Brain cells for BOARDS
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Which of the following is the main fuel for brain, needed for WBCs and RBCs, as well as most abundant carbohydrate?
a. Frutose
b. Galatose
c. Glucose
c. Glucose is the main fuel for the brain, essential for white blood cells (WBCs) and red blood cells (RBCs), and is the most abundant carbohydrate in the body.
Which polysacchrides provides a carbohydrate storage form of energy in animals and humans?
a. glycogen
b. starch
c. fibers
a. Glycogen is a polysaccharide that serves as a primary storage form of energy in animals and humans.
Polysacchardes inital digestion begins where?
a. small intestine
b. stomach
c. mouth
d. rectal
c. Mouth, where enzymes like salivary amylase start breaking down starches.
Where is glycogen stored?
a. liver
b. kidney
a. Glycogen is primarily stored in the liver and muscles, serving as a readily available energy source for the body.
Sugar alcohol do not promote tooth decay because they metabolize at
a. faster rate
b. slower rate
a. slower rate compared to regular sugars, which reduces the likelihood of acid production and harm to tooth enamel.
Artifical sweetners are
a. nonnutritive sweetners
b. nutritive sweetners
a. nonnutritive sweeteners that provide sweetness without significant calories or nutritional value.
Asparatame is active ingredient in what?
a. Sweet n Low
b. NutraSweet and Equal
c. Sunnette and Sweet One
d. Splenda
b. NutraSweet and Equal, which are popular artificial sweeteners containing aspartame as their active ingredient.
Is Asparatame stable in heat?
a. yes
b. no
b. no, as it breaks down when exposed to high temperatures, losing its sweetness and effectiveness.
What is the normal range of diabetes insulin blood glucose level?
a. 70-100 mg
b. 80-125 mg
c. 70-125 mg
d. 80-100 mg
b. 70-125 mg per deciliter is considered the normal range for fasting blood glucose levels in individuals without diabetes.
Islets of Langerhands in pancreas is part of which Diabetes Type?
a. 1
b. 2
a. 1, as these cells are responsible for producing insulin and are largely destroyed in type 1 diabetes.
Which diabetes type can be improved with diet and exercise?
a. 1
b. 2
b. 2, as lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
What are the four signs and symptoms of diabetes?
HAKP
The four key signs and symptoms of diabetes include hyperglycemia, acetone breath, ketonemia, and 3P (polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia)
What are the chronic complications with Diabetes?
(6 of them - HORNIX)
Hear disease, Oral candidasis, Retinopathy, Neuropathy, Increase Perio disease, Xerostomia
Which of the followng is best to schedule a diabetic patient?
a. early morning
b.later in the day
a. early morning, as blood glucose levels are generally more stable at this time, which can help prevent complications during treatment.
Hypoglycemia is less than what?
a. 70 mg
b. 75 mg
c. 80 mg
d. 85 mg
a. 70 mg
Essental amino acid cannot be synthesize in the?
a. liver
b. kidney
c. body
c. body, must be obtained from diet
Nonessential amino acid can be synthesize in the?
a. liver
b. kidney
a. liver, and derived from diet
a. Complete Protien (High)
b. Incomplete Protien (Low)
c. Complementary Protiens
matches with ?
a. whole grains
b. animal sources
c. plant protien
a. b
b. c
c. b
Thinking of anorexic, a patient have inadequate food intake of protien and calorie deficiency. Which of the following is it? (waste away)
a. Kwashiorkor
b. Marasmus
a. Marasmus, usually no edema, 6-18 months, skins and bones
If you have delayed tooth eruption and hypoplasia, which of the following are you experiencing?
a. Marasmus
b. Kwashiorkor
b. Kwashiorkor (big belly with retained fluid - protien deficiency)
Linoleic fatty acid and Linolenic fatty acid is part of which Lipid group?
a. Saturated Fat
b. Monosaturated Fat
c. Polyunsaturated Fat
c. Polyunsaturated Fat
Supragingival nutrient source is what?
a. saliva
b. gingival crevicular fluid and exudate
a. saliva
Demineralization occurs if pH drops to what for enamel
a. 4.5
b. 5.5
c. 6.5
d. 7.5
b. 5.5
Demineralization occurs if pH drops to what for cementum
a. 4.7
b. 5.7
c. 6.7
d. 7.7
c. 6.7
Caries = ?
Anticalculus = ?
Antihypersensitivity = ?
Antimicrobial = ?
Whitnening = ?
-hydrogen peroxide
-fluoride
-pyrohosphates
-triclosan
-potassium nitrate
Caries = Fluoride
Anticalculus = Pyrophosphate
Antihypersensitivity = Potassium nitrate
Antimicrobial = Tricosan
Whitnening = Hydrogen peroxide/carbamide
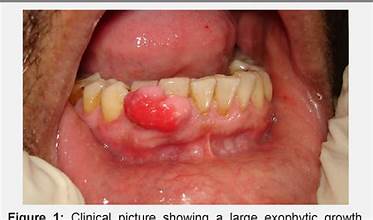
Which of the following is multinucleated gain cells presents and clinically look like a pygoenic granuloma?
a. chronic hyperplastic pulptitis
b. peripheral gaint cell granuloma
c. pyogenic granuloma
d. papillary hyperplasia
b. peripheral gaint cell granuloma
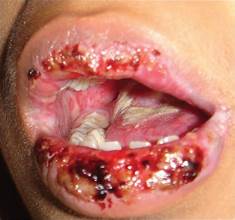
Which of the following have bull eyes or target lesions about 50% skin lesions and involved Stevens-Johnsons Syndrome?
a. kaposi sarcoma
b. herpatic whitlow
c. lichen planus
d. erythema mutiforme
d. erythema mutiforme
The most common cause of Hyperthroidism is ?
a. Goiter
b. Graves disease
c. Cretinism
d. Myxedema
b. graves disease
You must avoid what with Hyperthyroidism?
EPI
Which of the following is NOT an example of Hypothyroidsm?
a. hypotension
b. tachycardia
c. dry skin
d. obesity
b. tachycardia. It is brachycardia.
Bell palsy affect which cranial nerves?
a. Assessory
b. Vagus
c. Trigeminal
d. Facial
d. Facial
Widened PDL is part of which systemic disease?
a. Scleroderma
b. Marfan Syndrome
c. Epidermolysis Bullosa
d. Arthritis
Small intestine is most important in whch Pharmacokinetic phase?
a. absorption
b. distribution
c. metabolsm
d. elimination
a. absorption