7. sensory transduction and reflexes (how do nerves get initiated) UNFINISHED
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
define transduction
receptors that convert various forms of energy into electrical signals
forms:
mechanical: touch, pressure, joint, muscle length, sounds waves
chemical: smell and taste
electromag: light on retina
thermal
three types of proprioceptors
muscle sidles
golgi tendon organs
joint kinesthetic receptors
monitor stretch in locomotory organs, provide info about positions of diff body parts needed to coordinate movement
definition: measure changing length of muscle
location: imbedded in perimysium btwn muscle fascicles
muscle spindles
definition: monitor tension w/in tendons
location: near muscle-joint junction
golgi tendon organs
definition: sensory receptors in the joints that help you sense the position and movement of your body
location: sensory nerve endings w/in joint capsule
joint kinesthetic receptors
what is generator or receptor potential?
developed by mechanical stretch deforms membranes in receptor regions of sensory neurons; deformation causes Na channels to open
generated potentials (are/not) graded
graded
increasing stretch on mechanoreceptor produces increases in generator potential amplitude
explain conversion of generator potential into action potential
generator potential reaches a sufficient threshold potential (depolarization), which triggers the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels, causing a rapid influx of sodium ions that generates a full-blown action potential; essentially, the generator potential acts as a localized depolarization that, if strong enough, initiates the self-propagating electrical signal of an action potential at the axon hillock of a neuron.
what is frequency modulated coding?
stimulus intensity is encode into AP frequencies: higher receptor potentials produce higher frequency APs
as the intensity of a stimulus increases, the frequency or rate of action potentials, or "spike firing", increases
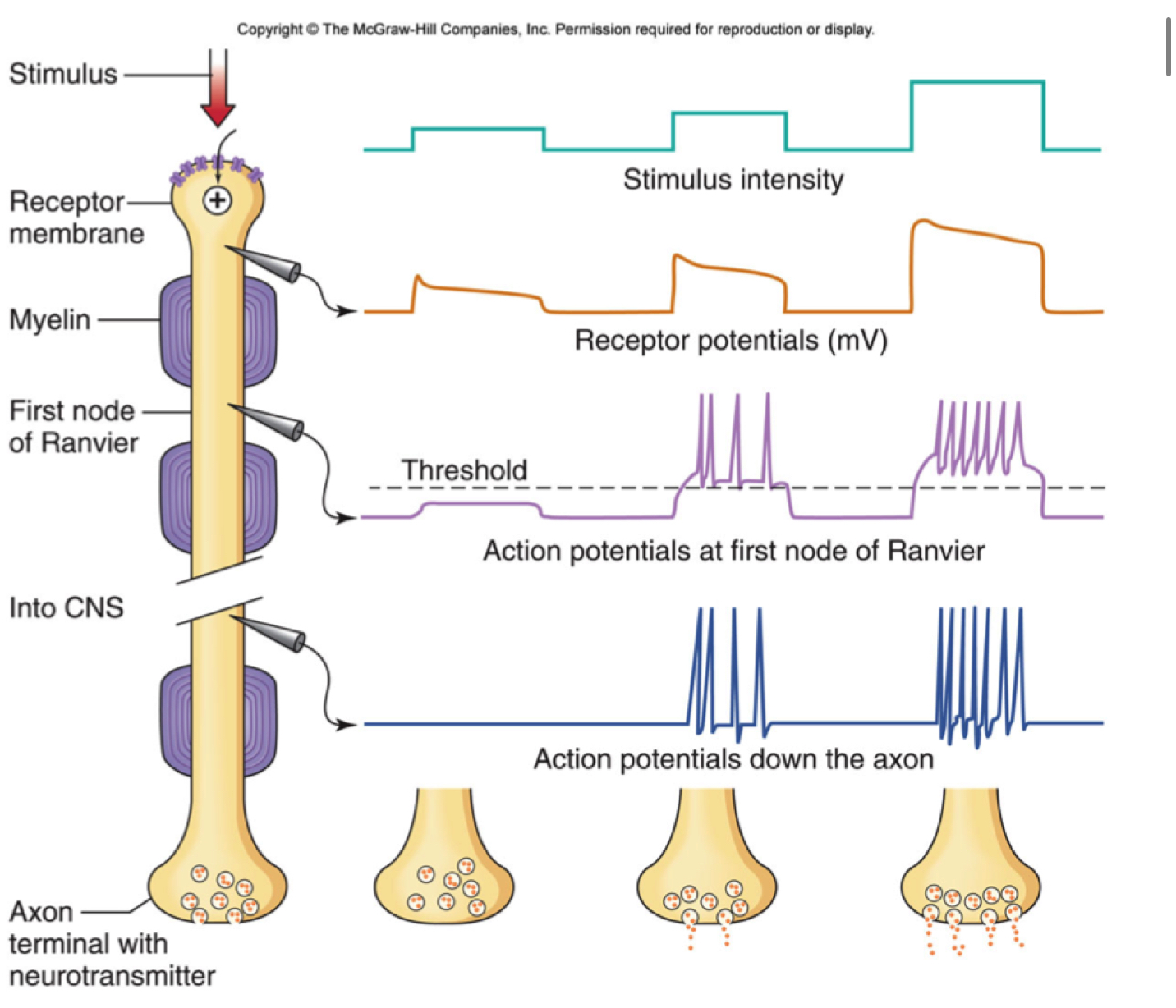
what is adaption and when does it occur?
when the generator potential gradually decreases resulting w the AP frequency decreasing
happens with prolonged stimulus some sensory neurons undergo