Organic Chemistry Carboxylics/Esters Slides Review
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3rd Partial
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Combination of carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group
•Plane Trigonal Geometry
•Acidic hydrogen on the hydroxyl group (OH)
•Basic behavior in the Oxygen group
Carboxylate ion
Carboxylic acids are strong acids. They are stabilized by the
resonance structure. Forming theCarboxylate ion
Carboxylic Acid BP comparison
Higher boiling points than alcohols, ketones and
aldehydes of similar molecular masses. Due to hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acid molecules.
Carboxylic Acid BP Variance
Double bonds – low melting point (double bonds
prevent the formation of stable crystal networks).
Dicarboxylic acids – High melting point (hydrogen bond forces
are very intense and higher temperatures are required to break
them).
Carboxylic Acid solubility variance
Solubility depends on the carbon chain. The longer the
carbon chain, the less solubility.
– Acids with more than 10 carbons are insoluble in water
– Acids are more soluble in alcohols
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
– More acidic than other organic substances
but weaker than inorganic or mineral acids.
– Diacids (DiCarboxylic Acids are weaker than acids with only
one carboxyl group.
– Substituents that stabilize the negatively
charged carboxylate ion make the acid stronger.
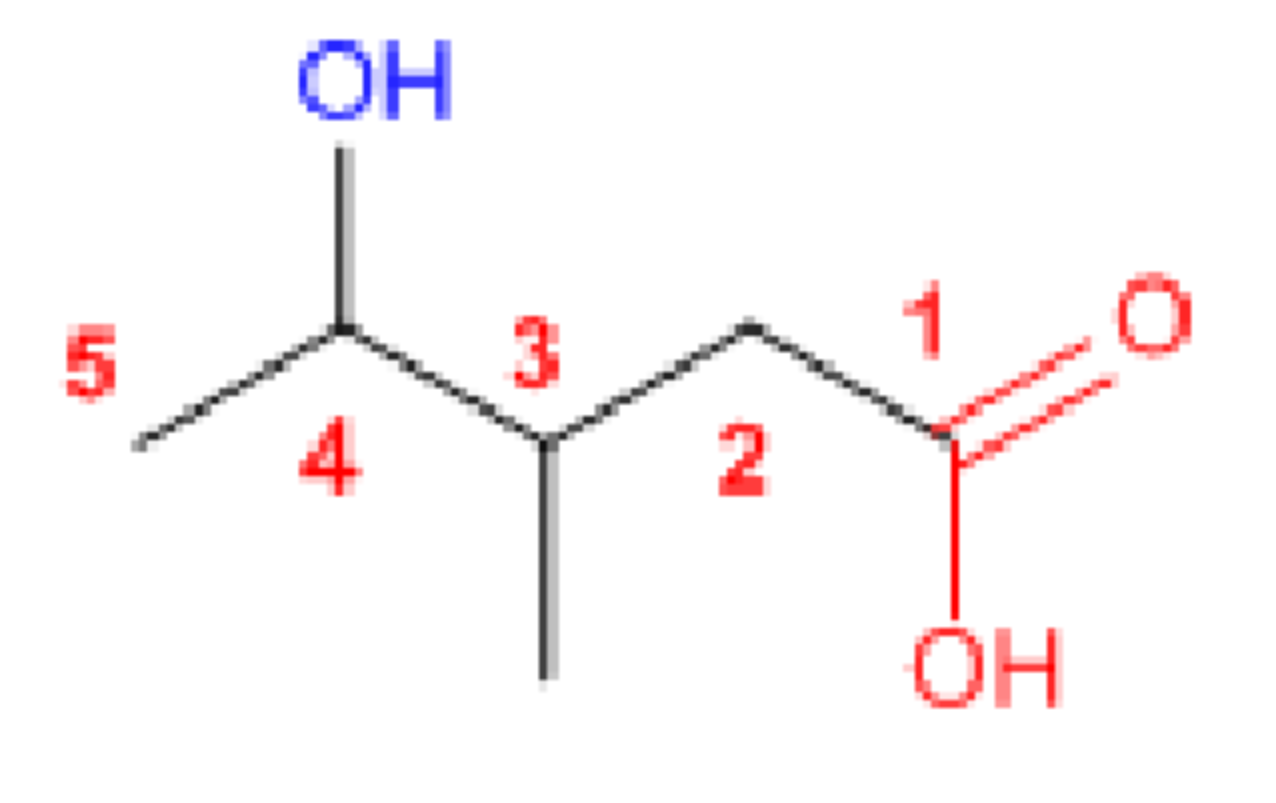
4-hydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid
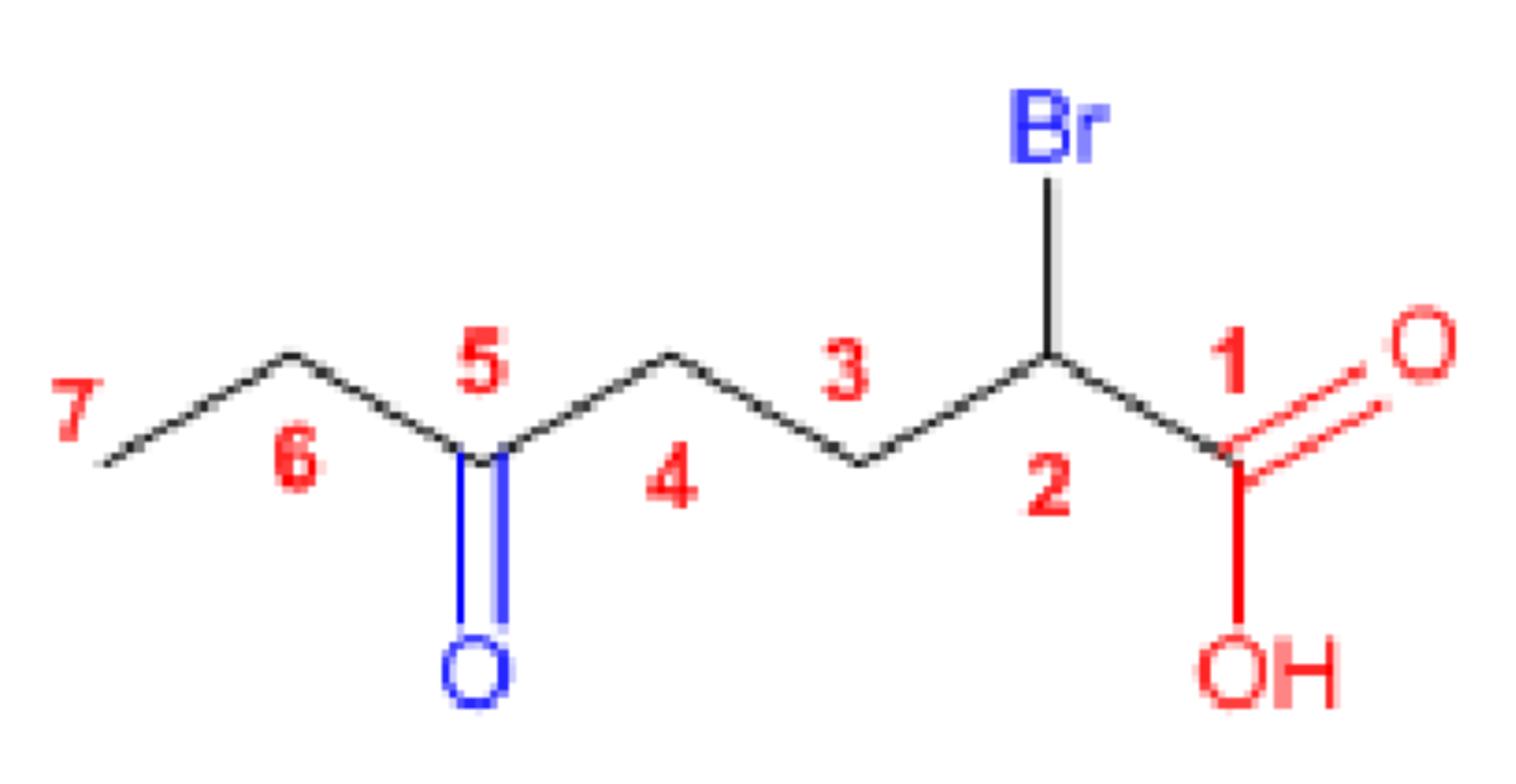
2-Bromo-5-oxoheptanoic acid
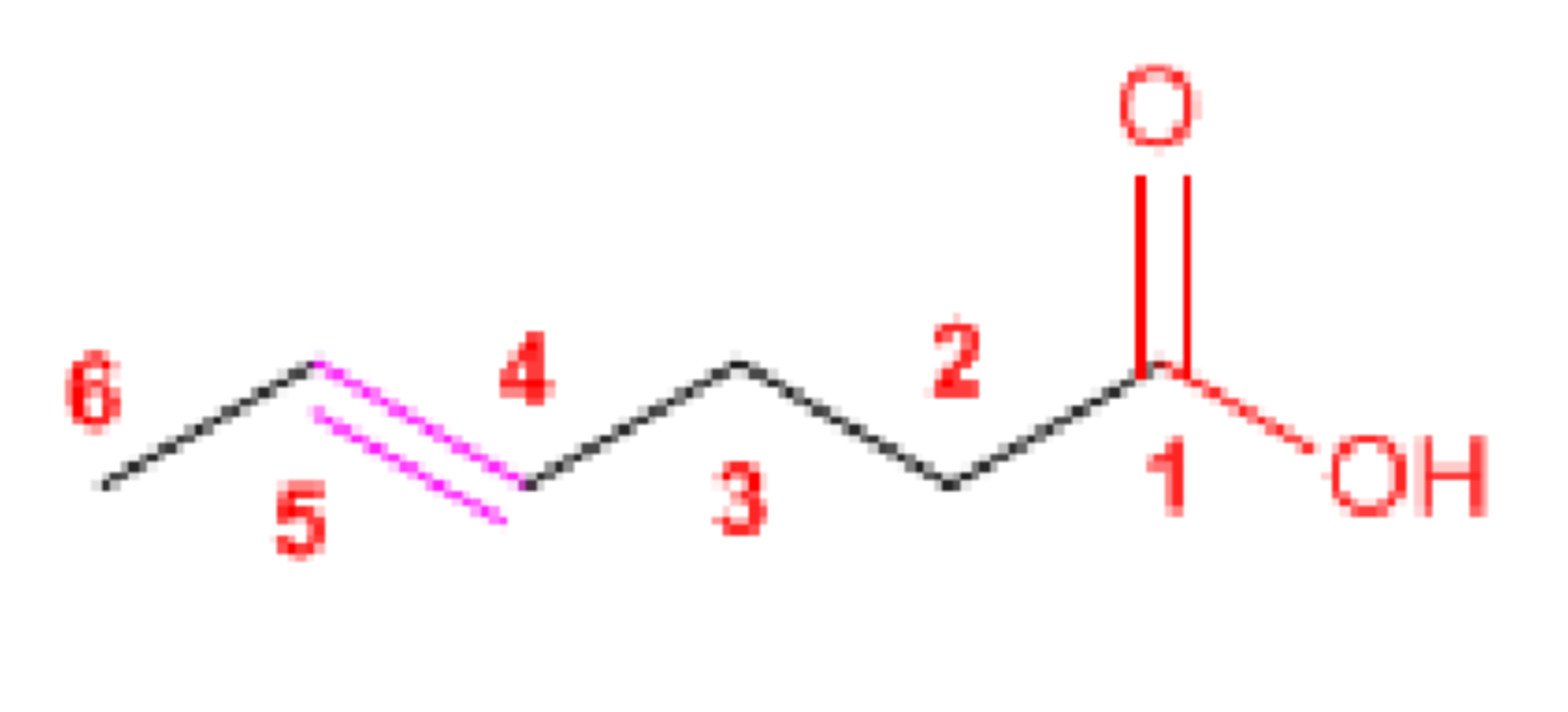
Hex-4-enoic acid
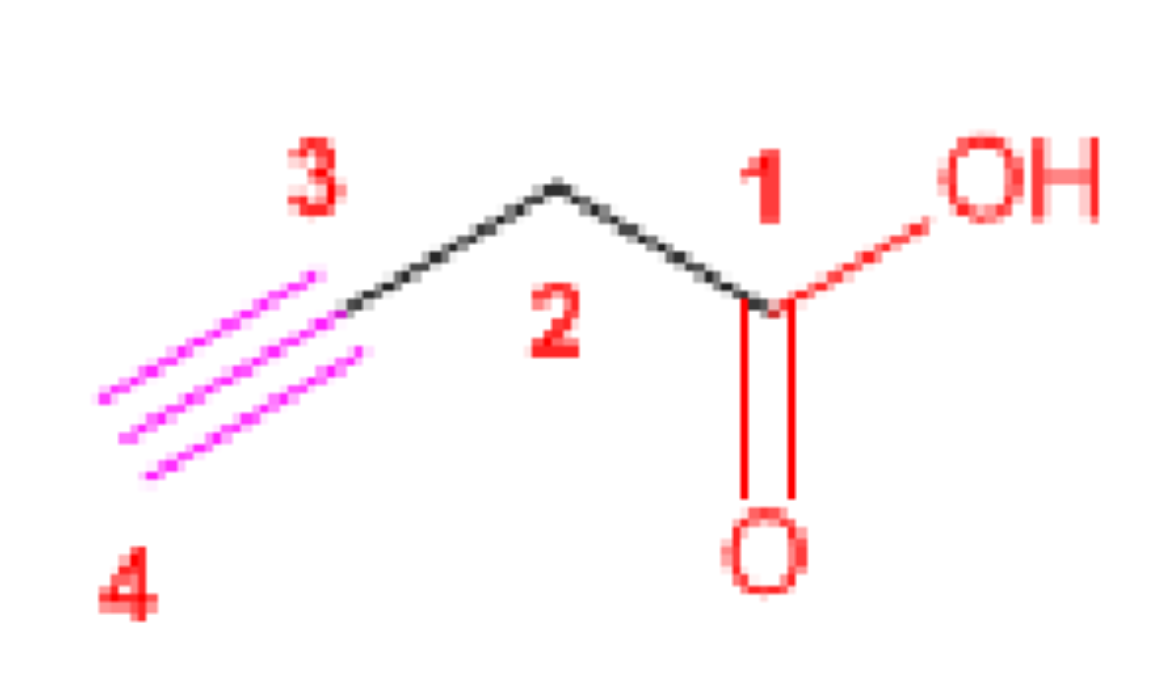
But-3-ynoic acid
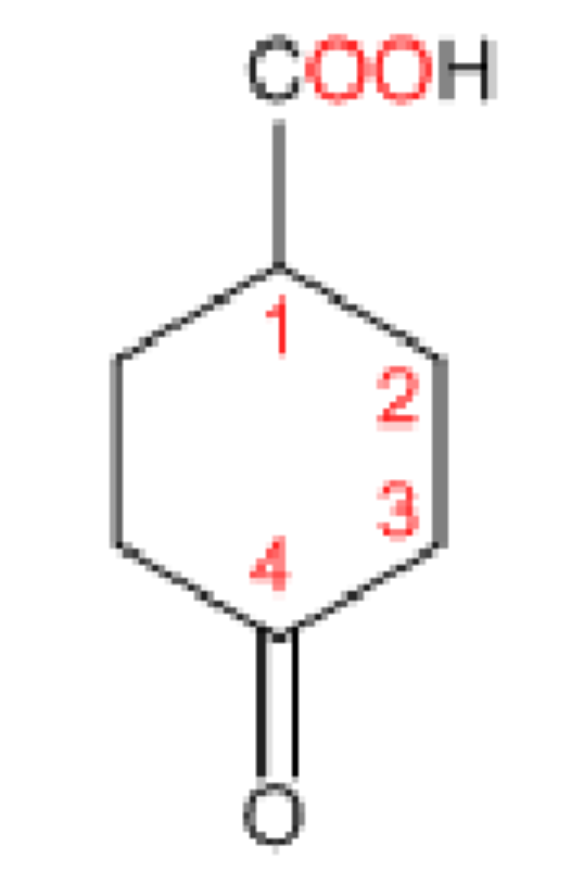
4-oxocyclohexanecarboxylic acid
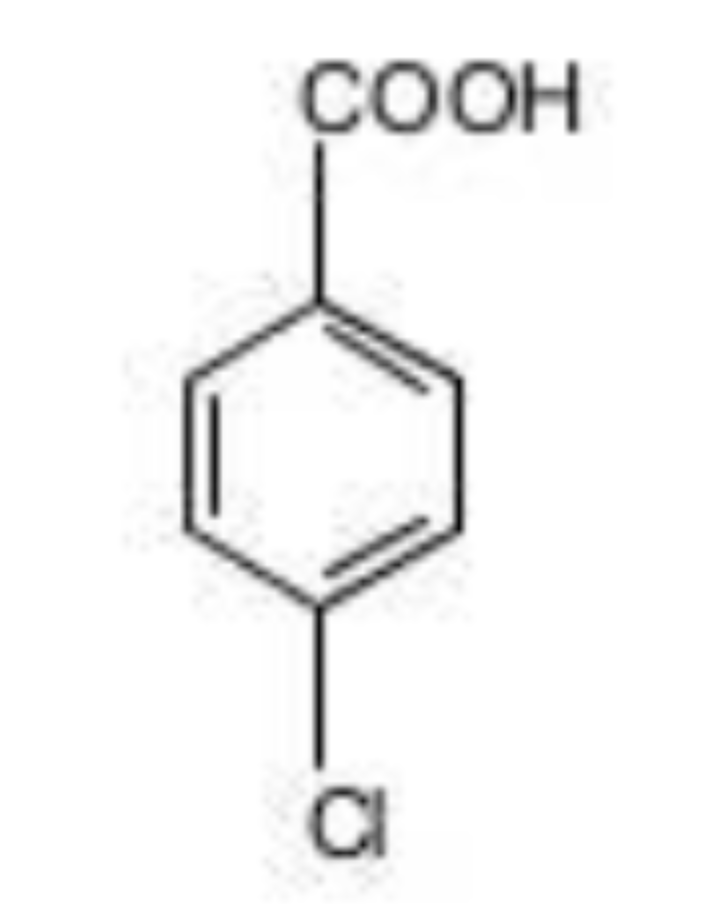
P-Chlorobenzoic acid
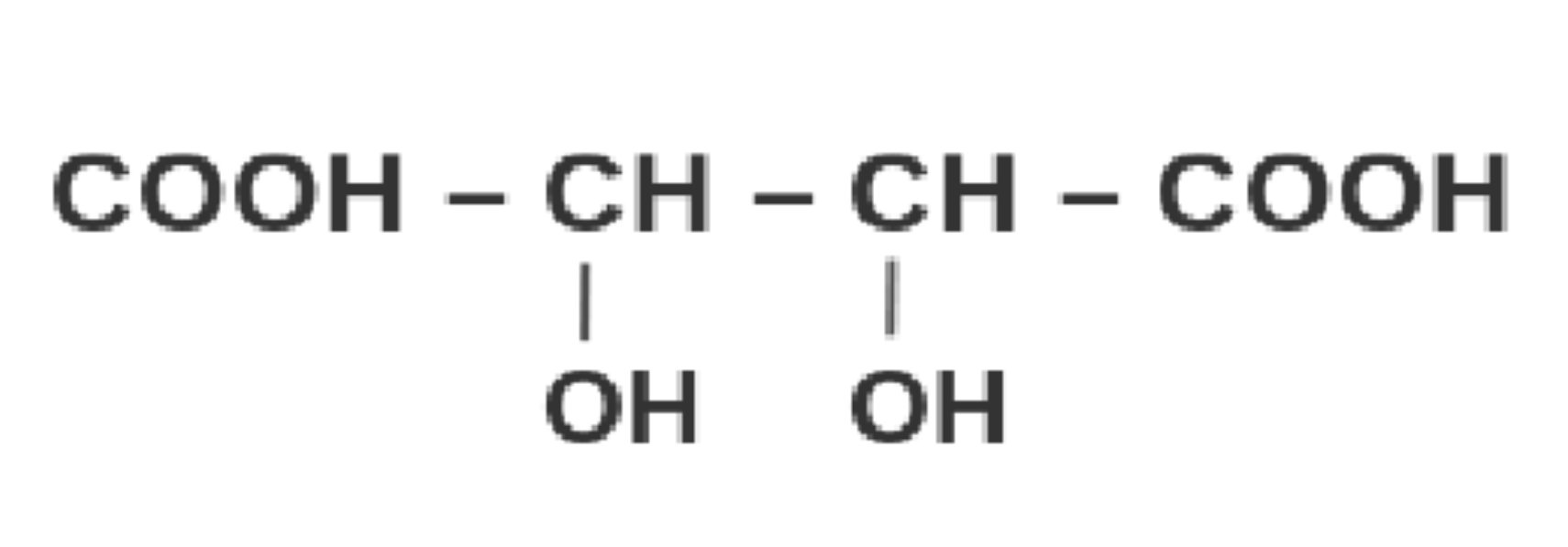
Tartaric Acid
2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid
Classification of Fatty Acids
saturated (no double bonds), monounsaturated (one double bond), and polyunsaturated (multiple double bonds) fatty acids.
Classification of Lipids
Saponifiable lipids: Contain ester bonds → can form soap
Examples: Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Waxes
Non-saponifiable lipids: Do not contain ester bonds → cannot form soap. Examples: Steroids (cholesterol), Terpenes. Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
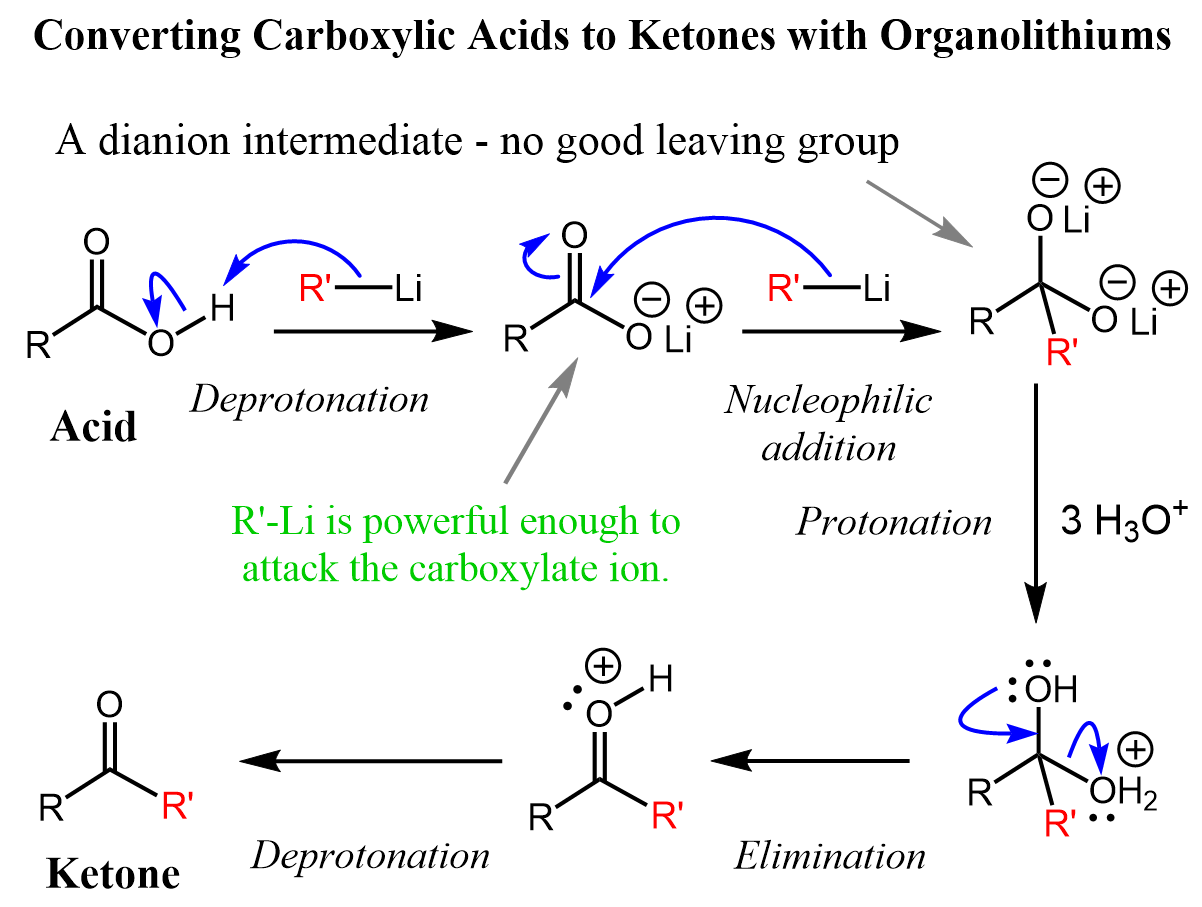
Converting Carboxylic Acids to Ketones with OrganoLithium
How to Form a Carboxylic Acid
Oxidation w/ KMnO4/K₂Cr₂O₇ : Oxidize an Aldehyde or Alcohol —> Carboxylic Acid…. Oxidative Cleavage of Alkene or Alkyne. (Terminal Alkynes form acid + CO2)…. Hydrolysis of Esters. Ester + H+ + H2O →Carboxylic and Alcohol.
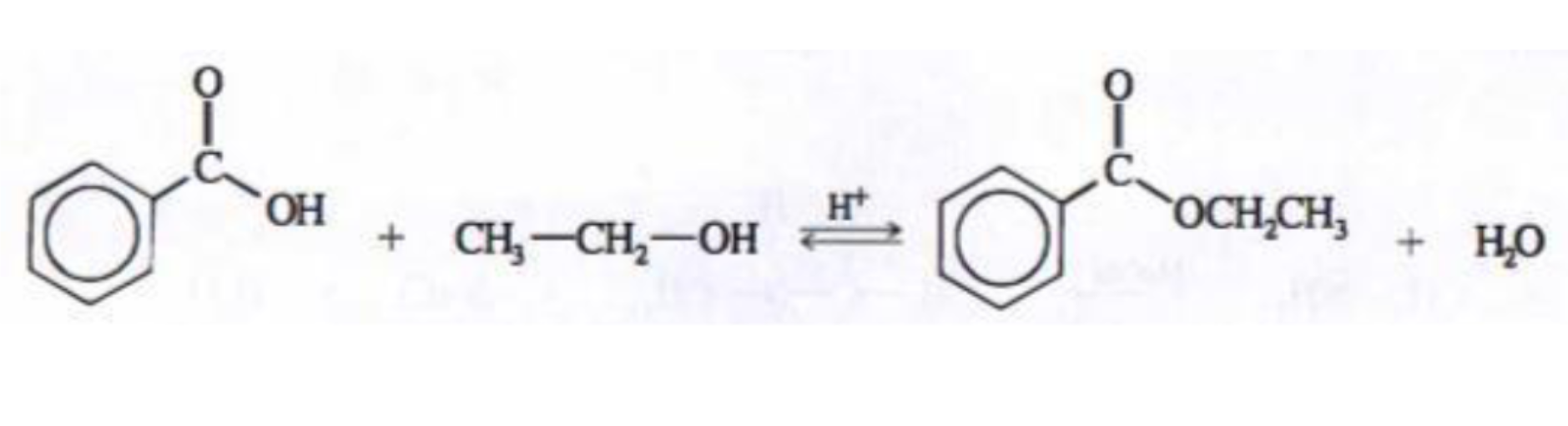
Formation of esters