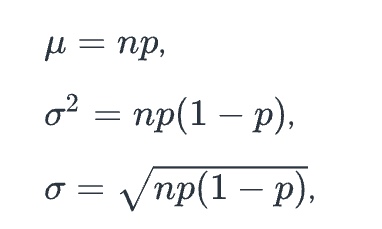Discrete Random Variables - Stats Module 3
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes binomial distribution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
random variable
A ___ ____ X is a function that associates numbers with some attributes of a sample outcome of an experiment.
You can have more than one randome variable.
Either discrete or continuous
relation
relationship between x and y coords. It maps inputs to outputs. e.g. y2 = x
function
any input has exactly one output. One output y per input x. e.g. If x=4, then y can only be 7.
One to one
Many to One
probability distribution
_____ _____ for a discrete random variable X is a formula, table, or graph that gives all possible values k of X, and the probability px(k) = P(X = k) associated with each value
These values k are mutually exclusive events
For a discrete probability distribution, see the attached properties
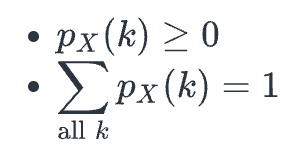
probability distribution table
cumulative distribution
_____ _____ for a discrete random variable X is a formula, table, or graph that gives all the possible values k and Fx(k) = P(X </= k), the probability that X is at most k.
cumulative distribution table
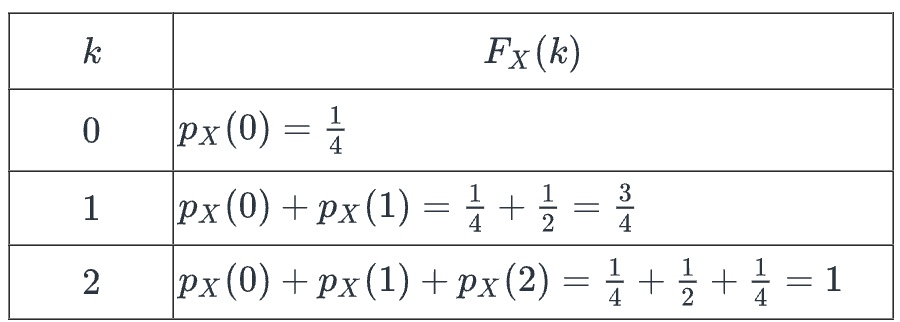
mean or expected value
Let X be a discrete random variable with probability distribution px(k). The
___ of X, which is denoted by (see attached) or E(X), is given as
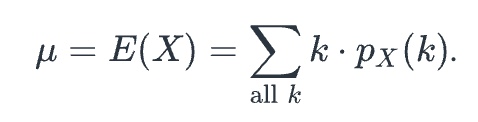
standard deviation
Let X be a discrete random variable with probability distribution px(k). The ___ of X, which is denoted by (see attached), is given as
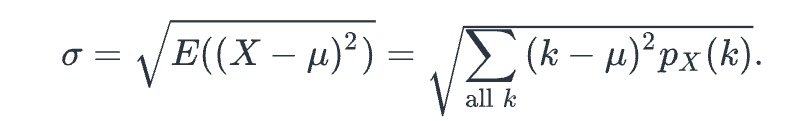
variance
Let X be a discrete random variable with probability distribution px(k). Attached is the square of the standard deviation (just take out the sqr root to solve for it)
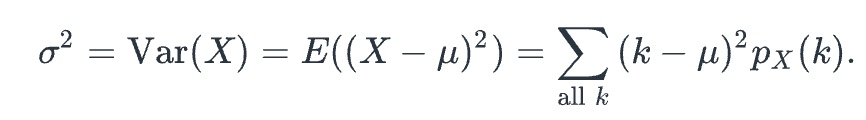
binomial experiment
conditions:
the experiment consists of n identical trials (e.g. imagine three distinguishable coins being tossed)
results in one of two outcomes: success or failure.
probability of success on a single trial: p
probability of failrue: q = 1-p
The trials are independent.
bernoulli trial
trials in binomial experiments
binomial random variable X
the number of successes in a binomial experiment. For the special case when n=1, we also call X a Bernoulli random variable.
probability of k successes
Let X be the binomial random variable corresponding to a binomial experiment consisting of n independent Bernoulli trials. If p is the probability of success in each trial, then the ____ is
for k = 0, 1, …, n
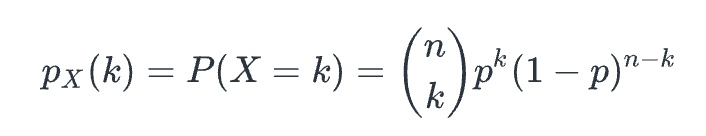
theorem 2
for the mean, variance, and standard deviation of X
where n = number of trials and p = probability of success