Physical Exams, Vaccinations, Biosecurity
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 410
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
describe aging cattle by teeth. (give the milestones)
central permanent incisors (age 2)
second permanent incisors (erupt 30 months, fully developed 3 yrs)
full set permanent incisors (age 4-5 yrs)
central incisors show wear (6 yrs)
all incisors show significant wear (10 yrs)
what should you look at when being “observant” during a physical exam?
herd
facility
sick animal/animals
pasture condition
hay quality
are other animal species in the same pasture?
what are the “big things” when performing a physical exam?
be observant
take a good history
identify potential zoonotic threats
wear gloves
proper restraint
a physical exam should always include a thorough _______ of the animal and the herd
history
when checking the herd for overall appearance and general health, what are some questions to ask yourself?
are there animals that appear too thin?
are there animals that appear sick and are laying down away from the herd/flock?
is the farm clean?
what is the deworming and vaccination schedule?
have any new animals been recently introduced into the herd?
what are we looking at when determining body conformation?
appearance
skeletal structure
muscling
fat balance
straightness of lines
structural soundness
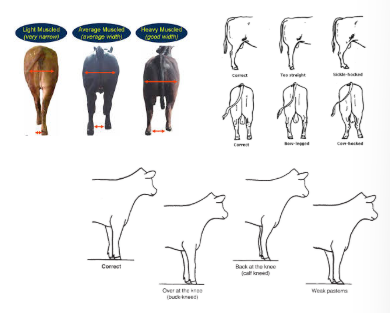
describe the ideal body conformation
long, straight back
no excess fat on brisket, flank, tail head
heavily muscled
proper height
max development of the round, rump, loin, rib
what’s the goal to keep cattle at an ideal body conformation?
produce maximum amount of high value cuts
what is the BCS scale for beef cattle?
1-9 (ideal 5-6)
what is the BCS scale for dairy cattle?
1-5 (ideal 3)
why is it important to record BCS in medical records?
very thin and very obese animals can have reproductive problems
nutrition and BCS help assess nutrition
BCS 1
BCS 1 are rare
extremely emaciated
NOT fit for transport**
very weak
reluctant to move
most often have a disease or high parasite burden
what is essential to evaluate an animal?
proper restraint
what restraint option is ideal?
cattle chute
what should you look for when examining the overall appearance of individual animals?
skin lesions, external parasites
what is the normal TPR (temperature, pulse, respiration) range for adult cattle and calves?
T - 100-102
P - 50-80 BPM Calf: 100-140 BPM
R - 25-50 BPM Calf: 30-60 BPM
what to look for when examining the head?
eyes: should be BAR, clear
nose: no discharge or lesions
mouth: no sores/lesions/bad odor
ears: discharge, ticks, mites
what else should you look for on a physical exam?
neck: pain, lymph node enlargement
heart/lungs: normal auscultation
gut sounds
examine all 4 legs
joints
hooves
examine udder and scrotum
general appearance of skin and all lymph nodes
rear end
evidence of loose stool
estrus in female?
what is rectal palpation for?
used for pregnancy detection in horses and cows
auscultation definition
using a stethoscope to listen to the heart and lungs
what animal has a thin rectum and tears easily?
horses
the rectum sits ________ to the vulva
dorsal
what is semen collection and testing for?
used to test fertility/assess reproductive health
when is semen collection/testing performed?
before breeding season and/or selling the animal
what is an electroejaculator?
rectally palpate to remove feces
place the electrode in the rectum
the pulse is gradually increased until the bull ejaculates
what to look for when viewing semen under the microscope?
assess number of sperm
assess for abnormal sperm
assess motility
what all is involved when processing cattle?
castration
dehorning
vaccinations
animal identification
castration
eliminates unwanted pregnancy
reduces aggression
increases human safety
ideally performed before 3 months of age
most often performed as a newborn
or at the time of weaning
surgical or banding
dehorning
reduces animal and human injury
ideally performed before 3 months of age
consult a veterinarian for pain management
vaccinations
varies based on operation and herd health protocols developed with your veterinarian
animal identification
ear notching, ear tags, branding
what are some additional helpful methods?
replace any missing ID tags
have medical records for each animal and a herd medical record
what is dehorning?
cutting the horn growth away from the skull
what is disbudding?
performed at a young age on dairy calves with a hot iron or caustic paste
when should caustic paste be used?
should only be used if the area is covered or the calf is pulled from the dam
what can caustic paste damage and how?
can damage the udder as the calf is attempting to nurse
disbudding destroys what?
horn producing cells
at what age can disbudding be performed?
can only be performed on calves less than 8 weeks of age before the horns become attached to the skull
polled is a _______ gene
dominant
banding
involves placing a rubber ring around the pampiniform plexus to restrict blood supply to the testicle
often done in pasture
when is it best to band cattle?
within first week of life
what must you make sure of when banding?
be sure both testicles are in the band
cutting castration
involves excising the scrotum with a blade and pull the testicles out of the body
open - excising the Tunica Vaginalis
closed - excising scrotum only
calf is confined in a squeeze chute
when should cutting castration be done?
often done as a newborn or around 6 months of age at weaning
name common cattle vaccines
IBR (Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis)
BVD (Bovine Viral Diarrhea)
BRSV (Bovine Syncytial Virus)
PI3 (Parainfluenza)
Leptospirosis
Vibrio - heifers and cows before breeding
7-way Blackleg
Brucellosis (only given to heifers under 12 months of age)
+ / - Anaplasmosis
what is brucellosis?
an intracellular bacterial zoonotic disease
the many variants of brucellosis depend on what?
the species they infect
is there an effective treatment for brucellosis?
no
brucellosis causes late term _________ in cattle
abortion
what species can brucellosis affect?
cattle, pigs, horses, sheep, goats, dogs
when should heifers be vaccinated for Brucelloses?
between 4-12 months old
where are cows ID’d after being given the brucellosis vaccine?
they are tattooed and tagged in the right ear
the brucellosis vaccine is a modified ______ vaccine
live
why are bulls not vaccinated against brucellosis?
they may develop orchitis (inflammation of testicle(s))
what is anaplasmosis?
a bacterial infection that causes severe, life-threatening anemia (Anaplasma marginate)
what animals spread anaplasmosis?
mostly by horse flies but sometimes by other biting flies, mosquitoes, ticks and needles and other surgical instruments
how is anaplasmosis transmitted?
infection occurs by the transmission from infected RBC’s to another animal
in what cattle breed does anaplasmosis most commonly occur in?
purebred herefords
clinical signs of anaplasmosis
aggression
staggering
weakness
jaundice/icterus (yellowing of the mucous membranes)
treatment for anaplasmosis
tetracycline
prevention against anaplasmosis
no approved vaccine
control horse flies and other biting insects
do not share needles or surgical instruments between animals
chlortetracycline mineral supplements
what is beef quality assurance (BQA)?
a voluntary program designed to help farmers maximize safe, beef production by teaching proper injection sites, proper management, and diligent record keeping
more than ____% of US beef comes from BQA certified farmers and ranchers
85%
deworming can be administered in these 3 ways:
injectable
pour-on
oral (drench)
all injections must be given in __________ to minimize lesions in high priced areas of meat
front of the shoulder
how far apart should injections be given?
4 inches
what type of injection is preferred over IM?
SQ
never administer more than _____ IM per injection site
10cc
always use the smallest needle possible to complete the injection but large enough to prevent…
breaking off in the muscle
the larger the bore, the smaller the ______
gauge
what are the steps to take if a needle were to break off in an animal?
attempt to remove the entire needle immediately
mark and record the area
sort the animal from the group
call a veterinarian for surgical removal
if a broken needle cannot be retrieved from the animal by a veterinarian, what happens next?
the animal cannot be harvested at a custom packer; the animal must be identified and cannot be marketed with the rest of the lot; these animals must be transported for harvest immediately
ideally, you should change needles between every ________
animal
why should you not mix MLV (modified-live vaccines) before they’re needed?
they can lose their effectiveness and cannot be stored
MLV should be given within an _______ after mixing
hour
(true/false) you can vigorously shake and leave MLV in the sunlight without any adverse effects on the vaccine
false, this may inactivate the vaccine
define internal biosecurity
measures taken to prevent transmission of diseases between different areas of the farm
management practices that follow internal biosecurity
isolating sick animals
cleaning and disinfecting
vaccination
define external biosecurity
measures taken to prevent diseases from entering a farm from outside sources
management practices that follow external biosecurity
quarantining new animals for a min. of 30 days
limiting visitors
employee training on how to handle sick animals
how is disease spread?
aerosol: nasal secretions, coughing, sneezing
direct contact: open wound or mucous membrane
oral-ingestion
reproductive: spread during mating or gestation
vehicles: contaminated objects used on multiple animals
vector-borne: spread by insects or ticks
fomites: contaminated soil, water, food
you are called to a farm to assess a sick animal. you immediately see there are multiple animals sick. what should you do about your other scheduled farm calls for the day?
call other farms and inform them of the situation. try to reschedule to another day or disinfect and change clothes
when to choose treatment over euthanasia?
likelihood of recovery
freely able to stand and walk
ability for transport
ability to get feed and water
remember withdrawal times
when to choose euthanasia over treatment?
non repairable fractures of the hip, legs, spine
immobility or inability to stand
loss of production and quality of life
emergent conditions causing excruciating pain
animals too weak to be transported
paralysis
diseases with no effective TX or pose a significant risk to human health
can cattle euthanized with injectable euthanasia be accepted for rendering?
no, due to Federal regulation
tools for euthanasia
gun
penetrating captive bolt
injectable solution — cannot enter the food chain
what is the location of optimal point of entry for shooting a cow?
intersection of 2 imaginary lines drawn from the lateral canthus (outer corner of the eye) to the center of the base of the horn
