(term 1) Test 1 + 2 Chemistry (Exam)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Precision
A set of data that is close to each other but not necessarily on the target.
Accuracy
A measurement that is close to the true value or target but may not be precise.
Percent error
A calculation used to determine the accuracy of a measurement compared to a theoretical value, expressed as a percentage.
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Element
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions.
Compound
A substance formed by two or more elements that are chemically bonded together.
Mixture
A physical combination of two or more pure substances.
Heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that has a visibly different composition and individual substances can be observed.
Homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which the components are uniformly distributed and cannot easily be distinguished.
Physical properties
Characteristics of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing its chemical composition.
Chemical properties
Characteristics that can only be observed during a chemical reaction, involving a change in chemical composition.
Physical change
A change in the form or state of a substance without any change in its chemical composition.
Chemical change
A change that transforms one or more substances into new substances with different chemical properties.
Periodic table
A tabular arrangement of the chemical elements organized by increasing atomic number.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
A theory that posits that all matter is made up of atoms, which are indivisible and indestructible, and that atoms of a given element are identical.
Electron configuration
The distribution of electrons in an atom or molecule's orbitals.
Cation
A positively charged ion that results from the loss of one or more electrons.
Anion
A negatively charged ion that results from the gain of one or more electrons.
Ionic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between positively and negatively charged ions.
Octet rule
The principle that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons.
Examples of physical changes.
Cutting/Breaking/Sand+water/salt +water /sugar+water/crystallization/Stretching/Crushing/
Crumpling/melting/freezing/boiling/Mixing (if it can be separated/Boiling water
Examples of chemical changes.
Smell (if it suddenly changes)
Digestion (acids help break down)
Combustion (explosion)
Baking (using yeast to rise a food)
Leaves changing color
Rusting
Rotting
Temperature change
Photosynthesis
Sour milk
Dimitri Mendelev
attempted to come up with a system to organize all known elements, he grouped them in order by their individual masses, from the lightest-heaviest. These masses would become known as atomic masses. He put elements in columns based on having similar properties
Groups
They are vertical and contain elements similar to each other.
periods
Do not have a relationship, only in that period because of the increasing atomic mass order.
Metals
everything to the left of the staircase except for hydrogen
Metal Properties
They tend to have high melting points
They are good conductors of electricity and heat
They are very shiny
They are very malleable (bendable/shapeable)
As you go down the chart they get more reactive
Nonmetals
To the right of the staircase
can be gasses, liquids, or solids but mostly gasses
If they are solid they are brittle with low melting points and very dull and bad conductors of electricity
For non-metals, they get more reactive as you go up the chart
Metalloids
Have properties of metals and nonmetals
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is not created nor destroyed.
Law of Definite Proportions
a chemical compound that always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass, every compound is built the same way every time
Law of Multiple Proportions
about multiple compounds made from the same elements. When two elements form more than one compound the ratios of the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are small whole numbers. They come in whole pieces called atoms
Define the Atomic Theory
All matter is made up of atoms. -> law of multiple proportions, atoms are indivisible and indestructible -> law of conservation of mass,
All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties ->law of multiple proportions
Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms in fixed proportions ->law of definite proportions
In a chemical reaction, atoms can only be separated, combined, or rearranged ->law of conservation of mass
Who discovered electrons
JJ Thompson
Plum Pudding Model
JJ Thompson created it, its was a bad model because it did not include a nucleas. He also believed electrons where negative.
Rutherfords Gold Foil Experiment
Ernest Rutherford did it, it used alpha particles which where shot through a sheet of gold foil and they would sometimes deflect. This led to the discovery of the nucleas.
Nucleas
It is small, heavy, and positively charged
Protons
are positive, located in the nucleas, weigh the same as nuetrons
Electrons
Are found in the electron cloud outside of the nucleas, they are negatively charged and weigh a lot less than protons and neutrons.
Nucleas
The nucleus weight the same as protons, and are neutral in charge (0), and located in the center of the atom
Nuetrons
are neutral and found in the electron cloud
Atomic Mass
Is a sum of protons and neutrons. it can be written like this carbon-12 (6 protons and 6 nuetrons) In the symbol it is placed on the upper left hand side.
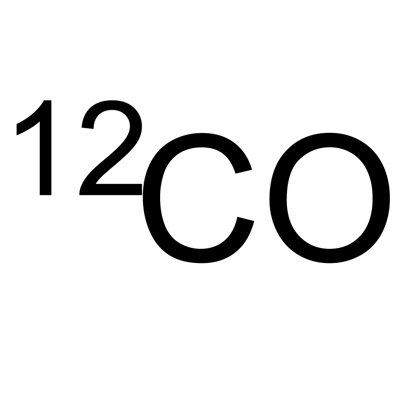
Ground State
electrons in their lowest possible energy
Orbit # Formula
2n² (n=shell #)
Periodicity
the idea that columns on the periodic table have similar properties
*when they have these similar properties they will have a similar number of valence electrons
Excited state
higher energy level than the ground state
relaxation
When an atom transfers from an excited state energy state to a ground state, by transferring energy to other atoms or through emission
Emission
when the frequency of radiation due to electrons transitioning from a high to low energy state, one of the multiple ways to do that
Electron Configuration
The shell's names go in order of s, p,d, f.
row/shell, where an electron is found
Remember when you are in your d-block row you will lose 1 row
When you are in the f-block row you lose 2 rows
Stabilizing Metals
Metals lose electrons and non-metals gain them
When negative ions are added to an atom it gets bigger and when positive ions are added to an atom it gets smaller