Day 30: Triplet Repeats
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HD, spinocerebellar ataxia, spinal bulbar muscular atrophy, fragile x, friedrech's ataxia, myotonic dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are the features of Friedreich’s ataxia?
slow to progress ataxia
dysarthria: slow or stuttered speech
cardiomyopathy in 2/3 of cases
diabetes in 1/3 of cases
scoliosis
deafness
What is the AOO in Friedreich’s ataxia?
<25yo
What is the inheritance of Friedreich’s ataxia?
AR, w/o anticipation
generally only one person per fam affected
What gene is associated with Friedreich’s ataxia?
FXN
What is the mechanism of disease for Friedreich’s ataxia?
GAA repeats in FXN
Typical = <33
Premutation = 34-65
Reduced penetrance = 44-66
Pathogenic = >66
How do you genetic test for Friedreich’s ataxia?
targeted analysis for GAA repeat in FXN
if only 1 repeat identified —> seq analysis, reflex del/dup
some cases, only 1 expanded allele + point mutation on other allele
multigene panel
How do you treat Friedreich’s ataxia?
PT/OT/SP
prostheses/walking aids/wheelchairs for ambulation
hearing aids
What are the features of spinocerebellar ataxia?
progressive cerebellar ataxia
uncoordinated muscle movement
loss coordination of the eyes, hands, speech
shaky gait
What is the AOO for spinocerebellar ataxia?
30-40yo
What is the life expectancy for spinocerebellar ataxia?
dependent on when symptoms appear
What is the inheritance of spinocerebellar ataxia?
AD
What genes are associated with spinocerebellar ataxia?
ATXN genes
Ex: Type 1 = AXTN7/1, Type 3 = AXTN3
What is the mechanism of disease for spinocerebellar ataxia?
CAG repeats in ATXN genes
How do you treat spinocerebellar ataxia?
supportive care, no cure
physical activity wih PT/OT
walking aids
speech therapy
How do you survey spinocerebellar ataxia?
neuro exam annually
nutrition
social supports
What are the features of spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
progressive neuromuscular degenerations of lower motor neurons
muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations of bulbar and limbs
gynecomastia
testicular atrophy
reduced fertility
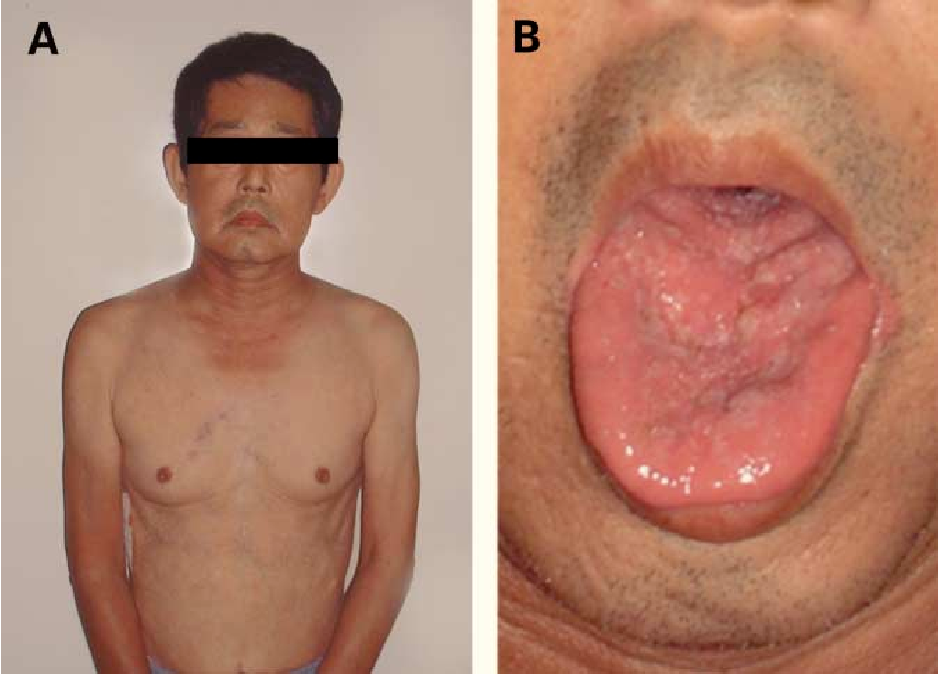
What is the inheritance of spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
X-linked
What is the mechanism of disease for spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
CAG repeat in AR
Normal = <34
Premutation = —
Reduced penetrance = 37
Full penetrance = 38<
How do you treat spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
walking aids
standard tx for dysarthria and dysphagia
anti-androgen drugs in clinical trial
How do you survey spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
assess strength, mobility, ADLs, speech, and feeding issues annually
eval for cardio/pulmonary functions
How do you genetic test for spinobulbular muscular atrophy?
targeted analysis of CAG repeats in AR
What are the features of Fragile X?
ID/DD/BD— autism, 50-70%
long face
prominent ears
large head circumference
macroorchidism: large testes
hypotonia
What is the mechanism of disease for Fragile X?
LOF, abnr. promotor methylation —> silencing of gene
CGG (CheckGiantGonads) repeats in the FMR1 gene
Normal = 5-44
Intermediate = 45-54
Pre-mutation = 55-200
Full mutation = >200
maternal anticipation
If someone is a carrier for Fragile X and is found to be in the pre-mutation range, what symptoms my they have? How many repeats?
pre-mutation = 55-200 CGG repeats
AFAB = 20% risk of FXPOI, primary ovarian insufficiency
occurs <40yo, ovaries stop working
FXTAS = 40% risk in AMAB, 16-20% risk in AFAB, tremor/ataxia syndrome
occurs 60yo, progressive cerebellar ataxia w/ tremor + cognitive impairment
What kind of expansion anticipation is Fragile X?
Maternal, more likely to expand when maternally inherited
Can the risk of expansion in Fragile X be reduced? How?
Yes, presence of AGG interruptions in the CGG repeat region
lower chance of expansion in offspring
What gene is associated with Fragile X?
FMR1
What is the inheritance of Fragile X?
X-linked
males > females
more severe and more frequent, but females can have sx
What are the features of a carrier with Fragile X?
50% of women have milder sx due to X inactivation or dosage compensation
ID/DD
How do you genetic test for Fragile X?
PCR w/ reflex to southern blot
PCR observes # of repeats
southern blot can also determine methylation status of promotor region
What are the features of classic myotonic dystrophy type 1?
muscle weakness and wasting
slowly progressive
myotonia
cardiac conductive defects
cataracts
baldness
What are the AOO for myotonic dystrophies?
classic = 10-30yo
congenital = prenatal
type 2 = 30s
What are the features of congenital myotonic dystrophy?
if lives, develop to classic DM1
reduced fetal movement
hypotonia at birth
general muscle weakness
respiratory compromise
ID
What gene is associated with myotonic dystrophy type 1?
DMPK
What is the inheritance of myotonic dystrophy type 1?
AD w/ anticipation
>34 CTG repeats (CheckTheGrip)
expansion in meiosis, more likely in egg than sperm
more repeats = less stability —> higher chance for expansion
What are the features of Huntington disease?
movement, cognitive, and psych abrn. —> degeneration of nerve cells in the brain
movement: chorea, loss of voluntary movements
cognitive changes
language, last to be affected
behavioral: aggression, outbursts, apathy
ˆlater in the disease
severe impairments requiring full dependency in end
suicide common
What is the inheritance of Huntington disease?
AD, 10% de novo
w/ anticipation and age dependent penetrance
What gene is associated with Huntington disease?
HTT, CAG repeat
Normal = <26
Intermediate = 27-35
Reduced penetrance = 36-39
Pathogenic = >40
Juvenile = >60
What is the AOO for Huntington disease?
~45yo, adult
Describe the mechanism of the diease for Huntington disease.
expansion is more likely when inherited paternally
contraction possible, tho rare
less repeats = older AOO
ex: 40-55 repeats —> adult onset, >60 = juvenile onset
What is juvenile Huntington disease?
onset before 20yo
How frequent is juvenile Huntington disease?
5-10% of Huntington disease cases
Describe the genetic testing protocol for Huntington disease?
Visit 1: GC visit, informed consent, mental health assessment
Visit 2: neuro exam, blood draw
Visit 3: result disclosure w/ support person, arrange follow up
What considerations should be made prior to testing for Huntington disease?
psychiatric problems must be resolved before testing
GC may decide to terminate testing if unfit
local counselor should be notified
support persons recommended
GC may exclude from testing if one is not present
What are the features of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
affects face, shoulder, upper arm, abs, lower leg muscles
asymmetric weakness
retinal vasculopathy
HL
rarely impacts heart+respiratory systems
How do you treat/survey facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
PT/OT for routing exercise
foot orthoses/wheelchair to improve mobility
surgical intervention to improve mobility
manage pain, audiology, ophthalmology
What is the inheritance of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
AD, 10-30% de novo
What is the mechanism of disease in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
inappropriate expression of DUX4
contraction of D4Z4 contraction on chr 4 (95%, FSHD1)
Normal = ≥12 repeat
Contracted, reduced penetrance = 10-11 repeats on permisive
contracted, full penetrance = ≤9 repeats on permissive
hypomethylation of D4Z4 from PV in SMCHD1 (<5%, FSHD2)
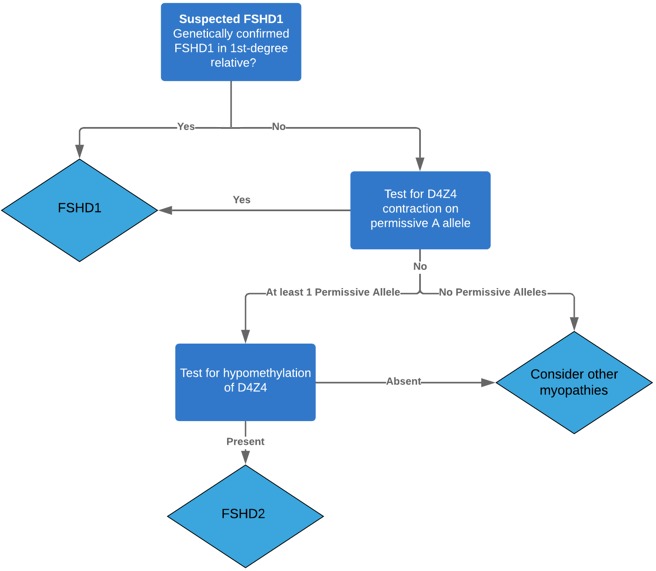
What is a permissive allele? What condition?
functional allele in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
What genes are associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
DUX4, SMCHD1 (<5%)
How do you genetic test for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy?
concurrent haplotype analysis w/ targeted analysis of contracted D4Z4 repeats via southern blot
methylation analysis
sequence analysis for SMCHD1