L30 kidney main functions and basic nephron processes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to renal and urinary physiology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
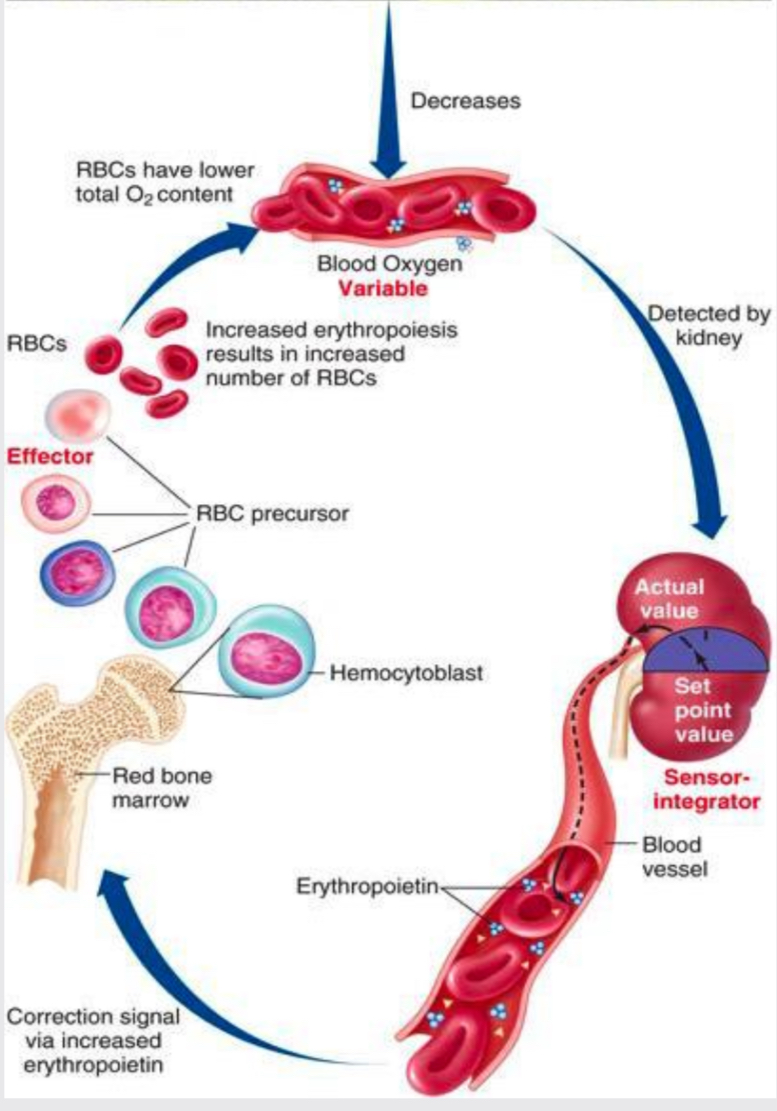
Endocrine function
Low blood oxygen levels detected by kidney causing EPO release stimulating bone marrow to produce RBC’s. Renal failure occurs when kidney cannot make enough EPO causing anaemia (low blood oxygen).
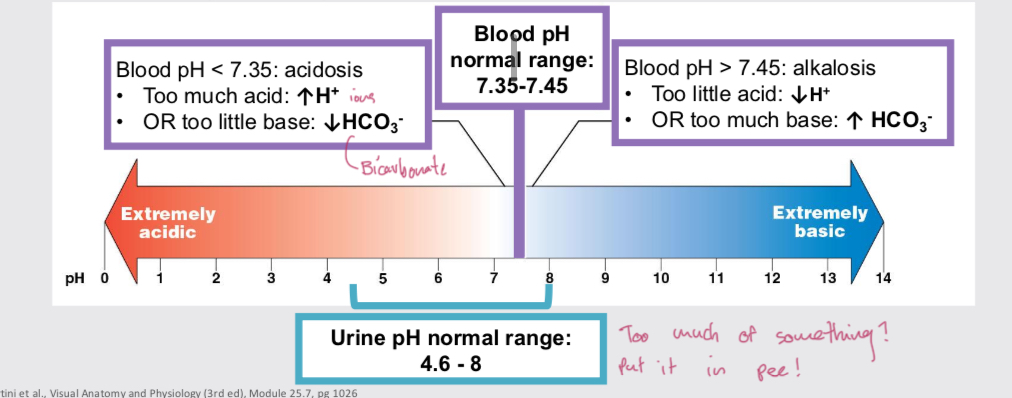
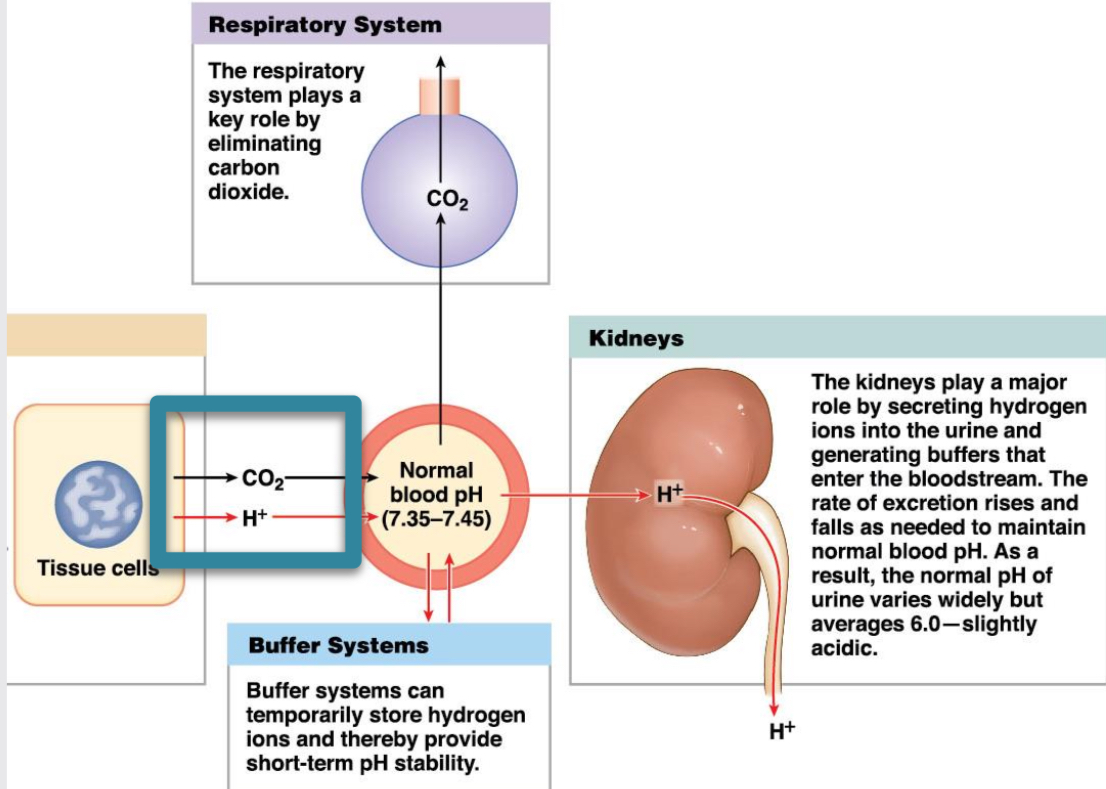
pH regulation function
CO2 and water form carbonic acid, forming bicarbonate and hydrogen ion. Acids and CO2 in body come from metabolic processes. Blood pH controlled by lungs and reabsorption and secretion of bicarbonate and H+ in kidneys.
Salt/ion homeostasis function
K+ concentration vital for many processes, like resting membrane potential of all cells. Neurons and cardiomyocytes need for APs. If kidneys fail, K+ build up in blood causing arrhythmias or death.
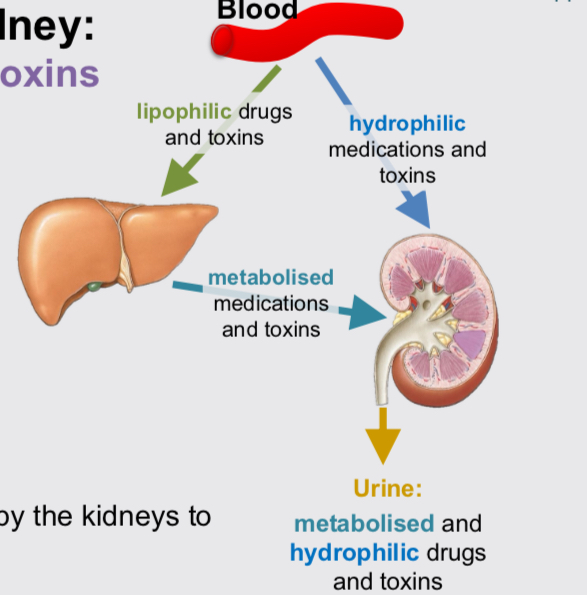
Medication and toxin excretion function
Aspirin can be excreted directly due to high water solubility (hydrophilic). Lidocaine (local anaesthetic) excreted after metabolism in liver due to fat soluble nature (lipophilic).
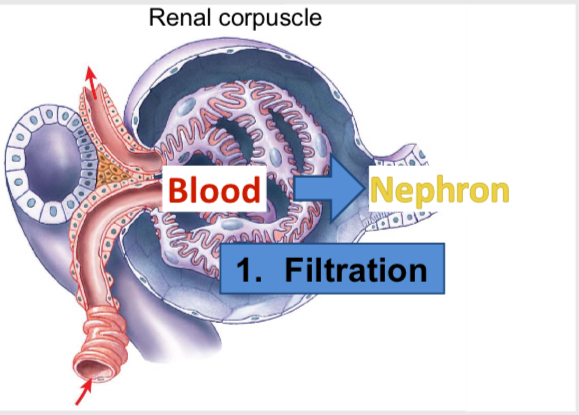
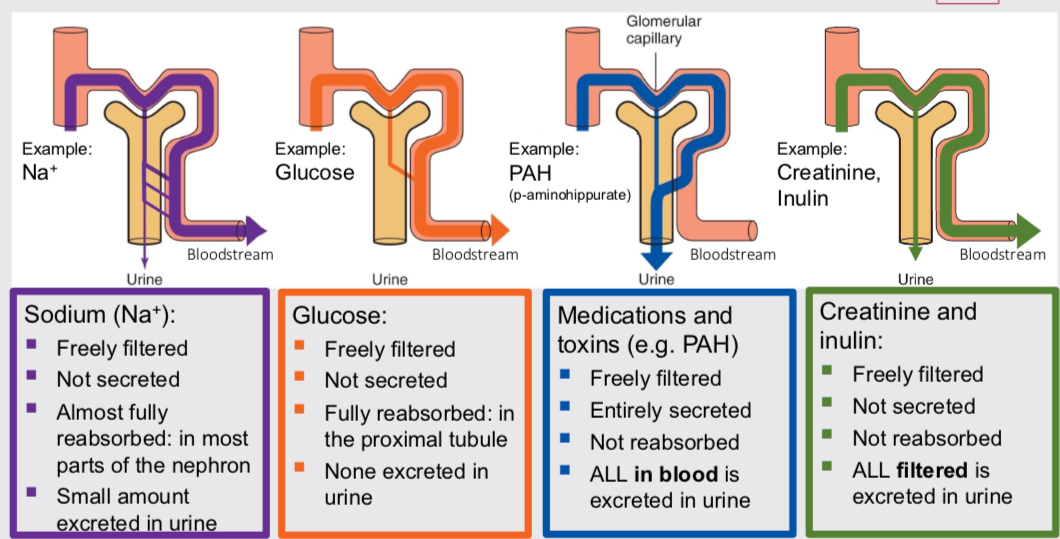
Filtration
Occurs in renal corpuscle, movement of plasma from blood into glomerular capsule (nephron). Creates plasma like filtrate of blood. Most things freely filtered at constant rate except large proteins and protein bound things.
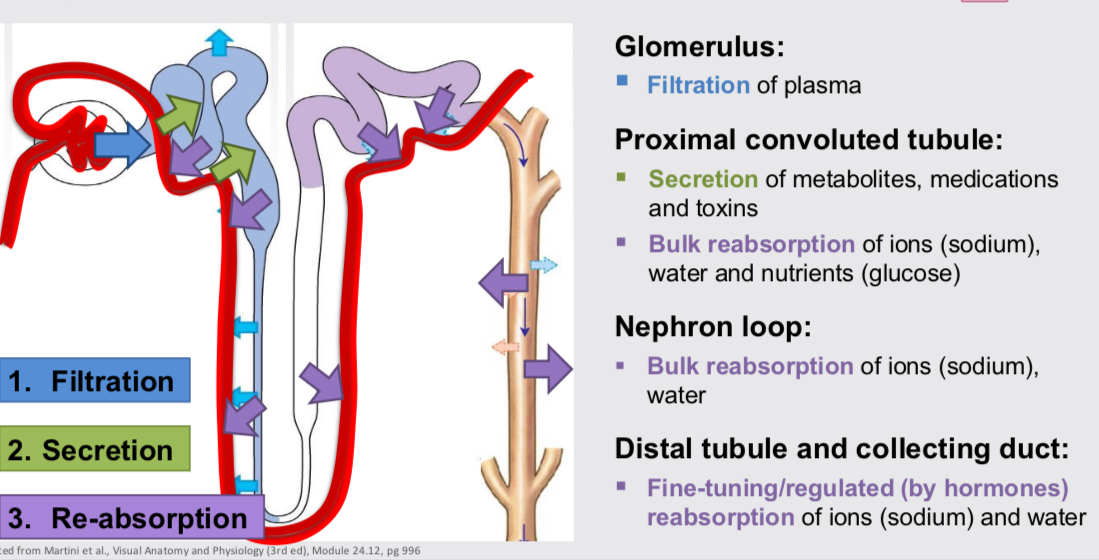
Reabsorption
Movement of solutes from the tubular fluid (nephron) back into the peritubular capillaries (blood). Returns useful things to blood so not excreted. PCT bulk sodium, water and glucose. Loop bulk sodium and water. DCT fine tuning sodium and water.
Secretion
Moving solutes from the peritubular capillaries (blood) into the tubular fluid for excretion in urine. PCT removes waste products like metabolites, medication and toxins
Volume and composition of fluids
Can change with water volume in body and osmolarity of water compartments. Increase in plasma volume increases BP (vice versa). Increase in ICF volume swells cells (vice versa)
Osmolarity
Concentration of solute molecules in a solution (mosmol/L). Isosmotic, same osmolarity/ solutes per litre in ECF as ICF.
Change in ECF water volume (fluid always goes to ECF first)
Hyposmotic, increase in water causing decrease in ECF osmolarity, water moves from ECF to ICF. Hyperosmotic, decrease in water of ECF increasing ECF osmolarity,, water moves from ICF to ECF.
Metabolic function
Gluconeogenesis in response to low blood glucose primarily during fasting. Used to make ATP for active transport in PCT (Na/K-ATPase generating sodium gradient).
Fluid compartments
ECF 1/3 of TBW, ICF 2/3. Plasma 1/5 of ECF, interstitial fluid 4/5.
Total body water (TBW)
60% of body weight in males, 55% in biological females.
Renin
An enzyme secreted by the kidneys that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Water homeostasis function
TBW relatively constant. Intake and loss of water must balance, urine output adjusted to maintain balance.
Major function of each part of nephron
Amount of substance excreted in urine=
amount filtered + amount secreted - amount re-absorbed.
different substance pathway examples