AP Environmental Science Unit 6
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Nonrenewable Energy sources
A source of energy that is a finite supply capable of being exhausted.
Nuclear, coal, oil etc.
renewable energy sources
sources of energy able to be replaced through ongoing natural processes
biomass, hydroelectric, solar, geothermal etc.
Global energy use
is not even between developed and developing countries
most used energy resource is fossil fuels, increasing trend towards renewables
Percentage change formula
Final-initial/initial *100 (always positive/ take absolute value)
as a country develops/ industrializes
need for fossil fuels increase
bike to car to plane use
farm to industrial production
factors that contribute to energy source preference
availability: what fuels can consumers gets easily
price: supply and demand
governmental regulations: subsidy and taxes
wood and charcoal
used in developing countries
easy to access
removal of trees can lead to soil erosion and deforestation.
Peat
decomposed organic material that can be used for fuel and mulch, a precursor to coal.
used in developing countries
using it indoors without proper ventilation can cause air pollution and health problems such as respiratory illnesses
stages of coal
peat, lignite, bituminous, anthracite
lignite
the least pure coal.
low heat capacity and low pressure, low sulfur and high moisture which causes smoke
bituminous coal
The most common form of coal; produces a high amount of heat and is used extensively by electric power plants. high sulfur
Note: Sulfur emissions mix with H2O vapor and cause acid deposition
anthracite
high price, best quality, high heating capacity, low sulfur content
natural gas
cleanest fossil fuel
negligible amount of SO2, mercury and particulates in comparison to coal and oil
mostly methane (CH4)
easily transportable
still produces carbon emissions
process of recovering crude oil from tar sands
not ideal, pumping oil from the ground is easier
removing water, sand and purfiying oil
Fractional distillation
heating up crude oil in refineries to take advantage of the different boiling points of the fuels for creating of differert forms of fuel like gasoline , diesel etc.
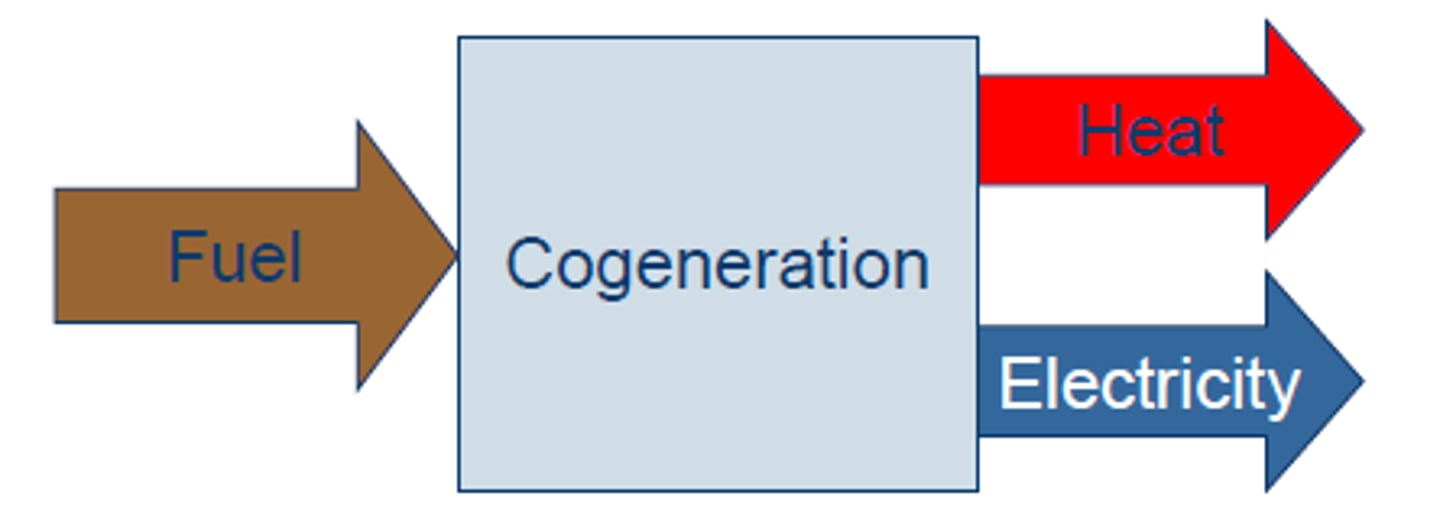
Cogeneration
Production of two useful forms of energy, such as high-temperature heat or steam and electricity, from the same fuel source.
more efficient
ex. creating electricity using an engine and using heat created by the engine to heat. w
Oil and Natural Gas Formation
ocean, sand and silt put pressure and heat on small plant and animal remains that eventually turn into oil and natural gas
age of rocks determines what resoures will be available
oil and gas formation happens at the same time
combustion process
Input: fuel and oxygen O2
Output: CO2, CO, H2O
Fuel+ O2 --- CO2+H2O
Producing electricity from coal
1) pulvirizing coal, using small coal
2) burning causes boiling and steam which turns a turbine
3) turning a turbine creates energy with help of a generator
requires water for use and for cooling
potential problems of producing electricity from coal
1) mining causes destruction of habitat
2) pulverized coal is easily flammable and harmful to respitory system
3) heavy use of water can deplete habitat for species
4) carbon dioxide increases greenhouse effect globally
5) impurities in coal such as mercury and sulfur is released into air and water
oil and natural gas extraction
+formed from plants and animal fossils in ocean
+liquid has to be pumped out, much drilling done at sea
+gas is collected through hydraulic fracturing gas found at many levels in rock
-oil extraction- habitat destruction, the potential for spills (leakage)
-gas extraction (hydraulic fracturing)- the destruction of habitat, water contamination, earthquakes
coal mining
+coal has to be dug out
+usability depends on how deep it can be found
+surface mining and subsurface mining methods are used
surface mining- removal of topsoil and habitat, overburden
subsurface mining- destruction of habitat, dangerous for humans
hydraulic fracturing (fracking)
pumping water at high pressure to break apart rocks and thereby release natural gas
hydraulic fracturing (fracking) process
1 well is made
2 pipe is inserted
3 fracking fluid inserted (sent down)
4 gas flows out because rock is fracked
environmental problems caused by fracking
1 well can contaminate water and destroy/harm habitat
2 if the pipe is not lined properly, may contaminate water
3 fracking fluid contains Volatile Organic Compound (VOCs) which may contaminate land, water and mix into the atmosphere
4 natural gas and methane may leak out
5 process may cause earthquakes
6 uses water as a resource
nuclear fission process
1 Uranium-235 placed into fuel rods
2 struck by an outside neutron
3 process of splitting U-235 releases large amounts of heat
4 heat used to generate steam from the water
5 steam turns a turbine
6 turbine powers a generator
7 generator makes electricity
8 steam cools and can be used again, heats get released
pros of nuclear power
1 low gas emissions
2 high power output
3 low cost (after initial construction)
4 no mining for fossil fuels
5 no primary/secondary air pollutants
cons of nuclear power
1 long-lived hazardous waste/nuclear accidents
2 thermal pollution
3 very high initial cost (billions)
4 mining for construction and uranium
5 nonrenewable resource
nuclear waste
spent Uranium-235 remains inactive
+U-235 breaks down and can't create heat as much
+This spent Uranium gathers neutrons
+becomes heavier - like plutonium
+ remains radioactive for up to 24,000 years (10 half lives)
issues with nuclear waste
+due to long lived waste, strorage is hard
+storage happens on site, burried deeply
+federal site commissioned at Yucca Mountain, Nevade (not currently used, people of Nevada opposed it)
+many sites means more chances of radioactive waste leaking into environment (eg. water)
Nuclear Power Accidents
Three Mile Island, Pennsylvania USA- 1979
Chernobyl, Ukraine - 1986
Fukushima, Japan - 2011
causes can be natural or human caused (mechanical)
Three Mile Island incident
the accident started in a non-nuclear portion of reactor:
1 water pump failed to allow water in
2 reactor never cooled down
3 fuel began to meltdown partially
4 no explosion or long-term high radiation exposure
Chernobly incident
accident arose from a safety test:
1 power turned off during simulation
2 extra power from turbine was supposed to keep reactor power up enough to cool
3 when test completed, control rods did not drop
4 explosion occured, releasing most radiation ever from an accident
Fukushima Incident
the accident caused by a natural disaster:
1 earthquake and tsunami occured in pacific
2 earthquake caused an emergency shut down
3 tsunami wave flooded 4 reactors
4 three nuclear reactors melted down at the same time
5 accident was deemed preventable
half-life of radioactive material
+ half life is a measure of time for half of an atomic nucleus to decay
+ decays into another atom, emitting radiation
+ ten half-lives generally means safety
biomass as a source of energy
+energy stored from phosynthesis
+biomass is the leading renewable energy source worldwide
+burning biomass is a direct source of heat for many in devaloping nations
+examples of biomass used as heat sources:
wood, peat, charcoal, crop residue, manure
positive consequences of biomass use for energy
+easily accessible
+relatively inexpensive
+ used for heating and cooking
negative consequences of biomass use for energy
+releases air pollutants (carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, particulates, and volatile organic compounds)
+typically burned indoors, intensifying health effects of pollutants
+overharvesting of trees for fuelwood results in deforestation
Biofuels
Fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, that are created from the fermentation of plants or plant products.
Ethanol
made by fermenting plant-based starches into sugars and eventually alcohol
+typically mixed with gasoline to create gasohol (90% gas, 10% ethanol)
+E-85 and flex-fuel vehicles can run on a mixture of 85% ethanol, 15% gas
Biodiesel
vegetable oil that can be used to run a car
+extraced and chemically modified oil from plants
+can be a direct substitute for diesel fuel
sources for biofuels
Ethanol
+corn (US)
+sugarcane (Brazil)
+sugar beets (US and Brazil)
Biodiesel
+soybeans (Brazil and US)
+oil palms (southeast asia)
+rapeseed (Europe)
pros of using biofuels
+combustion is carbon neutral (produces modern carbon which is already in the atmosphere)
+potentially renewable
+can be produces domestically (for US)
cons of using biofuels
+net energy is low (more gasohol is needed to go to the same distance
+harvesting of crops for ethanol has the potential for
increased use of fossil fuels in harvest
increased deforestation
reduction in fertility of agricultural land
more sustainable solutions being researched
Ethanol:
switchgrass (grass that can be harvested over and over year after year)
biodiesel:
SVO (straight Vegetable Oil) using oil used in restaurants to power vehicles
Algea
photovoltaic solar cells
A system of capturing energy from sunlight and converting it directly into electricity
energy from the sunlight releases electrons, the flow of electrons creates electricity
pros and cons of photovoltaics
pros
+generation of electricity
+can reduce habitat destruction depending on installation placement (can be placed on the roof of apartments)
+lange and small scale applications
cons
-use is limited by the availability of sunlight
-limited lifespan of nonrenewable PV cells
-expensive
-solar farms may negatively impact fragile desert ecosystems
active solar (concentrated solar power)
a liquid is being heated up by concentrated solar beams, surfaces reflecting the solar beams, liquid is heating the water, water is creating steam that will turn turbine and charging a generator
aside from electricity, heat is also produces with active solar system
pros and cons of active solar
pros
+generates electricity and heat
+large and small scale application
cons
-expensive
-requires maintenance
-solar farms may negatively impact fragile desert ecosystems
-solar farms require high solar intensity to maximize efficiency
Passive solar
A system that uses the sun's energy without requiring mechanical devices (pumps or fans) to distribute the collected heat. House has to face south. Keeping sunlight out during summers and in during winters
requires good insulation
pros and cons of passive solar
pros
+relatively inexpensive and low maintenance
cons
-some aspects are difficult to implement retroactively
-energy cannot be collected or stored
hydroelectricity from dams and reservoirs
as water comes from the gates (intake) has a kinetic energy that spins the turbine, turbine turns the generator and thus creates electricity
micro-hydropower
electricity produced in a small stream without having to build a big dam
tidal power
Energy generated by ocean tides in places where favorable topography allows for construction of a power plant.
waves helps creation of electricity
pros of hydroelectric power
+no air pollution
+no waste
+relatiively inexpensive electric generation
+additional services provided by the reservoir (recreational service, fishery, extra water for irrigation)
cons of hydroelectric power
-flooding of land for the reservoir
-disruption to flow rates of river
-high maintenance cost for tidal (saltwater harming machinery and steel)
-high construction cost for dams
-most viable sites are already used
geothermal energy process
1 water is pumped down an injection well
2 stored heat from the Earth's interior turns the water into steam
3 steam rises from the production well
4 kinetic energy of the steam turns a turbine
5 turbine turns a generator
6 generator producess electricity
pros of geothermal energy
+no combustion, no CO2 emissions,
+not dependent on variable weather factors, like solar and wind
cons of geothermal energy
-accessibility at reasonable cost is limited
-release of gases during drilling and processing (hyrogen sulfide gas)
-short term depletion of heat possible
-impact on groundwater
home heating with geothermal
1 fluid pumped down to earth
2 fluid heats because land cools slower
hydrogen fuel cell, process
1 Hydrogen fuel (H2) added to cell splits into protons (H+) and electrons (-) in the first reaction layer
2 protons and electrons take different paths,
-protons move across the membrane
-electrons are free to take an alternate route, creating a flow of electric current
3 in the second reaction layer, oxygen molecules (O2) are split and combine with protons and electrons
-Water vapor is the only emission from the fuel cell
hydrogen fuel cell
a cell that generates electricity from a controlled reaction between hydrogen and oxygen
water is the only emission and byproduct
source of hydrogen fuel
+hydrogen can come from water
electrolysis- electric current used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen
decreases net energy of fuel cell because energy is used for creating the energy
+can come from natural gas
splitting methane (CH4) using heat-results in CO2 pollution
hydrogen fuel cell technology
it is expensive because...
1 it is a new technology with research and devalopment costs
2 scale of technology is low
3 raw materials are rate and expensive (platinium and other rare earth minerals are used as catalysts)
pros and cons of hydrogen fuel cells
pros
+no CO2 emissions (if produced from water)
+electricity is more efficient than internal combustion
cons
-technology is expensive
-producing hydrogen fuel from fossil fuel is not clean
producing wind energy
1 kinetic energy from moving air cought in turbine
2 kinetic energy from the turbine turns the generator inside the windmill
3 generator produces electricity
Pros and cons of wind energy
pros
+renewable
+clean
+allows for multiple use of lands
cons
-birds abd bats can be killed by turbines
-maintanance is required
-locations must have consistent winds to provide consistent power supply (need backup power on days that are not windy)
energy conservation
the practice of finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently.
It is important because every energy source has its downsides.
energy conservation at home
+adjust the thermostat (petek)
+use energy-efficient appliances
+conserve water with shorter showers and doing larger laundry
+reduce irrigation energy
+planting trees to match energy needs (gölge oluşturma, sıcaklık stabil tutma, rüzgar kesme)
energy conservation in transportation
+fuel economy standards (CAFE)
+Battery electric vehichles and hybrids are more efficient than the internal combustion engine and their energy can be renewably sourced
+carpooling
+public transportation
corporate Avarage Fuel Economy Standards (CAFE)
mandates level of fuel efficiency that corporates and cars need to hit to operate in US
energy conservation in building design
passive
+passive solar windowns
+thermal mass
+insulation
+lightining from the sun
+green roof (with trees)
active
+geothermal or solar heating systems
+solar panels