Chapter 9: Articulations
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts and terminology related to articulations, including types of joints, motion, and anatomical features.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Stability
The state of being stable; high when mobility is low and low when mobility is high in relation to joints.
Mobility
The ability of joints to move or not.
Structural classification of joints
The categorization of joints based on their structural components: cartilaginous, fibrous, and synovial.
Cartilaginous joints
Joints joined together by cartilage, which can be hyaline or fibrous cartilage.
Fibrous joints
Joints where bones are held together by dense regular connective tissue.
Synovial joints
Joints where bones are separated by a fluid-filled cavity; classified as diarthroses.
Gomphoses
Fibrous joints between teeth and the maxilla and mandible, classified as synarthroses.
Sutures
Fibrous joints between skull bones, classified as synarthroses.
Syndesmoses
Fibrous joints between parallel bones in the forearm and leg, classified as amphiarthroses.
Synchondroses
Cartilaginous joints joined by hyaline cartilage, classified as synarthroses.
Symphyses
Cartilaginous joints joined by a pad of fibrocartilage, classified as amphiarthroses.
Types of Synovial joints
Includes: plane (uniaxial), hinge (uniaxial), pivot (uniaxial), saddle (biaxial), condylar (biaxial), ball-and-socket (multiaxial).
Joint cavity
The space in synovial joints that separates articulating bones.
Uniaxial joints
Joints that move in one plane or axis.
Biaxial joints
Joints that move in two planes or axes.
Multiaxial joints
Joints that move in three planes or axes.
Flexion
Movement that decreases the angle at a joint.
Extension
Movement that increases the angle at a joint.
Gliding motion
Surfaces sliding back and forth or side to side.
Protraction
Anterior movement of a body part.
Retraction
Posterior movement of a body part.
Opposition
Movement of the thumb toward the palmar tips of the fingers.
Depression
Inferior movement of a body part.
Elevation
Superior movement of a body part.
Rotation
When a bone turns on its own longitudinal axis.
Pronation
Medial rotation of the forearm; palm turns inferiorly or posteriorly.
Supination
Lateral rotation of the forearm; palm turns superiorly or anteriorly.
Angular Motion
Motion that increases or decreases the angle between bones.
Abduction
Lateral movement of a body part away from the midline.
Adduction
Medial movement of a body part toward the midline.
Circumduction
Movement where the proximal end of a bone is stationary while the distal end makes a circular shape.
Glenohumeral Joint
Fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum
Ligament: coracoacromial ligament, coracohumeral ligament, and glenohumeral ligament.
Tendon of biceps brachii long head.
Rotator cuff muscles
Bursae: subscromial, subscoracoid, subdeltoid, and subscapular.
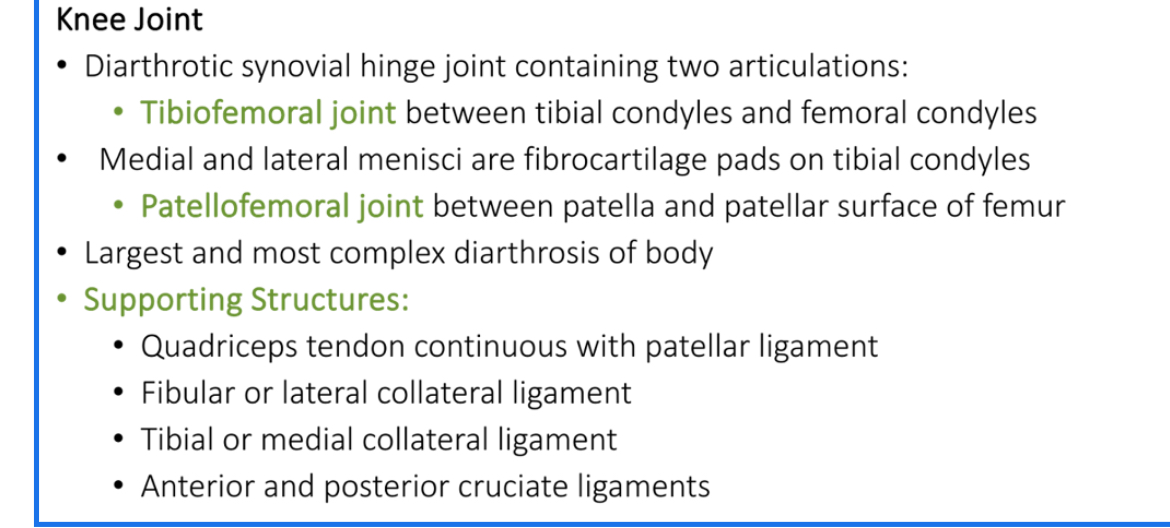
Knee Joint