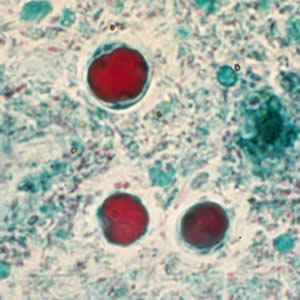
Intestinal Amoeba
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Protozoa
microscopic one celled organism that can be free living or parasitic in nature
multiplies in humans which contributes to their survival
permits serious infections to develop from just a single organism
identification criteria for intestinal amoeba species
size
number of nuclei
nuclear structure
karyosome, peripheral chromatin, chromatoidal bar, life cycle stage
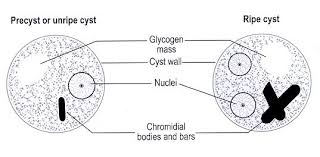
karyosome
(endosome) a mass of chromatin
peripheral chromatin
nuclear DNA not included in the karyosome
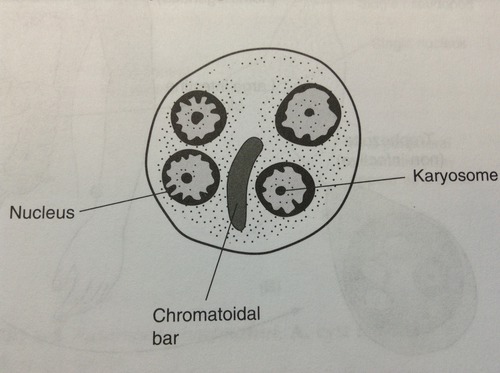
chromatoidal bar
a rod-like internal structure outside of the nucleus of an amoeba in its cyst phase usually comprised of ribonucleoproteins in crystalline form
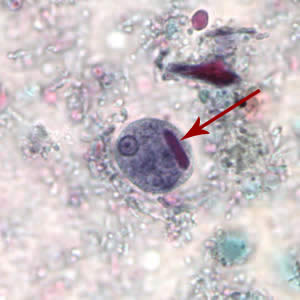
trophozoite
motile stage that feeds, multiplies, and maintains colony within the host
cyst
immotile stage protected by a resistant cyst wall formed by the parasite and can be readily transmitted to a new host (infectious)
general life cycle of intestinal amoeba
direct fecal oral transmission in food or water with no intermediate host
infectious cyst stage is ingested
organisms excyst in the intestinal tract
multiplication through binary fission
colonization of fecal area by trophozoites
intestinal amoeba treatment is only given in cases of
Entamoeba histolytica (most common pathogen)
intestinal amoeba carrier treatment
metronidazole (luminal amebicide)
invasive intestinal amebiases treatment
systemic drugs like lodoquinol and paromomycin
“cyst passers”
asymptomatic colonization with Entamoeba hisstolytica
Amebic dysentery
colitis caused by Entamoeba histolytica with flask shaped ulcers in the colon
Extraintestinal amebiases
caused by Entamoeba histolytica and can disseminate and cause disease to liver, lung, pleural abscesses, peritonitis, skin, and genital lesions
lesions are described as “anchovy paste”
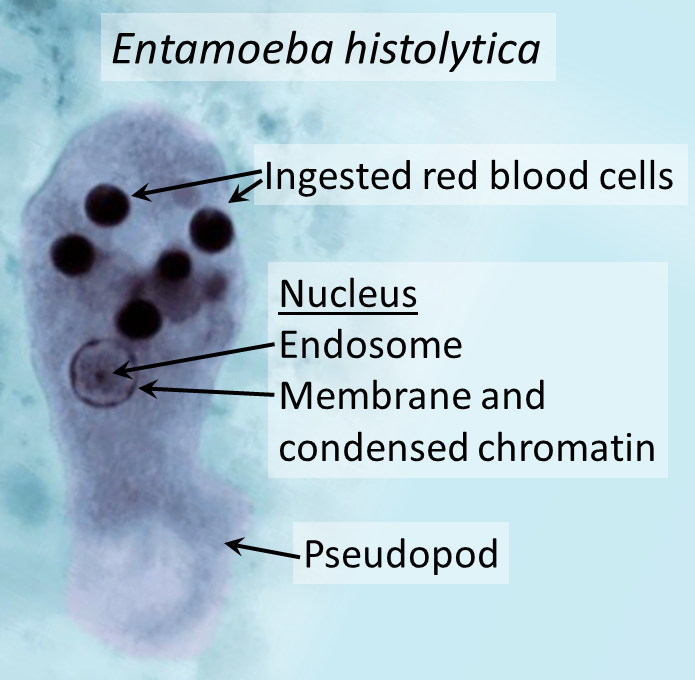
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite
15-25 um
single bull’s eye nucleus with central karyosome
can contain ingested RBCs
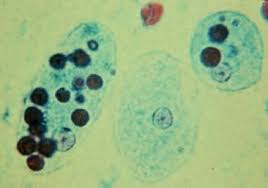
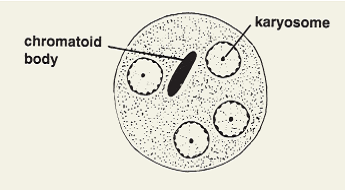
Entamoeba histolytica cyst
10-20 um
4 nuclei
when cyst matures, can have central chromatoidal body
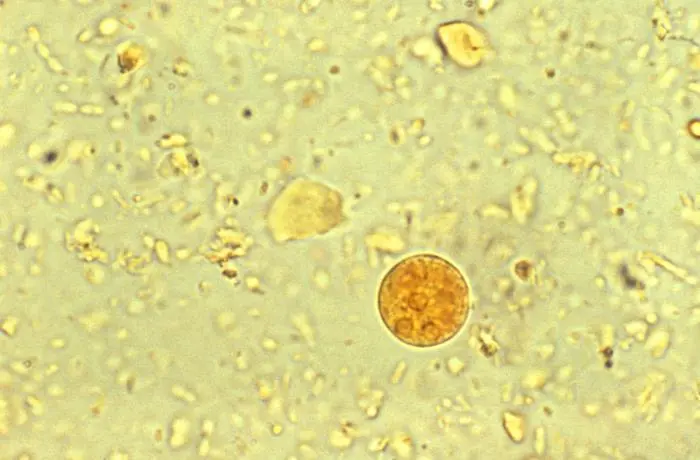
Entamoeba dispar
originally thought to be a secondary strain of Entamoeba histolytica but is a different, non-pathogenic species
Entamoeba dispar vs. Entamoeba histolytica
cannot distinguish between the two, unless RBCs are engulfed
non-pathogenic Entamoeba dispar does not engulf RBCs
pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica does engulf RBCs
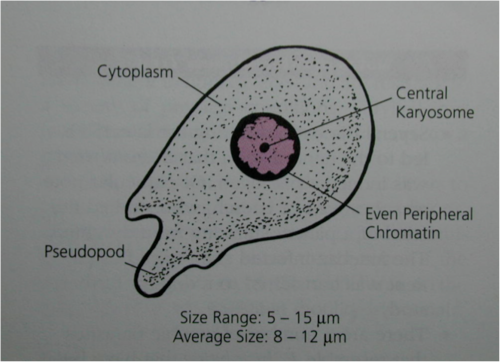
Entamoeba hartmanni troph
4-12 um
small, central karyonsome
even, peripheral chromatin
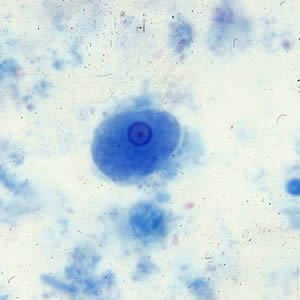
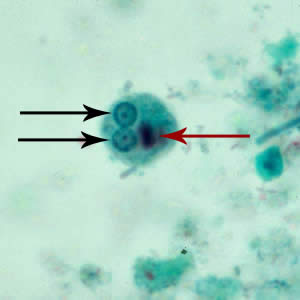
Entmoeba hartmanni cyst
5-10 um
small, central karyosome
1-4 nuclei
cigar shaped chromatoidal bar (criss-cross)
even distributed chromatin
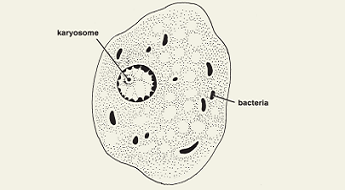
Entamoeba coli troph
15-50 um
large, eccentric karyosome
uneven chromatin
“dirty” vacuolated cytoplasm
bacteria in cytoplasm
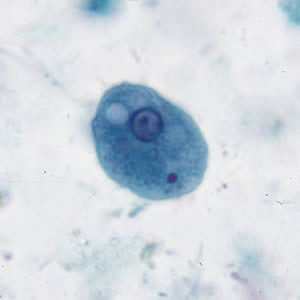
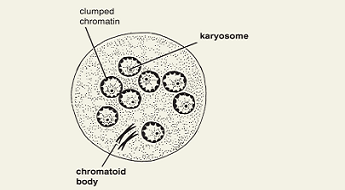
Entamoeba coli cyst
10-25 um
2-8 nuclei
large, eccentric karyosome
splinter shaped chromatoidal bars
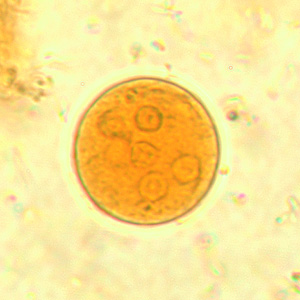
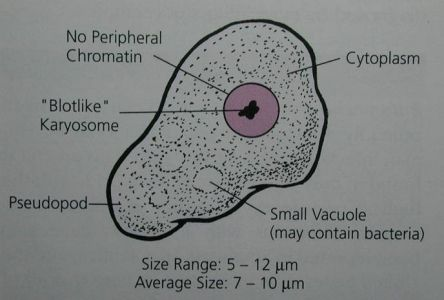
Endolimax nana troph
5-12 um
prominent “blot-like” karyosome
no peripheral chromatin
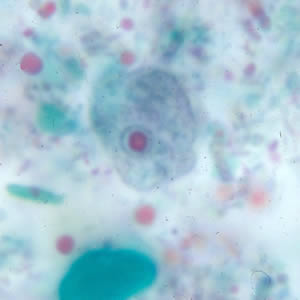
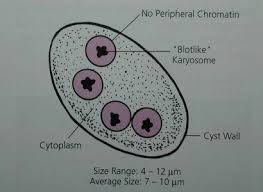
Endolimax nana cyst
5-12 um
usually oval shaped
4 nuclei
prominent karyosome in nuclei
granular, vacuolated cytoplasm
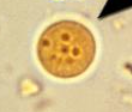
Iodamoeba butschlii troph
6-20 um
no peripheral chromatin
achromatic granules around large karyosome
vacuolated cytoplasm
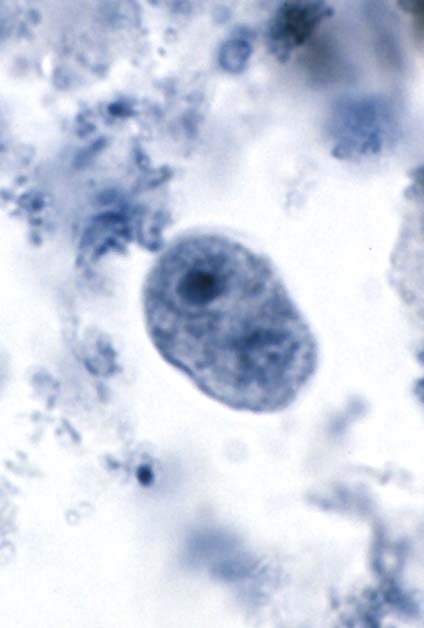
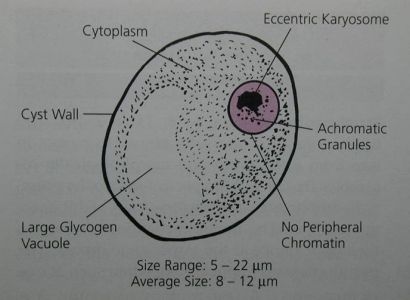
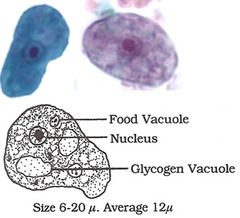
Iodamoeba butschlii cyst
6-15 um
prominent glycogen vacuole
vacuolated cytoplasm
ONLY amoebic cyst with ONE nucleus
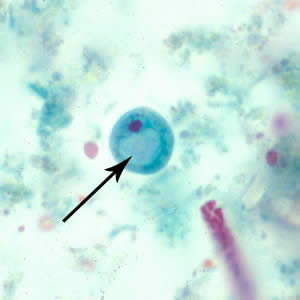
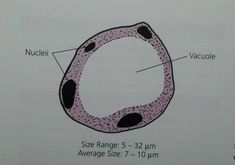
Blastocystis hominis cyst
multiplies by binary fission
3-5 um
large vacuole surrounded by several small nuclei
can be confused with yeast
no troph form, only spherical form seen