3.4 marketing mix
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
marketing mix def
combination of elements used by a business to enable it to meet the needs and expectations of customers
7 Ps
product
place
price
promotion
people (who makes contact with the customers)
process (processes that make and deliver the product)
physical environment
what is an effective marketing mix
achieves marketing objectives
meets customer needs
is balance and consistent
creates competitive advantage
influences on the marketing mix
business resources - finance
technology
importance of customer relationship
political and legal factors - laws
economic factors - growth
social factors - environmental concerns
technological factors - social media marketing
competition factors - enhancing the products features
consumer products
brought by final consumers for personal consumption
convenience product - brought frequently
shopping product - brought less frequently, require thought
speciality products - unique characteristics, buyers make special effort
industry products
brought for further processing
materials and parts - raw materials
capital items - goods used for production or operations
supplies and services - energy
introduction stage
new product launched
low sales
low capacity utilisation
high unit cost
heavy promotion
negative cash flow
growth stage
expanding market
fast growing sales
rise in capacity utilisation
cash flow may become positive
unit costs fall in economies of scale
maturity stage
slower sales as rivals enter the market
high capacity utilisation
high profits
prices and profits start to fall
decline stage
falling sales
decline in capacity utilisation
market saturation
decline in profits
why products decline
technological advancements
changes in consumer habits
increased competition
failure to innovate
extension strategies
lower prices
change promotion
change product
develop new market segment
reposition the product
boston matrix
an example of product portfolio analysis
helps firms decide on appropriate market strategies
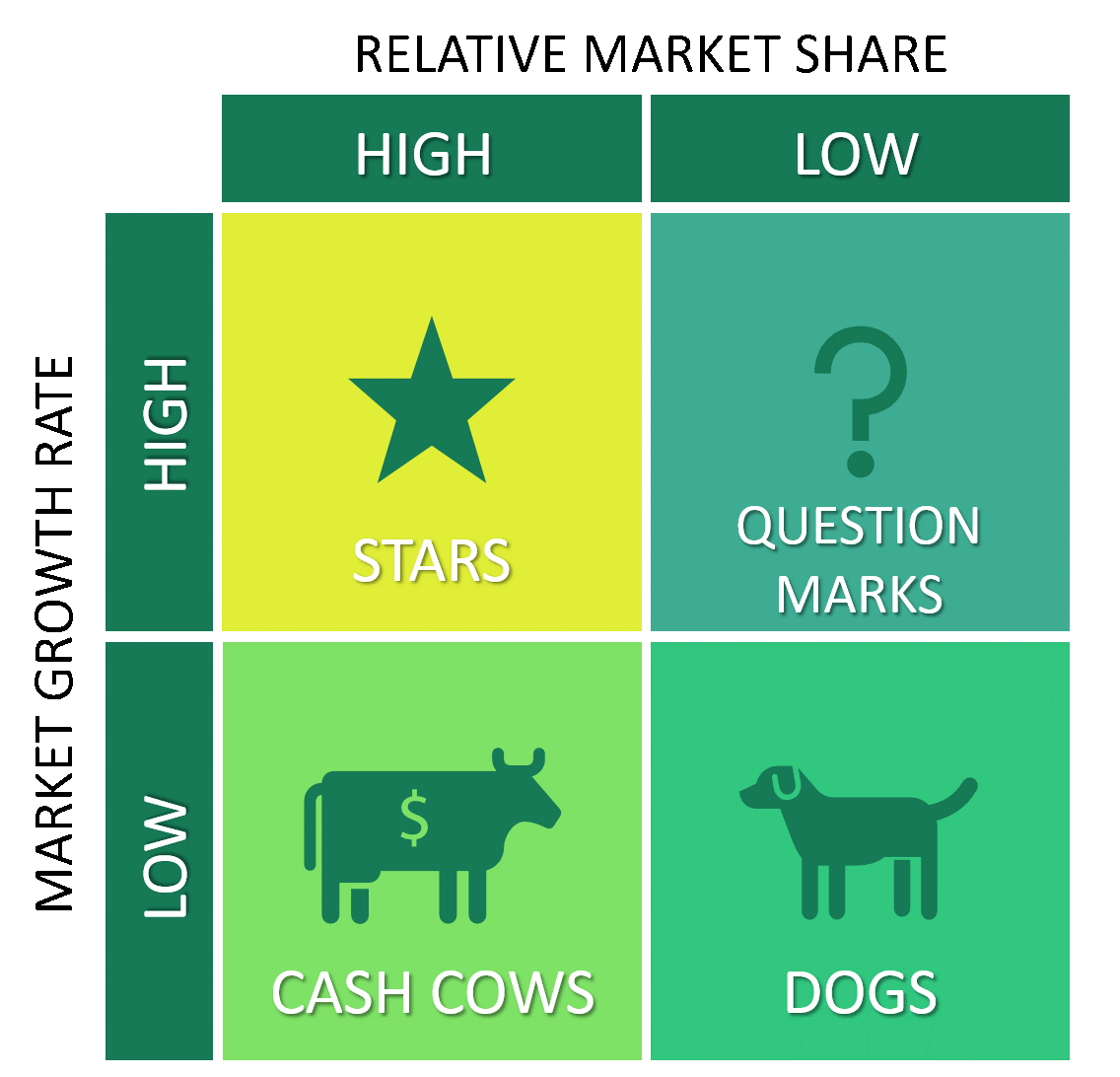
problem child / question mark
high growth, low market share
requires large investment
heavy promotional spending
expensive to maintain
future cash cows
stars
high growth, high market share
heavy promotional spending, expensive to maintain
future cash cows
cash cows
high market share, low growth
constant stream of profit
reinvest in new product ideas
dogs
low market share low growth
limited growth potential
fulfil niche market
can generate profits
what are price takers and makers
price taker - have no option but to charge the current market price
price makers - able to fix their own prices
price leaders - market leaders whose prices are followed by rivals
price followers - follow the market leaders price
what is price skimming
set a high price to maximise profit (can drop it later)
objective is to maximise profit to recover development cost
ADV of price skimming
works well for products that create excitement amongst early adopters
best used in introduction or growth stage
what is penetration pricing
offer a product at a low price to start
aim is to gain market share and build customer loyalty
price is increased when target market share has increased
uses of promotion
main aim is to ensure customers are aware of the product and let them know its better than rival products
increased sales
attract new customers
launch new product
create an image
advertising
used for mass marketing
TV, radio, newspaper
consumers see many adverts each day
personal selling
person on person
two way communication
high prices low volume
direct marketing
promotional material directed through
email, social media
allows business to generate a specific response
ADV
increasing sales to existing customers
building customer loyalty
generating new business
value of Boston matrix
useful tool for analysing product portfolio decisions
ignores issues like developing a sustainable competitive advantage
DIS price skimming
potential alienation of customers due to high initial prices
limited sales volume if product isn’t accepted widely by the market
vulnerability to competitors who enter the market with lower prices alternatives
ADV penetration pricing
rapid market growth
highly competitive
customer loyalty
DIS penetration pricing
low initial profit margins
difficulty of raising price after initial period
especially if product is price elastic
sales promotion
short-term incentives aimed at boosting sales, such as discounts, coupons, or special offers
ADV direct marketing
increasing sales to existing customers
building customer loyalty
generating new business
public relations
crate goodwill towards a business or product
achieve favourable publicity
improves brand image and reputation
sponsorship
takes place when a payment for an event, person or organisation is given in return for direct promotional benefits and brand exposure
branding def
establishing a distinctive and lasting identity for a product or service in the minds of consumers
needs to be carefully managed
a successful brand can create desirability
provides business with a USP
ADV branding
encourages repeat purchases
differentiates a businesses
easier to get retailers to stock your product
reduce price elasticity
DIS branding
high advertising cost
high R and D costs
value of new product development
process of creating and introducing new products to meet consumer needs and enhance market competitiveness
increased sales and brand growth
distribution def
to make products available in the right place at the right time in the right quantities
distribution channel
moves a product though the stages from production to final consumption
direct distribution channel
sells products directly from manufacturers to consumers without intermediaries
indirect distribution channel
involves intermediaries such as wholesalers or retailers to sell products to consumers
multi channel distribution
a strategy that uses multiple channels to reach consumers, combining both direct and indirect distribution methods for product delivery
retailer
final step in the distribution chain
deals directly with customer
choose final price
hold stock
wholesalers
buy in large quantities to sell to retailers
reduce producers transport costs
make money buy bulk buying at a low price from producers and adding a margin
distributor
an intermediary that sells products to retailers or directly to consumers, providing a critical link in the supply chain
usually specialise in a particular industry
offer products from many producers
hold stock
producer - distributor - consumer
agents
specialist type of distributor
does not hold stock
tend to work in tertiary sector (services)
earn commission based on sale achieved
producer - agents - consumer
what type of distribution
channel length channel to use (direct or indirect)
choice of intermediary
one or several channels
control over channel
geography - where do customer live
better se of resources
retailing expertise
segmentation
business size
nature of product - perishable, fragile
importance of an integrated marketing mix
a unified approach that aligns product, price, place, and promotion strategies to effectively meet customer needs and maximize impact on the market
ecommerce
the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet, facilitating transactions through online platforms
ADV ecommerce
allows businesses to reach a global audience, breaking geographical barriers
reduced overhead costs compared to traditional stores
convenience, customers can shop 24/7 from anywhere with internet access
e-commerce platforms can offer personalised shopping experiences based on consumer data
businesses can easily scale operations without the need for physical locations
DIS ecommerce
increased competition
dependency on technology
limited customer interaction
start-up cost
digital marketing
promoting products or services using digital channels, such as social media and email
aims to reach consumers where they spend a significant amount of their time online
ADV digital marketing
large customer base
cost effective
allows for targeting market segments
DIS digital marketing
including rapid technological changes
high competition
need for continuous adaptation
social media marketing
promoting products or services through social media platforms, engaging with customers directly and building brand awareness
ADV social media marketing
reaches a wide audience
fosters customer relationships
allows for real-time feedback
Disadvantages social media marketing
can result in negative feedback
requires constant attention
can be time-consuming to manage