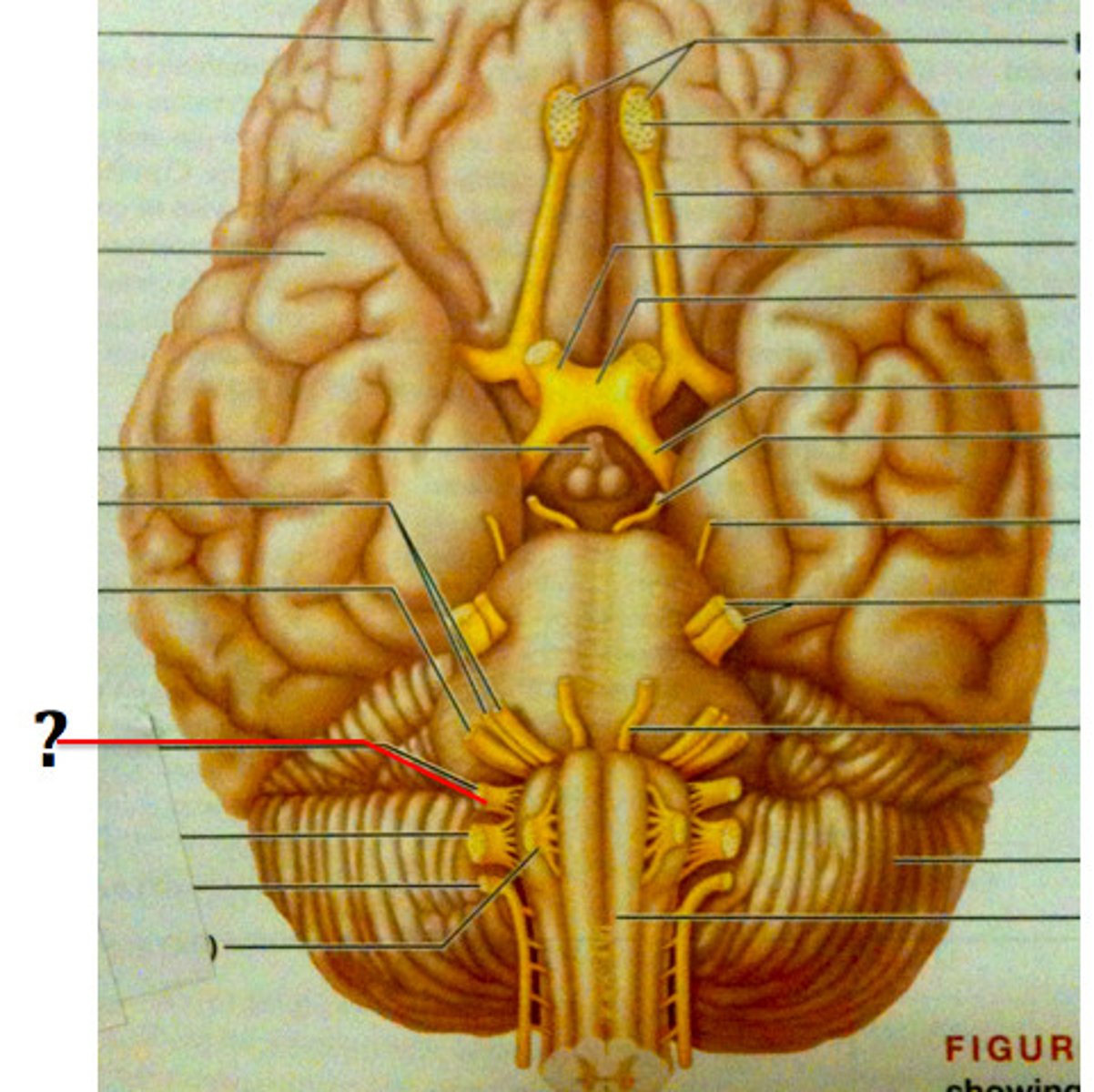
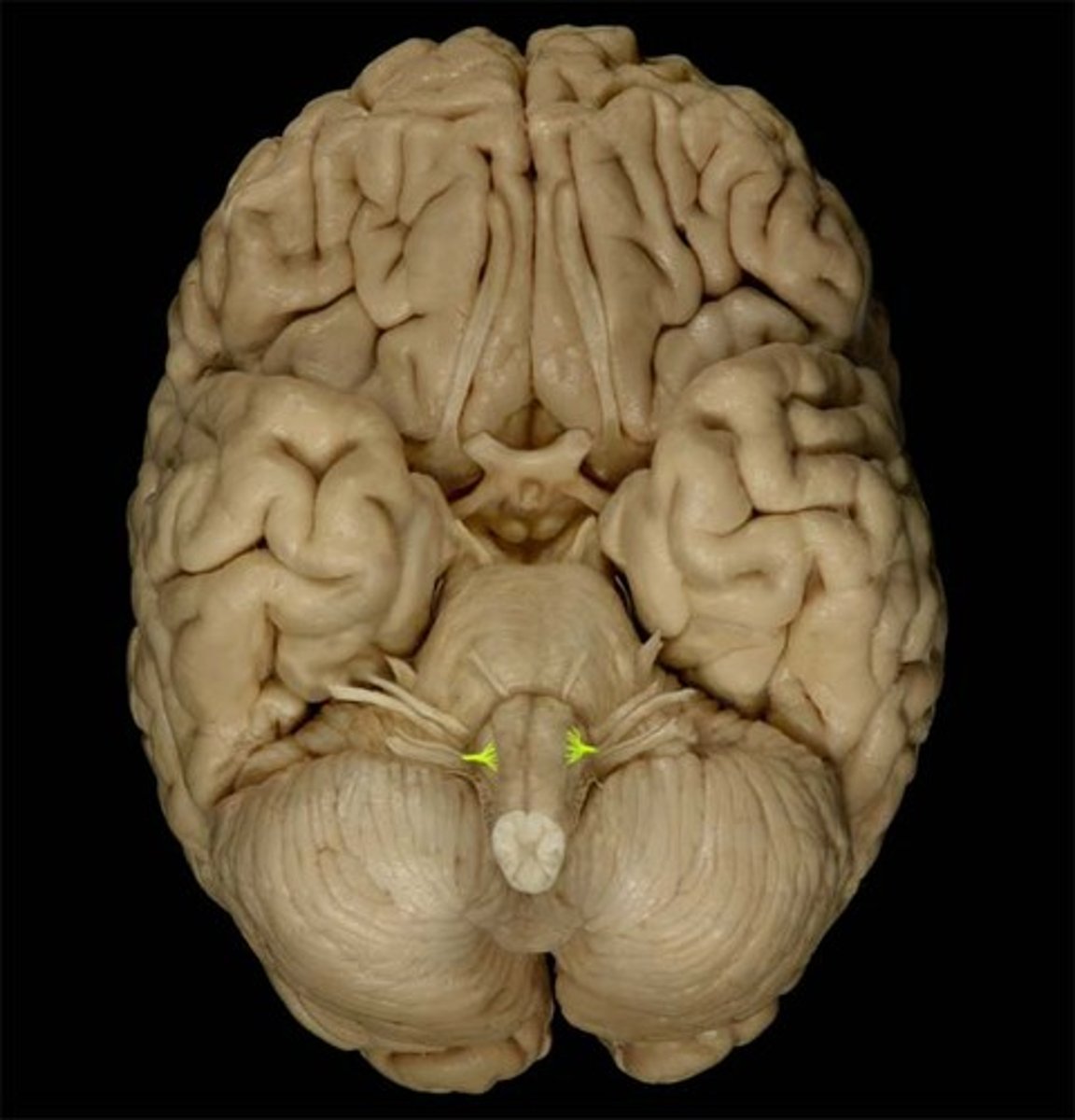
CN X
-vagus
-assess mouth for movement of soft palate and the gag reflex
-assess swallowing and speech
-motor: heart, lungs, bronchi gastrointestinal tract
-sensory: heart, lungs, bronchi, trachea, larynx, pharynx, gastrointestinal tract, external ear
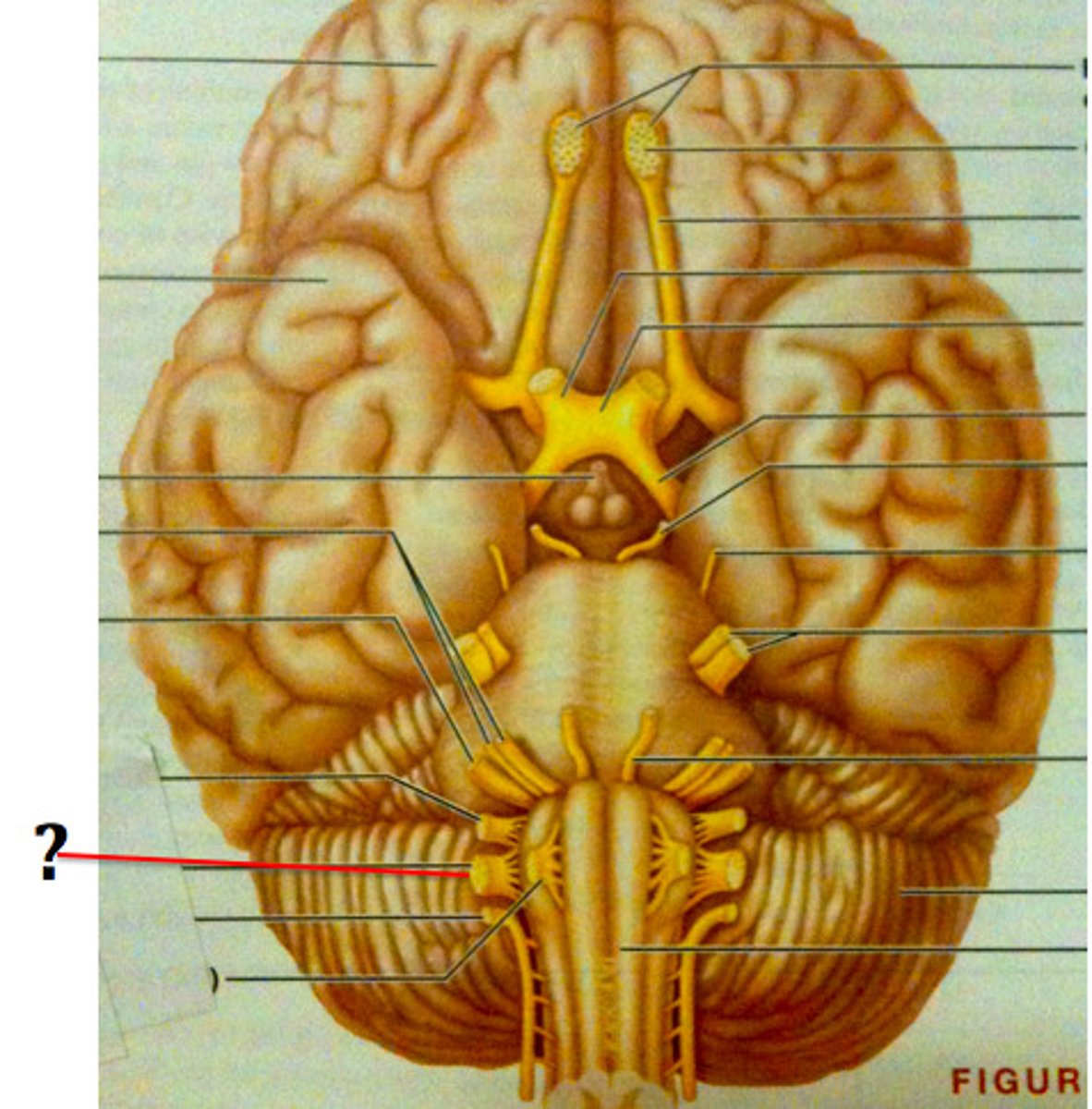
CN XI
accessory; motor: sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
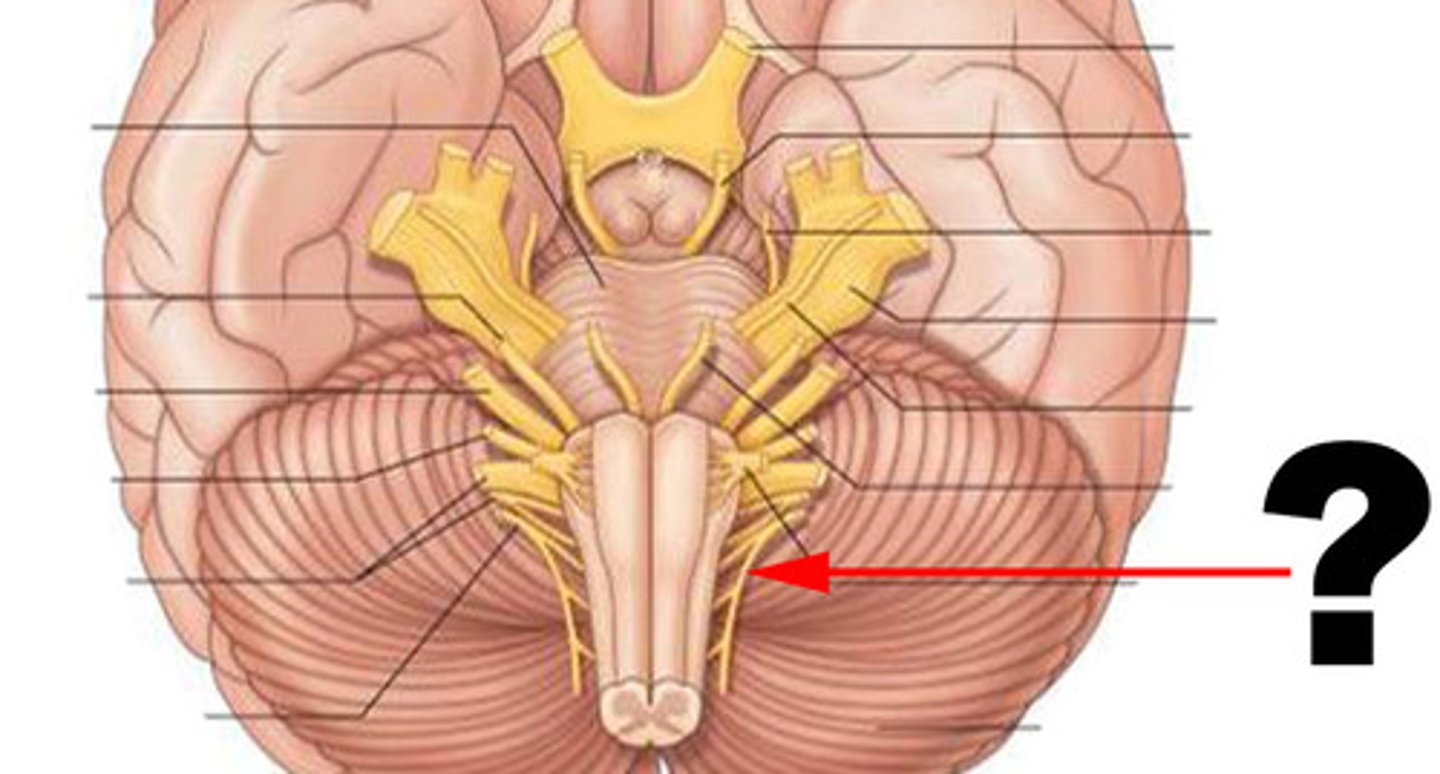
CN XII
Hypoglossal (tongue movement)
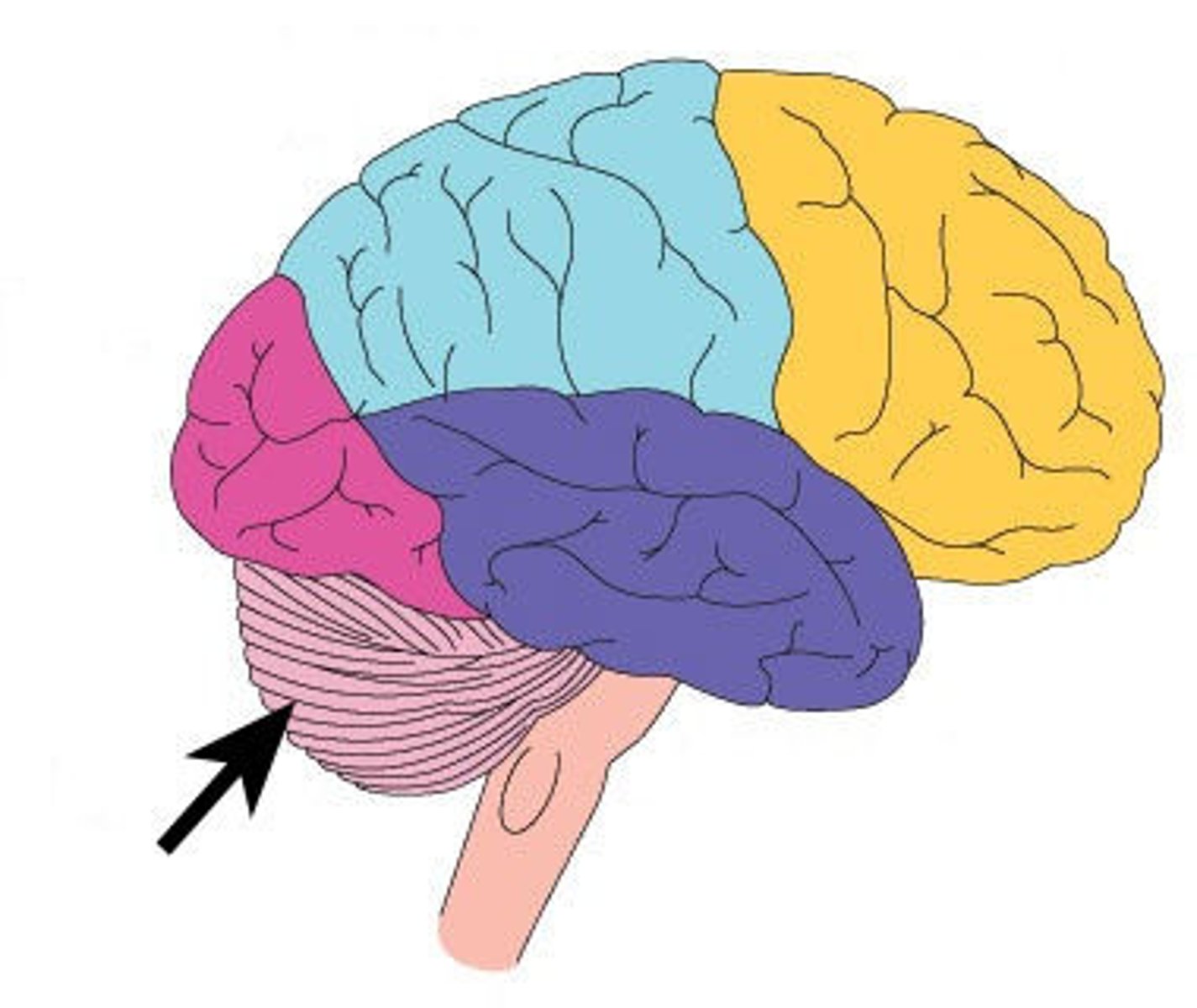
cerebellum
-posterior and inferior to the cerebrum
-"Little brain"
-connects the rest of the nervous system through the brainstem
-has its own deep cerebellar nuclei, white matter, cortex
-motor function (coordination)
-motor learning (movement adaptation)
meninges
3 protective membranes that surround brain and spinal cord
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
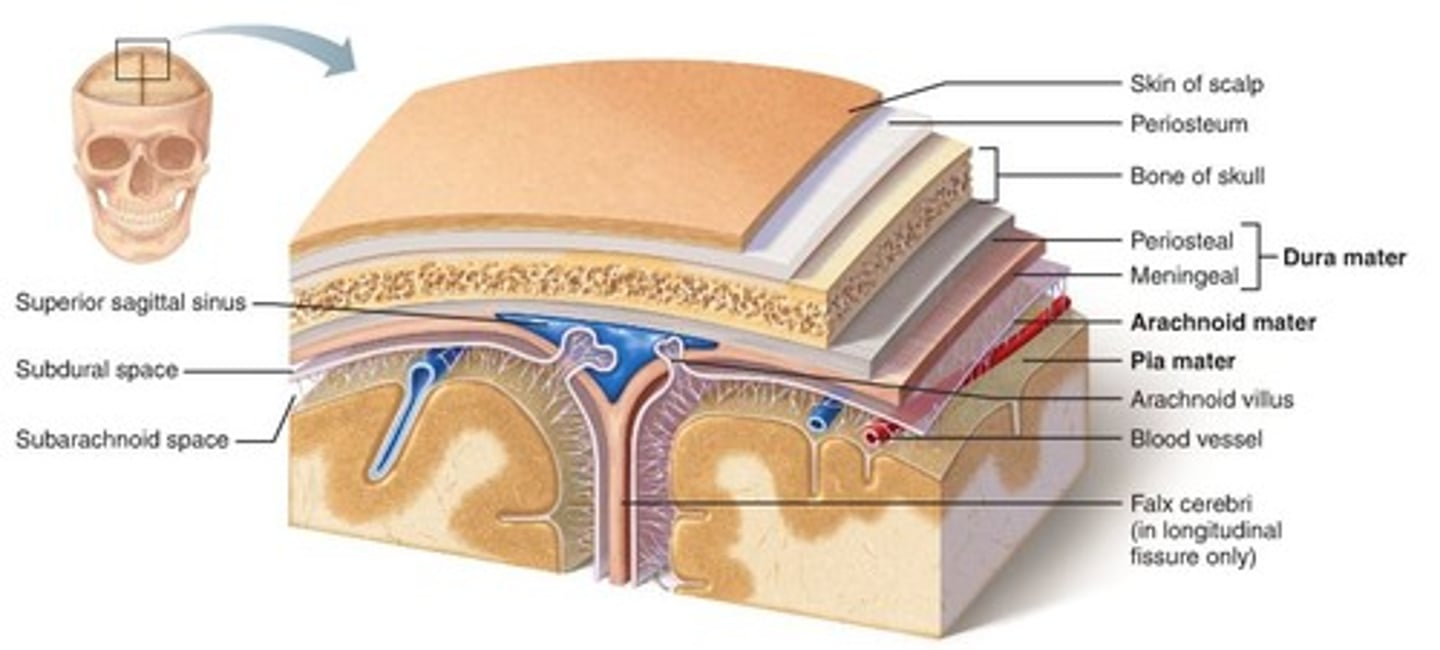
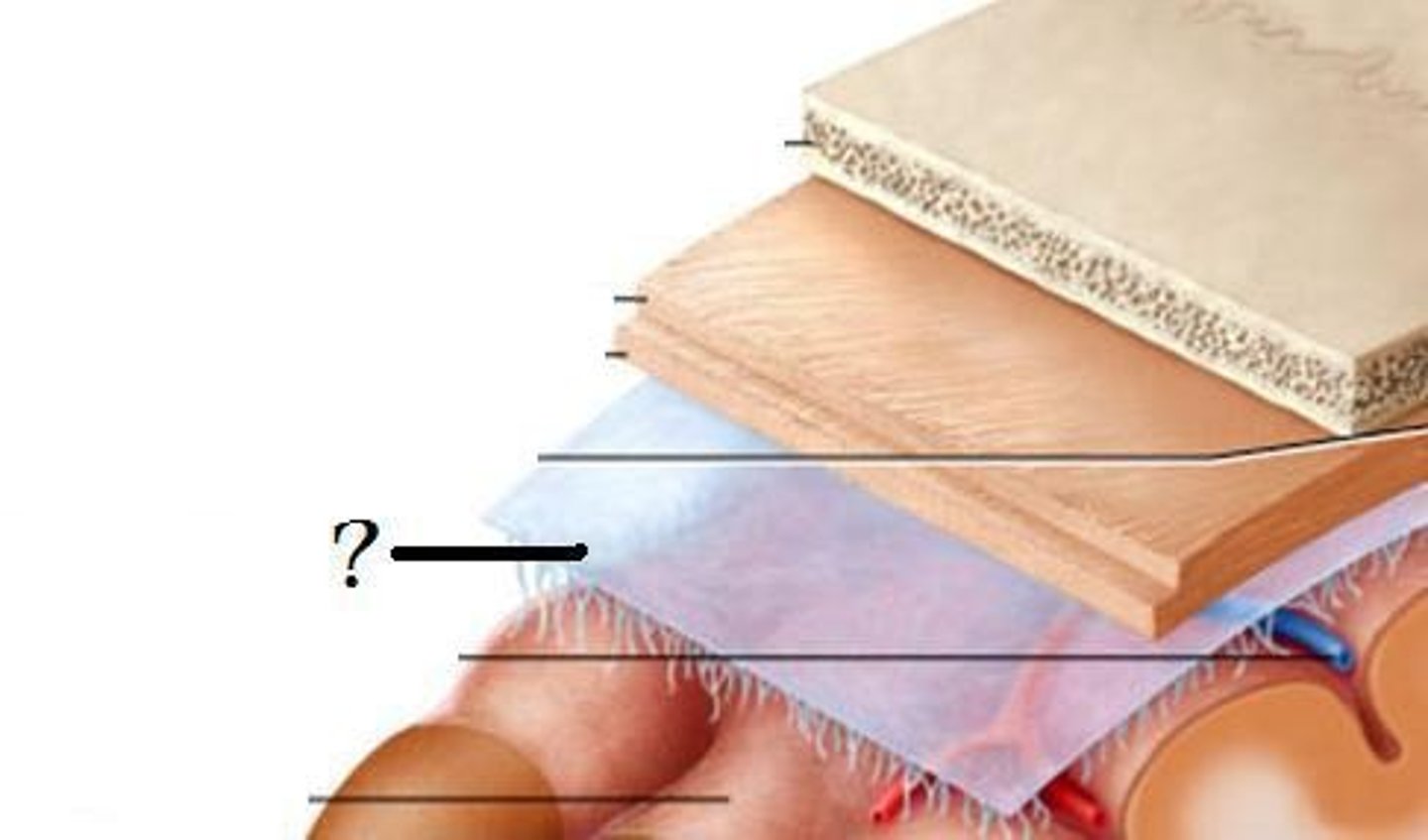
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
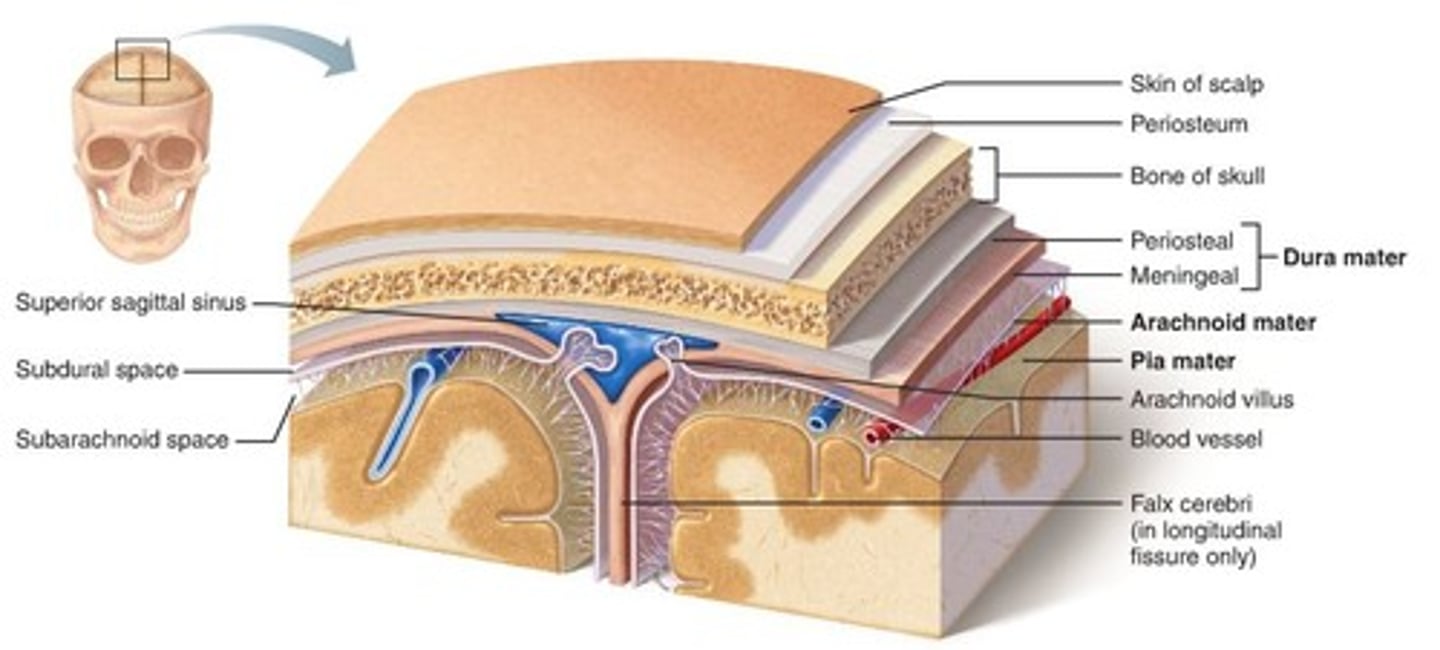
arachnoid mater
middle layer of meninges
epidural space
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
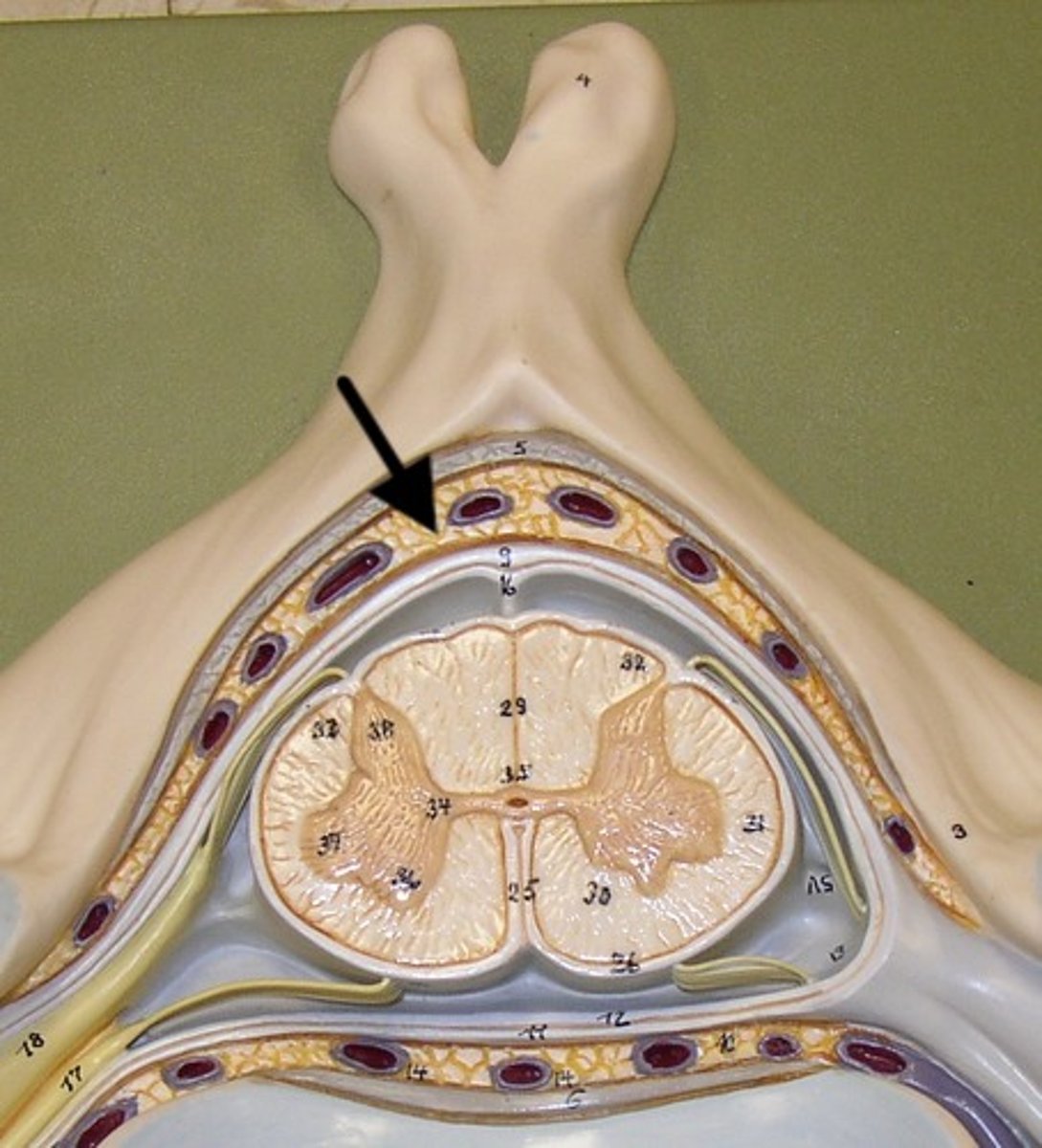
subdural space
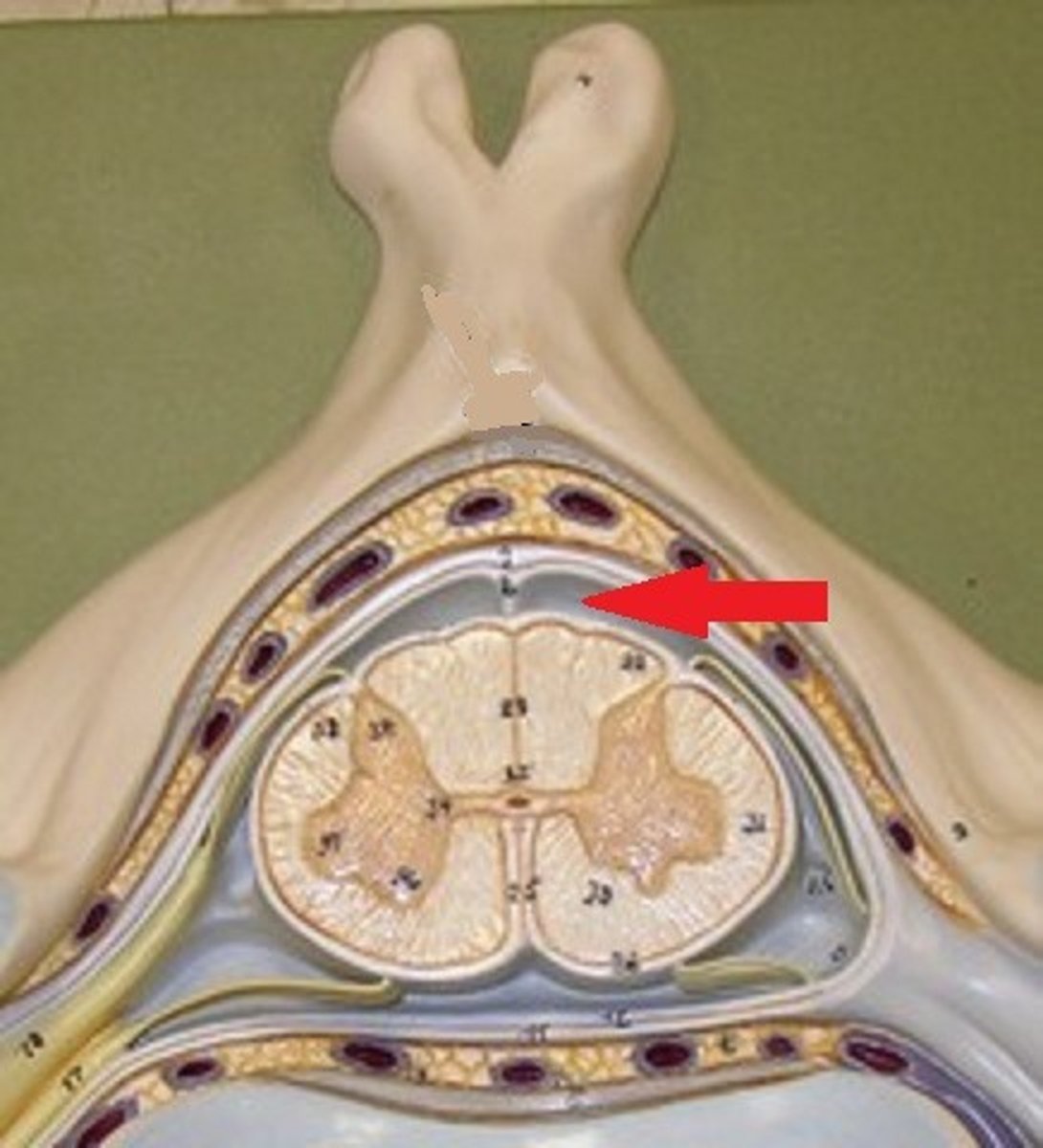
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
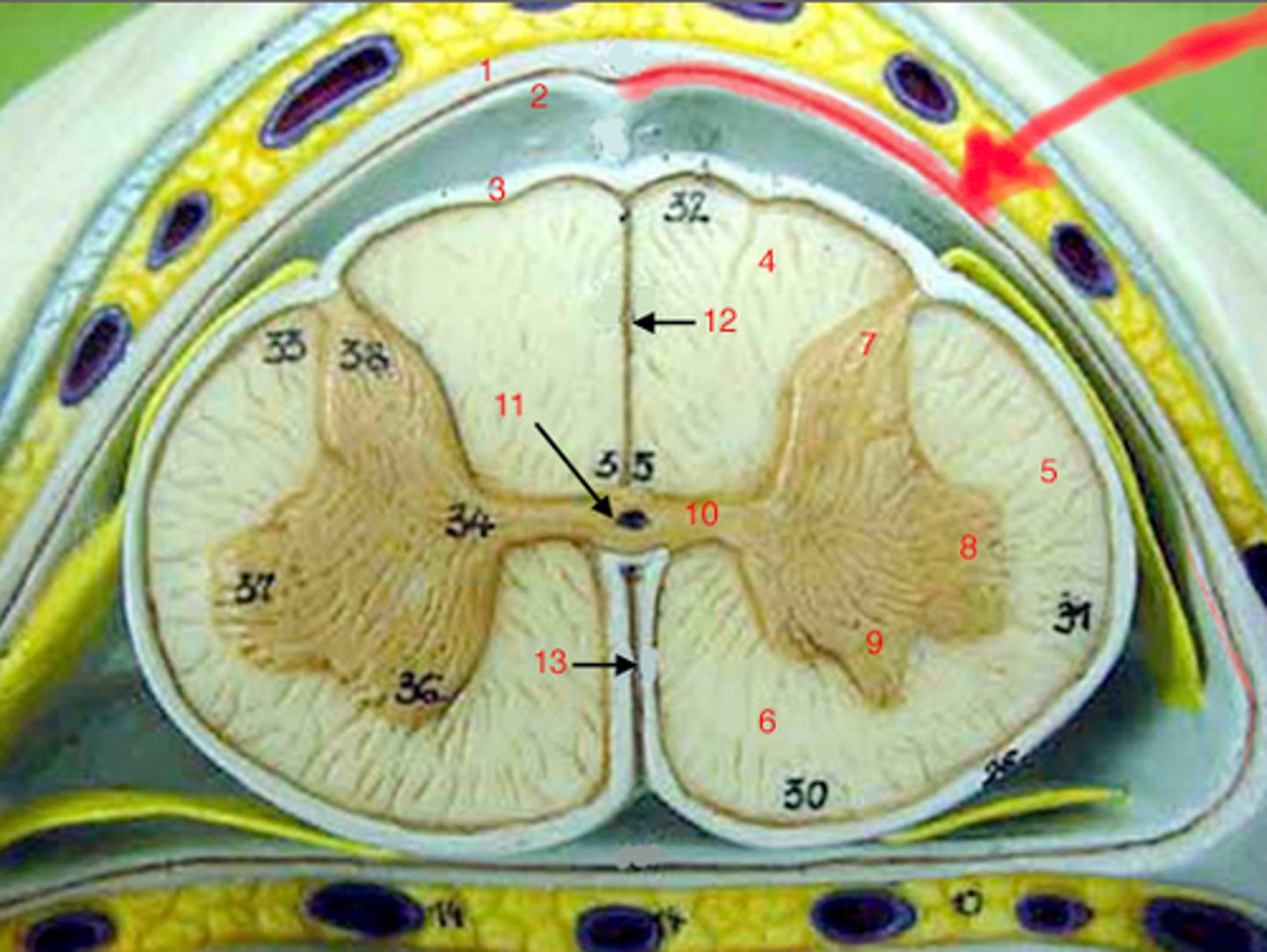
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
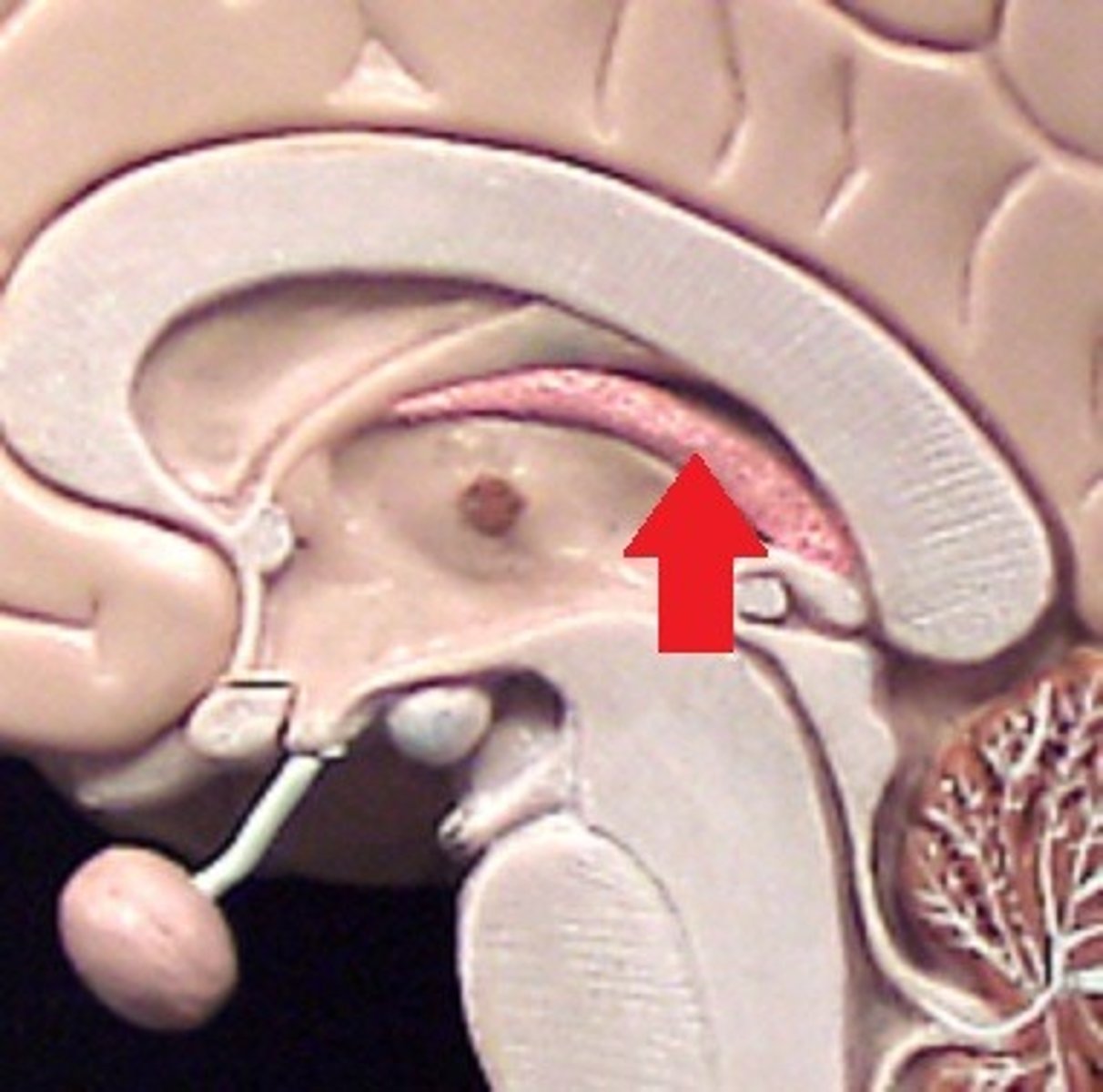
choroid plexus
produces CSF
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
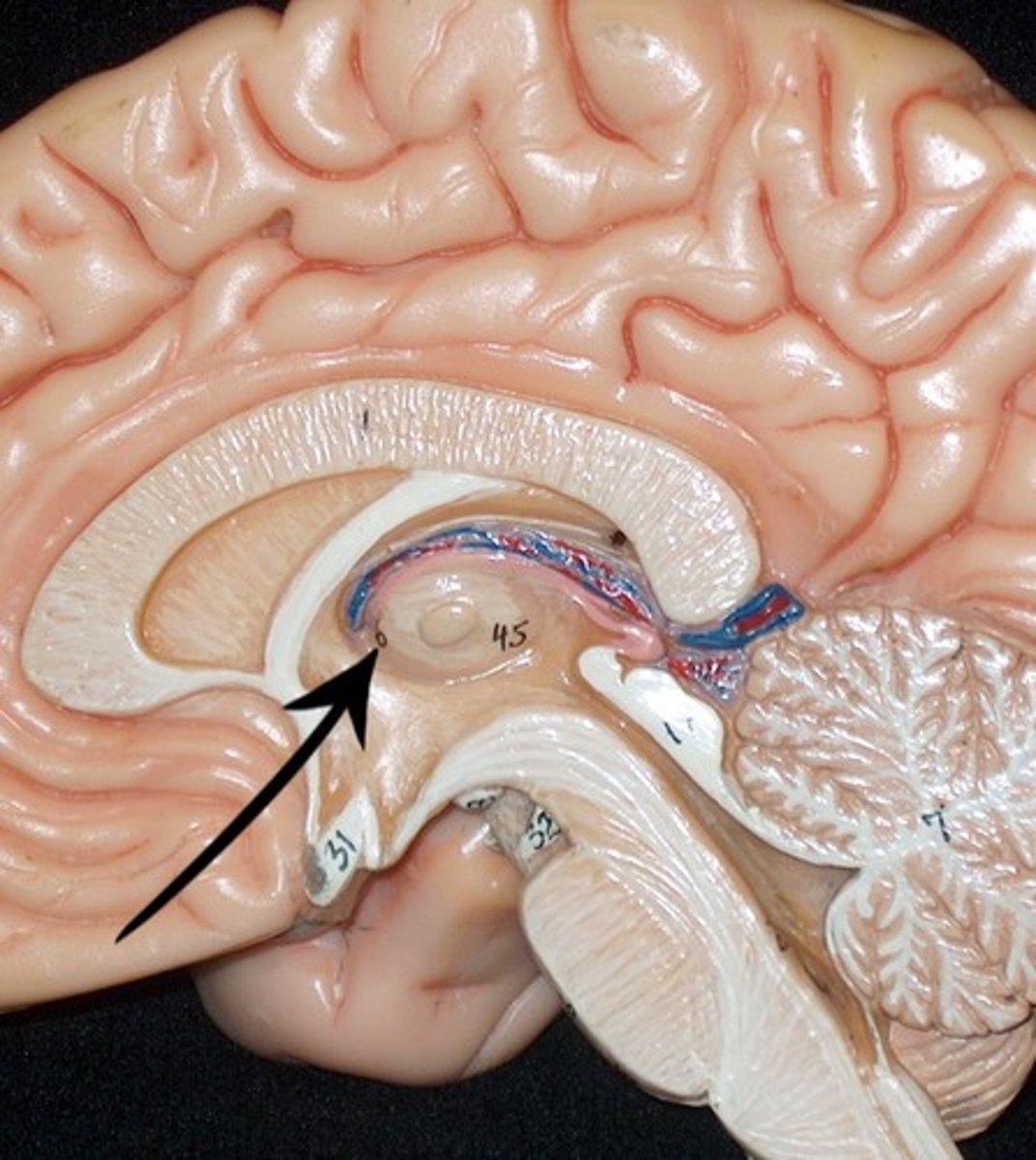
interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
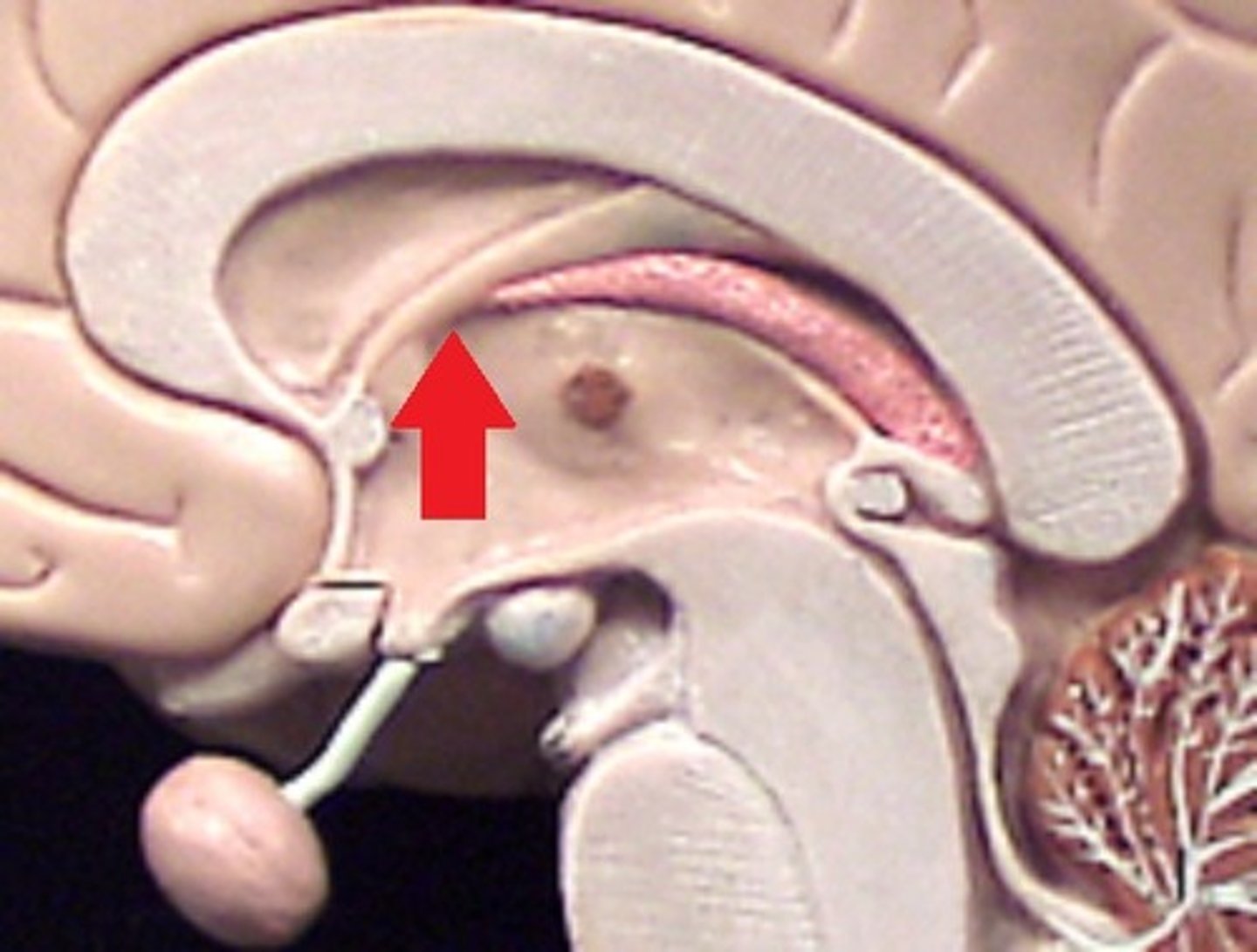
4th ventricle
between brainstem and cerebellum
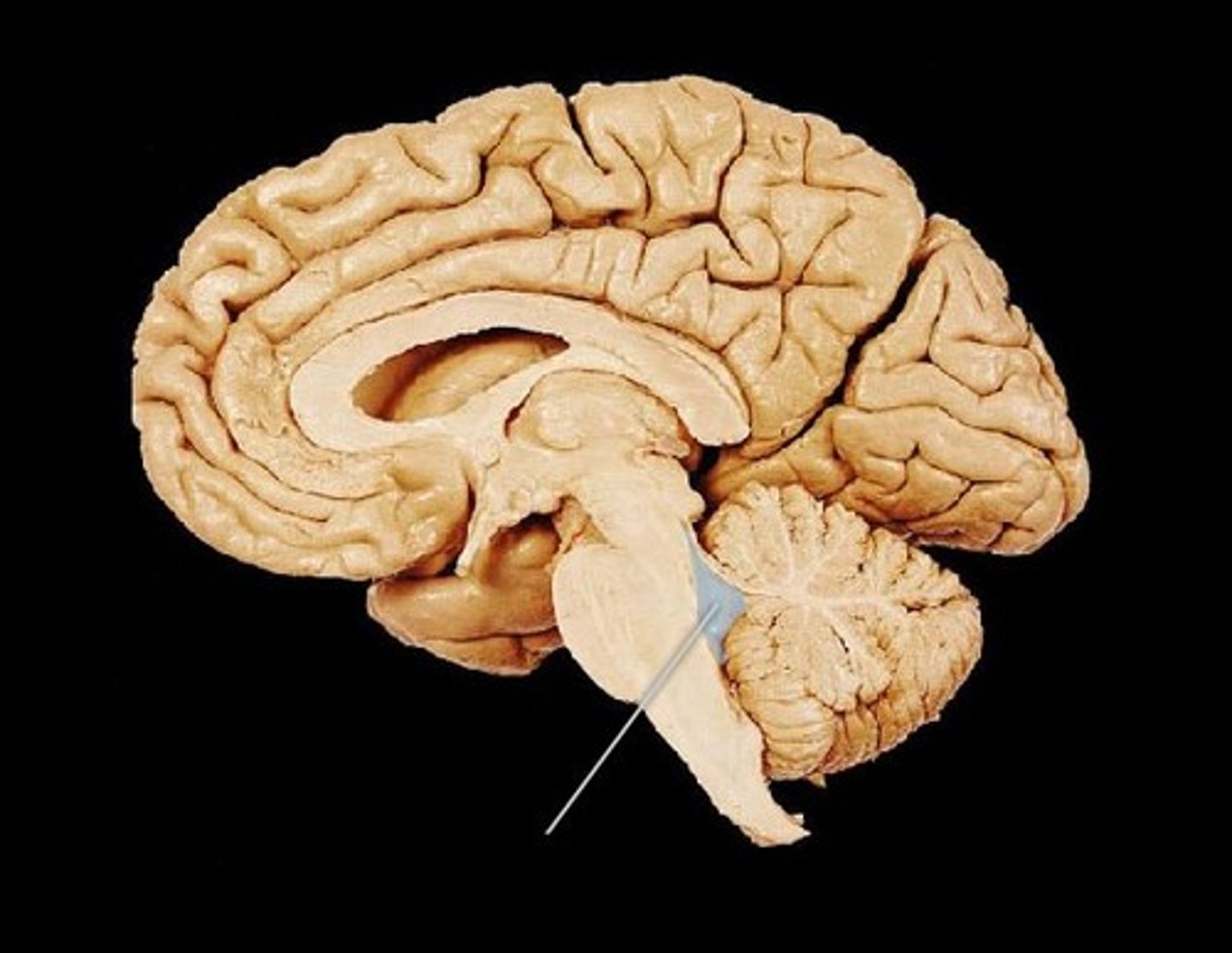
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
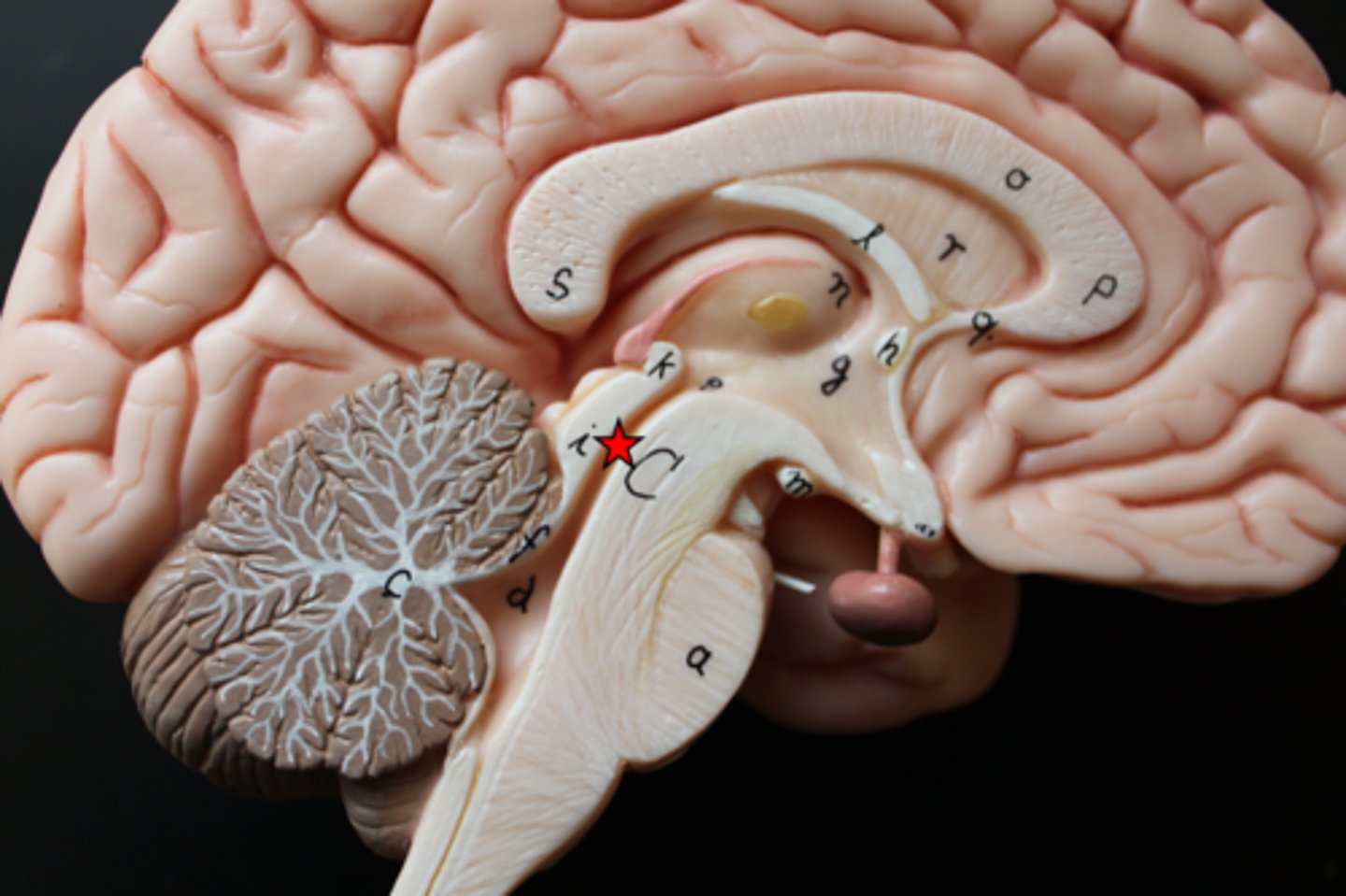
central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata