B&C Chapter 9
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Memory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Learning
Acquisition of new information
What do memory and learning involve?
Cellular and circuitry changes in the nervous system
Memory
Outcome of learning
3 Stages of processing
Encoding: (acquisition & consolidation)
Storage: (retention of memory traces)
Retrieval: (access to stored memory traces)
Amnesia
Memory loss, mostly due to brain damage
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memory before brain lesion
H.M. Patient
Famous patient with severe anterograde amnesia post bilateral hippocampus lesion
Double Dissociation
Strongest evidence for distinct systems.
Area A damage impairs function A but not function B
Area B damage impairs function B but not function A
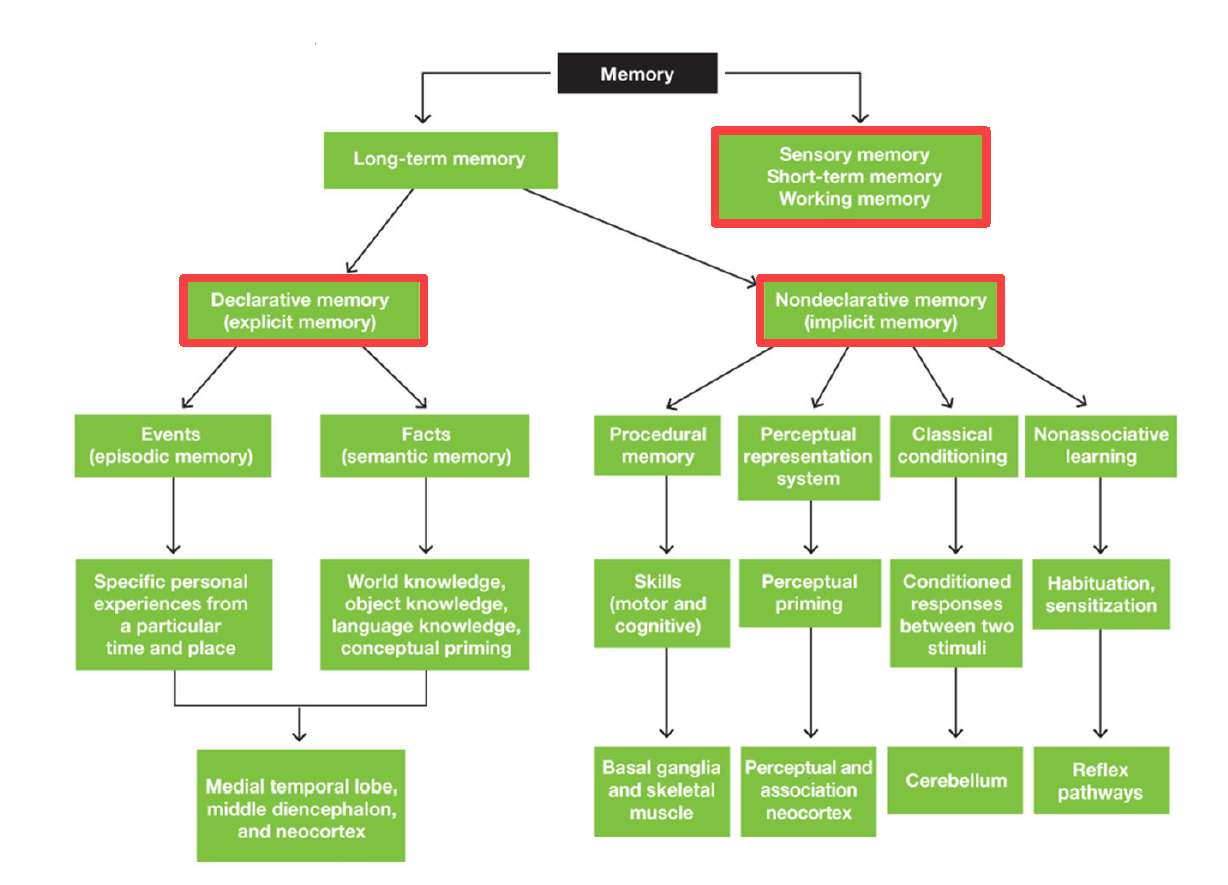
2 main divisions of memory
Long term memory
Sensory memory / Short term memory / Working memory
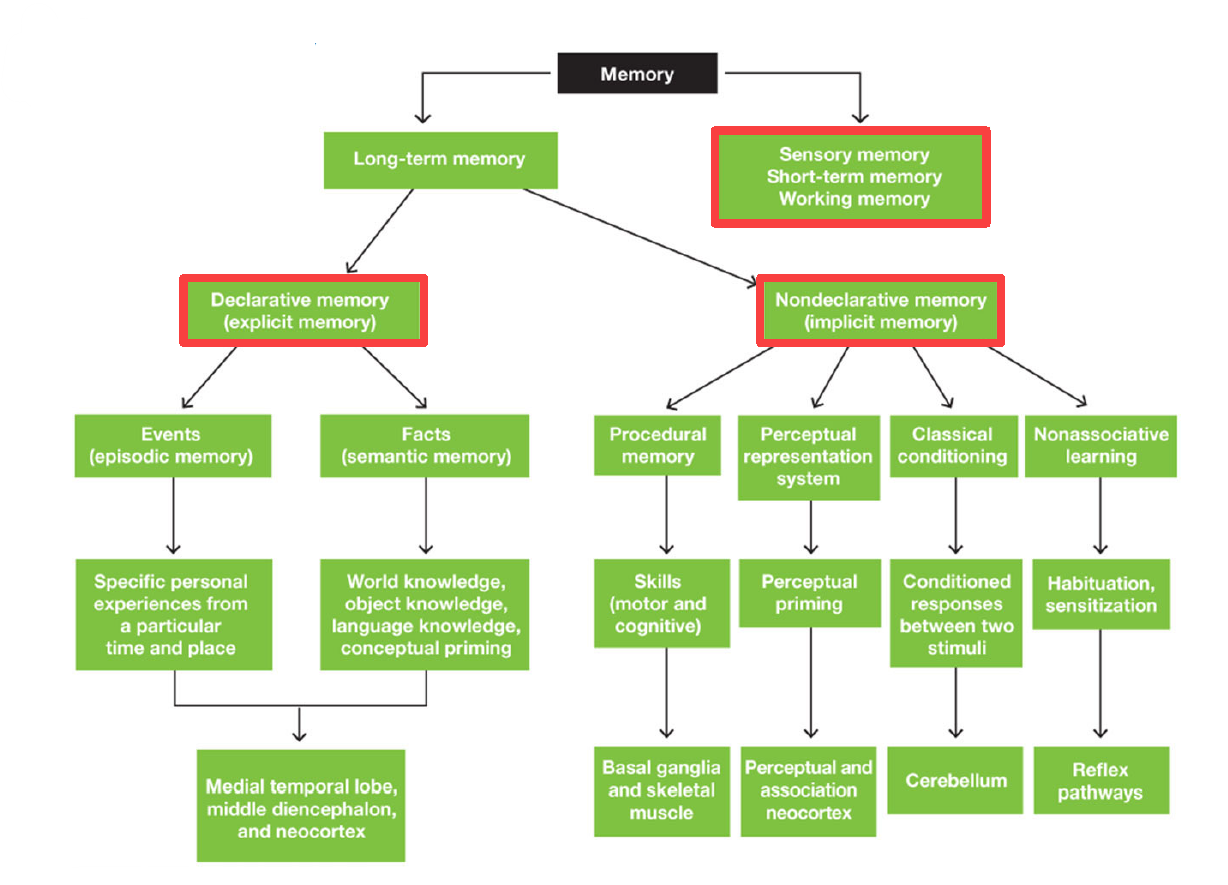
2 main divisions of Long term memory
Declarative Memory (Explicit memory)
Nondeclarative Memory (Implicit memory)
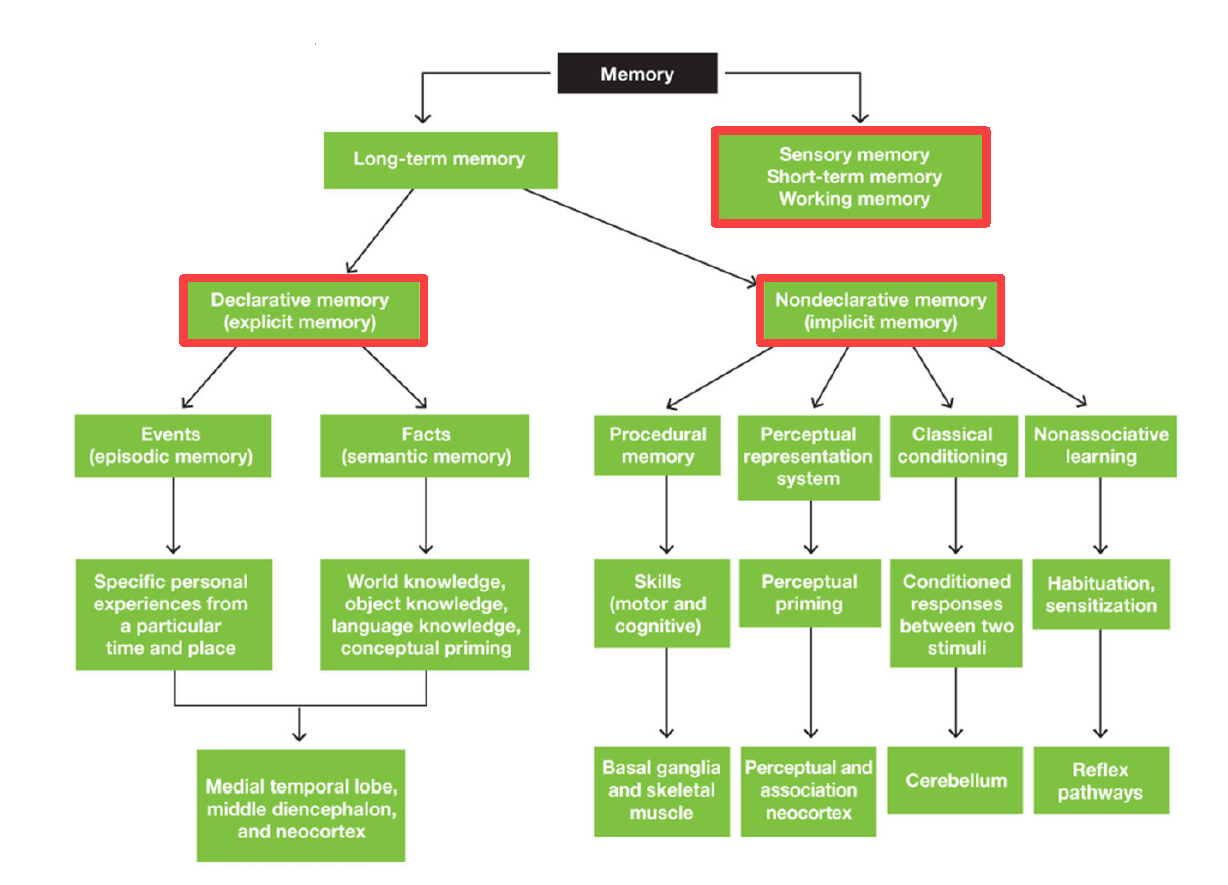
2 divisions of declarative memory
Episodic Memory (Events): specific personal experiences from particular time & place
Semantic Memory (Facts): world/object/language knowledge & conceptual priming
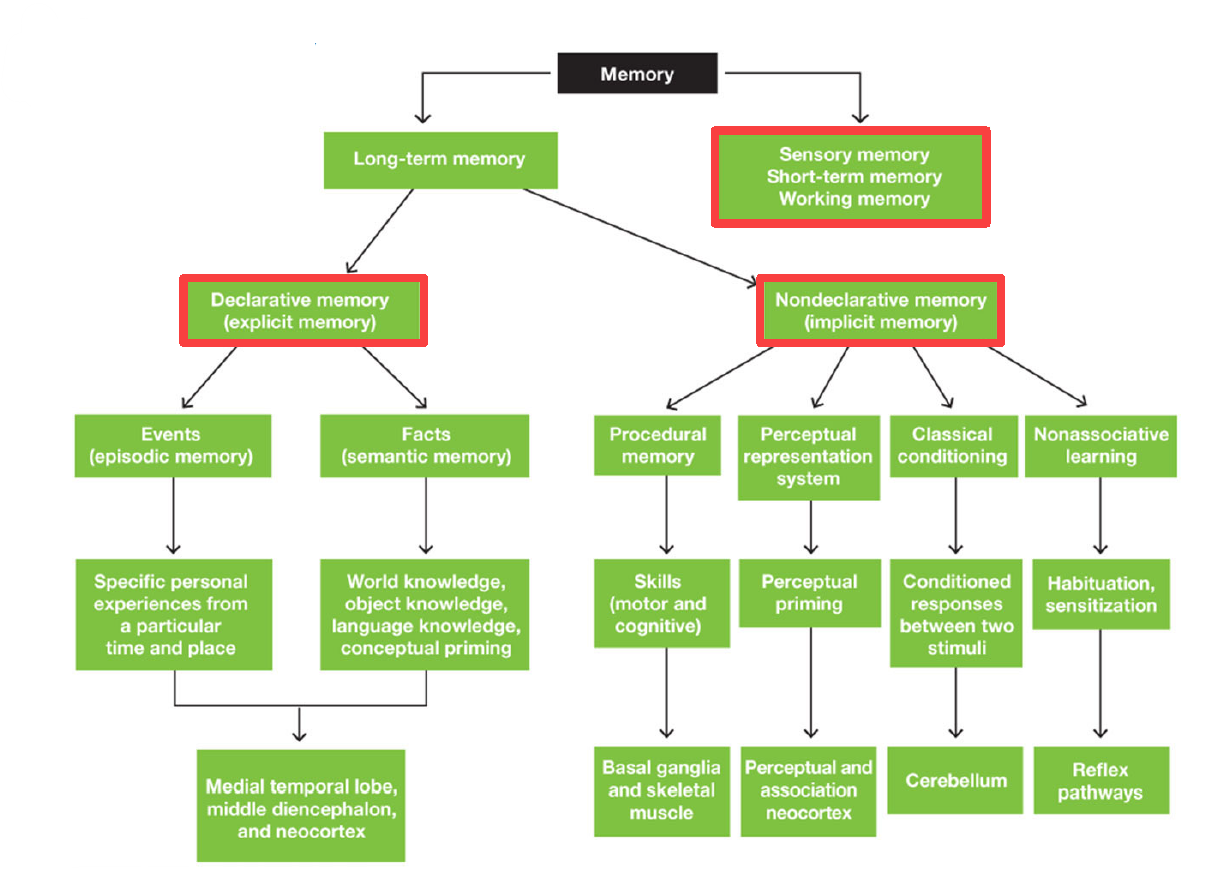
3 Areas of brain responsible for Declarative Memory
Medial temporal lobe
Middle diencephalon
Neocortex

4 divisions of Nondeclarative memory
Procedural memory (motor & cognitive skills)
Perceptual representation system (perceptual priming)
Classical conditioning (conditioned responses between 2 stimuli)
Non-associative learning (habituation & sensitization)
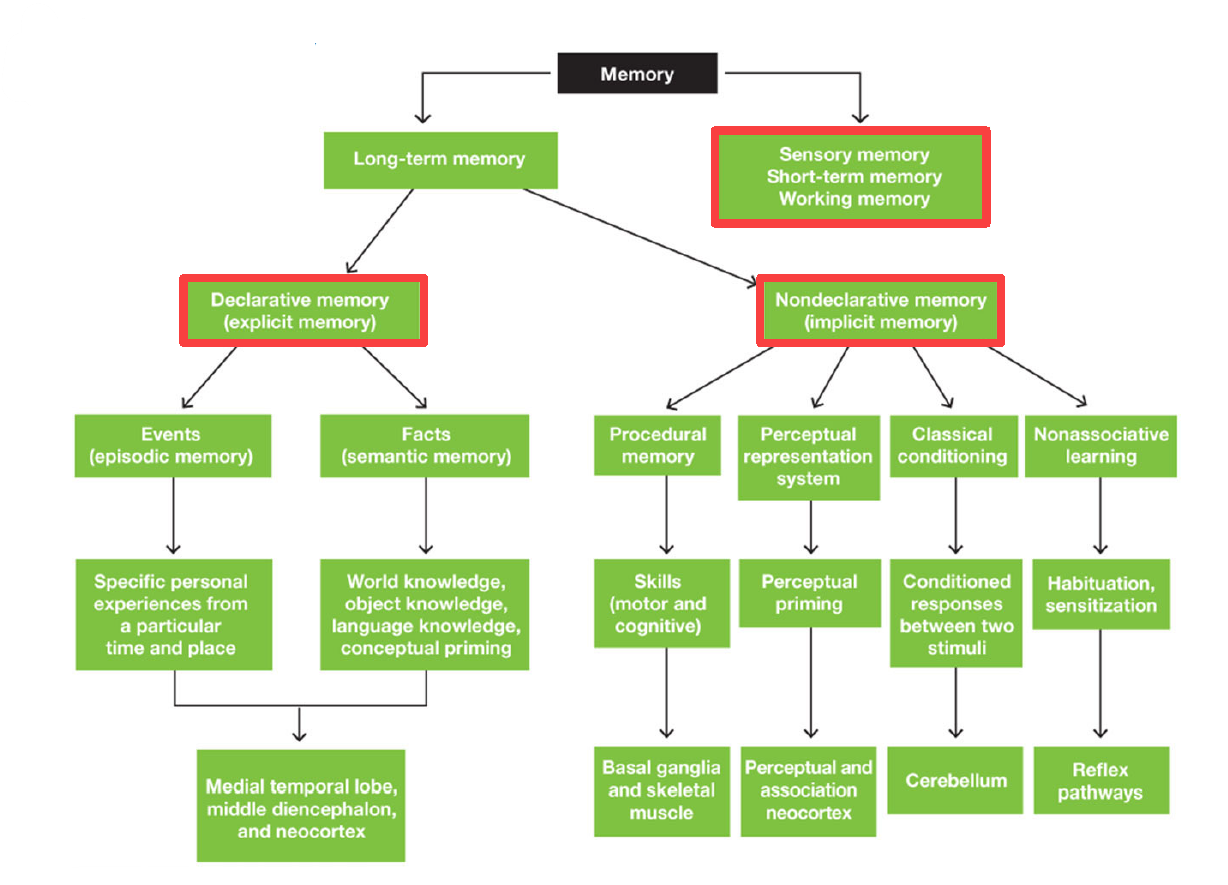
Areas of brain dedicated for procedural memory
Basal ganglia & skeletal muscle
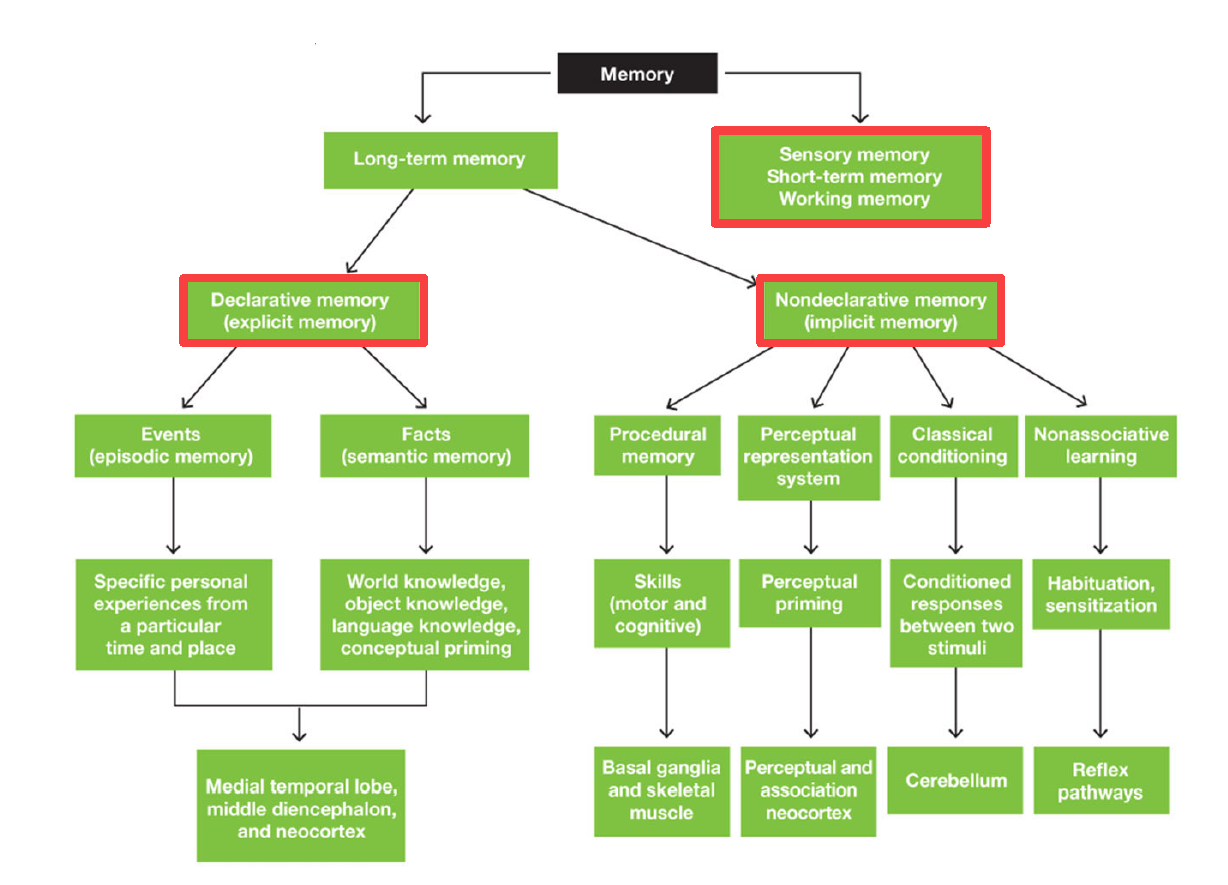
Areas of brain dedicated for perceptual representation system
Perceptual Association Neocortex
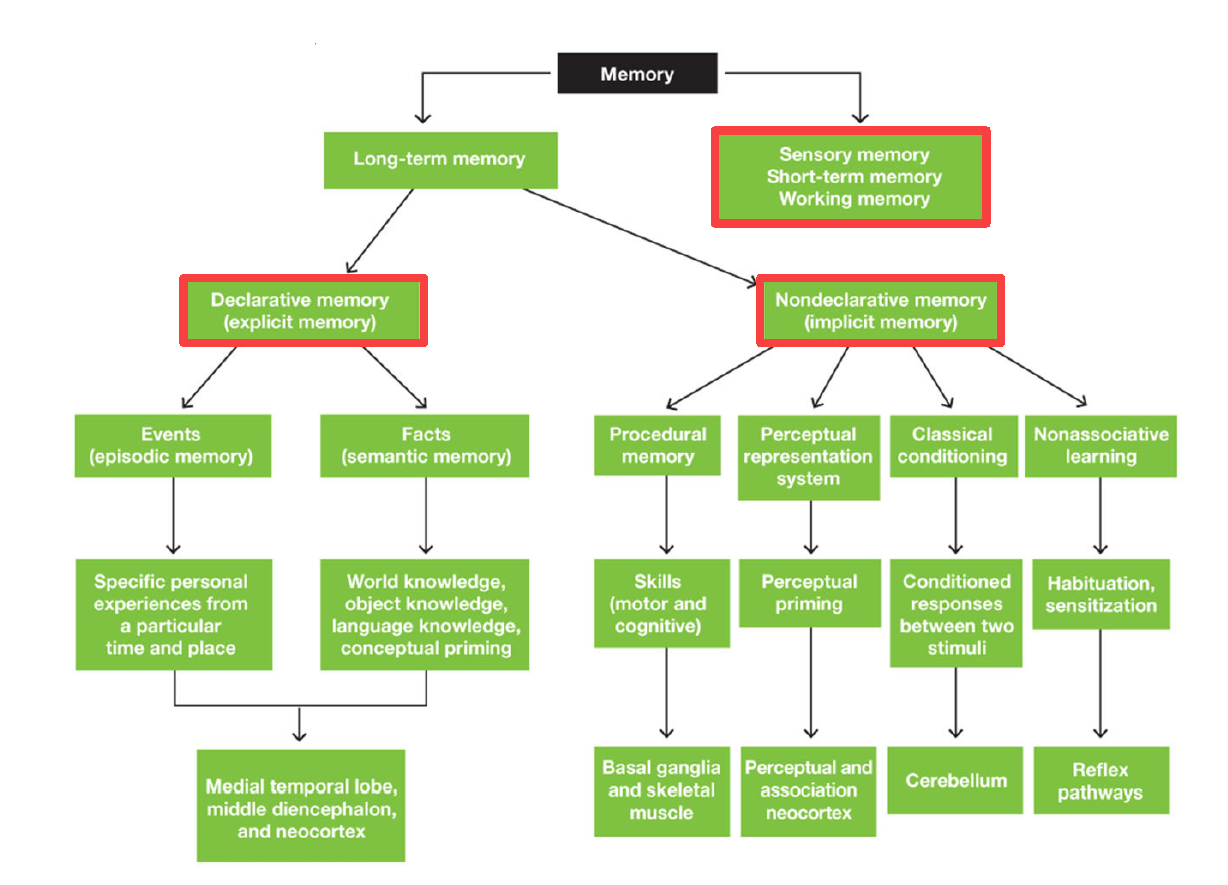
Area of brain dedicated for Classical Conditioning
Cerebellum
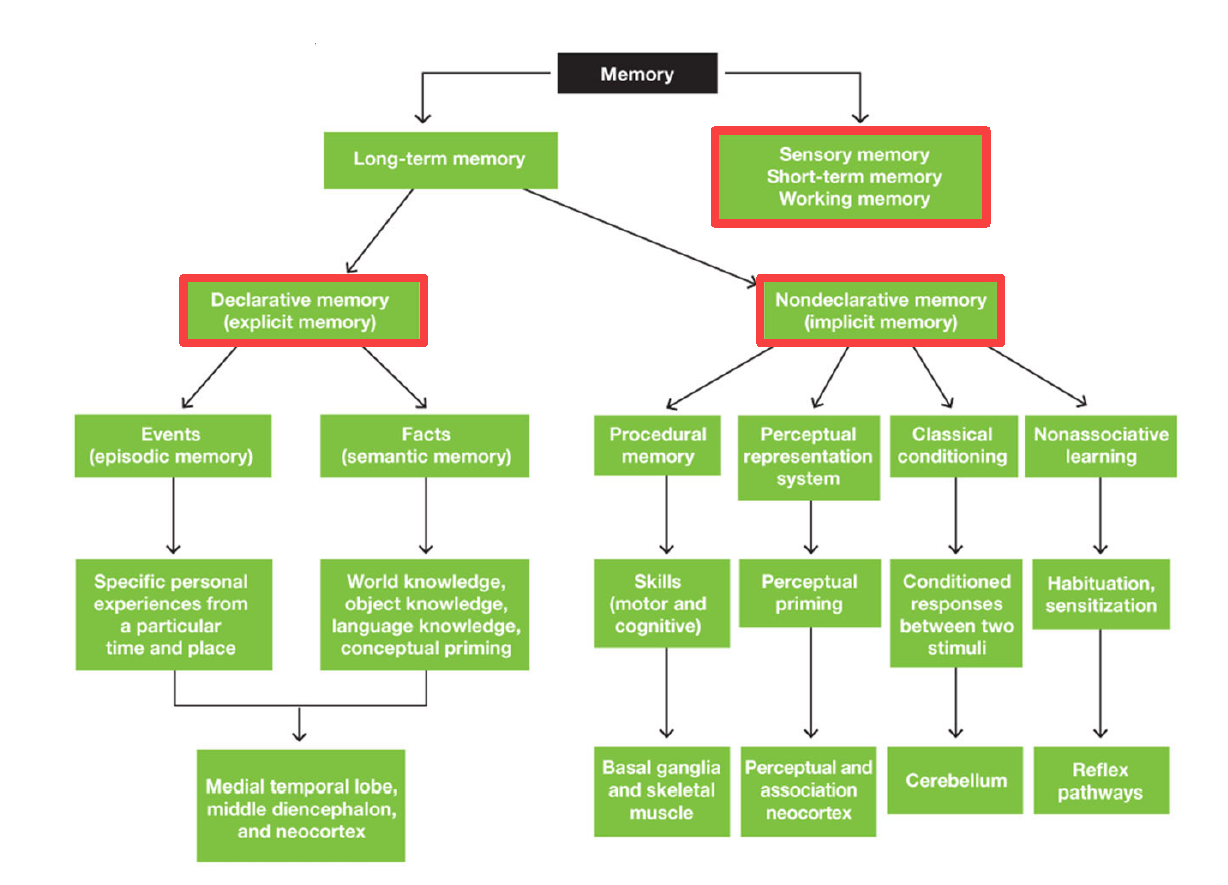
Area of brain dedicated for nonassociative learning
Reflex pathways
Sensory memory:
Time course
Capacity
Conscious Awareness
Mechanism of loss
Milliseconds to seconds
High capacity
No awareness
Primarily decay
Short Term/Working Memory:
Time course
Capacity
Conscious Awareness
Mechanism of loss
Seconds to minutes
Limited (5-9)
Yes
Interference & decay
Long Term Nondeclarative Memory:
Time course
Capacity
Conscious Awareness
Mechanism of loss
Minutes to years
High capacity
No conscious awareness
Primarily interference
Long-Term Declarative Memory:
Time course
Capacity
Conscious Awareness
Mechanism of loss
Minutes to years
High
Yes
Primarily Interference
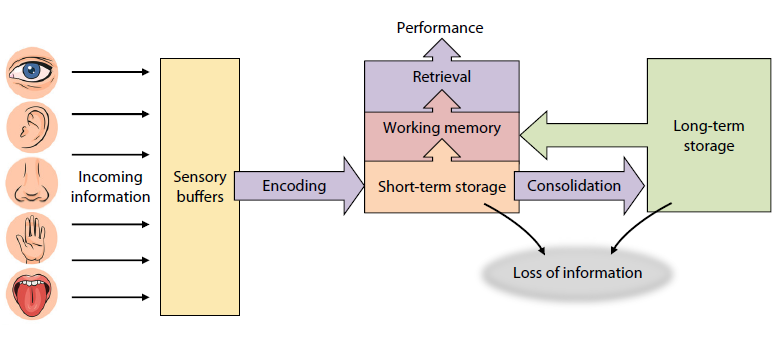
7 Processing stages of memory
Sensory buffers
Encoding
Short term storage
Consolidation
Long term storage
Working memory
Retrieval
Echoic Memory (auditory):
Persistence
Capacity
Time course
Unattended auditory information persists like an echo
High capacity (partially accessible)
Can last up to 10 seconds
Iconic Memory (visual):
Persistence
Capacity
Time course
Unattended visual info persists like an informational afterimage
High capacity & partially accessible
300-500 ms
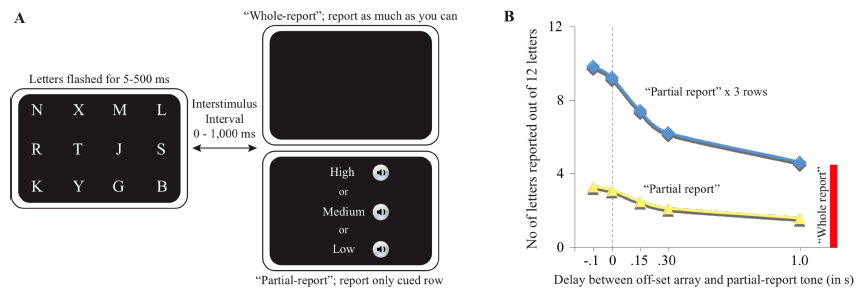
What did the Sperling paradigm show about how much information our brain can hold in a very short time?
Whole report: People can verbally recall ~4 items from a set of 12.
(short term memory)
Partial report: When cued to a specific row, people recall ~3–4 items from that row.
(sensory memory)
The Modal Model
Influential, hierarchical, serial model of memory.
Basis for account of partial vs whole report.
Sensory Inputs
Sensory register
Short-term storage
Long term storage
Debate over the Modal Model
Is it serial? Does information have to be encoded in short term memory before being stored in long term memory?